MAPK Signaling

Activated MAPKs transduce the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs), e.g. RSK, MSK, or MNK family, and MK2/3/5. There are three main MAPK families, signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (Erk1/2 or p44/42), the c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1-3 (JNK1-3)/ stress activated protein kinases (SAPK1A, 1B, 1C), the p38 isoforms (p38α, β, γ, and δ). ERK signaling is involved in cell division, migration and survival. p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK pathways are activated by cellular stress. The p38 MAPK pathway regulates cell motility, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. JNK/SAPK signaling affects apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MAPK pathway results in tumorgenesis and other pathological conditions.
-
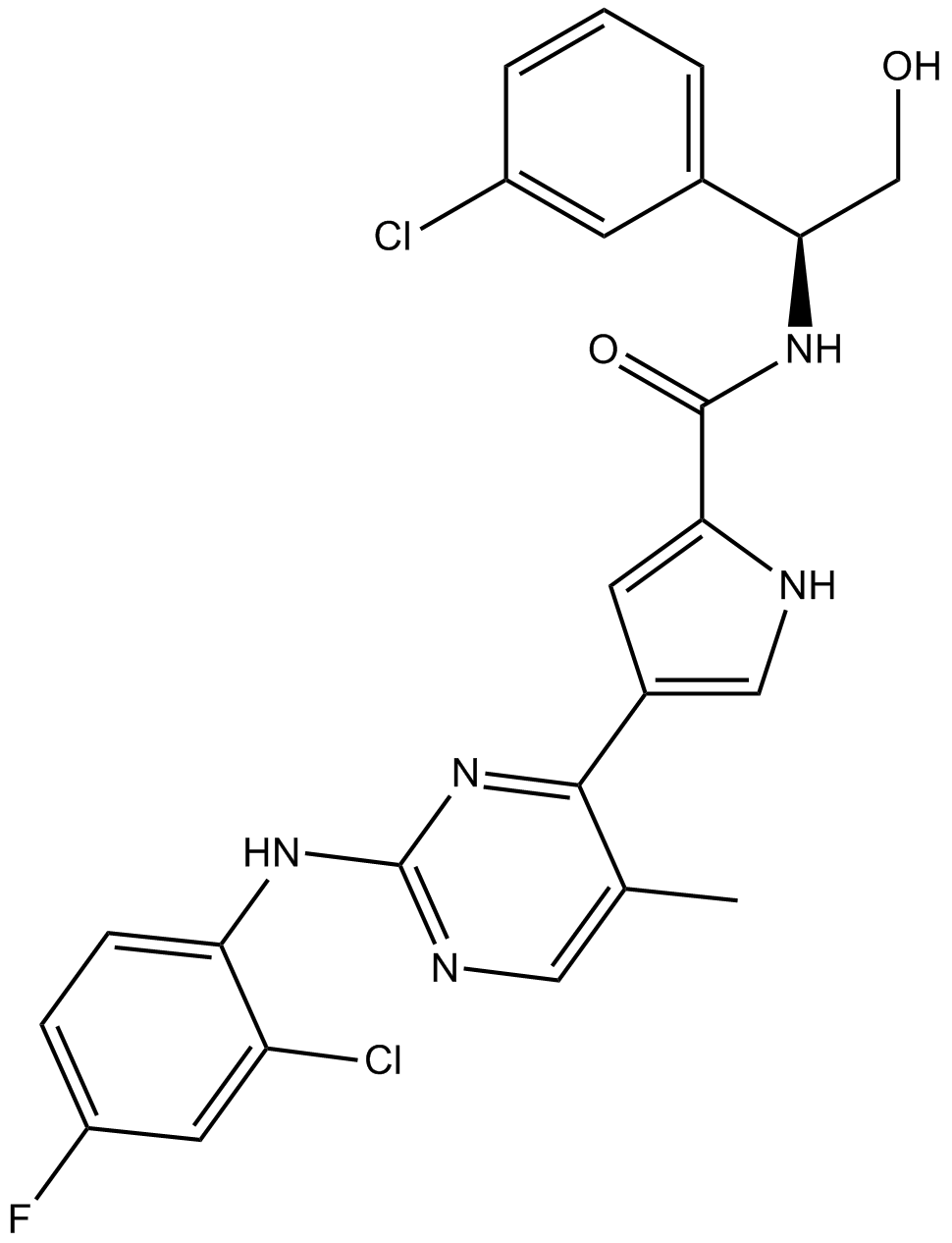 A3931 VX-11e5 CitationTarget: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor
A3931 VX-11e5 CitationTarget: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor -
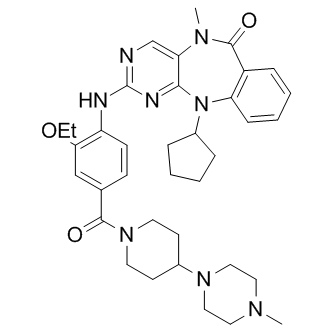 A3942 XMD17-109Target: ERKSummary: ERK-5 inhibitor
A3942 XMD17-109Target: ERKSummary: ERK-5 inhibitor -
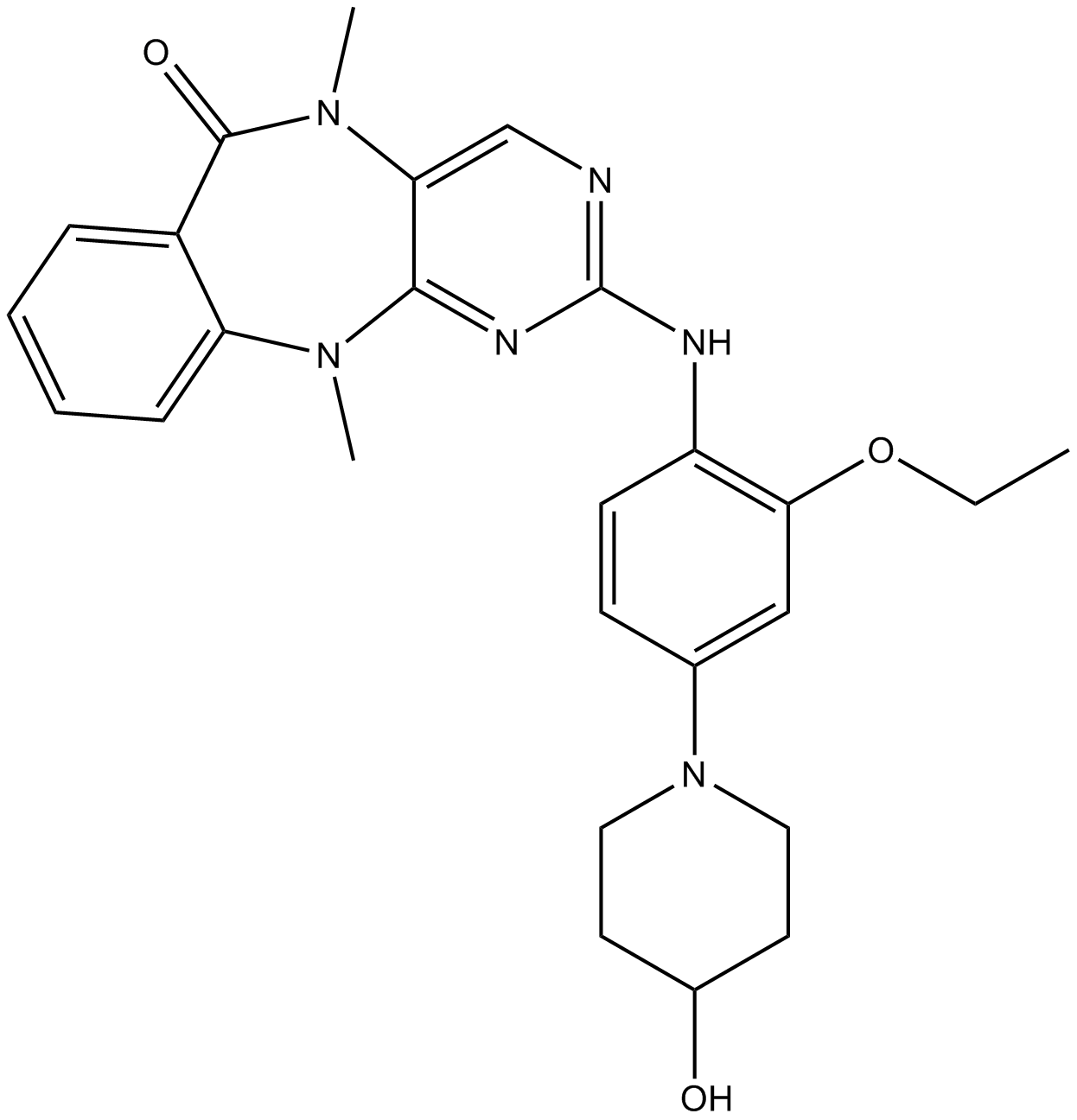 A3943 XMD8-92Target: ERKSummary: BMK1/ERK5 inhibitor
A3943 XMD8-92Target: ERKSummary: BMK1/ERK5 inhibitor -
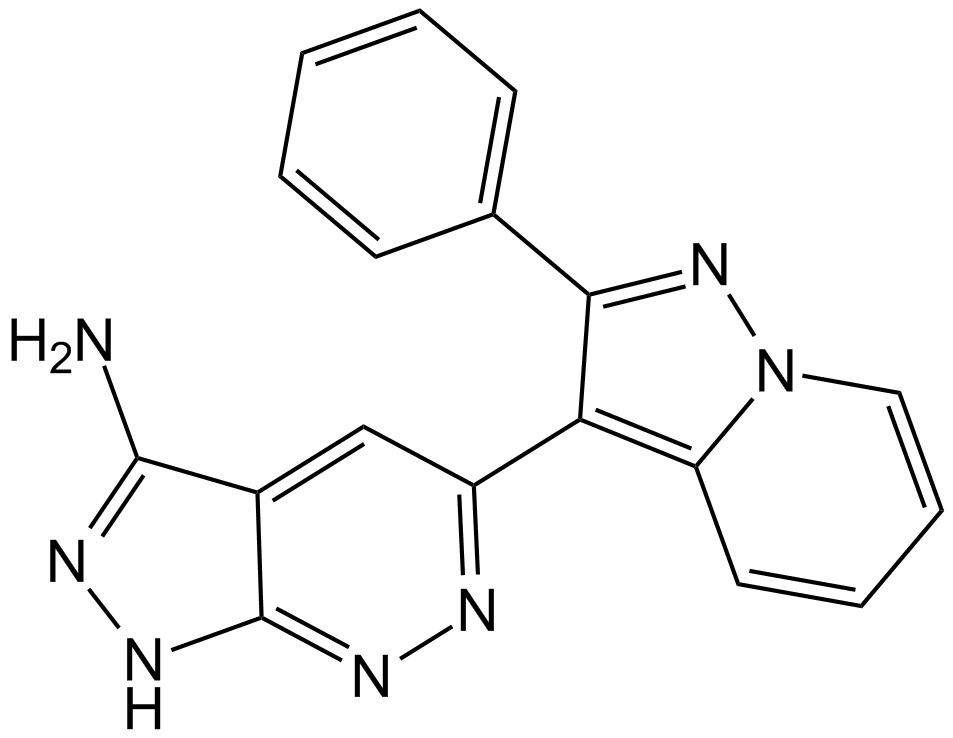 A8304 FR 180204Target: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor
A8304 FR 180204Target: ERKSummary: ERK inhibitor -
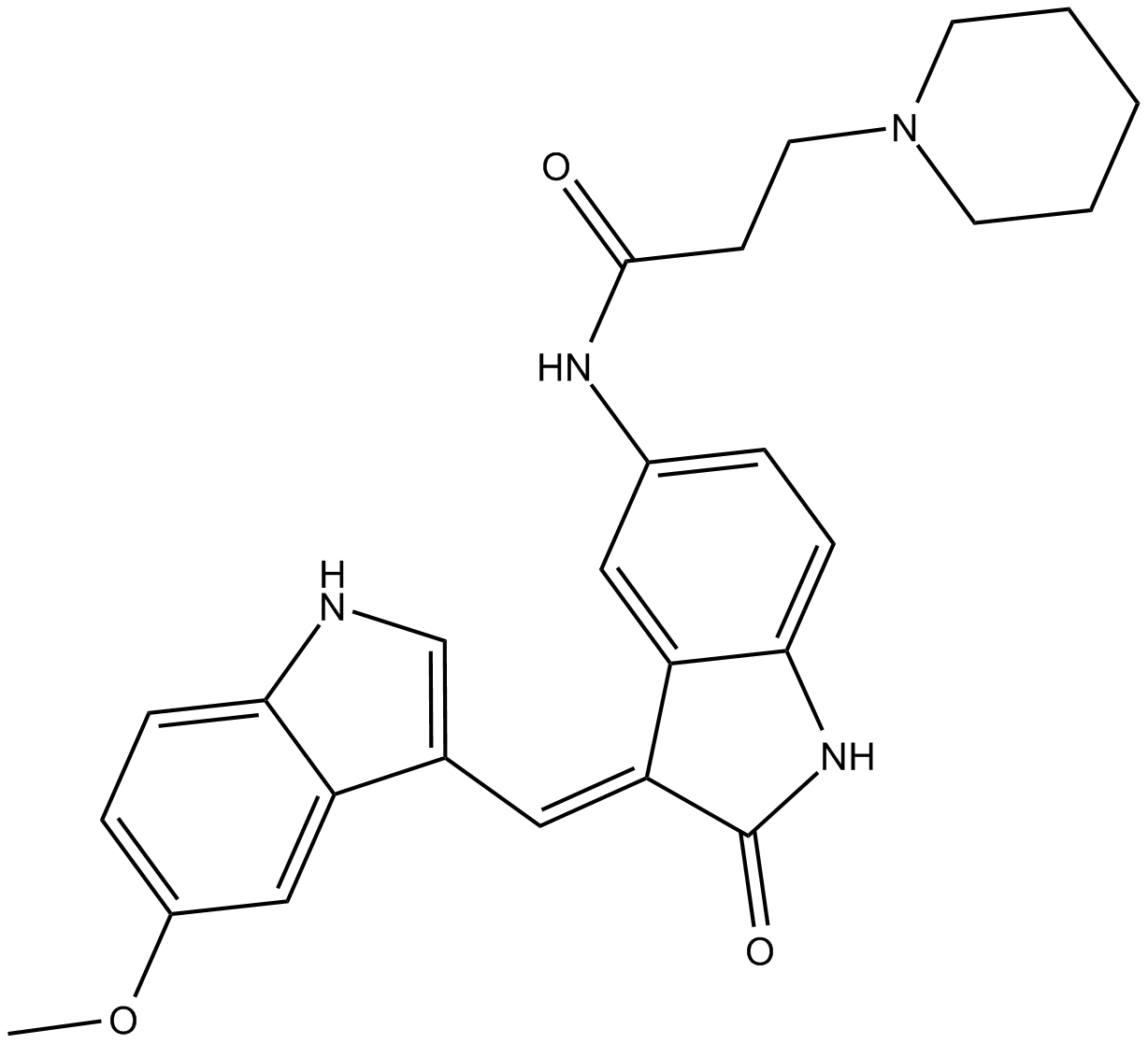 B6024 DEL-22379Summary: inhibitor of the dimerization of ERK
B6024 DEL-22379Summary: inhibitor of the dimerization of ERK -
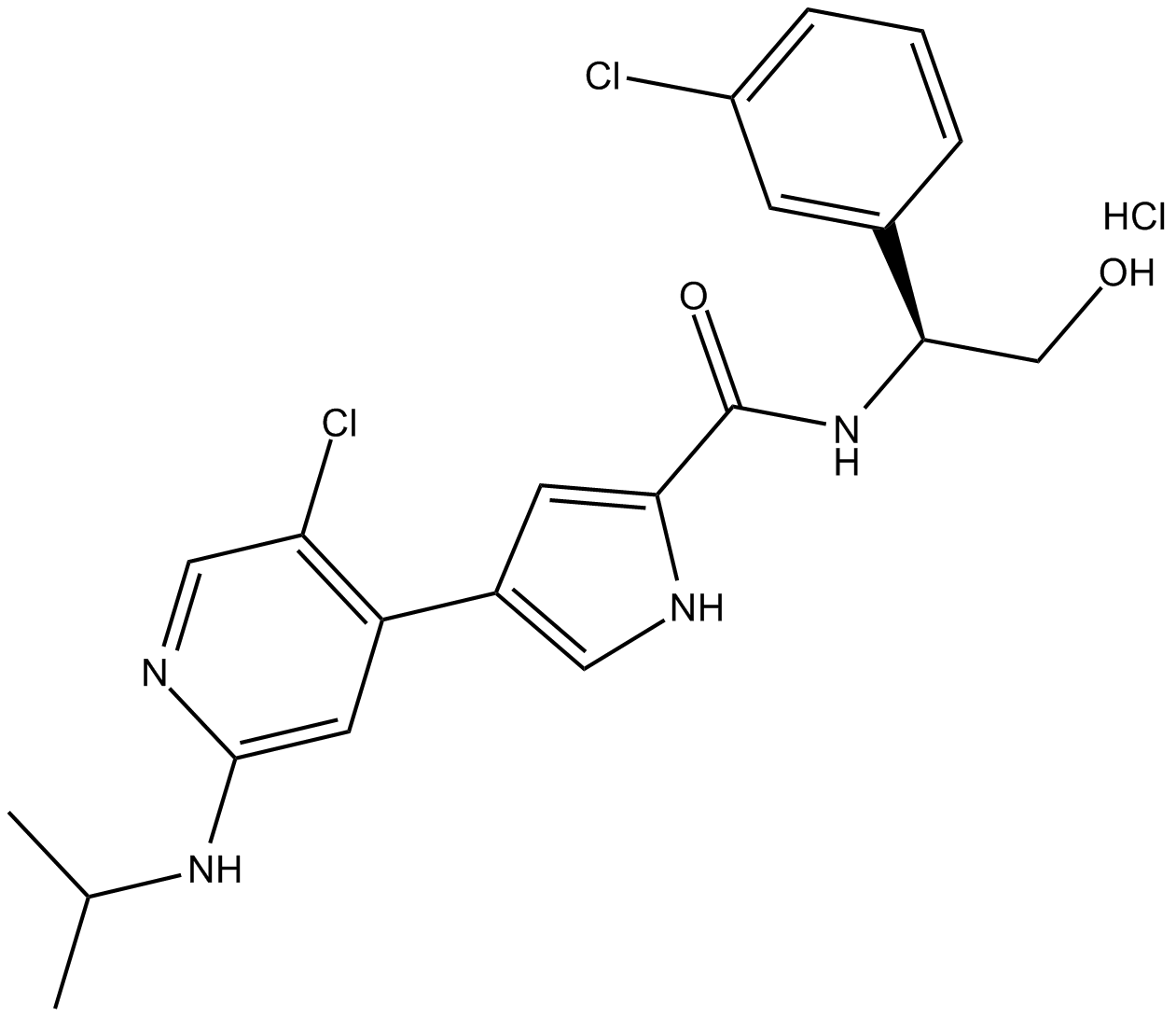 C3921 Ulixertinib (hydrochloride)Summary: reversible ERK1/2 inhibitor
C3921 Ulixertinib (hydrochloride)Summary: reversible ERK1/2 inhibitor -
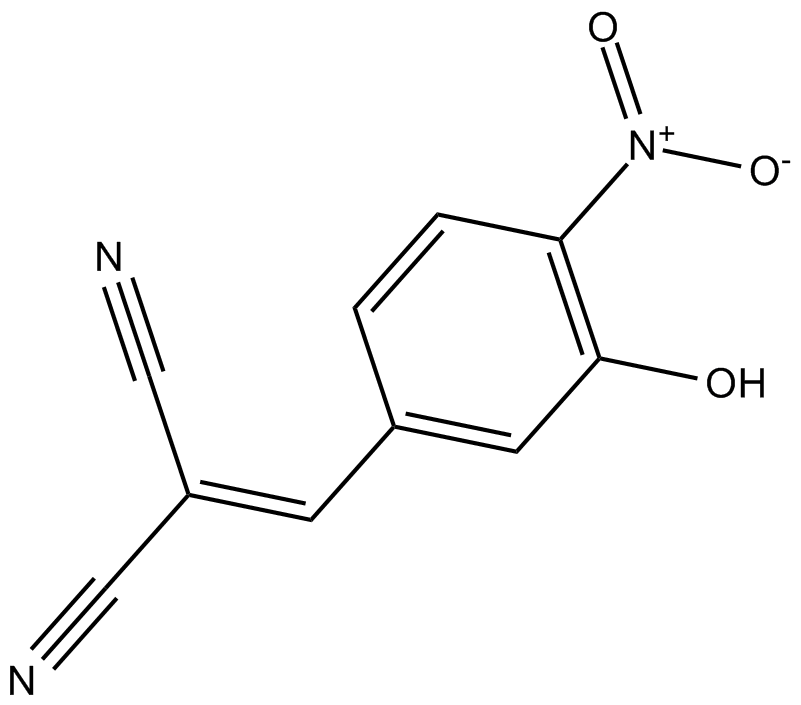 C4338 AG-126Summary: ERK1 (p44) and ERK2 (p42) inhibitor
C4338 AG-126Summary: ERK1 (p44) and ERK2 (p42) inhibitor -
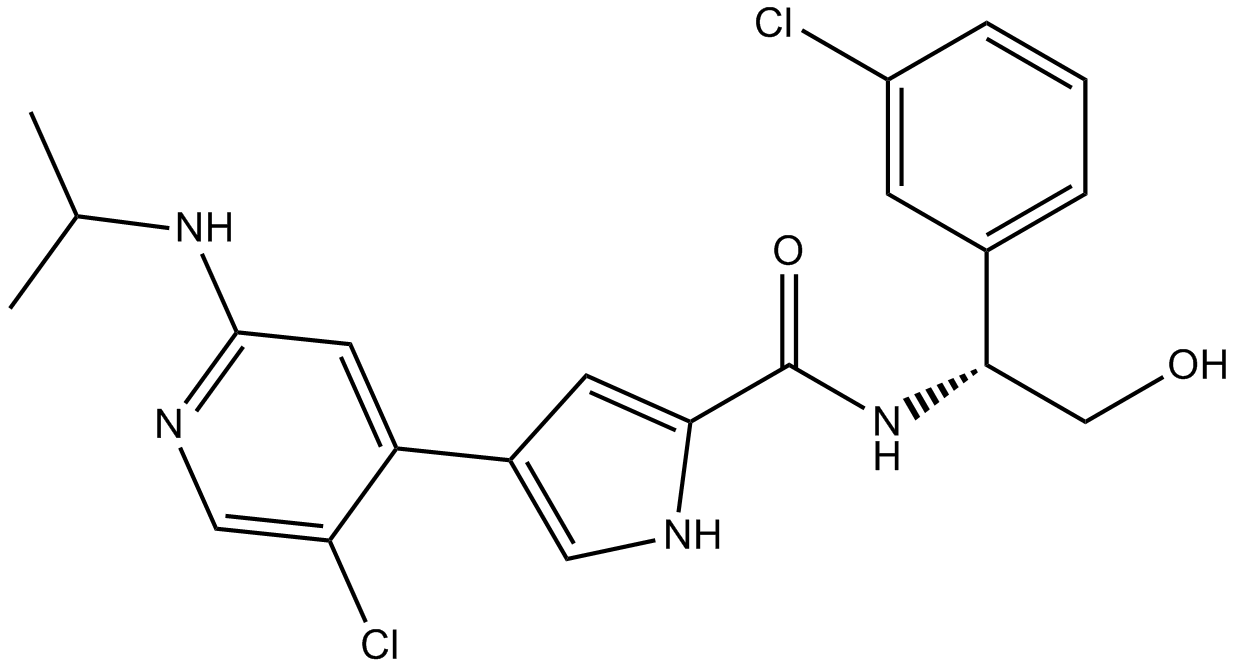 B1106 VRT752271Target: ERKSummary: ERK1/ERK2 inhibitor
B1106 VRT752271Target: ERKSummary: ERK1/ERK2 inhibitor -
 B5593 PluripotinSummary: dual inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1, MAPK3) and RasGAP
B5593 PluripotinSummary: dual inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1, MAPK3) and RasGAP

