Immunology/Inflammation

The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
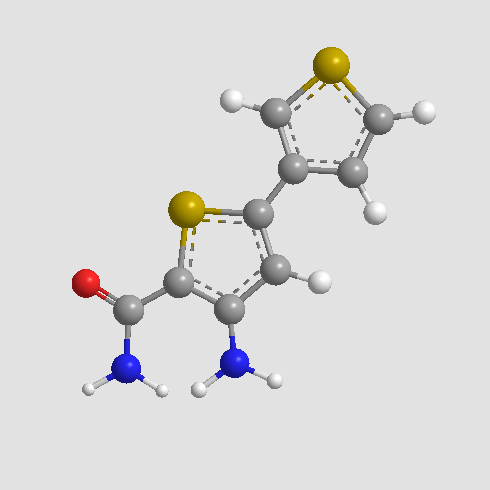 B1585 SC-514Summary: ATP-competitive IKK-2 inhibitor, orally active
B1585 SC-514Summary: ATP-competitive IKK-2 inhibitor, orally active -
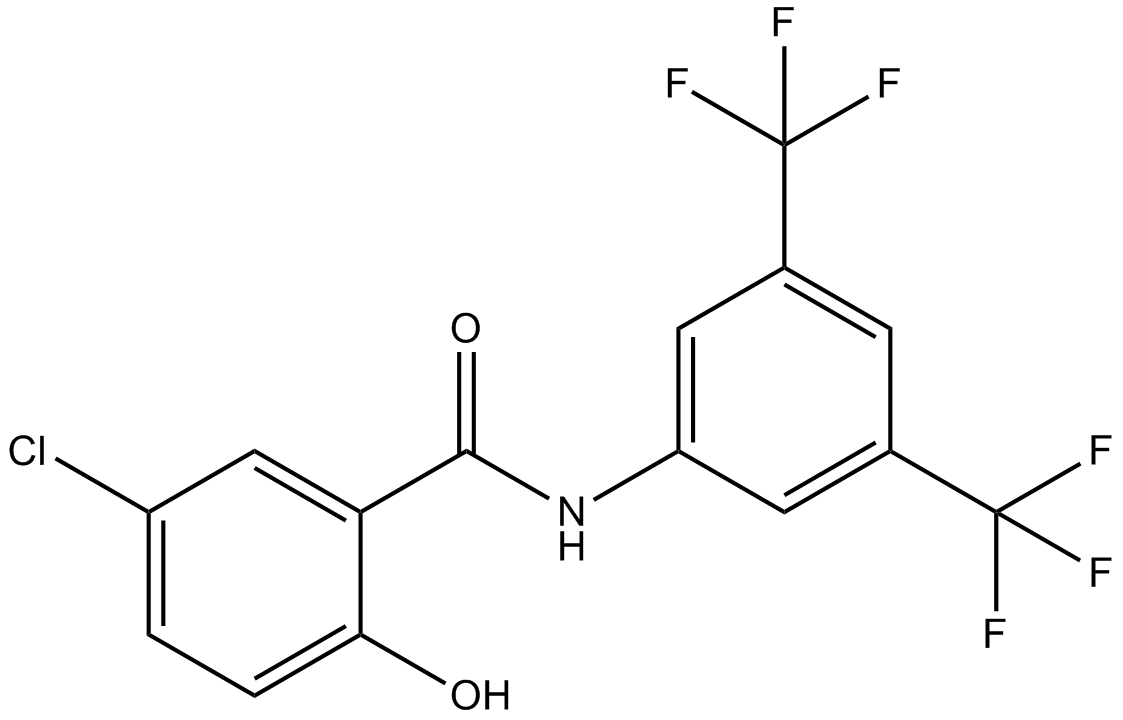 B1587 IMD 03541 CitationSummary: IKKβ inhibitor
B1587 IMD 03541 CitationSummary: IKKβ inhibitor -
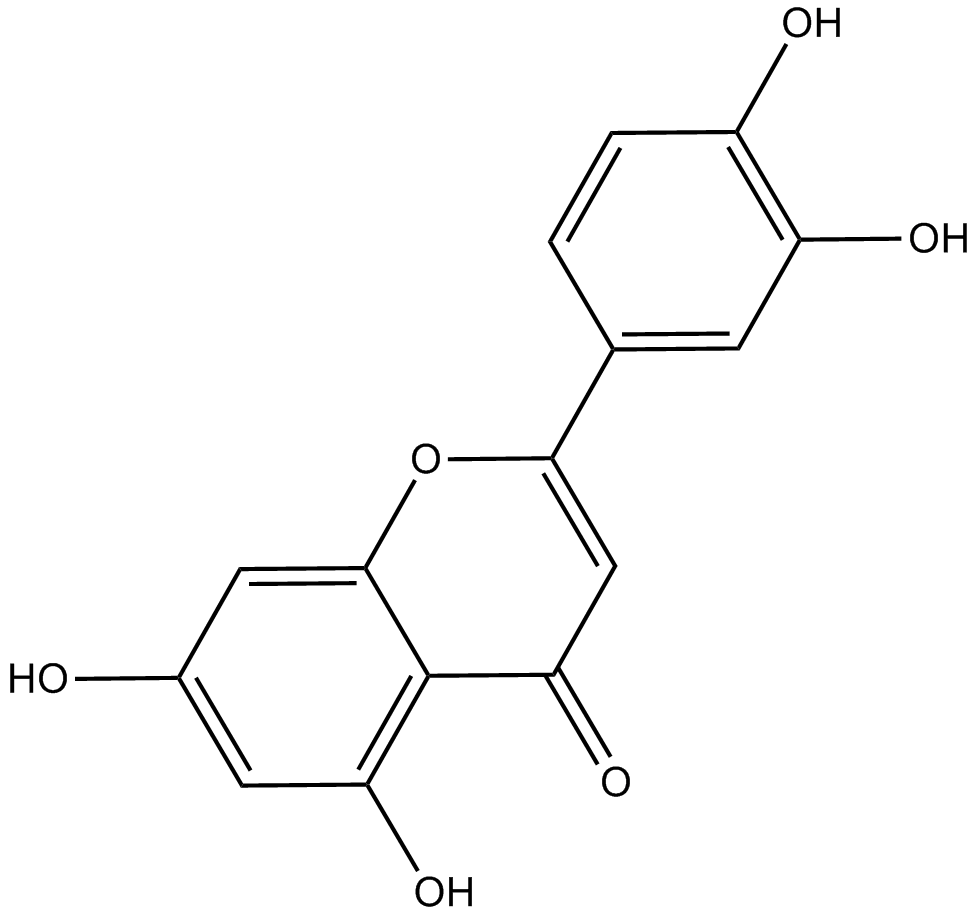 N1831 LuteolinTarget: AP-1|MMP|15-lipoxygenasesSummary: Antioxidant and free radical scavenger
N1831 LuteolinTarget: AP-1|MMP|15-lipoxygenasesSummary: Antioxidant and free radical scavenger -
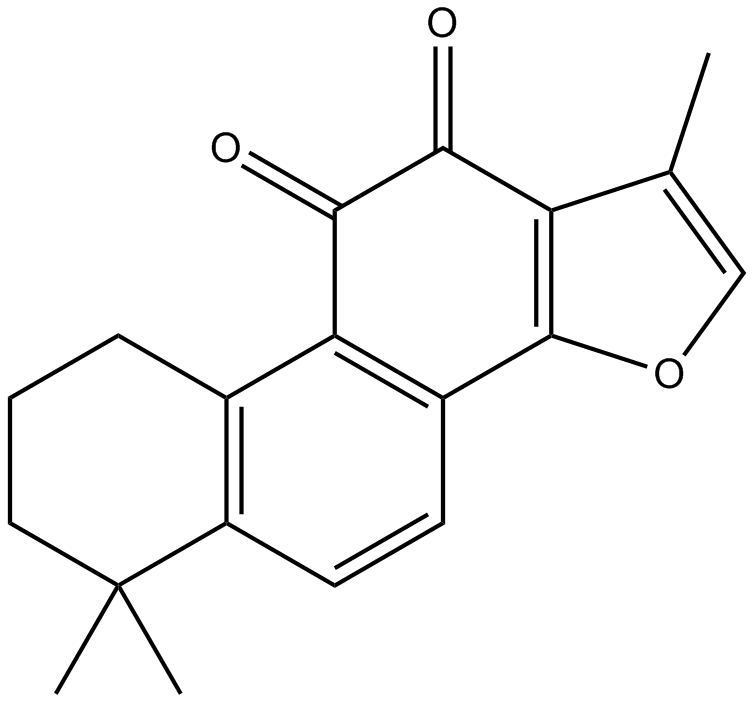 N1846 Tanshinone IIATarget: AP-1|MAGLSummary: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory reagent
N1846 Tanshinone IIATarget: AP-1|MAGLSummary: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory reagent -
 B4655 BMS-345541(free base)Summary: IKK-1/IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective
B4655 BMS-345541(free base)Summary: IKK-1/IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
 A3248 BMS345541 hydrochlorideTarget: IKKSummary: IKK inhibitor,highly selective
A3248 BMS345541 hydrochlorideTarget: IKKSummary: IKK inhibitor,highly selective -
 A3485 IKK-2 inhibitor VIIISummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A3485 IKK-2 inhibitor VIIISummary: IKK-2 inhibitor,potent and selective

