DNA Damage/DNA Repair
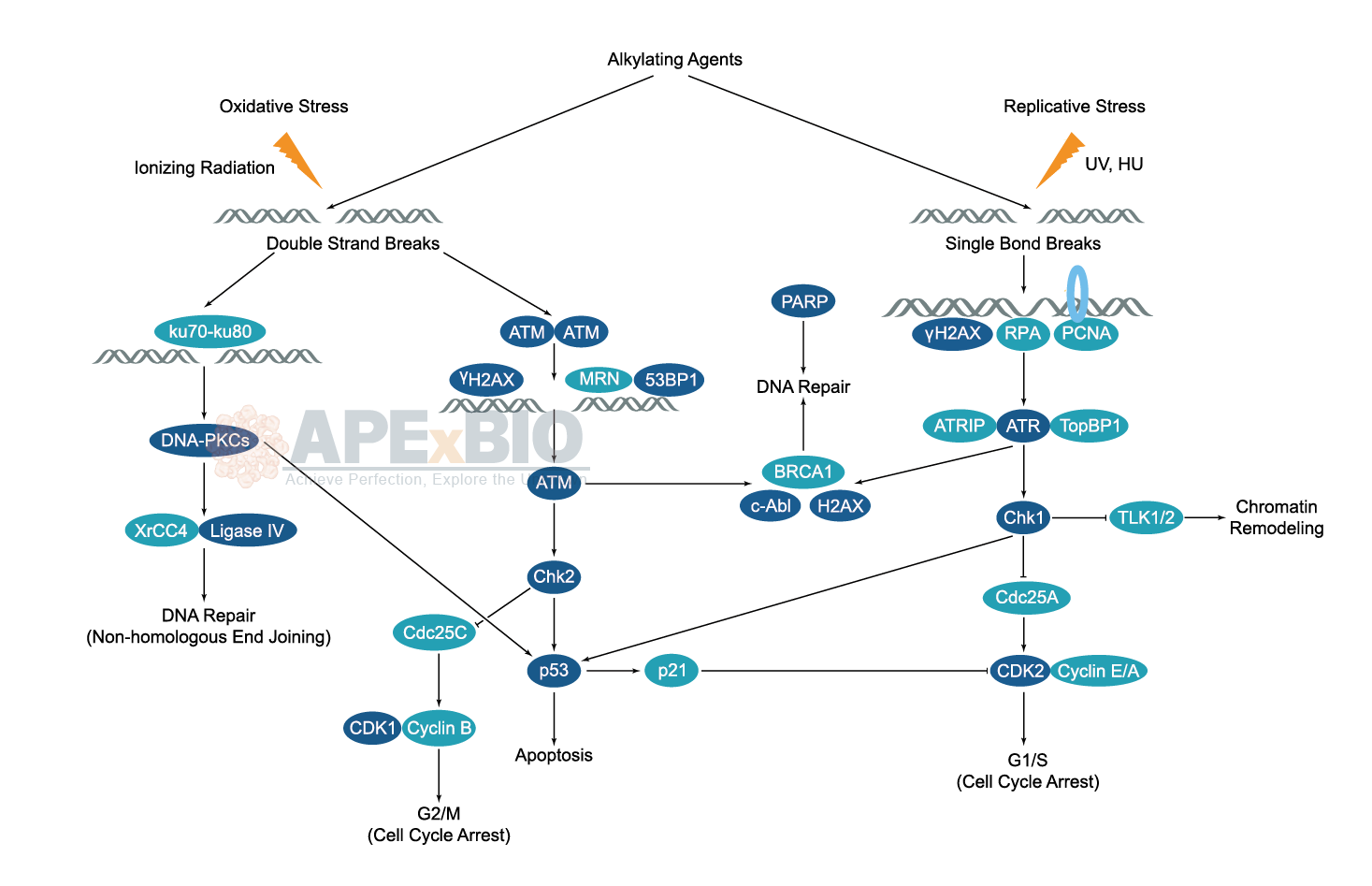
The DNA in a human cell receives tens of thousands of damages per day due to both external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) stress. The exogenous damages are caused by chemical contamination, UV light, ionizing radiation and alkylation/methylation etc, while the endogenous damages are coming from oxidation, alkylation and hydrolysis of bases etc. Since single strand and double strand breaks of DNA will occur after the damage, unrepaired DNA damage leads to cell senescent, apoptosis and malignancies etc. To overcome this threat, cell has developed DNA damage response, to detect DNA damage and mediate its repair.
DNA repair involves multiple mechanisms such as mismatch, base excision, and nucleotide excision repair etc. A group of proteins and pathways are participated in those processes. ATM/ATR kinases and DNA-PK are crucial for the detection of the DNA damage. Chromatin remodelers regulate chromatin accessibility for the DNA repair factors to function. RPA, Rad51 and the fanconi anemia proteins act directly on repairing the DNA damage. p53 network, the RAS GTPase superfamily, and the ubiquitin system also play important part in the DNA damage response. Aberrant DNA damage response is linked to aging, cancer and immune diseases.
-
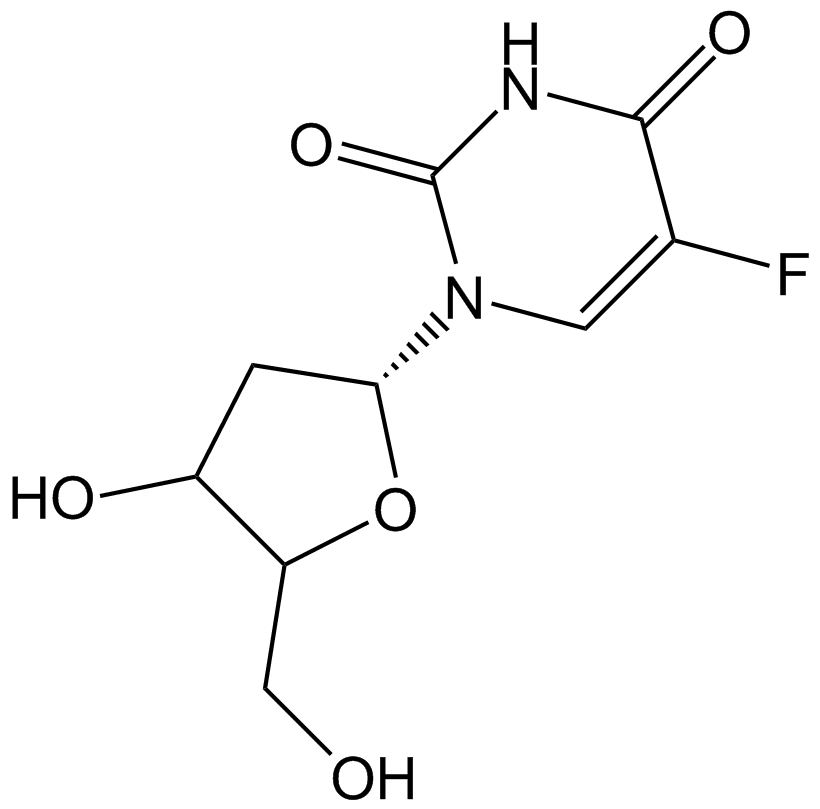 A2402 FloxuridineTarget: Synthases/SynthetasesSummary: Antineoplastic antimetabolite
A2402 FloxuridineTarget: Synthases/SynthetasesSummary: Antineoplastic antimetabolite -
 A2171 CarboplatinSummary: Antitumor agent that forms platinum-DNA adducts.
A2171 CarboplatinSummary: Antitumor agent that forms platinum-DNA adducts. -
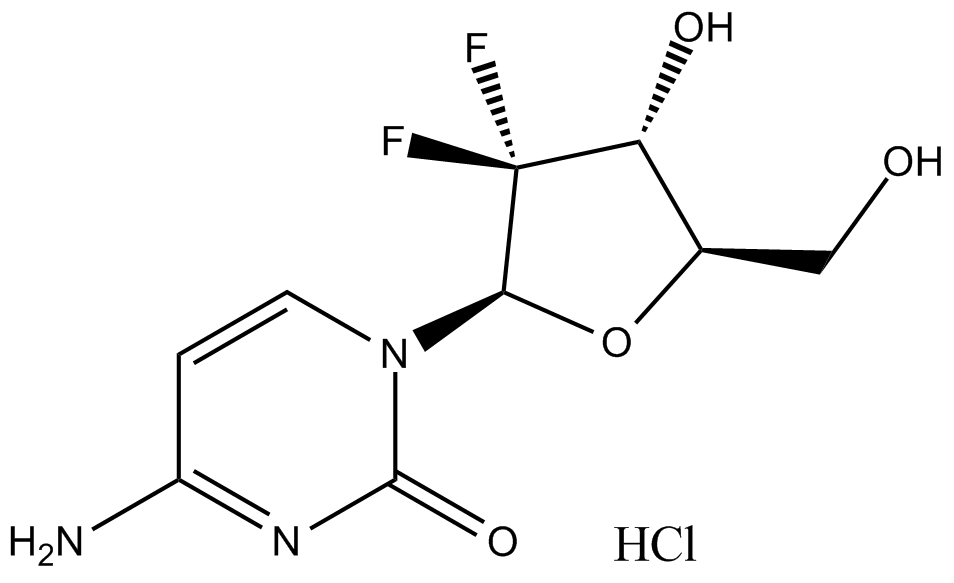 A1402 Gemcitabine HClSummary: Inhibits DNA synthesis,deoxycytidine analog
A1402 Gemcitabine HClSummary: Inhibits DNA synthesis,deoxycytidine analog -
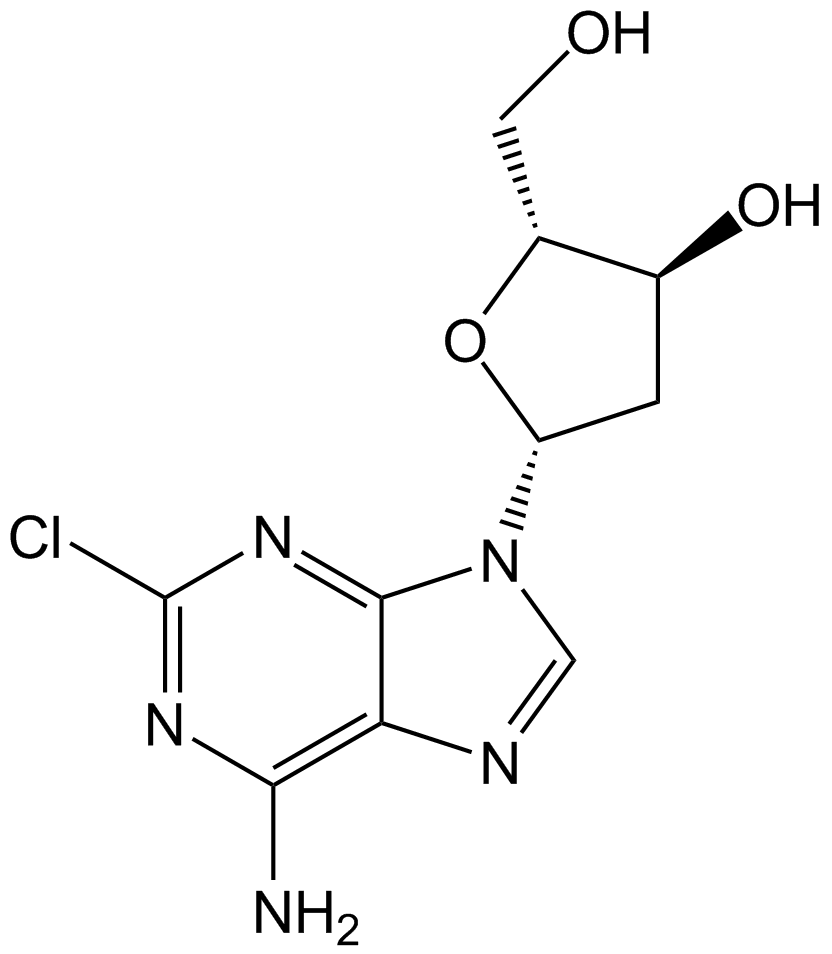 A2187 CladribineTarget: Adenosine DeaminasesSummary: Apoptosis inducer in CLL cells
A2187 CladribineTarget: Adenosine DeaminasesSummary: Apoptosis inducer in CLL cells -
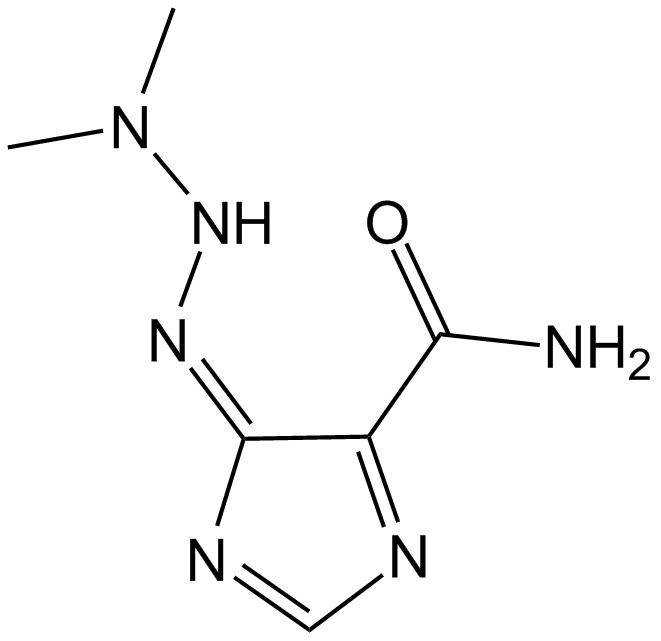 A2197 DacarbazineTarget: DNA AlkylatingSummary: Antineoplastic( malignant melanoma and sarcomas)
A2197 DacarbazineTarget: DNA AlkylatingSummary: Antineoplastic( malignant melanoma and sarcomas) -
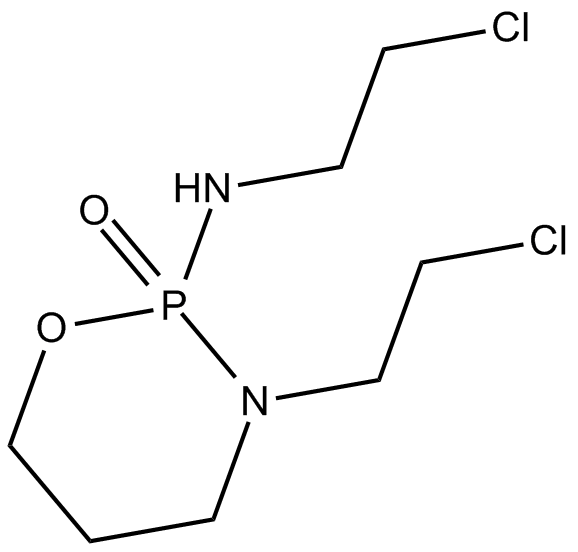 A2097 IfosfamideTarget: DNA AlkylatingSummary: Cytostatic agent
A2097 IfosfamideTarget: DNA AlkylatingSummary: Cytostatic agent -
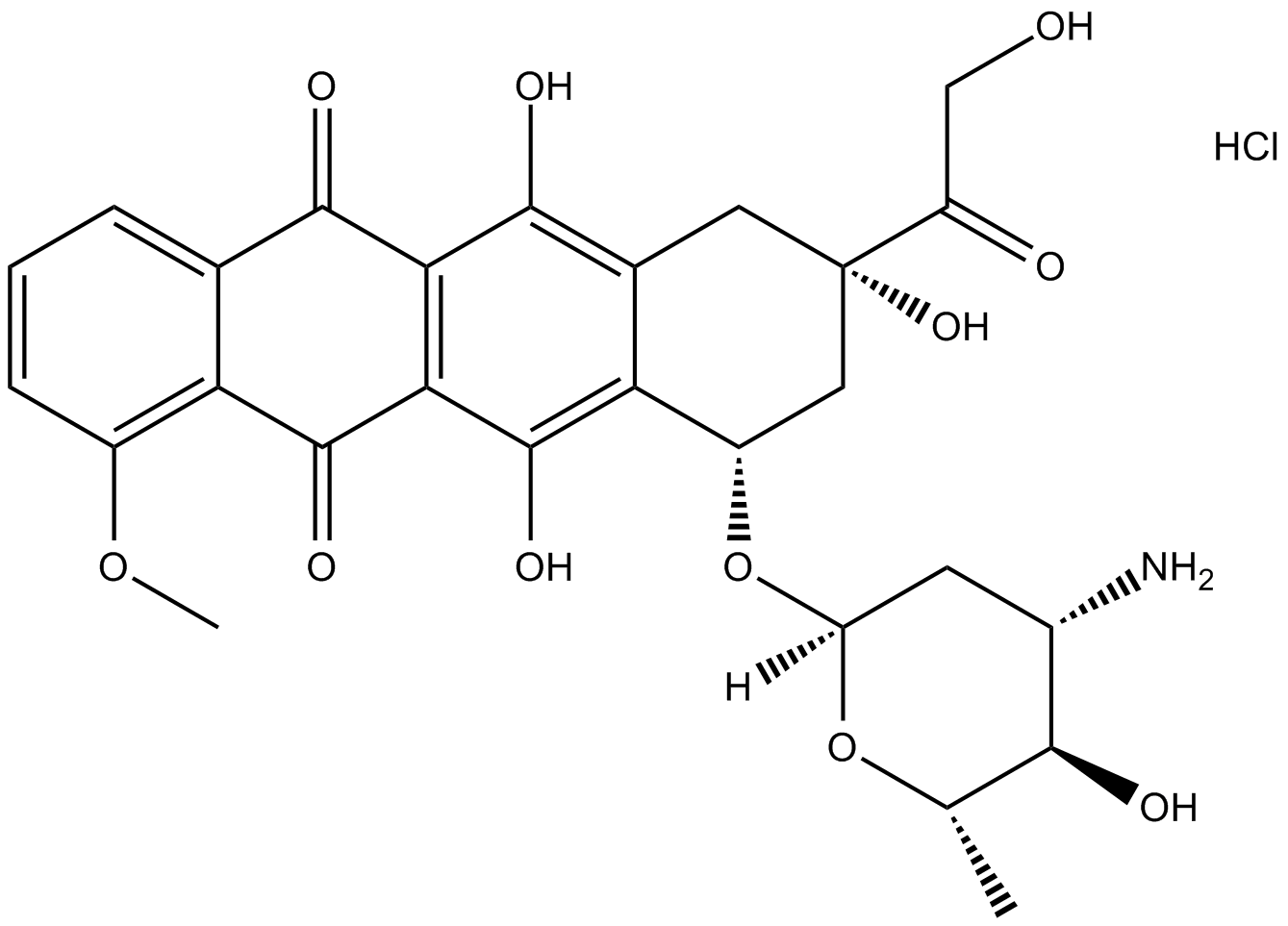 A2451 Epirubicin HClTarget: TopoisomerasesSummary: Antibiotic antitumor agent
A2451 Epirubicin HClTarget: TopoisomerasesSummary: Antibiotic antitumor agent -
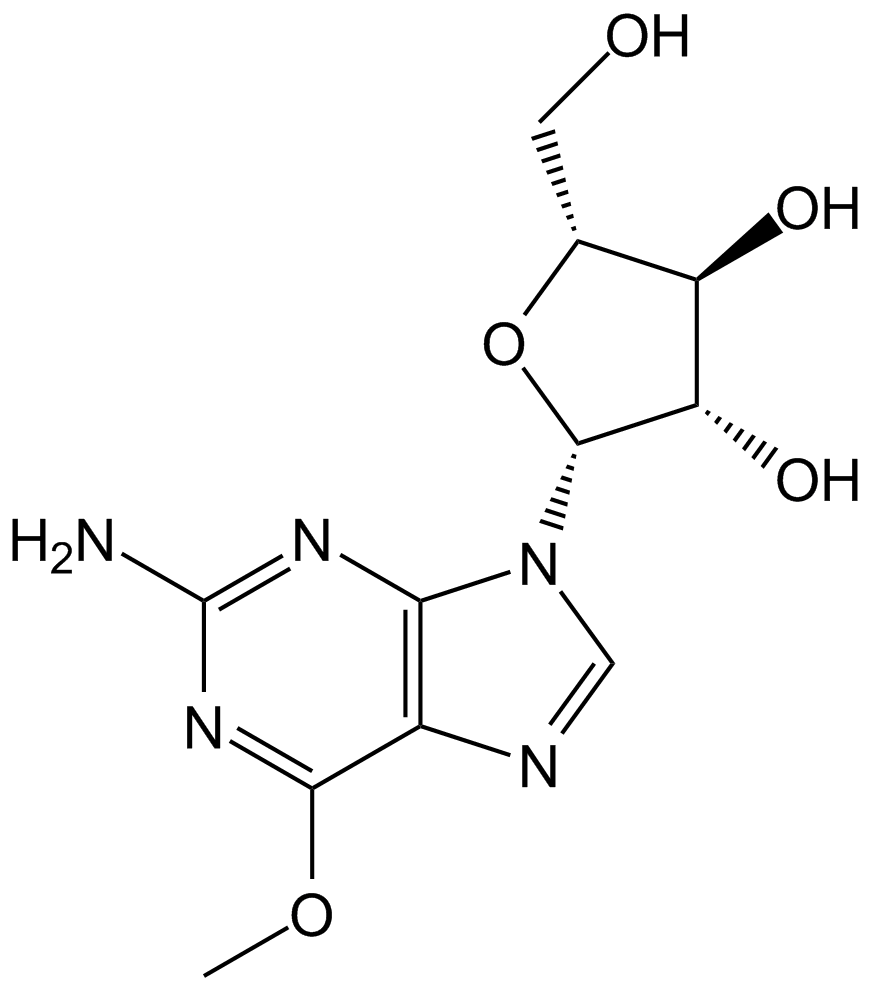 A1379 NelarabineSummary: Prodrug of ara-G for T-LBL/T-ALL
A1379 NelarabineSummary: Prodrug of ara-G for T-LBL/T-ALL -
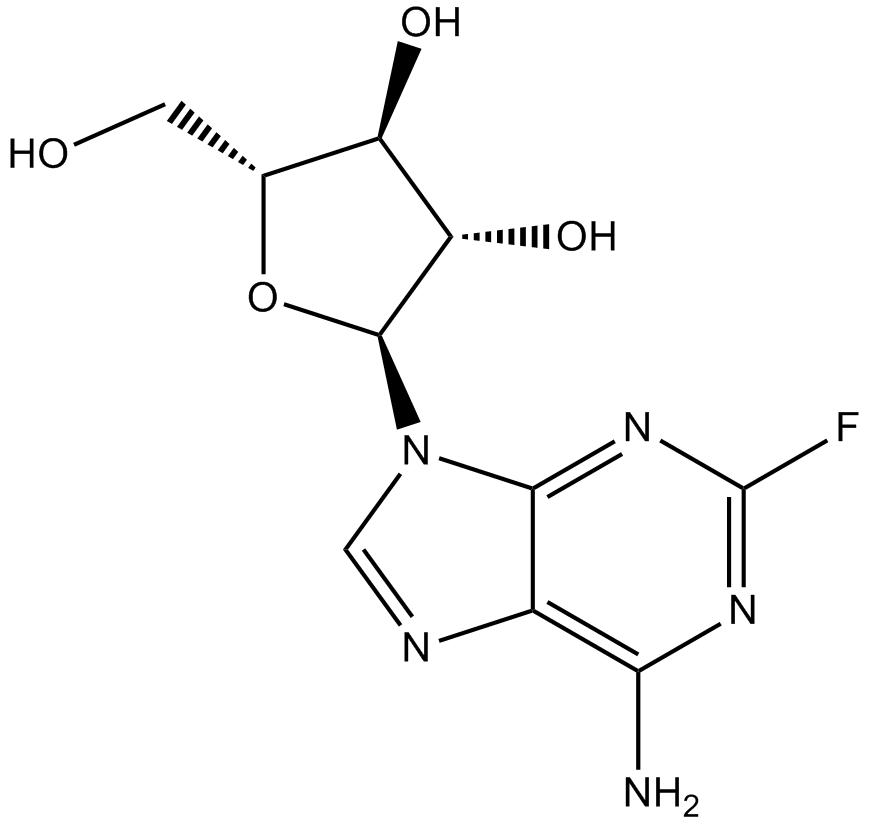 A5424 FludarabineSummary: DNA synthsis inhibitor
A5424 FludarabineSummary: DNA synthsis inhibitor -
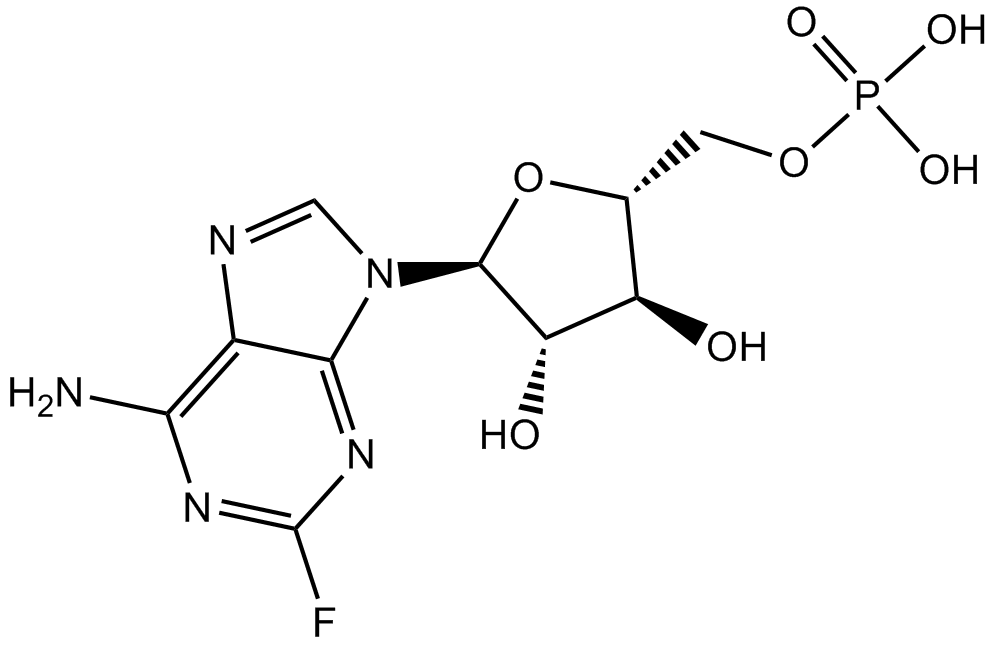 A8317 Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)2 CitationTarget: STATSummary: Inhibits STAT1 activation and DNA synthesis
A8317 Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)2 CitationTarget: STATSummary: Inhibits STAT1 activation and DNA synthesis

