Angiogenesis
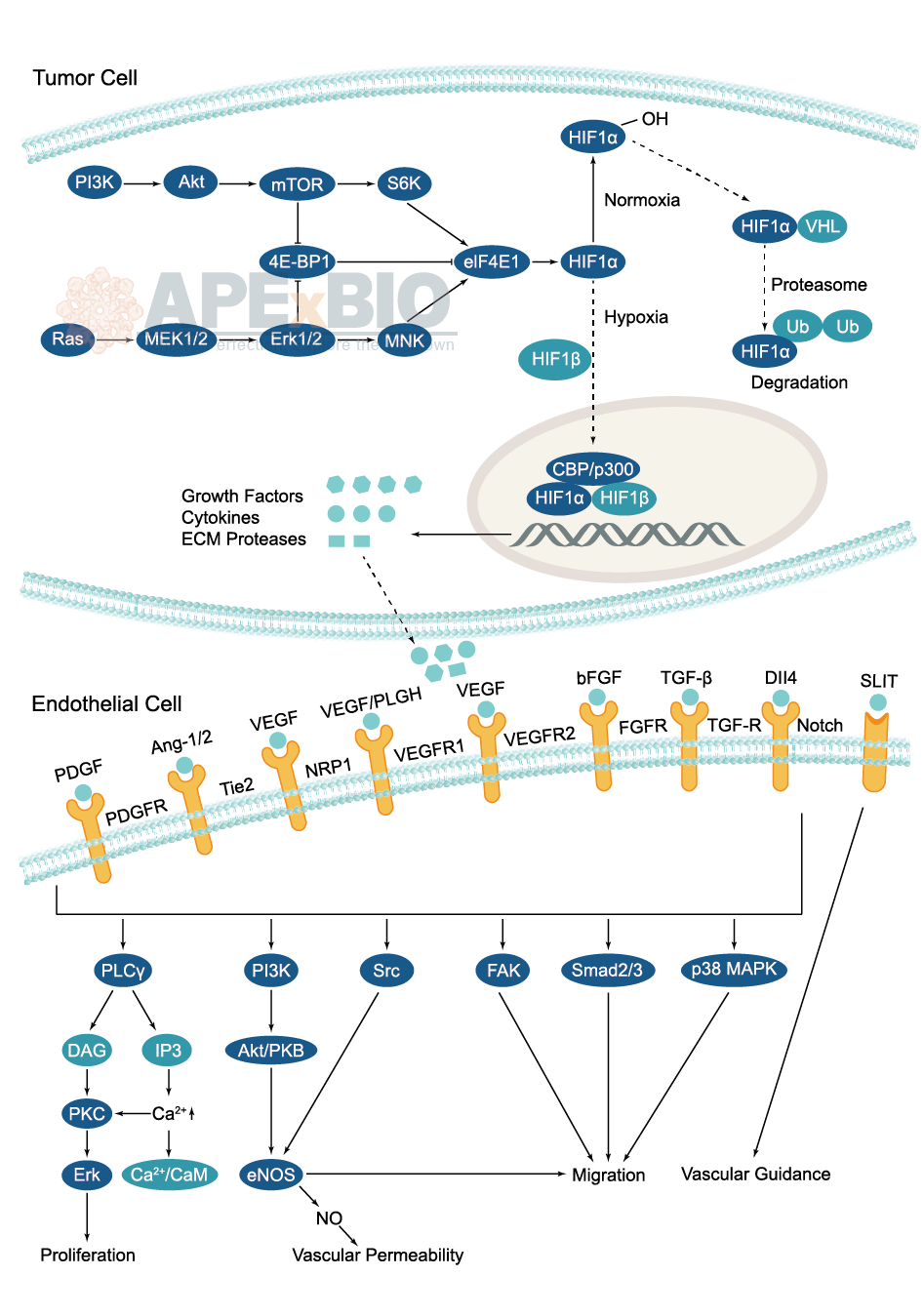
During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
 A4509 PX 12Target: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor
A4509 PX 12Target: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor -
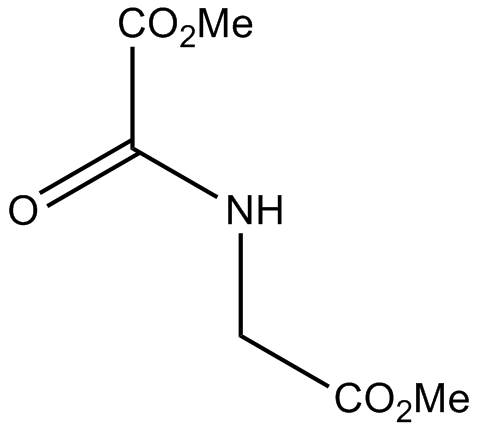 A4506 DMOGTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable
A4506 DMOGTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable -
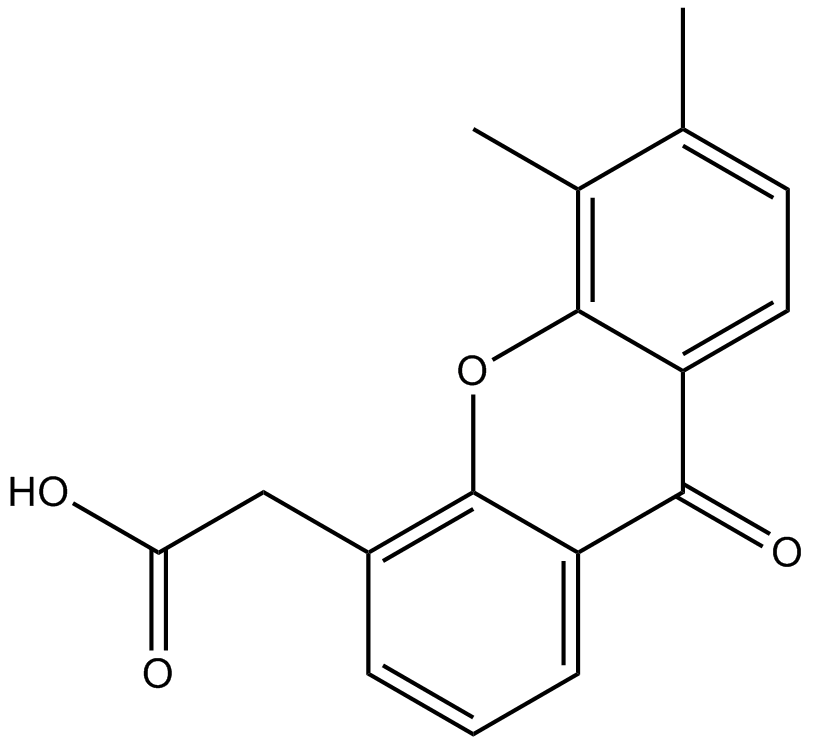 A8233 DMXAA (Vadimezan)2 CitationTarget: DT-diaphorasesSummary: Tumnor vascular disrupting agent, apoptosis inducer
A8233 DMXAA (Vadimezan)2 CitationTarget: DT-diaphorasesSummary: Tumnor vascular disrupting agent, apoptosis inducer -
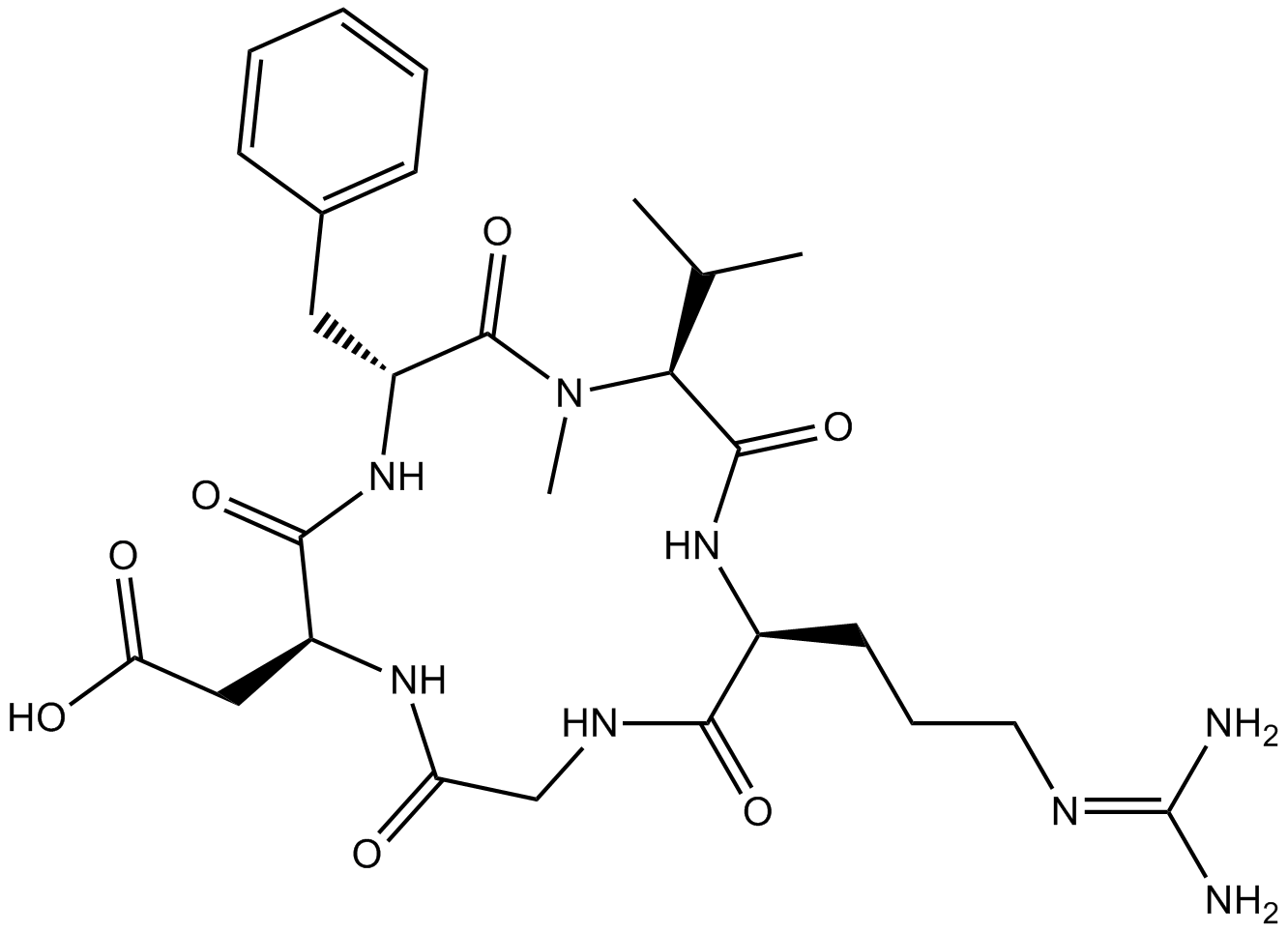 A8660 Cilengitide1 CitationTarget: IntegrinsSummary: Integrin inhibitor for αvβ3 and αvβ5
A8660 Cilengitide1 CitationTarget: IntegrinsSummary: Integrin inhibitor for αvβ3 and αvβ5 -
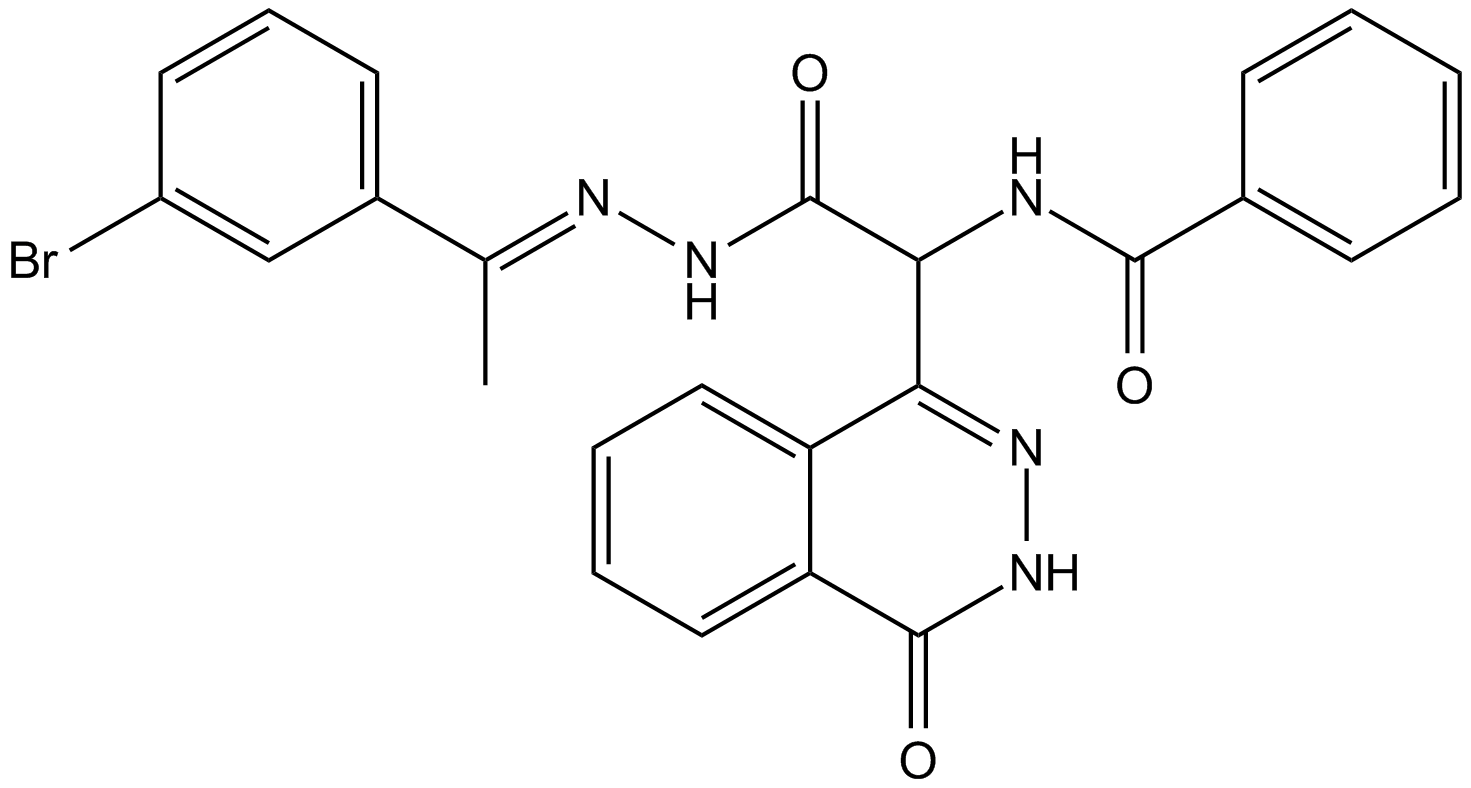 A8669 AC 55541Target: PARSummary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective
A8669 AC 55541Target: PARSummary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective -
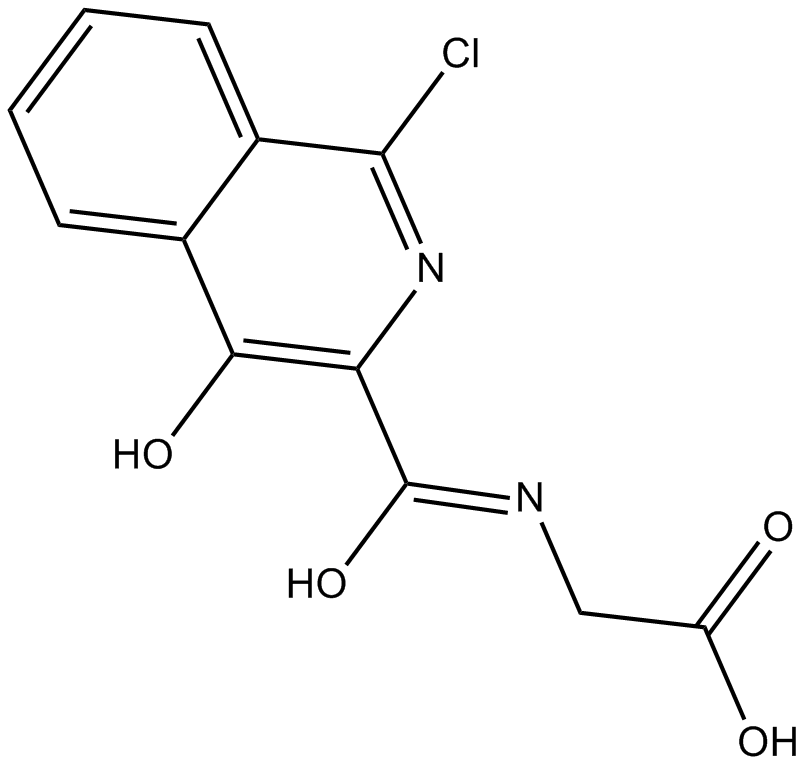 B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor -
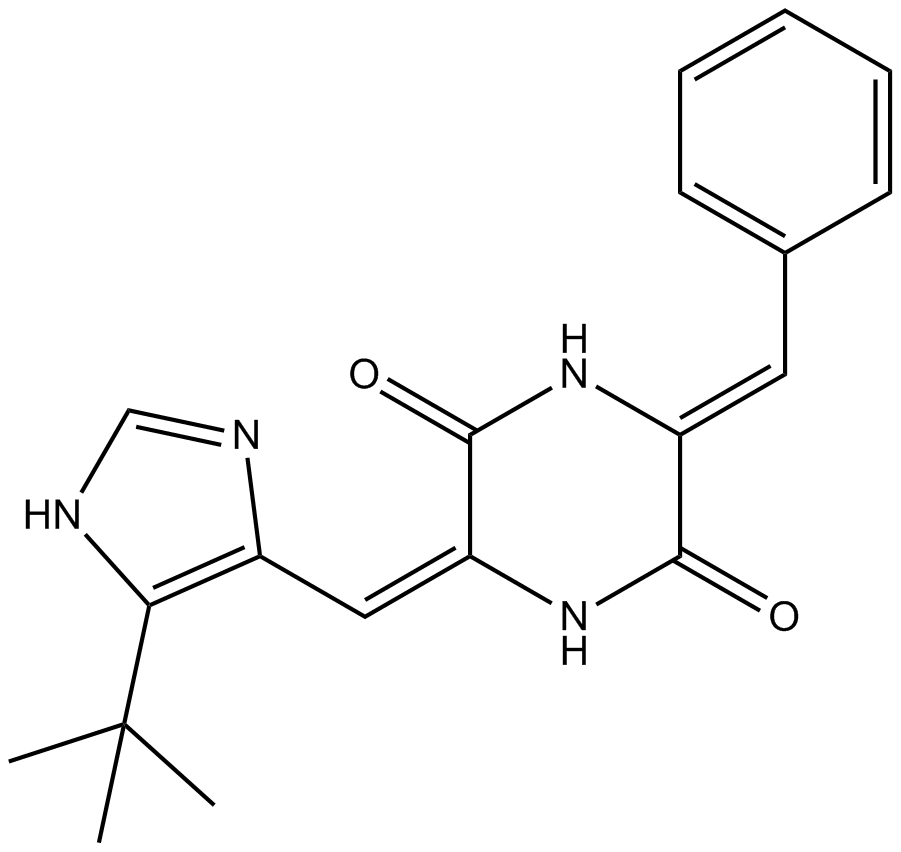 B2298 Plinabulin (NPI-2358)Target: Vascular Disrupting Agents (VDA)Summary: vascular disrupting agent
B2298 Plinabulin (NPI-2358)Target: Vascular Disrupting Agents (VDA)Summary: vascular disrupting agent -
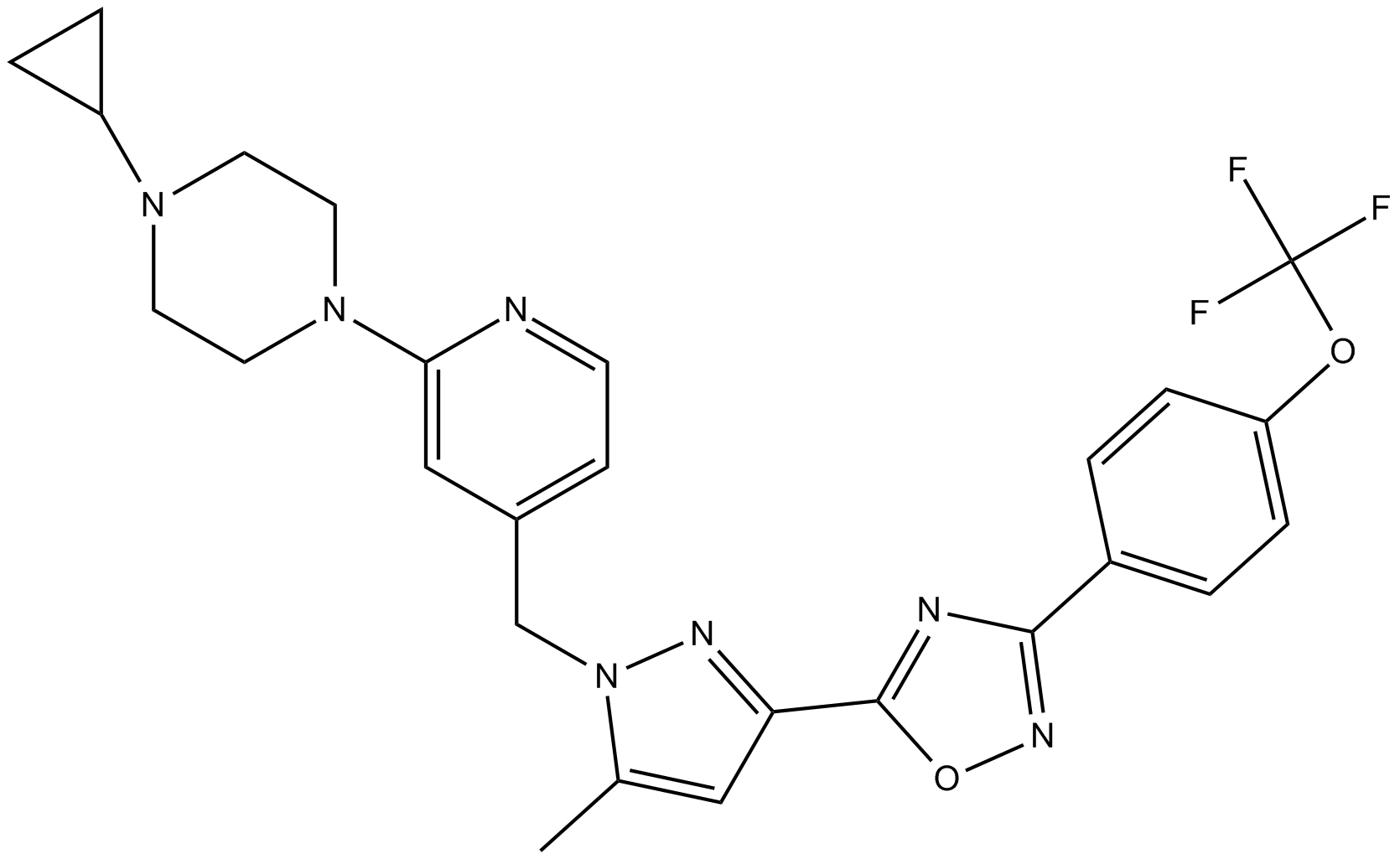 B1115 BAY 87-2243Target: Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs)Summary: HIF-1 inhibitor,potent and selective
B1115 BAY 87-2243Target: Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs)Summary: HIF-1 inhibitor,potent and selective -
 A3302 CGI-17461 CitationTarget: BTKSummary: Btk inhibitor
A3302 CGI-17461 CitationTarget: BTKSummary: Btk inhibitor

