Search results for: 'research area cell cycle e1 enzyme'
-
 BA8440 AtabecestatSummary: Atabecestat (JNJ-54861911) is a potent brain-permeable and orally active beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibitor that potently reduces reduced Aβ protein expression in cerebrospinal fluid.
BA8440 AtabecestatSummary: Atabecestat (JNJ-54861911) is a potent brain-permeable and orally active beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibitor that potently reduces reduced Aβ protein expression in cerebrospinal fluid. -
 K1071 HyperScript™ Reverse TranscriptaseSummary: Thermally stable reverse transcriptase used to synthesize complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template.
K1071 HyperScript™ Reverse TranscriptaseSummary: Thermally stable reverse transcriptase used to synthesize complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template. -
 P1179 Recombinant Mouse IGF-1Summary: The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) belonged to the insulin gene family, are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types
P1179 Recombinant Mouse IGF-1Summary: The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) belonged to the insulin gene family, are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types -
 P1203 Recombinant Rat IGF-1Summary: The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) belonged to the insulin gene family, are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types
P1203 Recombinant Rat IGF-1Summary: The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) belonged to the insulin gene family, are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types -
 P1149 Recombinant Human IFN-beta1bSummary: IFN-βs are proteins produced by many cell types including lymphocytes (NK cells, B-cells and T-cells), macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, osteoblasts and others.
P1149 Recombinant Human IFN-beta1bSummary: IFN-βs are proteins produced by many cell types including lymphocytes (NK cells, B-cells and T-cells), macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, osteoblasts and others. -
 BA3203 XL44Summary: XL44 is a binding agent for the hRpn13 protein and induces apoptosis through an hRpn13-dependent mechanism, while also limiting cell survival through a PCLAF-dependent mechanism.
BA3203 XL44Summary: XL44 is a binding agent for the hRpn13 protein and induces apoptosis through an hRpn13-dependent mechanism, while also limiting cell survival through a PCLAF-dependent mechanism. -
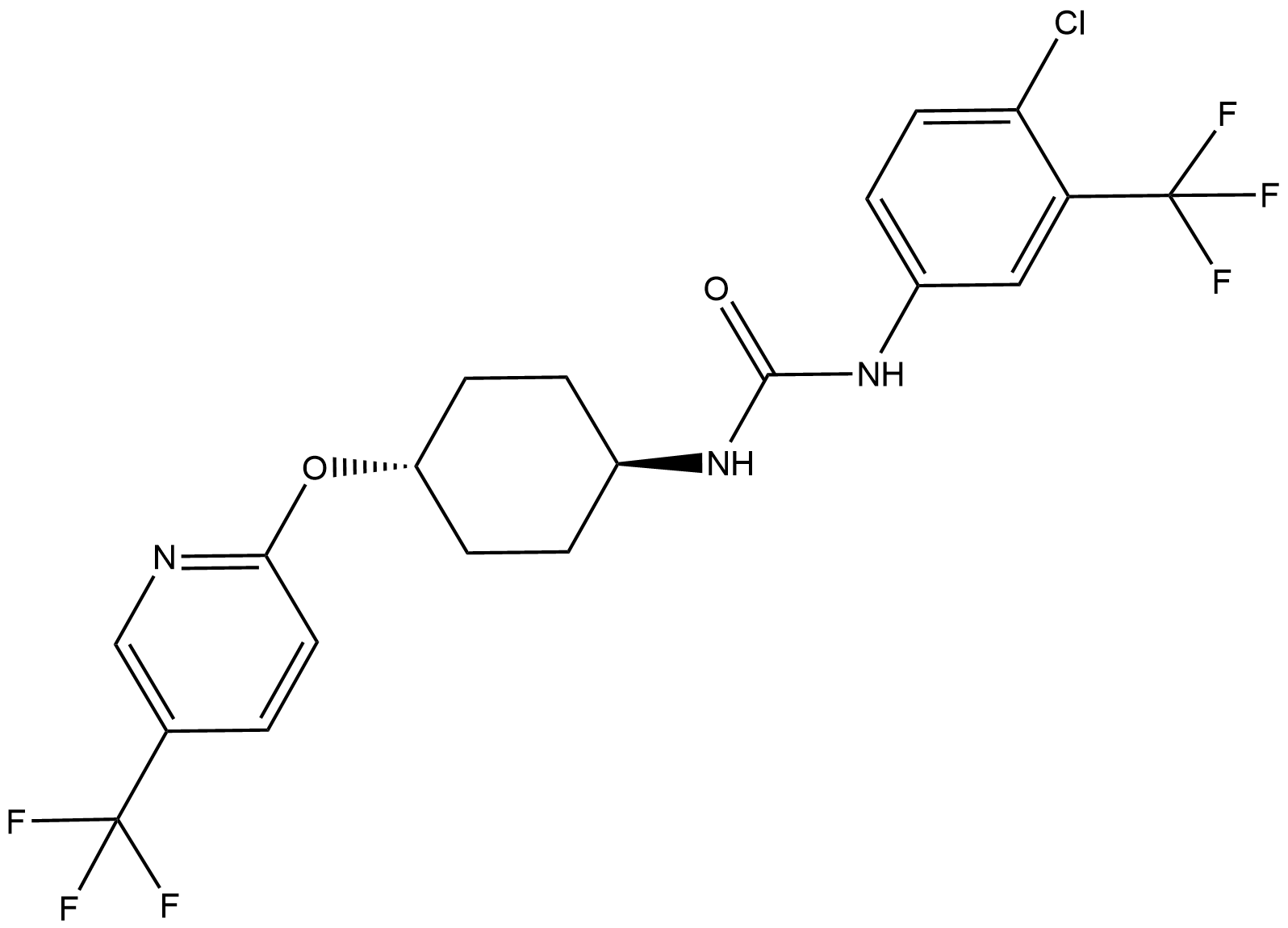 BA3456 UC2288Summary: UC2288 is a novel, cell permeable and orally active attenuating reagent (with relatively selective activity against p21) based on the structural synthesis of sorafenib.
BA3456 UC2288Summary: UC2288 is a novel, cell permeable and orally active attenuating reagent (with relatively selective activity against p21) based on the structural synthesis of sorafenib. -
 R1119 EZ Cap™ CM-EGFP Probe mRNA (m1Ψ)Summary: Cell membrane (CM) probes mRNA with EGFP, modified by N1-Methylpseudo-UTP (m1Ψ), providing higher transcription efficiency and suppressing RNA-mediated innate immune activation.
R1119 EZ Cap™ CM-EGFP Probe mRNA (m1Ψ)Summary: Cell membrane (CM) probes mRNA with EGFP, modified by N1-Methylpseudo-UTP (m1Ψ), providing higher transcription efficiency and suppressing RNA-mediated innate immune activation. -
 P1168 Recombinant Mouse IL-13Summary: Murine Interleukin-13 (IL-13) is expressed by the IL13 gene located on the chromosome 11 and secreted by many cell types, especially T helper type 2 (Th2) cells.
P1168 Recombinant Mouse IL-13Summary: Murine Interleukin-13 (IL-13) is expressed by the IL13 gene located on the chromosome 11 and secreted by many cell types, especially T helper type 2 (Th2) cells. -
 BA4056 ZIMSummary: ZIM, norbornene derived from 4-Aminoantipyrine, is a potent DNA damage inducer that causes genomic and chromosomal damage as well as inducing cell death and activating phagocytosis.
BA4056 ZIMSummary: ZIM, norbornene derived from 4-Aminoantipyrine, is a potent DNA damage inducer that causes genomic and chromosomal damage as well as inducing cell death and activating phagocytosis.

