PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling
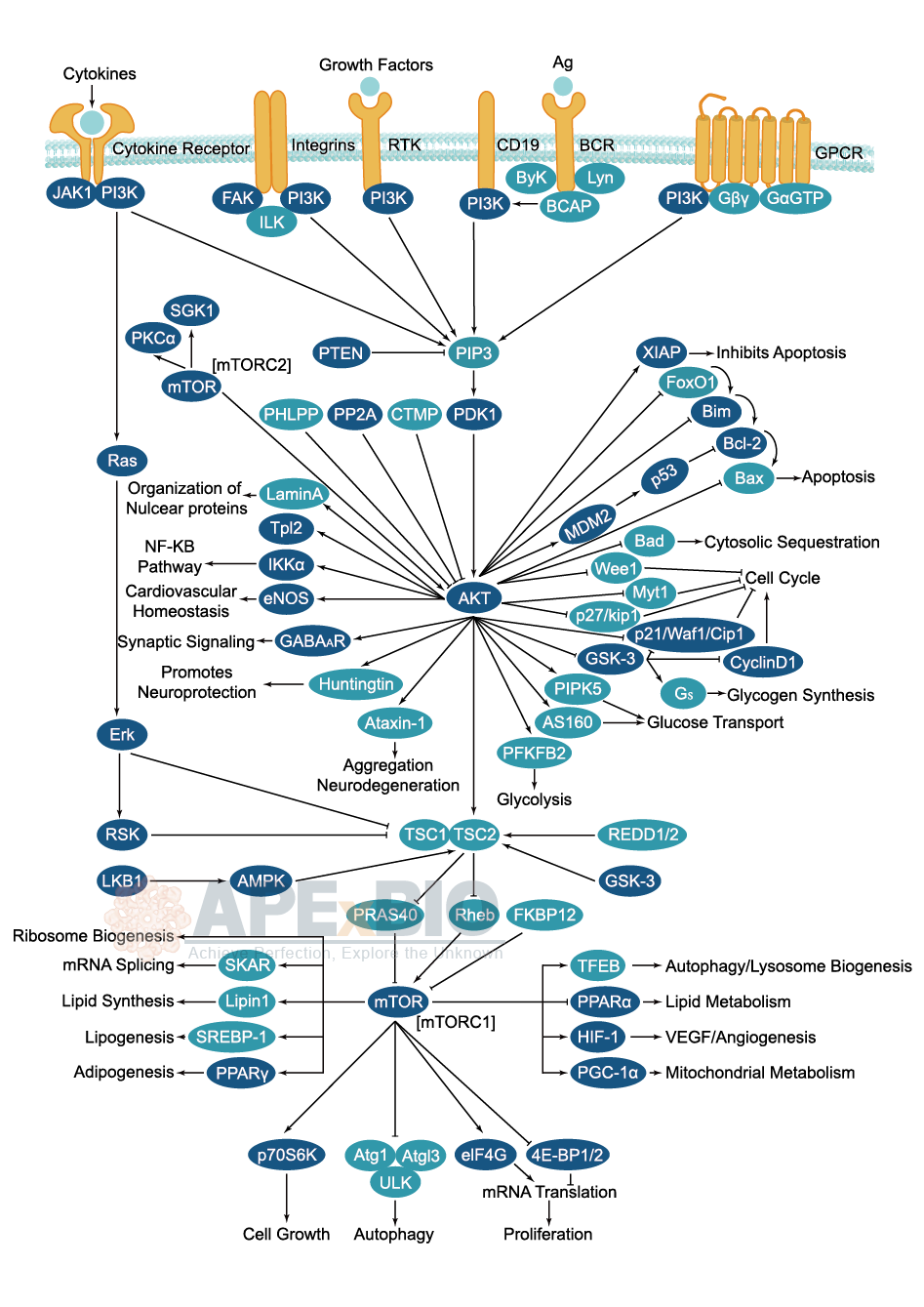
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is a key regulator in growth, survival, cell cycle proliferation, protein synthesis and glucose metabolism. Growth factors, hormones, and cytokines can activate this pathway by binding their cognate receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), cytokine receptor, or GPCR, resulting in the activation of lipid kinase PI3K which produces PIP3 at the plasma membrane.
The binding of PIP3 translocates Akt to cell membranes, enables Akt activation through phosphorylation at Thr308 mediated by phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1 (PDK1). In addition, Akt is phosphorylated at Ser473 by the mTOR-rictor complex, mTORC2. PTEN is a negative regulator of Akt signaling that reverses the function of PI3K by removing 3’-phosphate groups. Akt activity is also negatively regulated by the phosphatases PP2A and PHLPP. Akt propagates its signal to affect DNA transcription, cell cycle and apoptosis. Akt can activate mTOR directly by phosphorylation or indirectly, by phosphorylation and inactivation of mTOR inhibitor TSC2 and PRAS40. Together these mechanisms stimulate cell growth and G1 cell cycle progression through signaling via p70 S6 Kinase and inhibition of 4E-BP1. Defects in PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling are implicated in cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular disease etc.
-
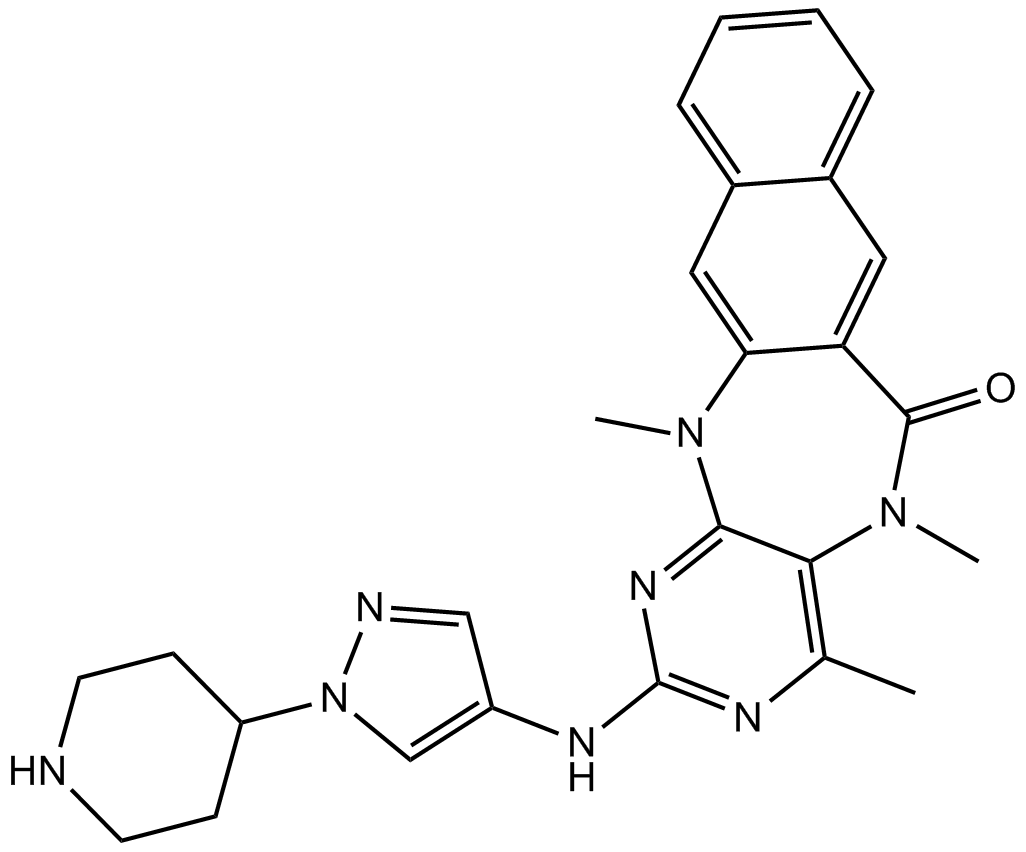 A8890 HTH-01-015Target: NUAKSummary: NUAK1 inhibitor,highly specific and selective
A8890 HTH-01-015Target: NUAKSummary: NUAK1 inhibitor,highly specific and selective -
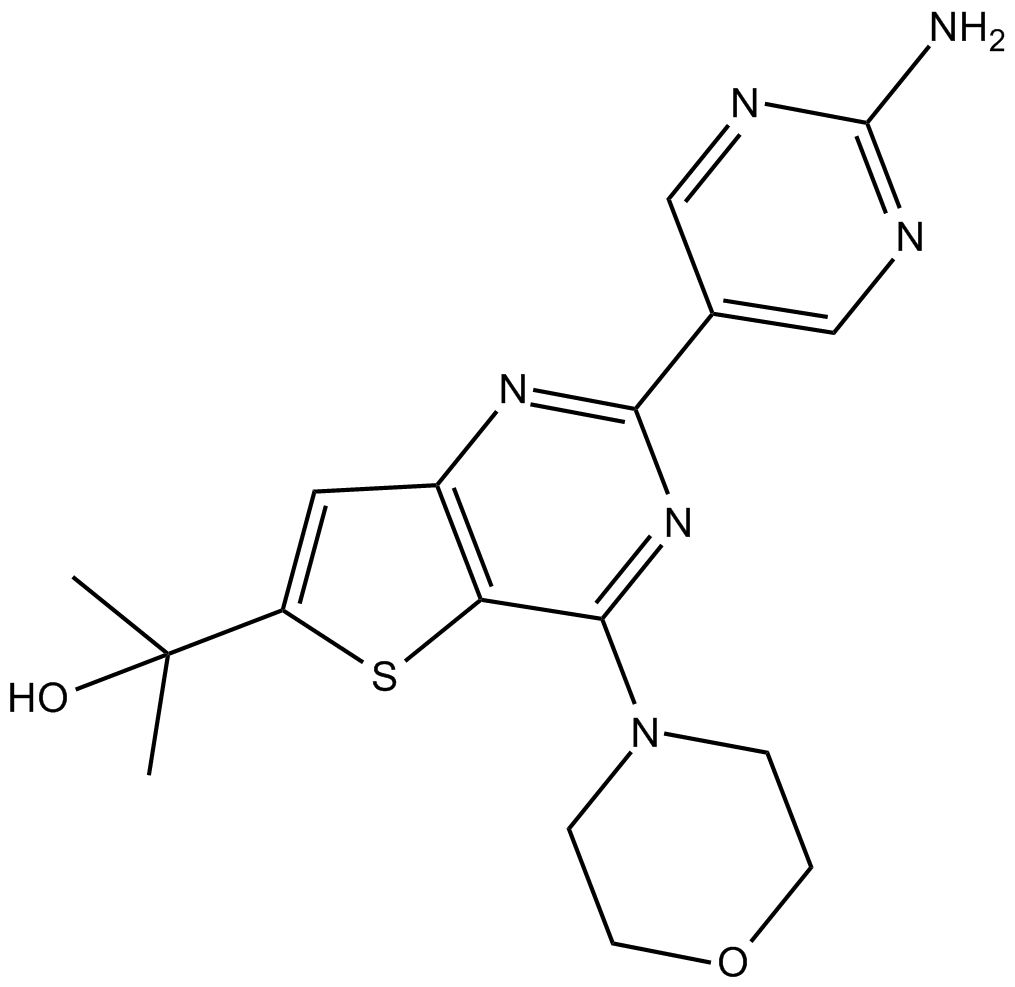 B8000 GNE-493Summary: Pan-PI3K/mTOR inhibitor
B8000 GNE-493Summary: Pan-PI3K/mTOR inhibitor -
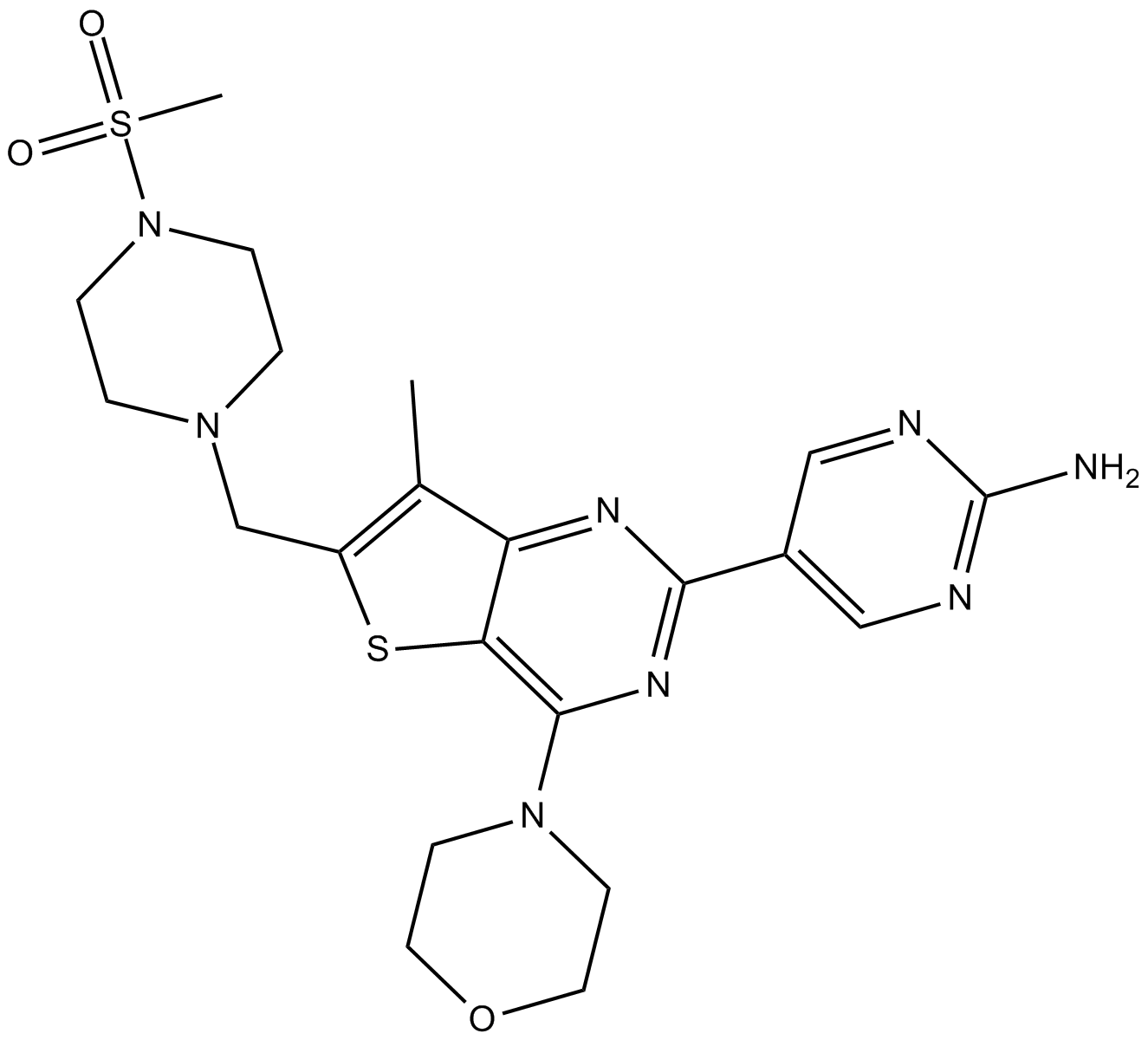 B8001 GNE-477Summary: dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor
B8001 GNE-477Summary: dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor -
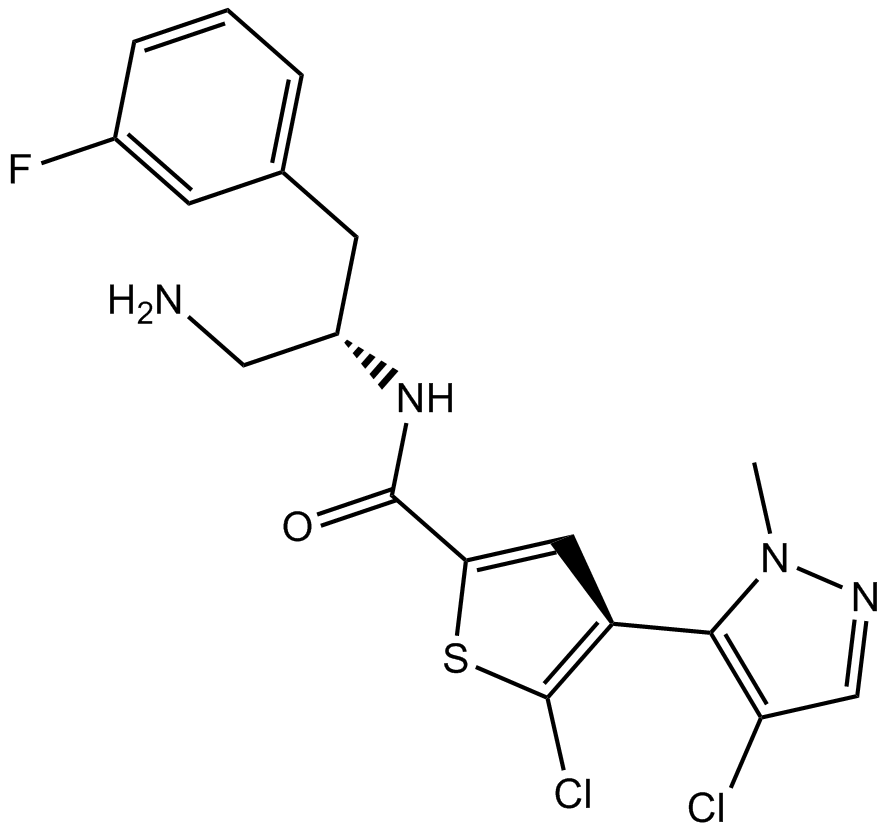 B4811 AfuresertibSummary: pan-AKT inhibitor
B4811 AfuresertibSummary: pan-AKT inhibitor -
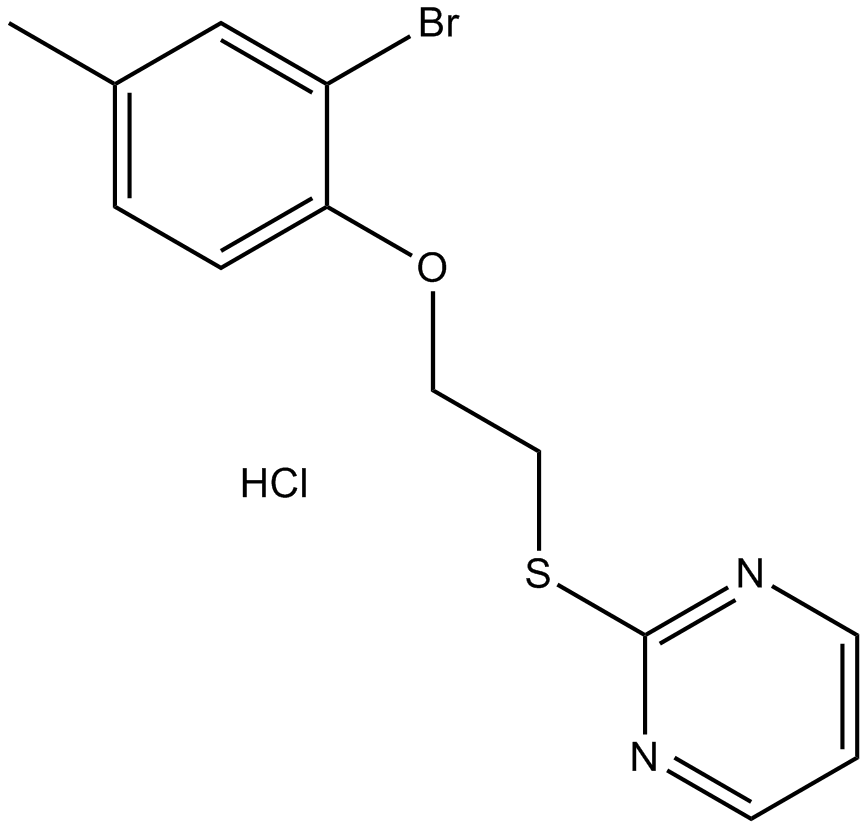 B4840 ZLN024 hydrochlorideSummary: novel AMPK allosteric activator
B4840 ZLN024 hydrochlorideSummary: novel AMPK allosteric activator -
 B4898 BikininTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK3 inhibitor and Brassinosteroid activator
B4898 BikininTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK3 inhibitor and Brassinosteroid activator -
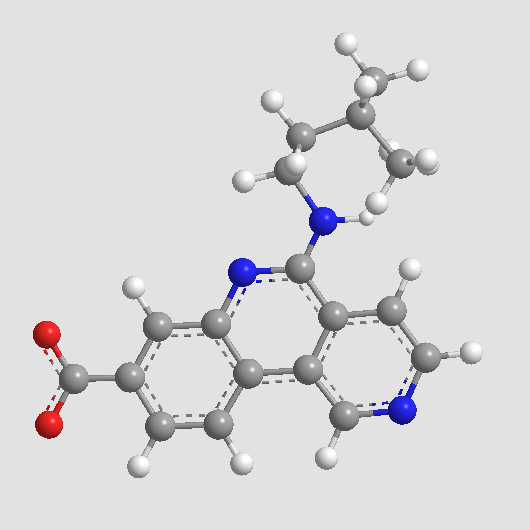 B4903 CX-4945 sodium saltSummary: CK2 inhibitor
B4903 CX-4945 sodium saltSummary: CK2 inhibitor -
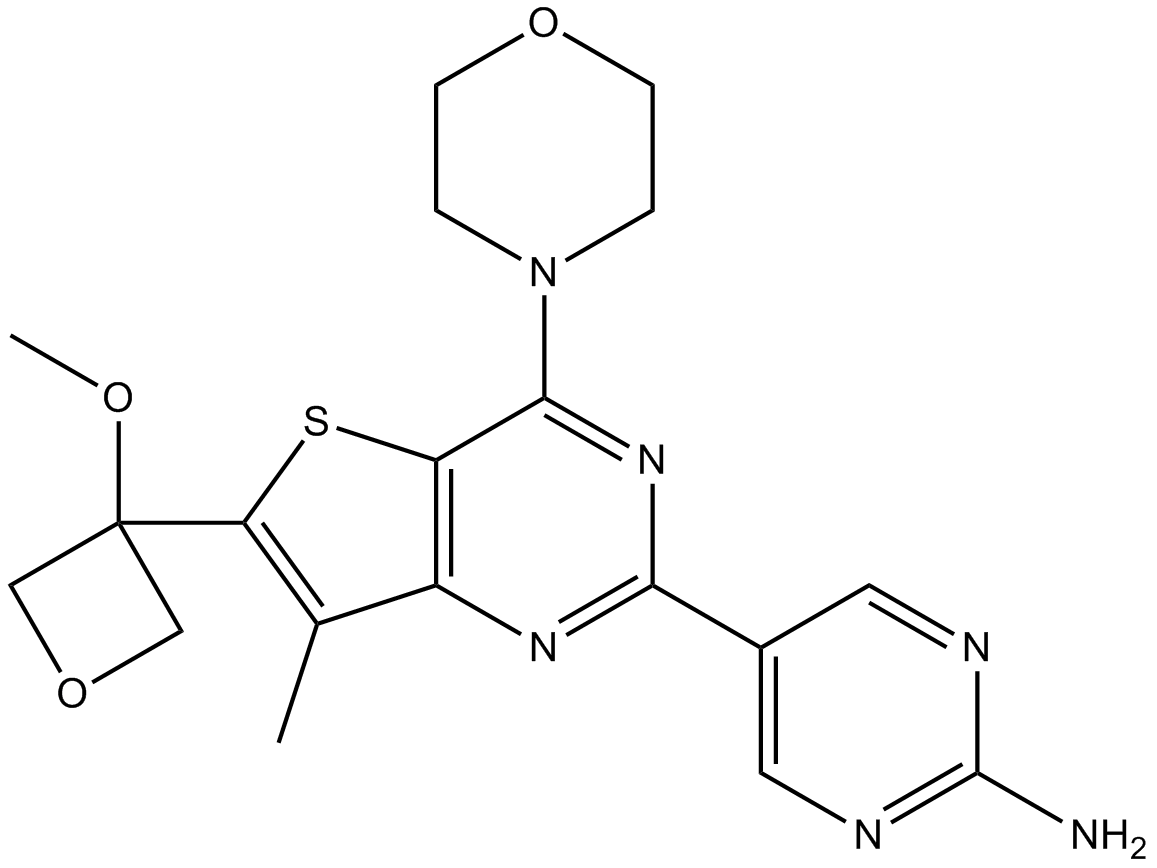 B4991 GNE-317Summary: potent, brain-penetrant PI3K inhibitor
B4991 GNE-317Summary: potent, brain-penetrant PI3K inhibitor -
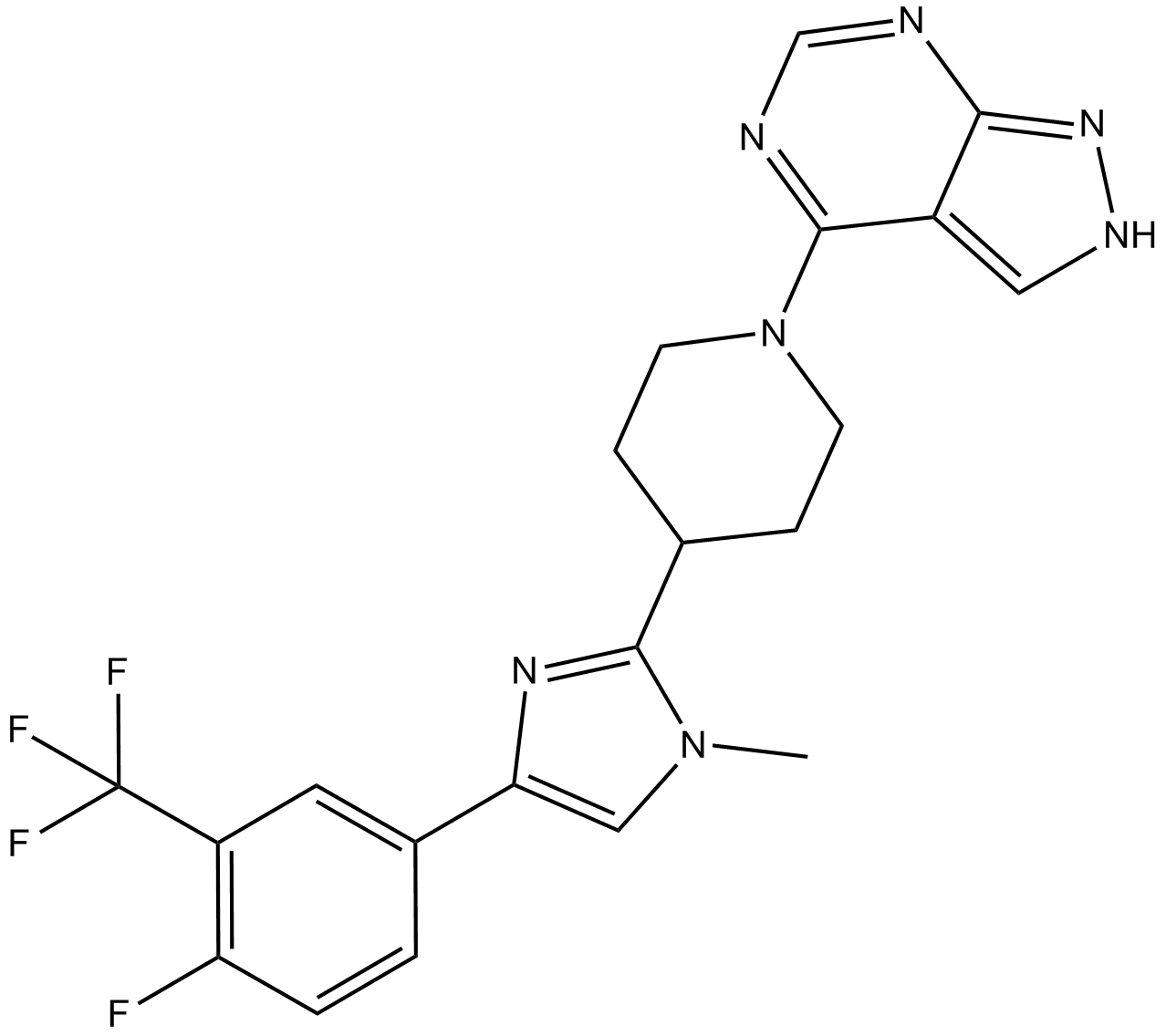 B5815 LY2584702Target: p70 rskSummary: p70 S6 kinase inhibitor
B5815 LY2584702Target: p70 rskSummary: p70 S6 kinase inhibitor -
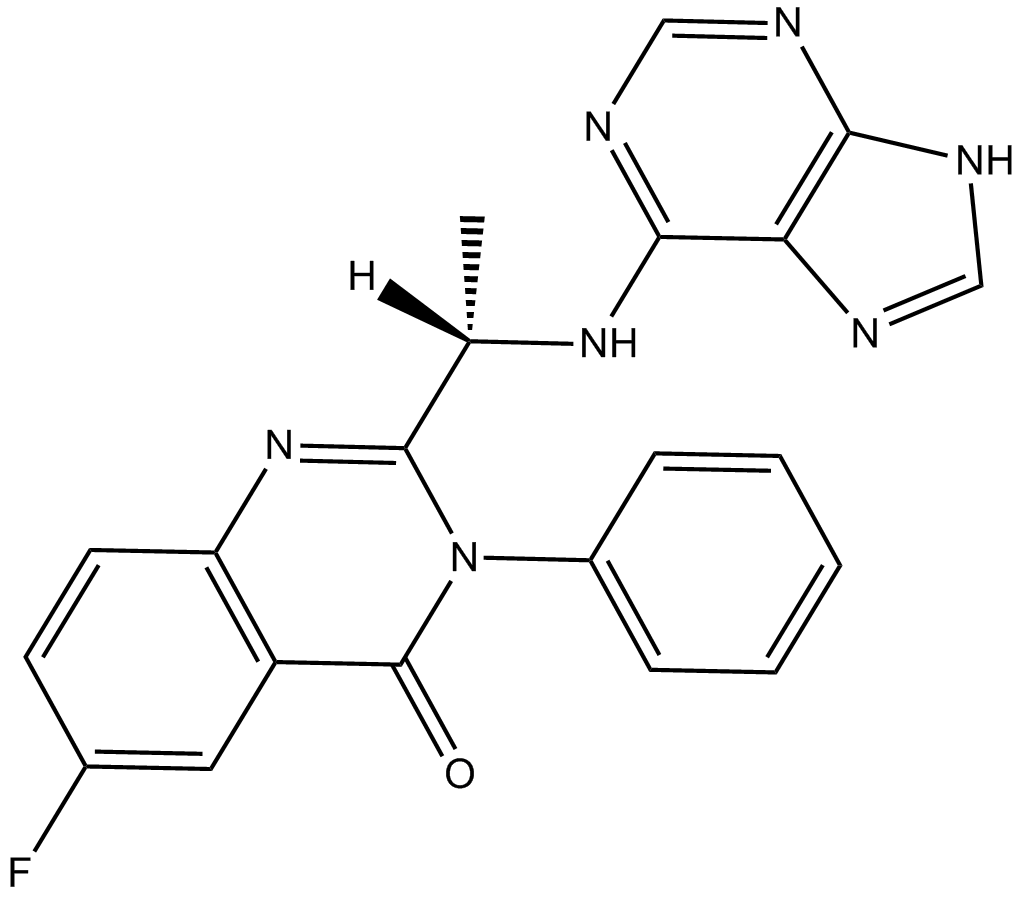 B5831 Acalisib (GS-9820)Target: PI3KSummary: PI3Kδ inhibitor
B5831 Acalisib (GS-9820)Target: PI3KSummary: PI3Kδ inhibitor

