Neuroscience
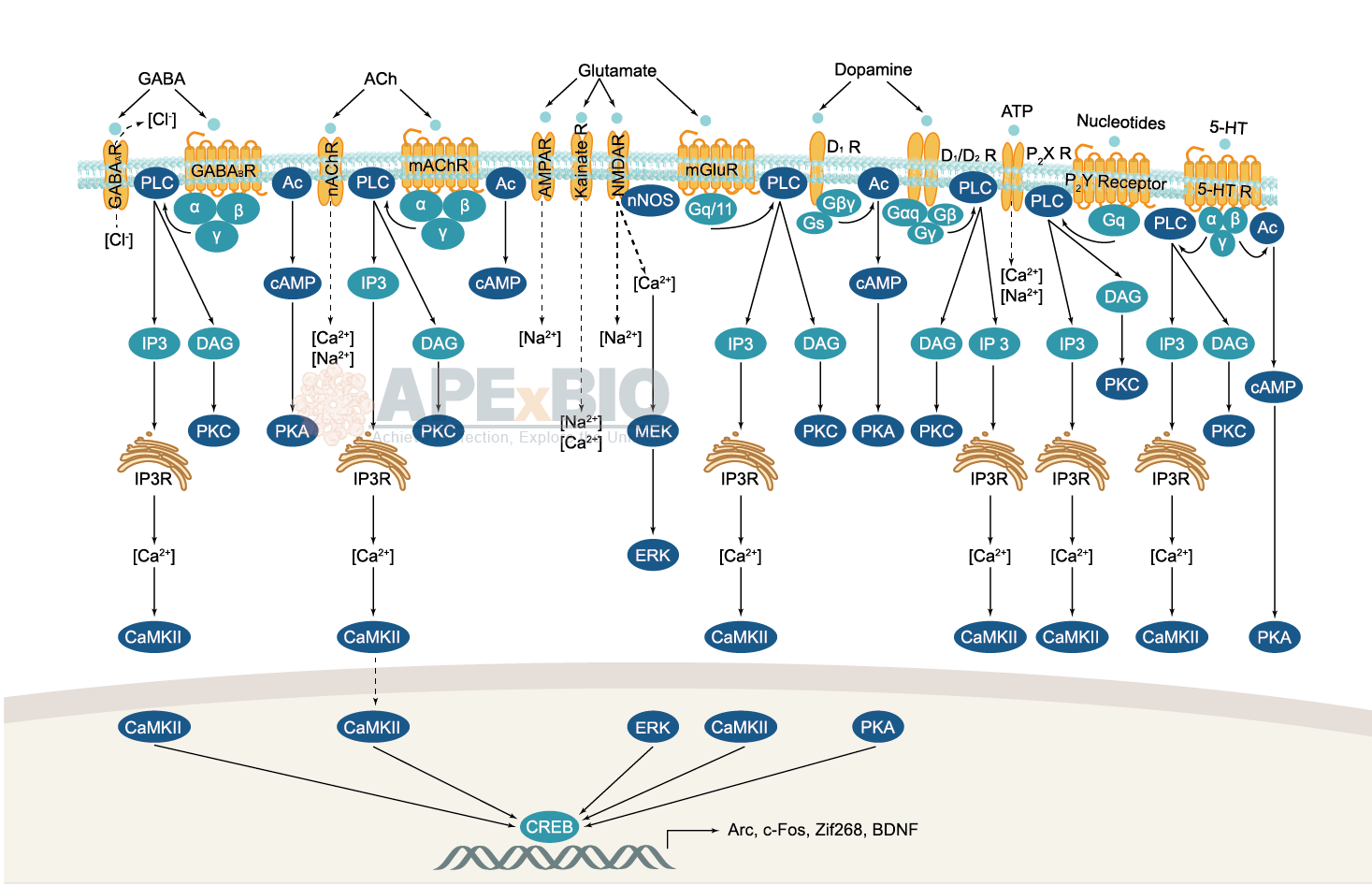
Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
 B5634 NCX 466Summary: cyclooxygenase (COX)-inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) donor
B5634 NCX 466Summary: cyclooxygenase (COX)-inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) donor -
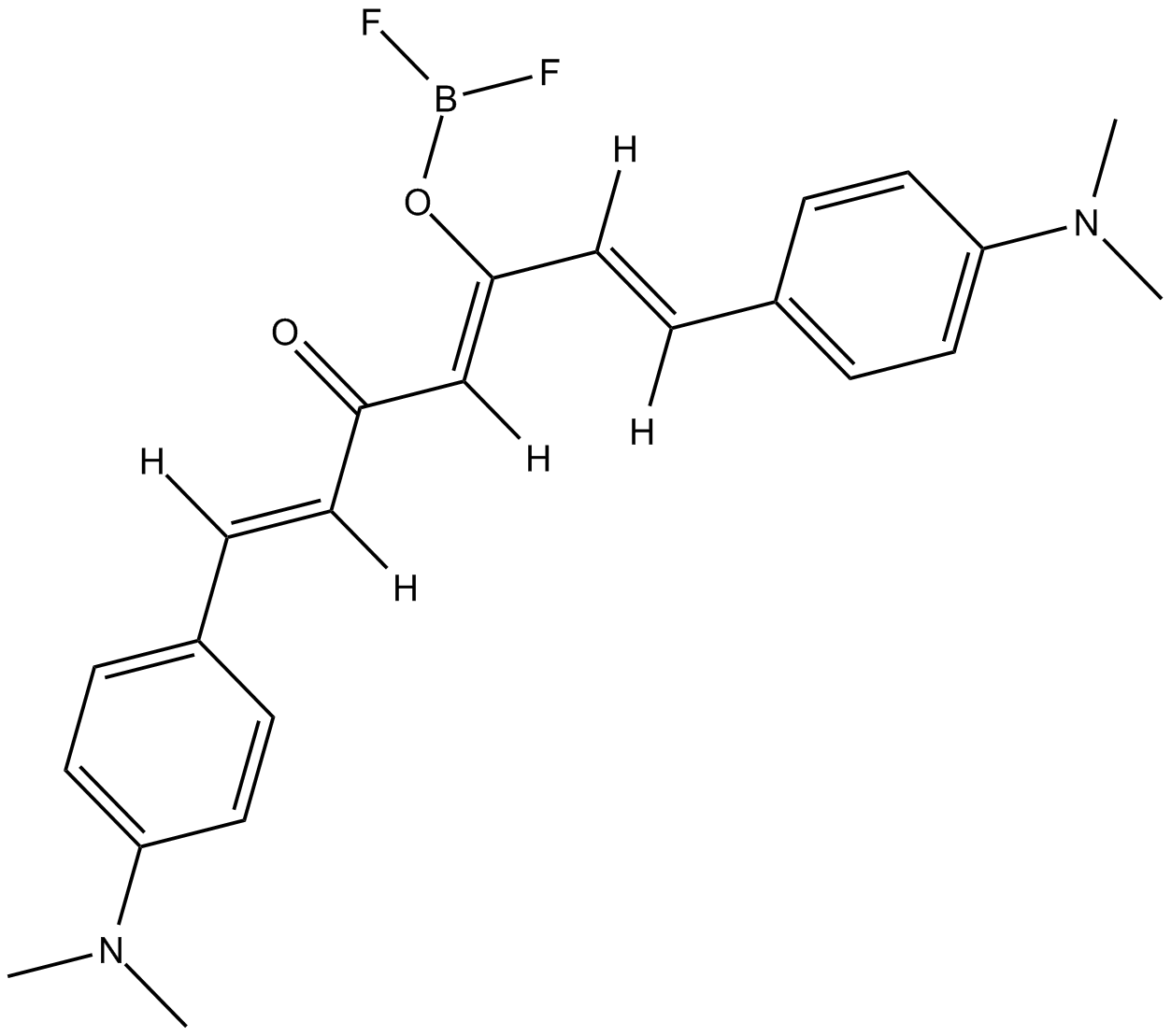 B5719 CRANAD 2Summary: near-infrared probe that binds to Aβ40 aggregates
B5719 CRANAD 2Summary: near-infrared probe that binds to Aβ40 aggregates -
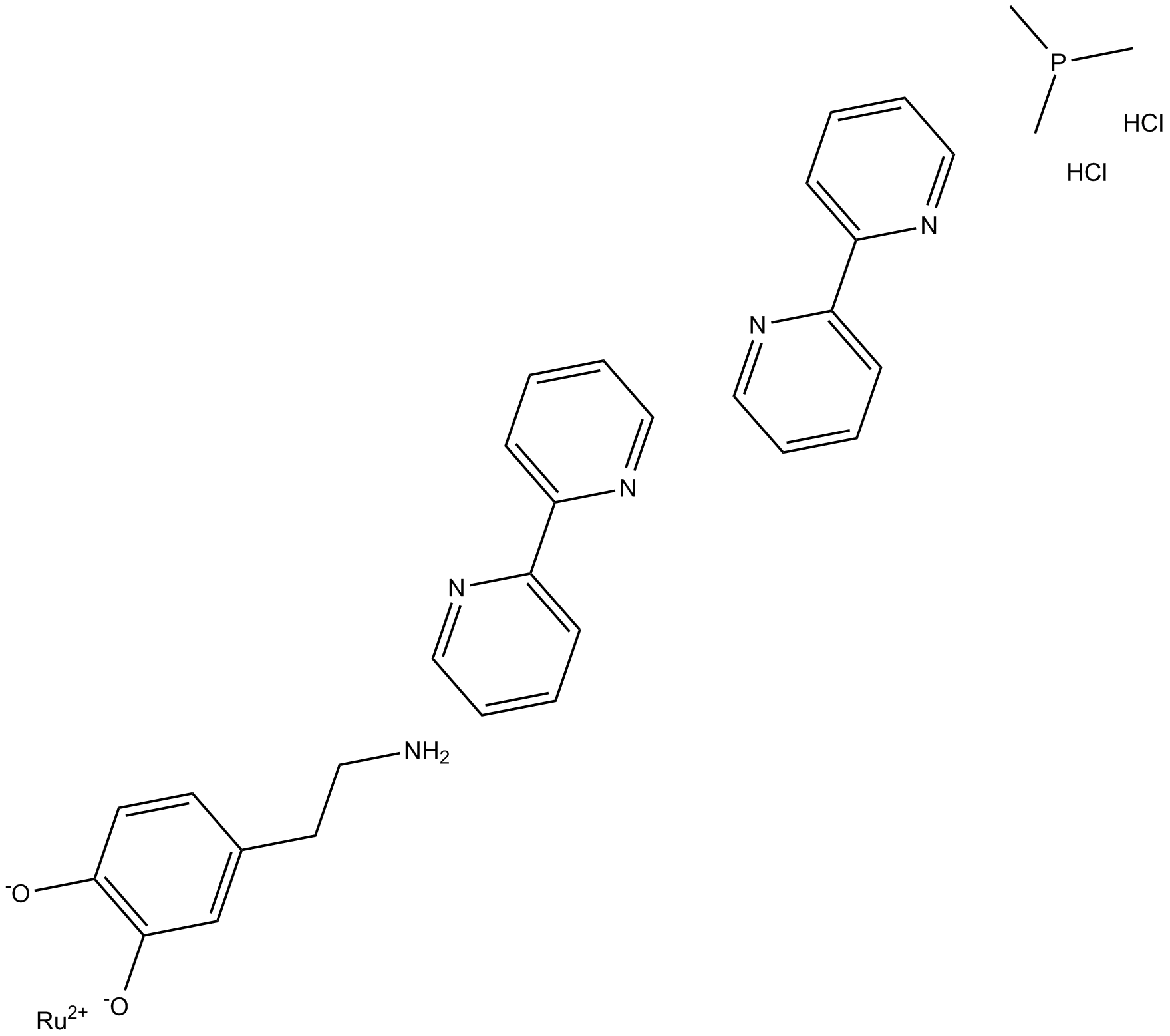 B5774 RuBi-DopaSummary: dopamine receptor activator
B5774 RuBi-DopaSummary: dopamine receptor activator -
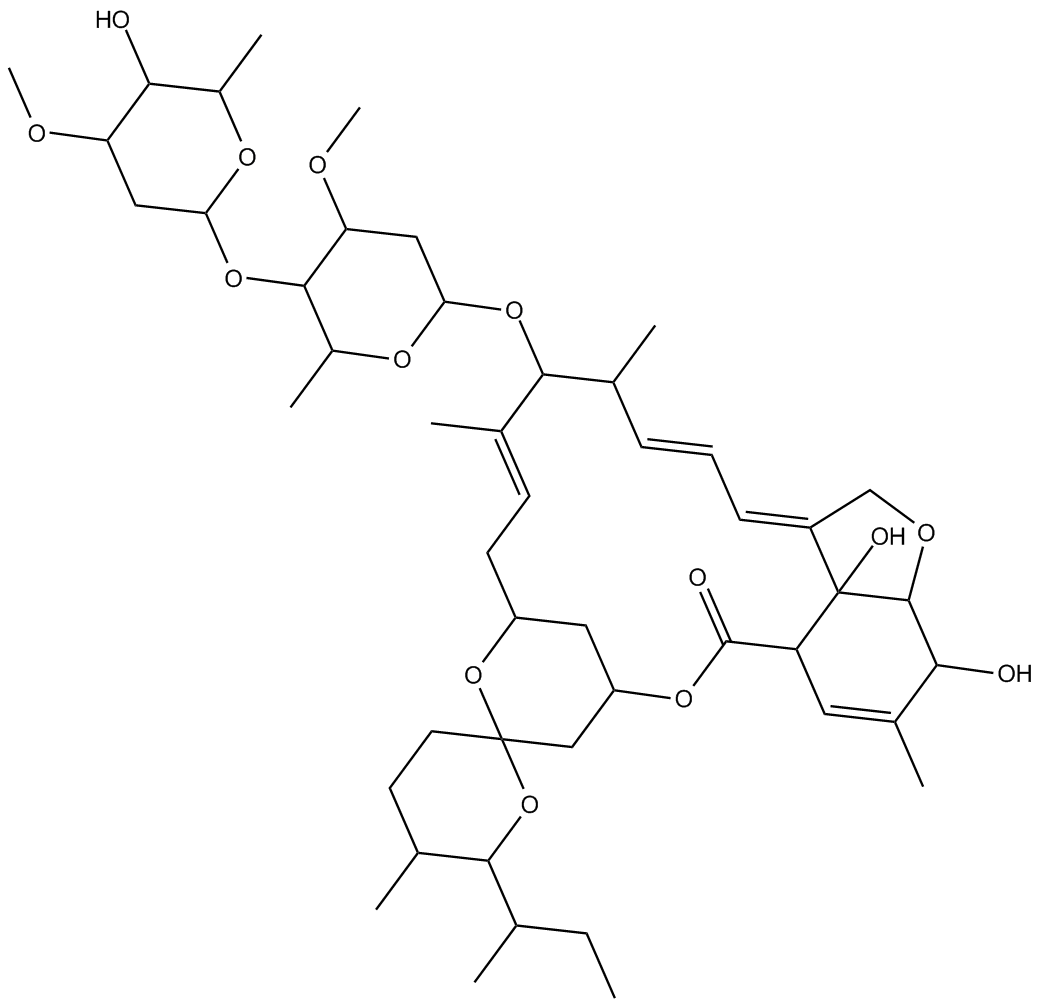 B5812 Ivermectin B1a-d2Summary: Deuterated ivermectin B1a
B5812 Ivermectin B1a-d2Summary: Deuterated ivermectin B1a -
 B6201 D-AP4Summary: broad spectrum excitatory amino acid receptor antagonist
B6201 D-AP4Summary: broad spectrum excitatory amino acid receptor antagonist -
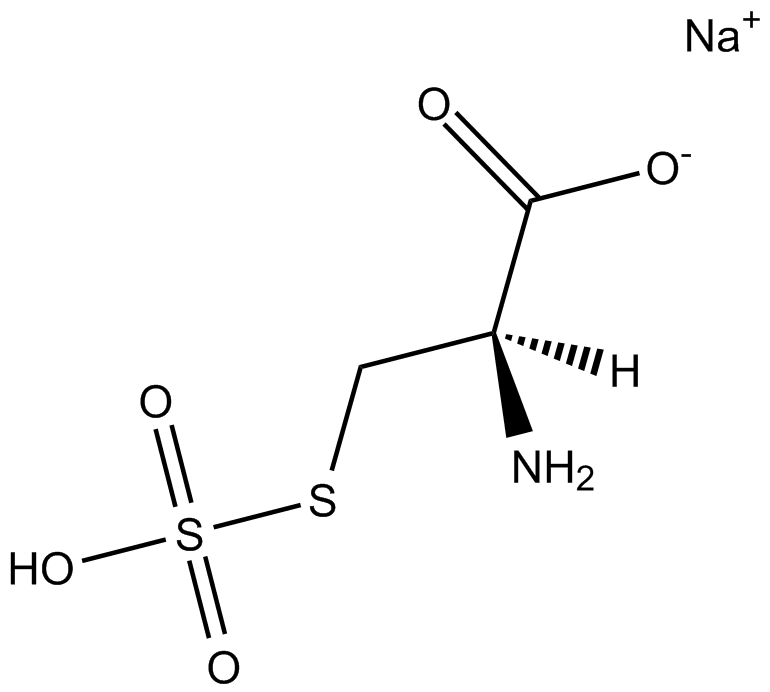 B6211 S-Sulfo-L-cysteine sodium saltSummary: EAA receptor agonist
B6211 S-Sulfo-L-cysteine sodium saltSummary: EAA receptor agonist -
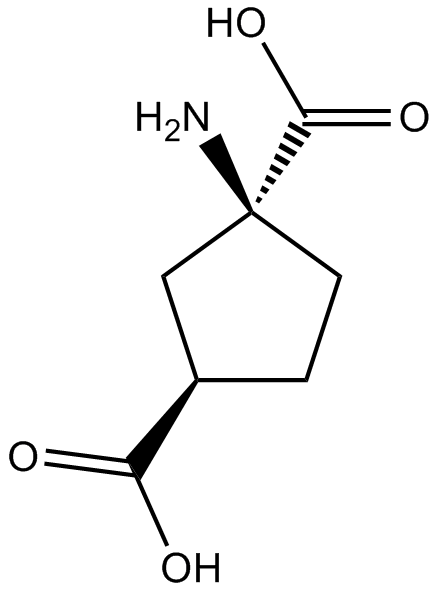 B6220 (±)-trans-ACPDSummary: metabotropic glutamate receptors agonist
B6220 (±)-trans-ACPDSummary: metabotropic glutamate receptors agonist -
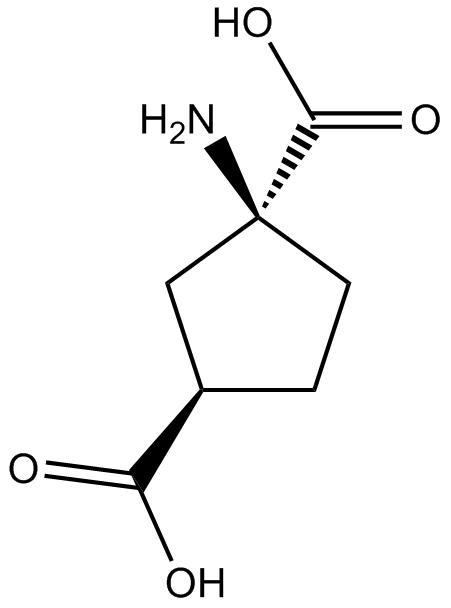 B6245 (1S,3R)-ACPDSummary: group I and II mGlu receptor agonist
B6245 (1S,3R)-ACPDSummary: group I and II mGlu receptor agonist -
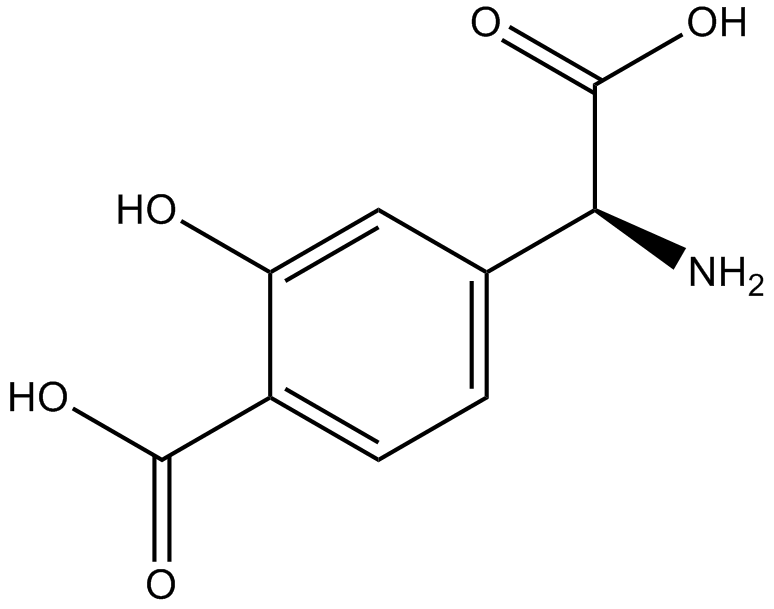 B6253 (RS)-4-Carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycineSummary: broad spectrum EAA agonist/antagonist
B6253 (RS)-4-Carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycineSummary: broad spectrum EAA agonist/antagonist -
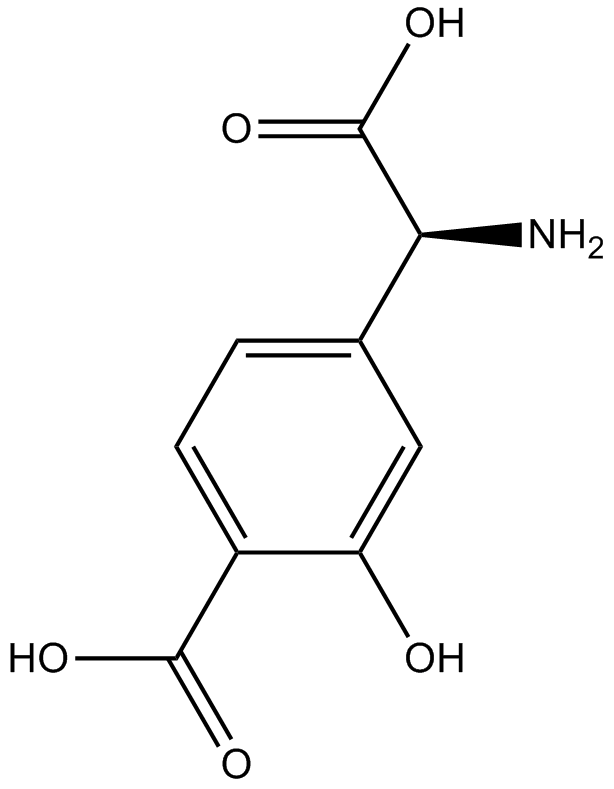 B6255 (S)-4-Carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycineSummary: group I mGlu1a/1a receptor antagonist and mGluR2 agonist
B6255 (S)-4-Carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycineSummary: group I mGlu1a/1a receptor antagonist and mGluR2 agonist

