Neuroscience
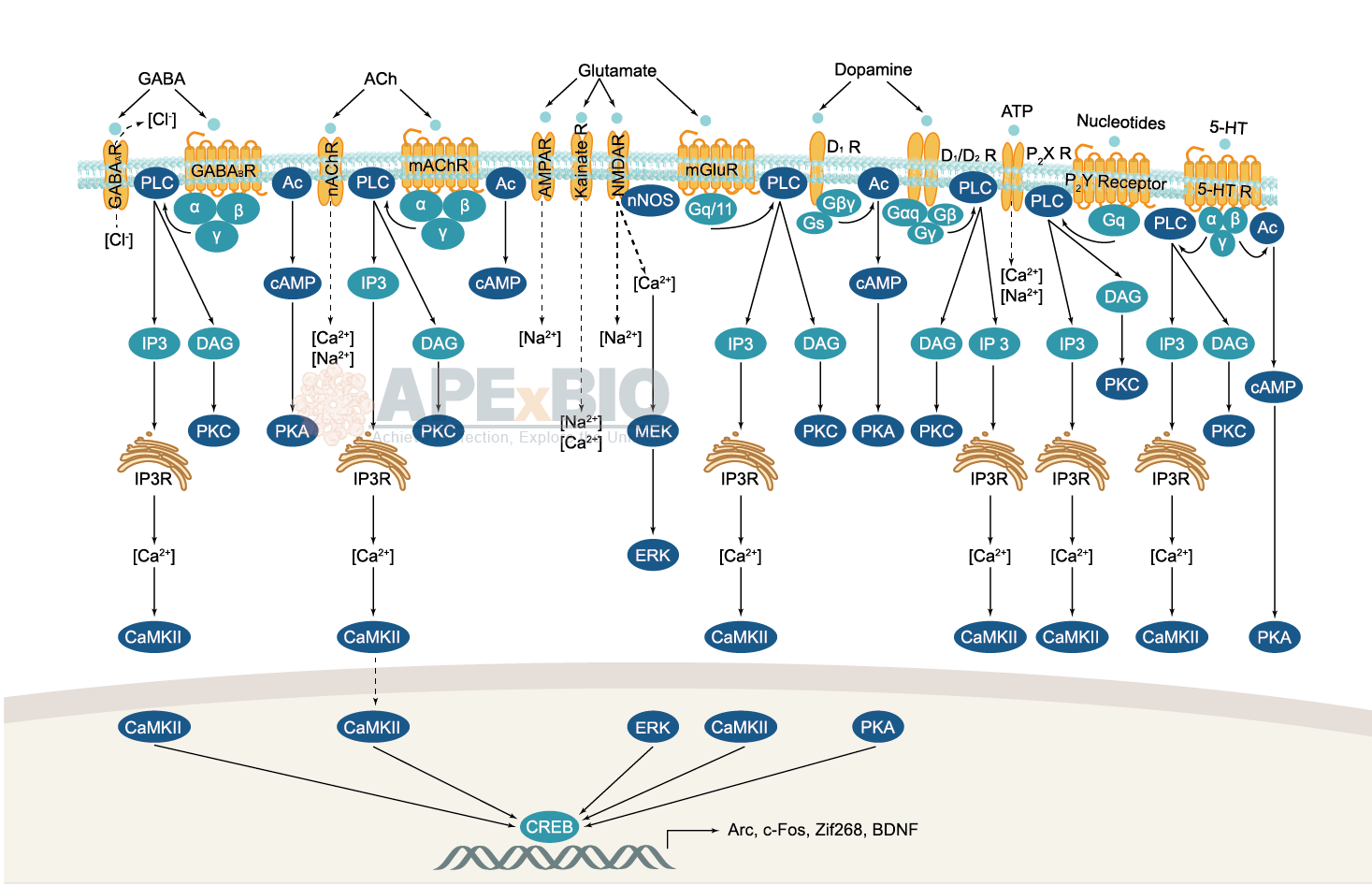
Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
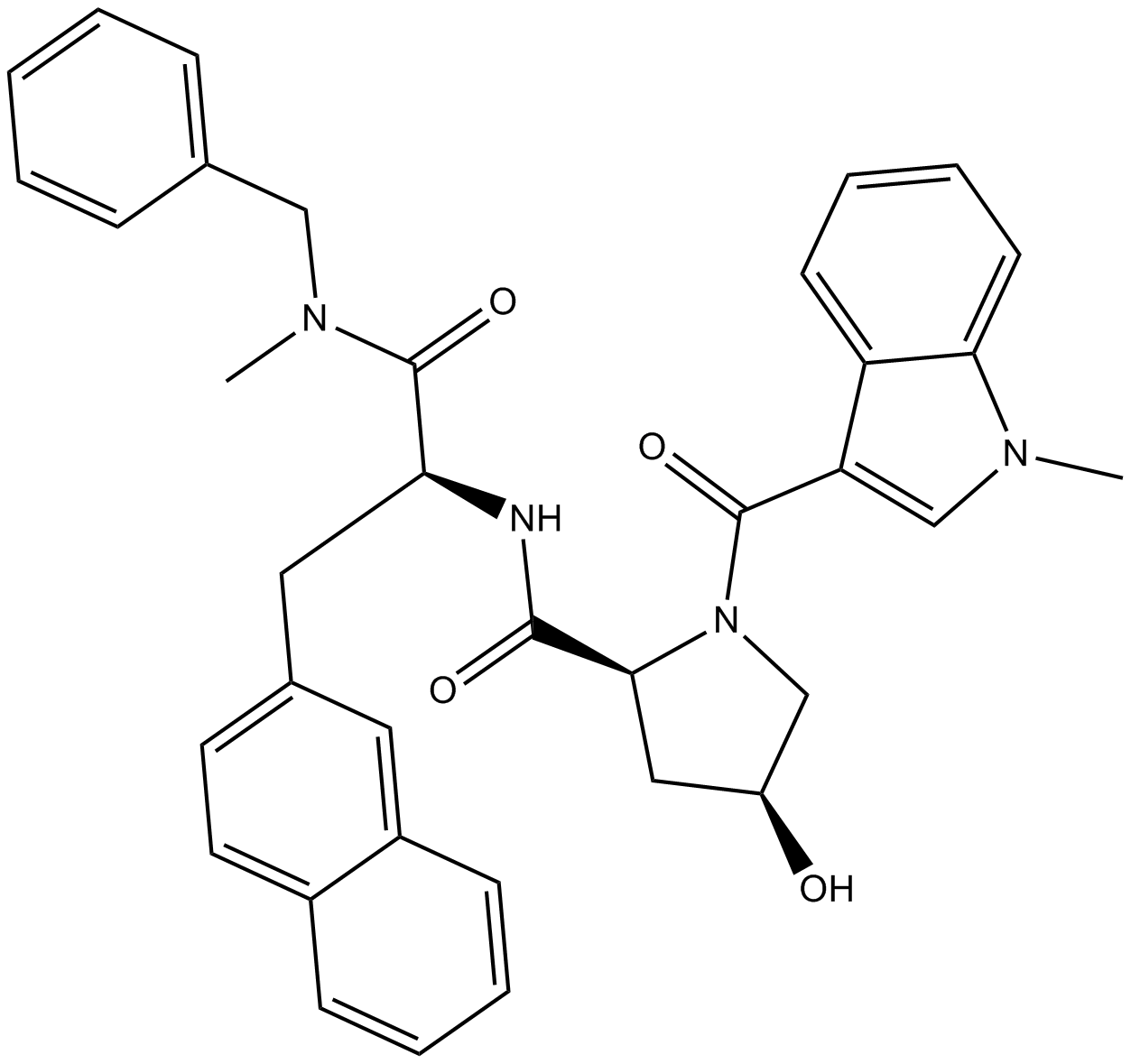 B5300 FK 888Summary: Selective, high affinity tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist
B5300 FK 888Summary: Selective, high affinity tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist -
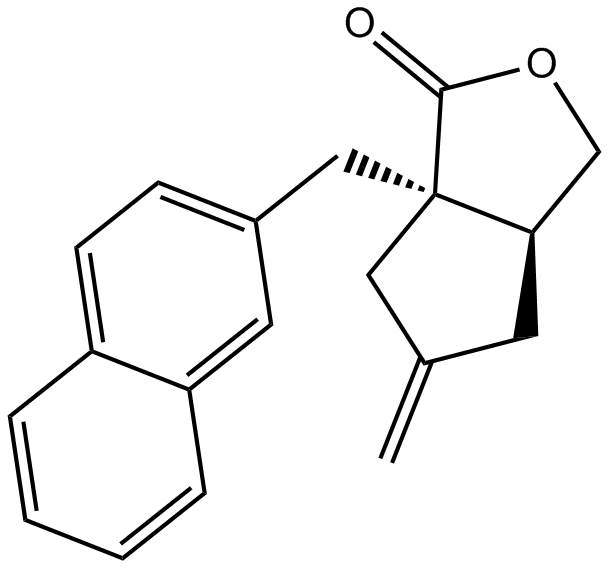 B5309 Bay 36-7620Summary: Selective mGlu1 receptor non-competitive antagonist
B5309 Bay 36-7620Summary: Selective mGlu1 receptor non-competitive antagonist -
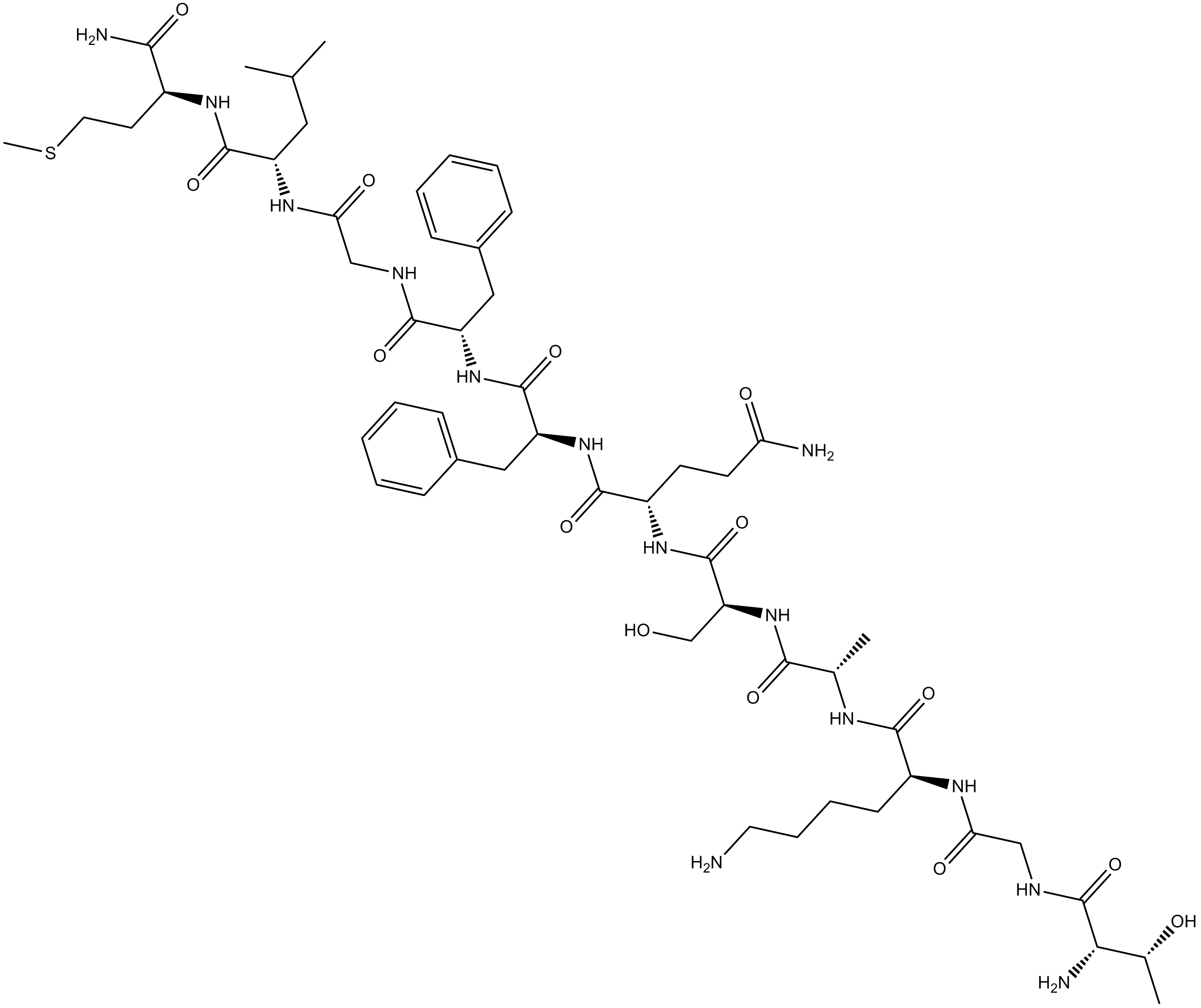 B5318 Hemokinin 1 (human)Summary: selective agonist at the tachykinin NK1 receptor
B5318 Hemokinin 1 (human)Summary: selective agonist at the tachykinin NK1 receptor -
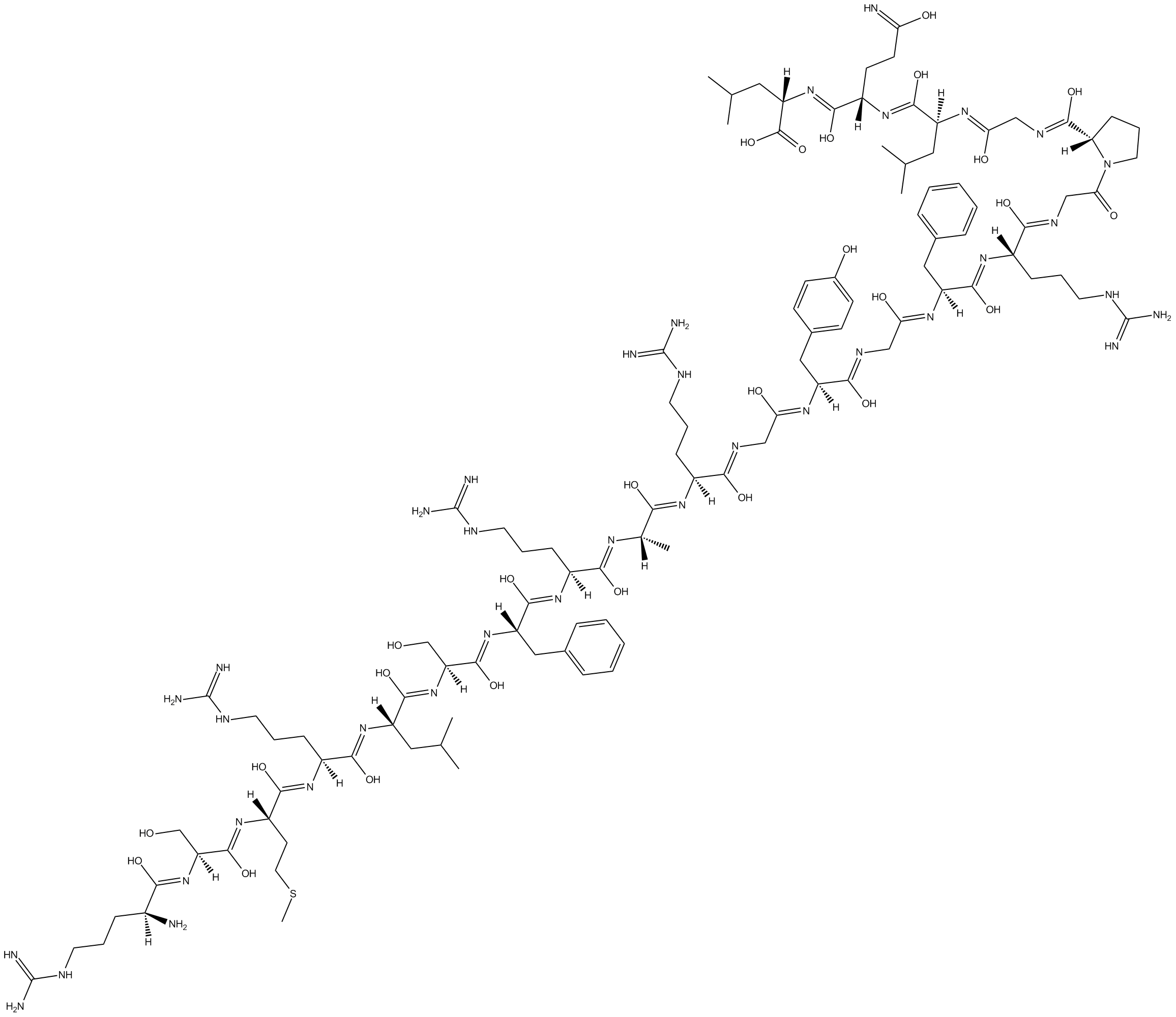 B5332 CatestatinSummary: Non-competitive nicotinic cholinergic antagonist
B5332 CatestatinSummary: Non-competitive nicotinic cholinergic antagonist -
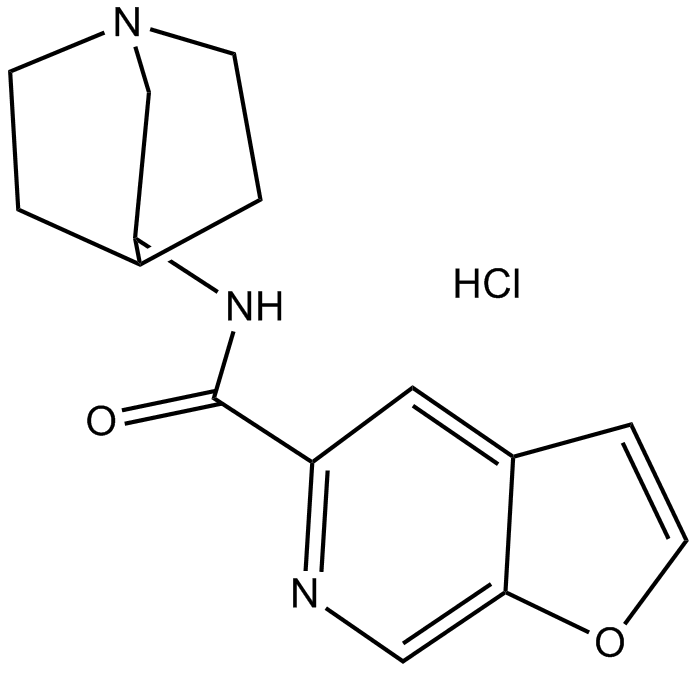 B5373 PHA 543613 hydrochlorideSummary: Potent α7 nAChR agonist
B5373 PHA 543613 hydrochlorideSummary: Potent α7 nAChR agonist -
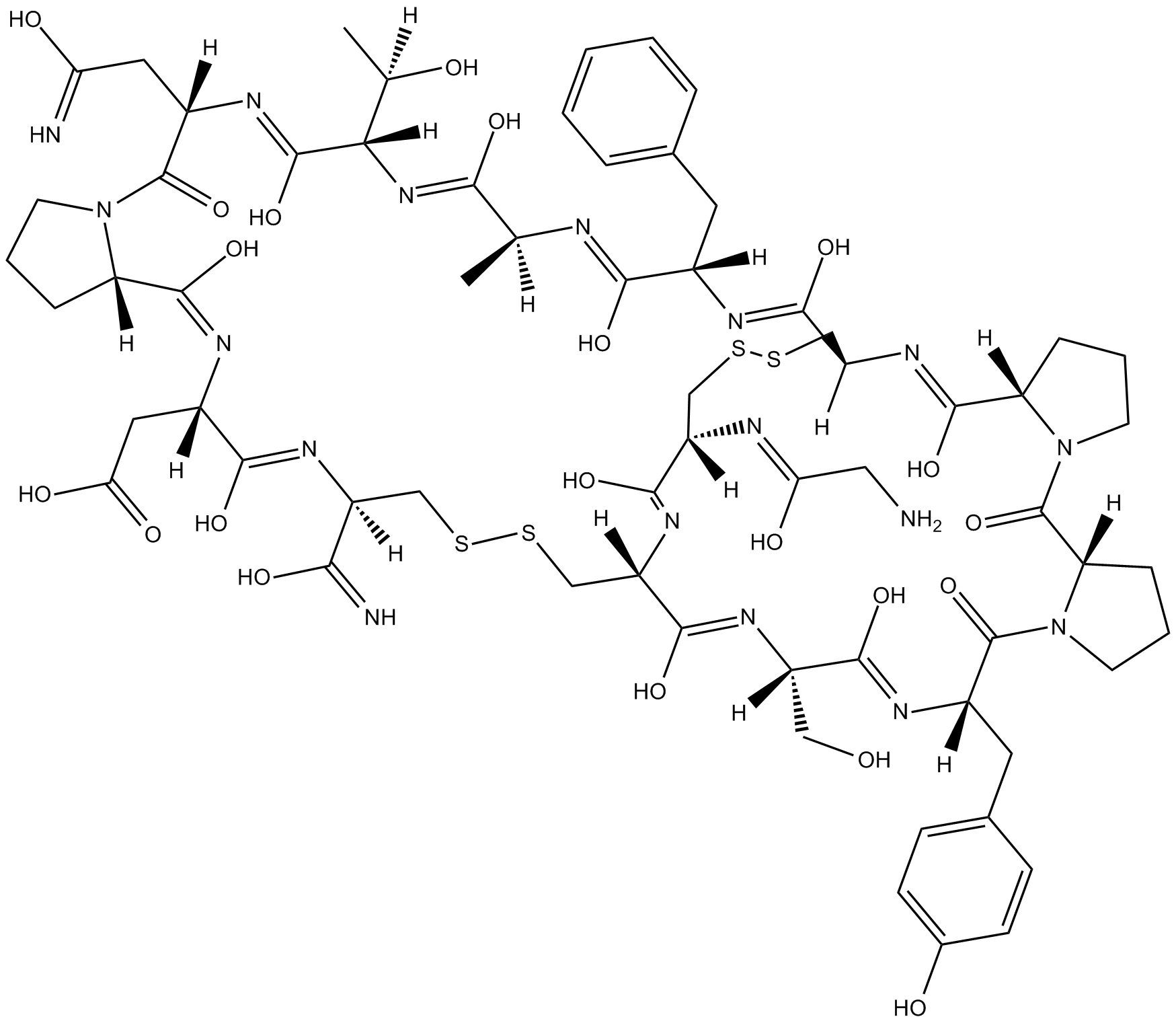 B5376 α-Conotoxin AuIBSummary: Selective antagonist of α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
B5376 α-Conotoxin AuIBSummary: Selective antagonist of α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors -
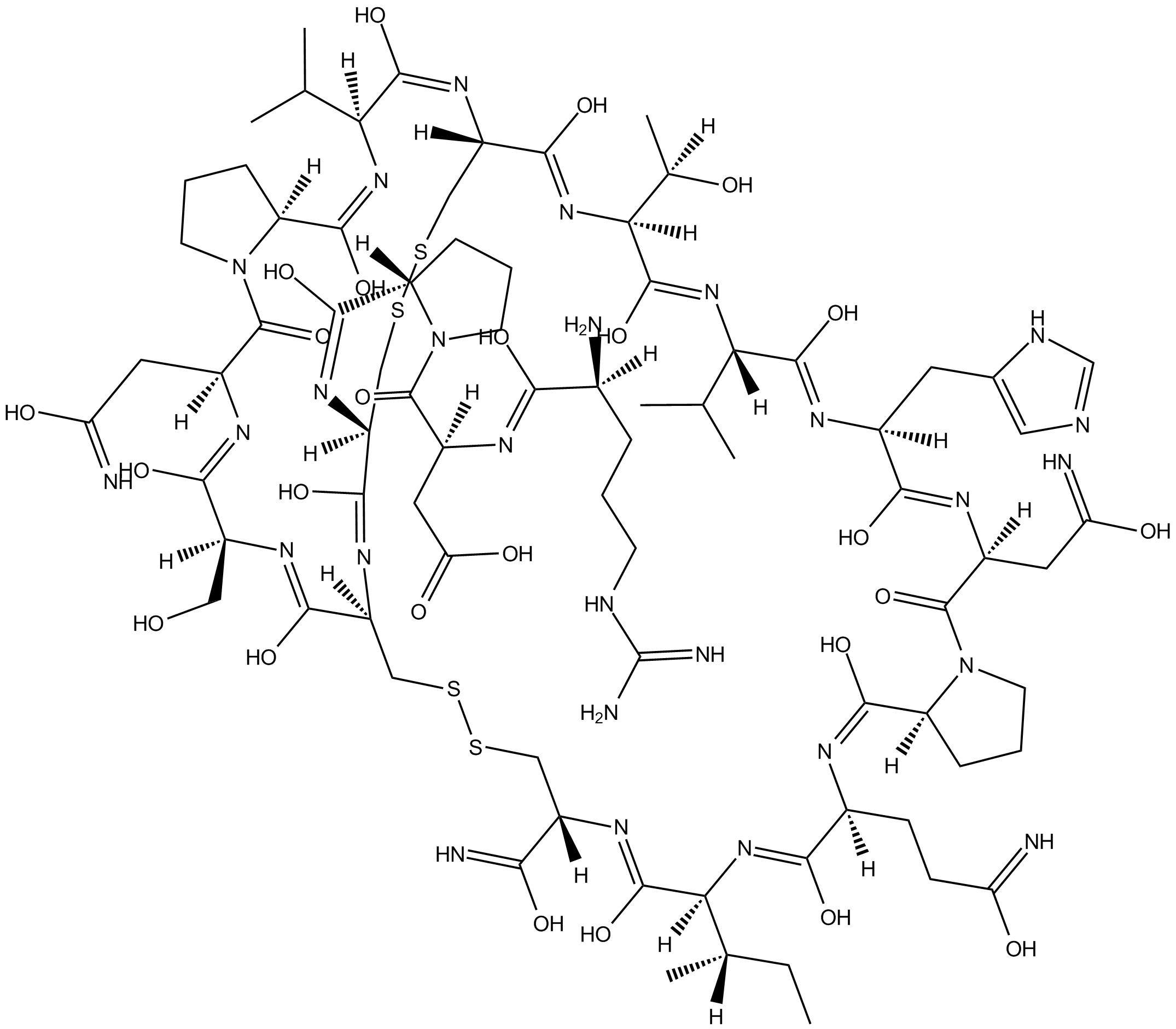 B5377 α-Conotoxin PIASummary: Selective antagonist of α6-containing nicotinic receptors
B5377 α-Conotoxin PIASummary: Selective antagonist of α6-containing nicotinic receptors -
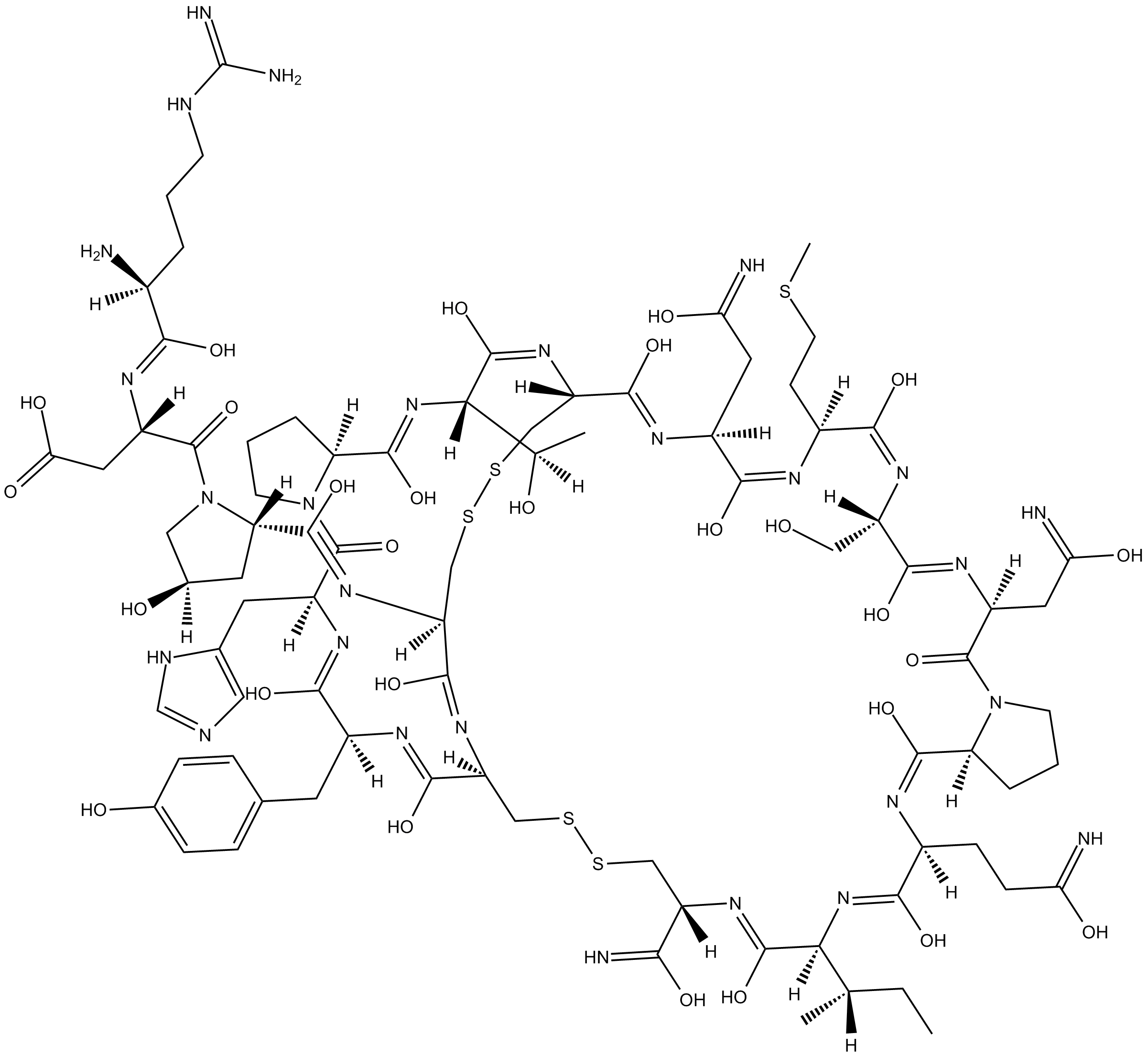 B5380 α-Conotoxin EISummary: α-Conotoxin EI is a selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) modulator that potentiates α₁β₁γδ and α₄β₂ subtypes at low concentrations and inhibits α₁β₁γδ and α₃β₄ subtypes at high concentrations.
B5380 α-Conotoxin EISummary: α-Conotoxin EI is a selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) modulator that potentiates α₁β₁γδ and α₄β₂ subtypes at low concentrations and inhibits α₁β₁γδ and α₃β₄ subtypes at high concentrations. -
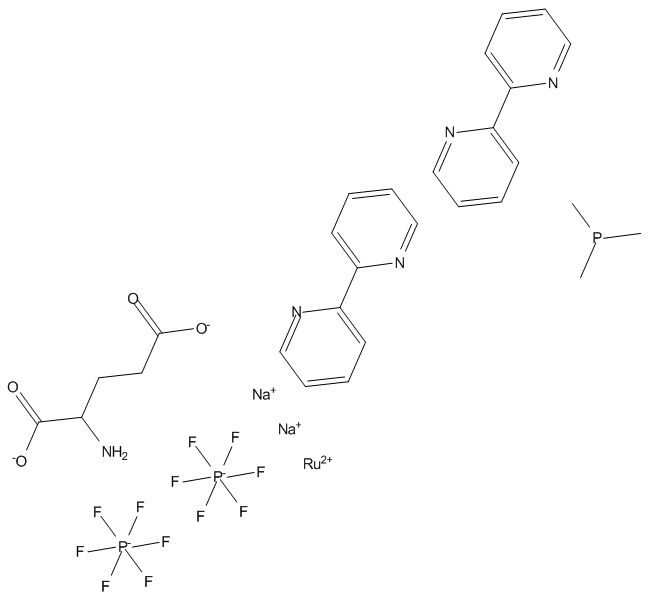 B5454 RuBi-GlutamateSummary: Ruthenium-bipyridine-trimethylphosphine caged glutamate
B5454 RuBi-GlutamateSummary: Ruthenium-bipyridine-trimethylphosphine caged glutamate -
 B5526 LPYFD-NH2Summary: neuroprotective peptide that binds to amyloid beta (Aβ)
B5526 LPYFD-NH2Summary: neuroprotective peptide that binds to amyloid beta (Aβ)

