Neuroscience
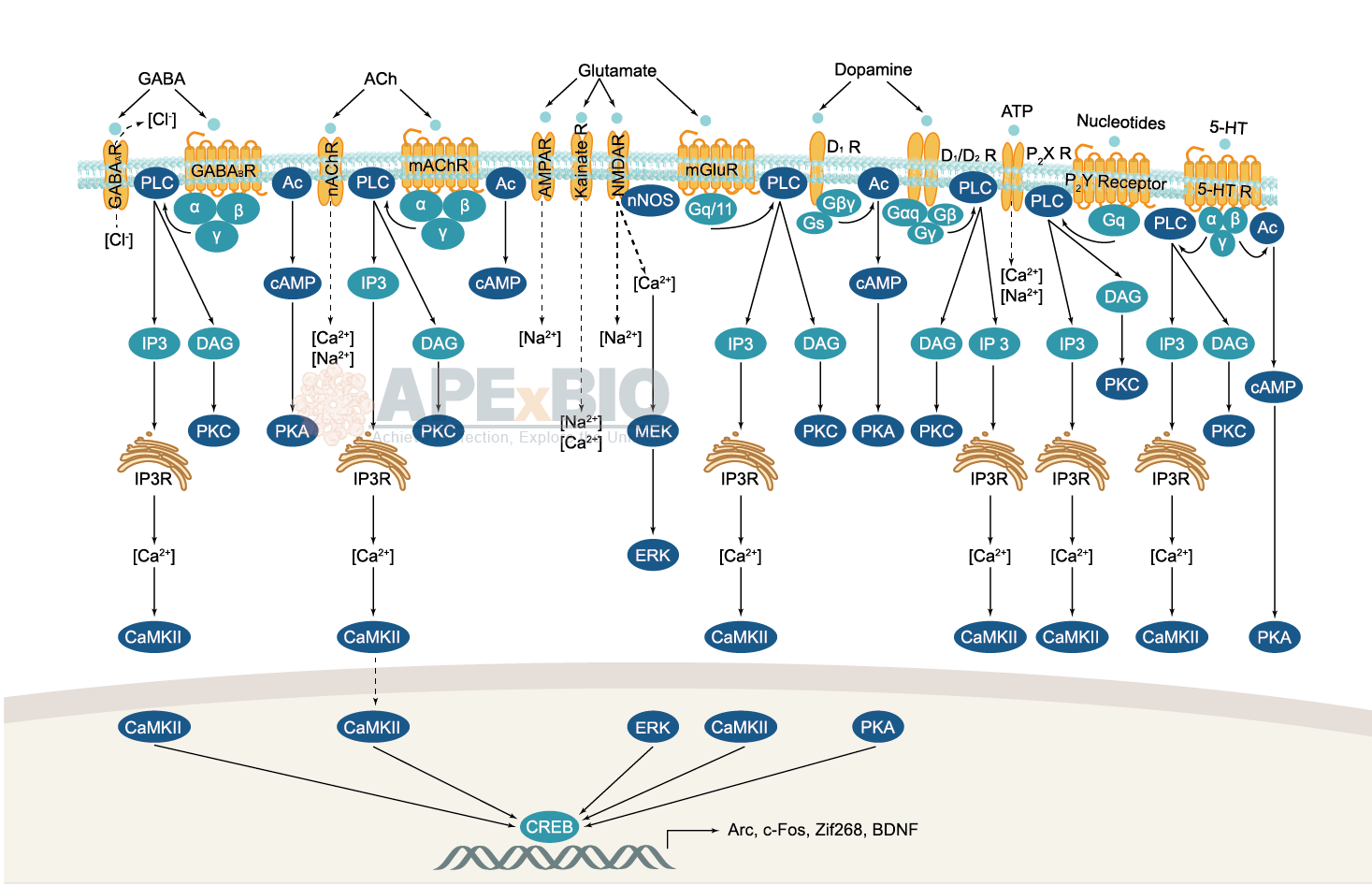
Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
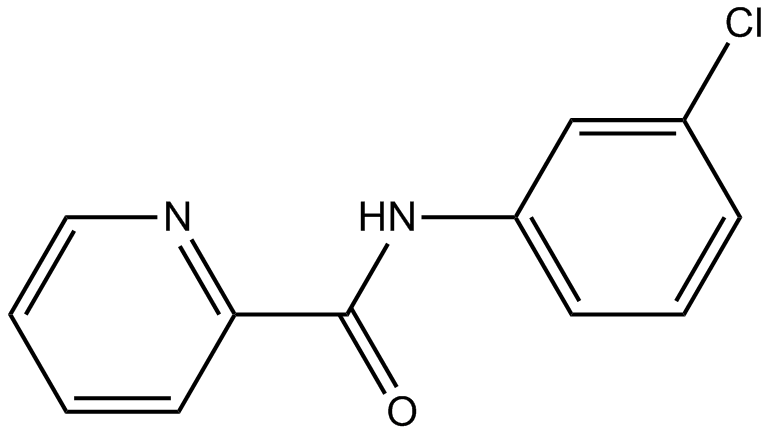 B1631 VU 0364770Summary: Positive allosteric modulator(PAM) of mGlu4
B1631 VU 0364770Summary: Positive allosteric modulator(PAM) of mGlu4 -
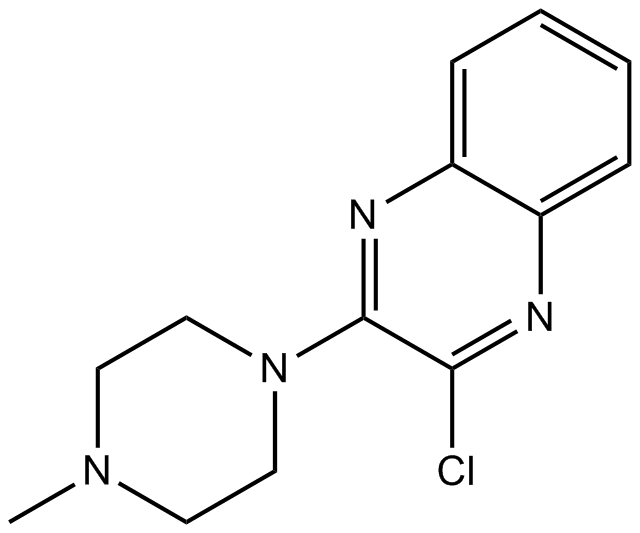 B2259 VUF 10166Target: 5-HT3 ReceptorsSummary: 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
B2259 VUF 10166Target: 5-HT3 ReceptorsSummary: 5-HT3 receptor antagonist -
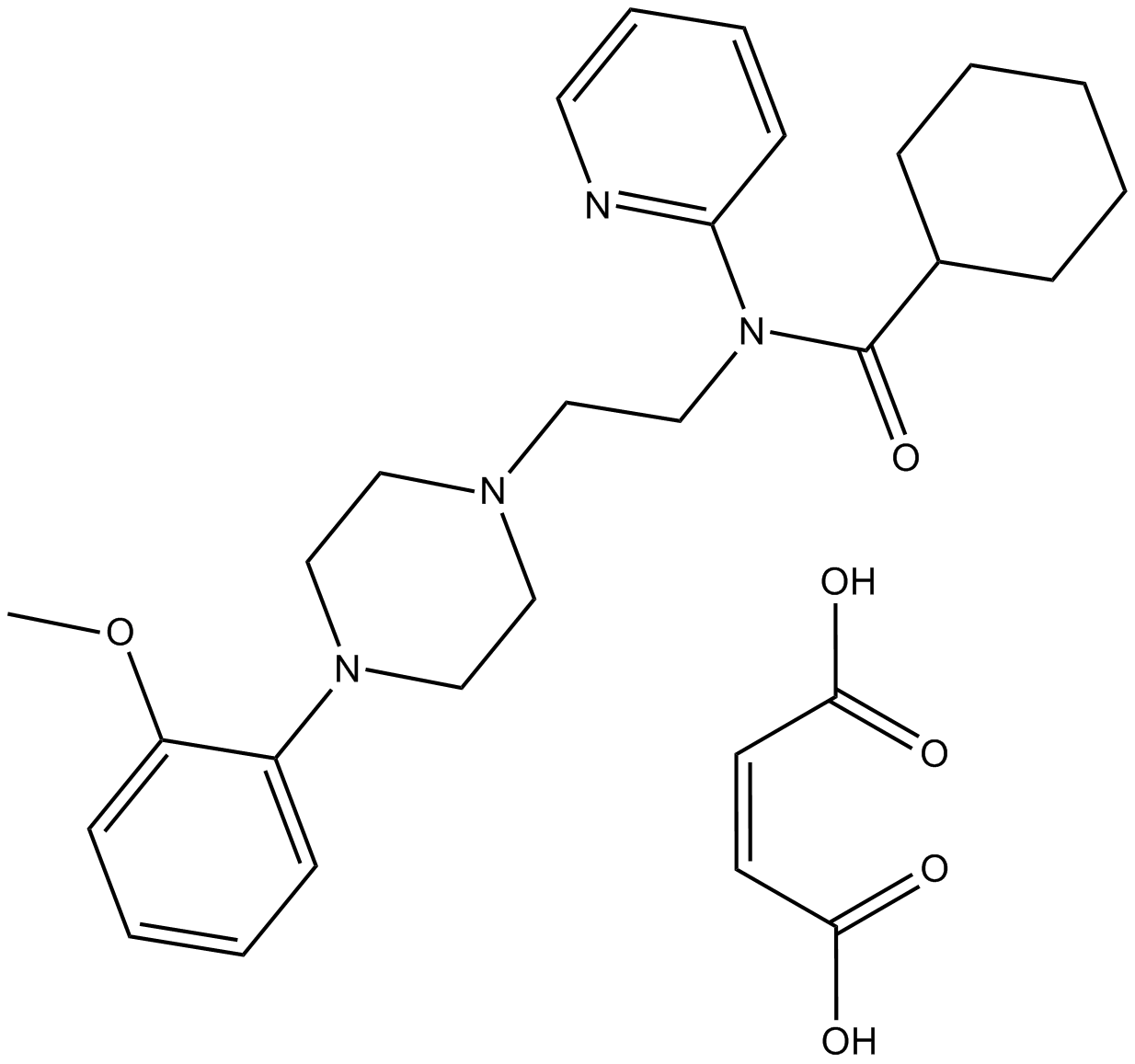 B2260 WAY-100635 maleate saltSummary: 5-HT1A receptor antagonist
B2260 WAY-100635 maleate saltSummary: 5-HT1A receptor antagonist -
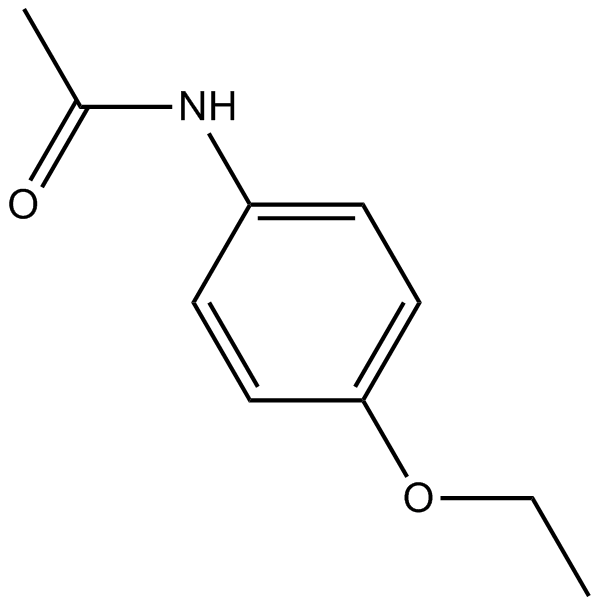 B1453 PhenacetinSummary: Non-opioid analgesic
B1453 PhenacetinSummary: Non-opioid analgesic -
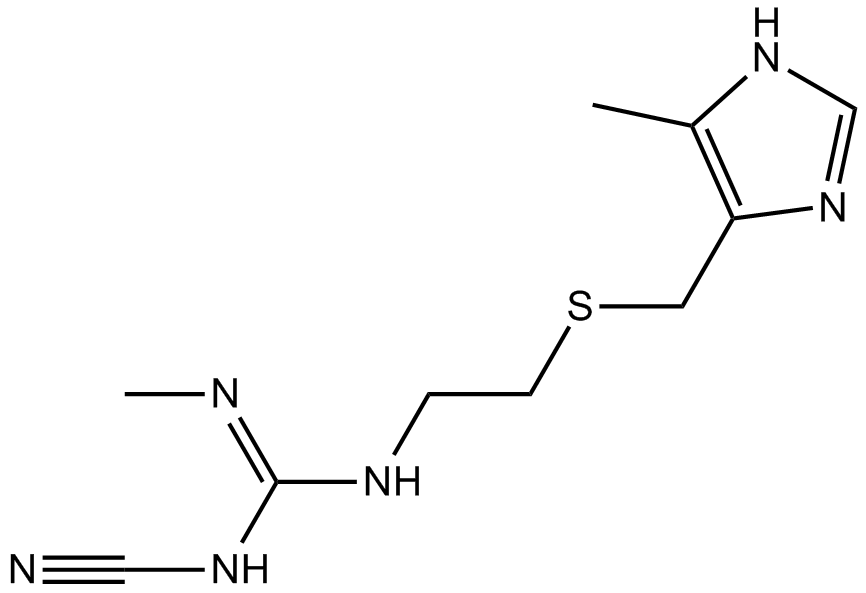 B1557 CimetidineSummary: H2 receptor antagonist
B1557 CimetidineSummary: H2 receptor antagonist -
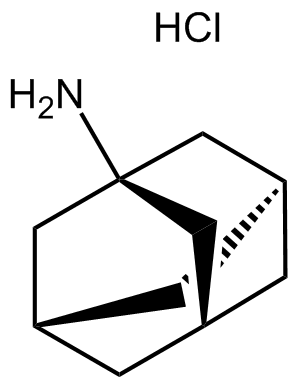 B1486 Amantadine HClSummary: Dopamine receptor agonist
B1486 Amantadine HClSummary: Dopamine receptor agonist -
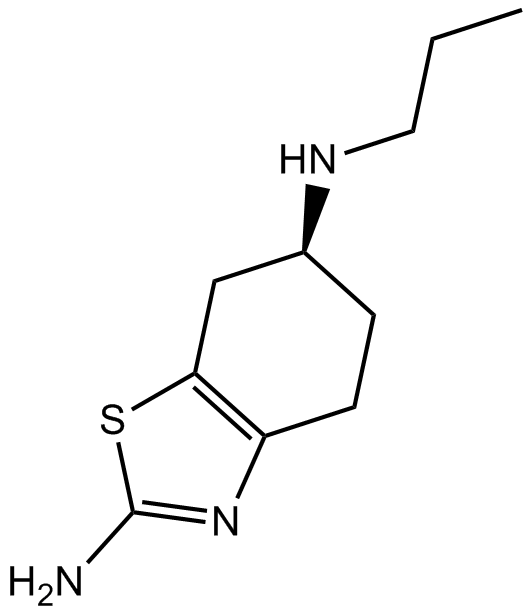 B1488 PramipexoleTarget: D2 Receptors|D3 Receptors|D4 ReceptorsSummary: Dopamine agonist
B1488 PramipexoleTarget: D2 Receptors|D3 Receptors|D4 ReceptorsSummary: Dopamine agonist -
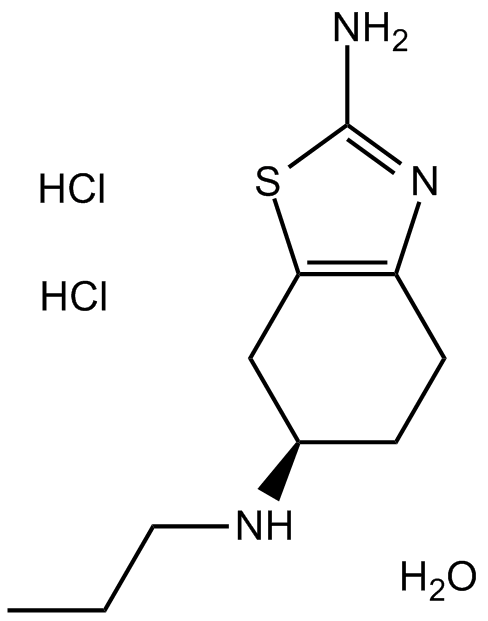 B1487 Pramipexole 2HCl MonohydrateSummary: Novel non-ergoline dopamine receptor agonist
B1487 Pramipexole 2HCl MonohydrateSummary: Novel non-ergoline dopamine receptor agonist -
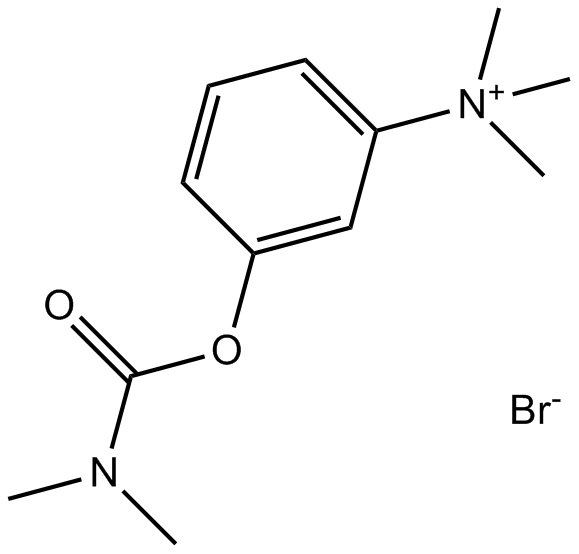 B1594 Neostigmine BromideSummary: Cholinesterase inhibitor
B1594 Neostigmine BromideSummary: Cholinesterase inhibitor -
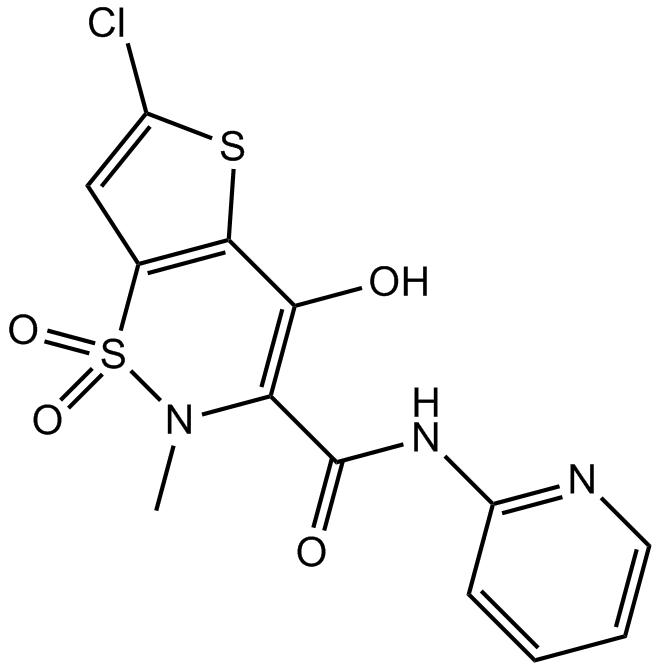 B1441 LornoxicamTarget: COXSummary: COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor
B1441 LornoxicamTarget: COXSummary: COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor

