Metabolism
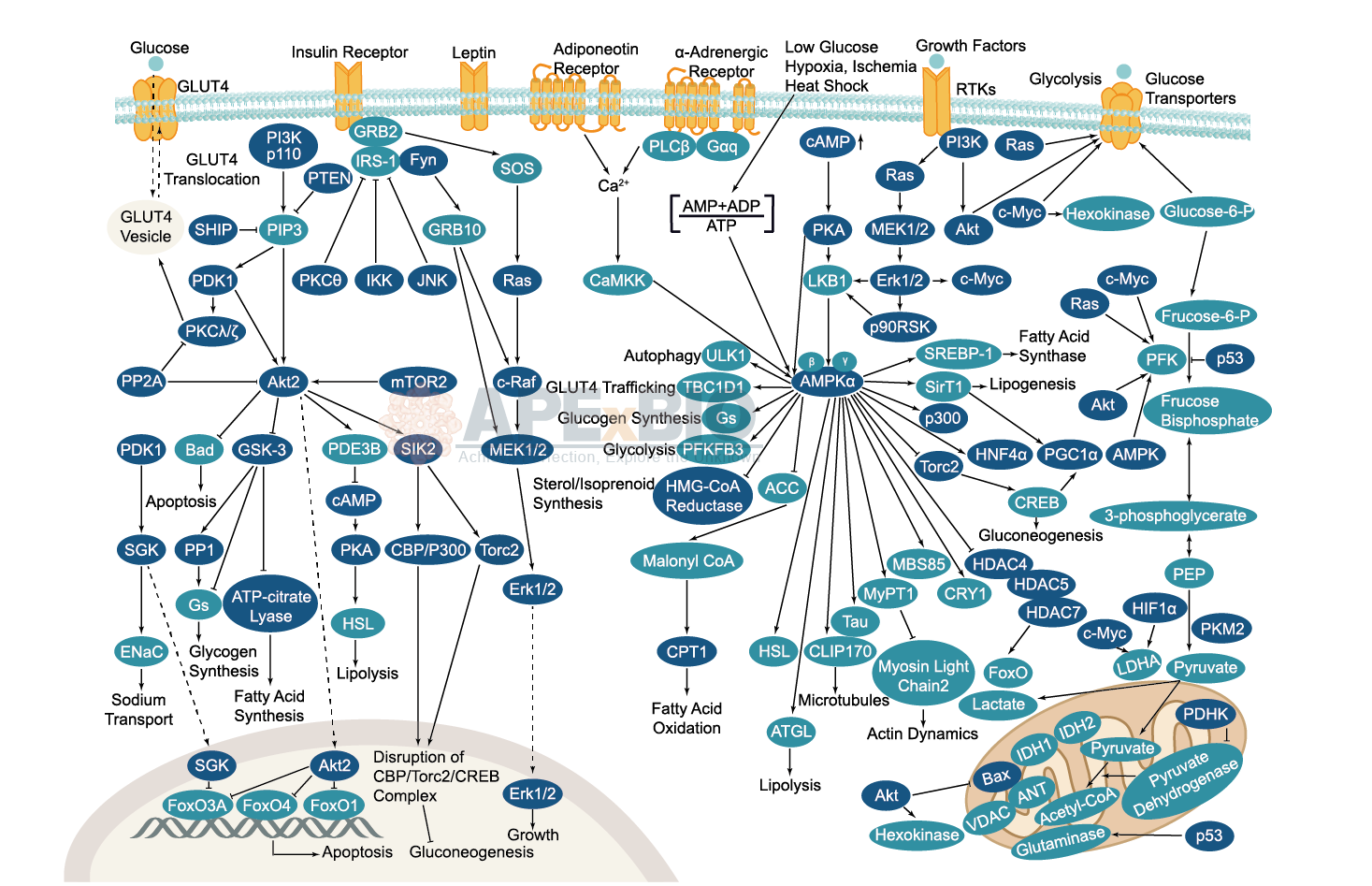
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
 B7471 S26948Summary: PPARγ agonist
B7471 S26948Summary: PPARγ agonist -
 B7539 CDP 840 hydrochlorideSummary: PDE4 inhibitor,potent and selective
B7539 CDP 840 hydrochlorideSummary: PDE4 inhibitor,potent and selective -
 B7553 TesaglitazarSummary: Dual-specificity PPARα/γ agonist
B7553 TesaglitazarSummary: Dual-specificity PPARα/γ agonist -
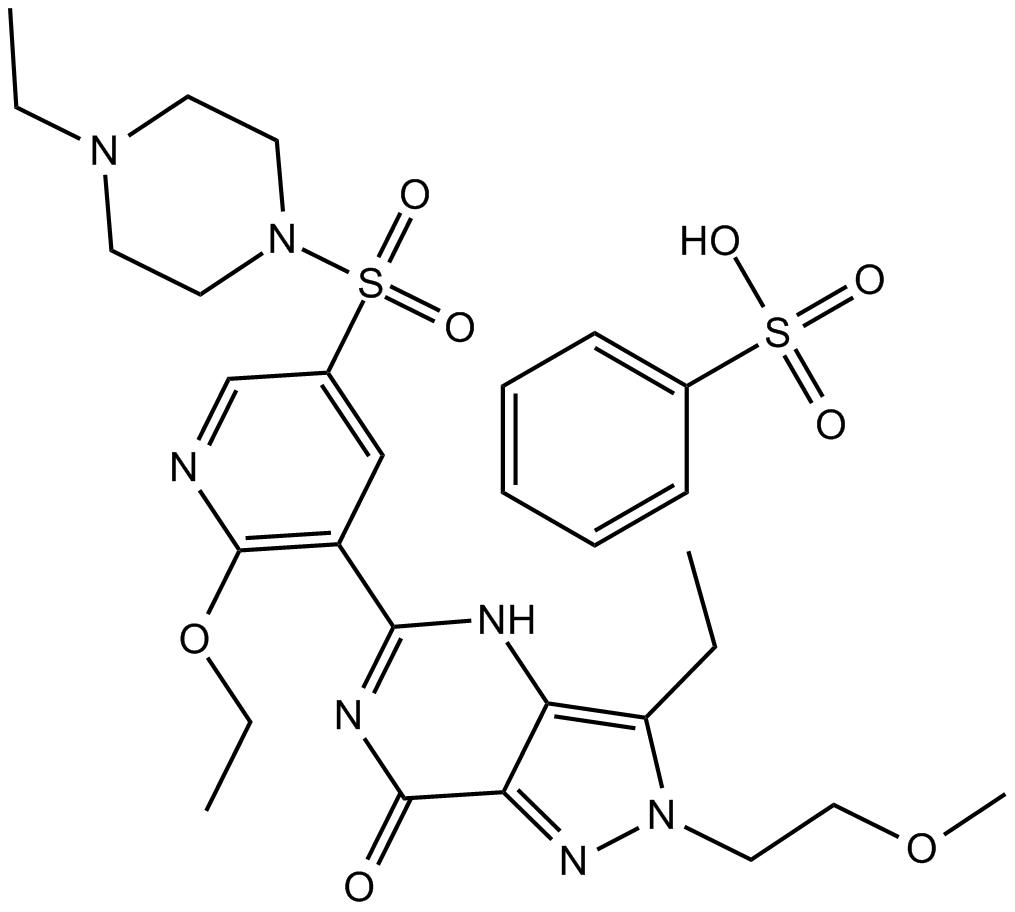 B7599 Gisadenafil besylateSummary: PDE5 inhibitor
B7599 Gisadenafil besylateSummary: PDE5 inhibitor -
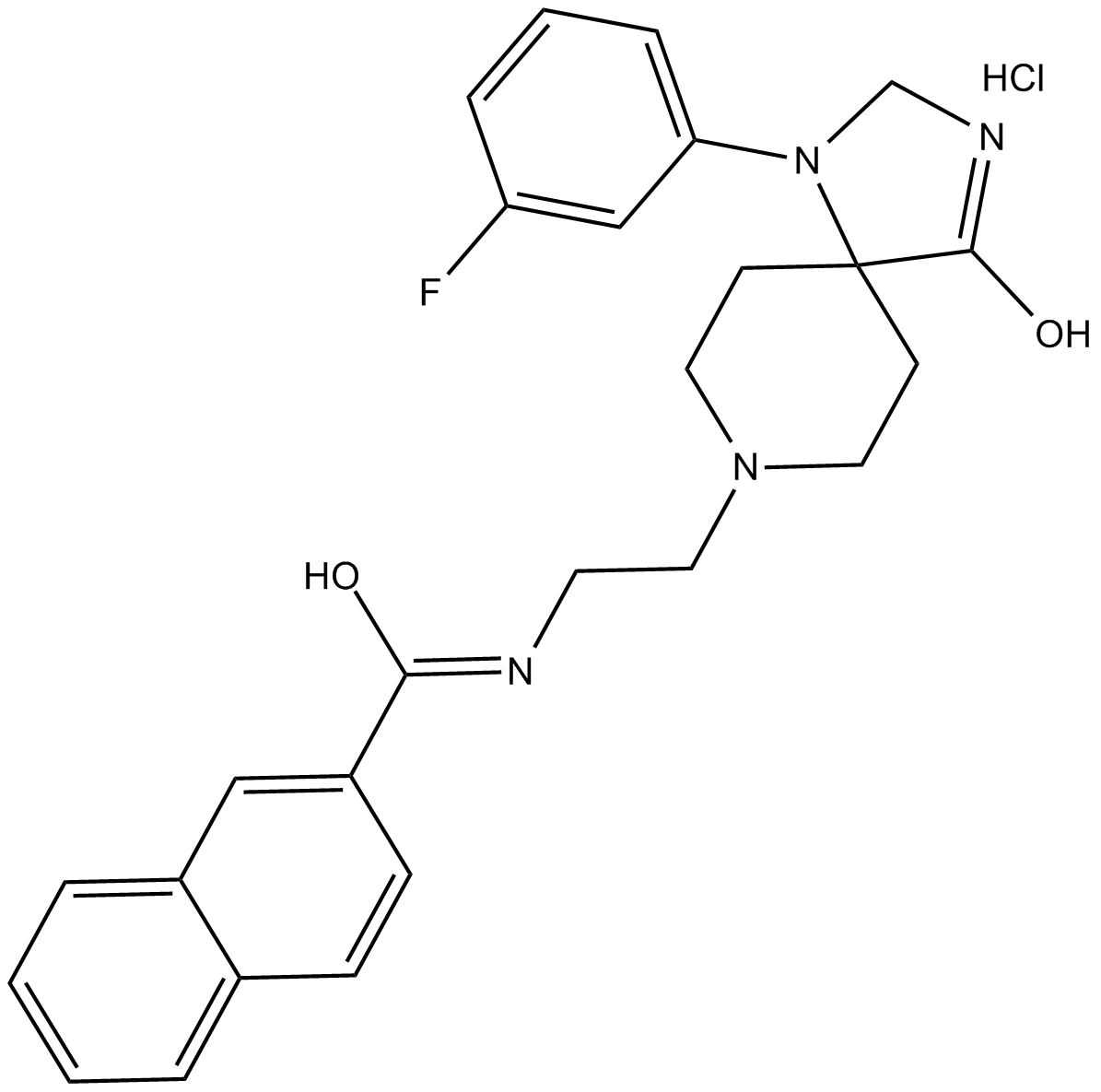 B7603 VU 0364739 hydrochlorideSummary: phospholipase D2 (PLD2) inhibitor
B7603 VU 0364739 hydrochlorideSummary: phospholipase D2 (PLD2) inhibitor -
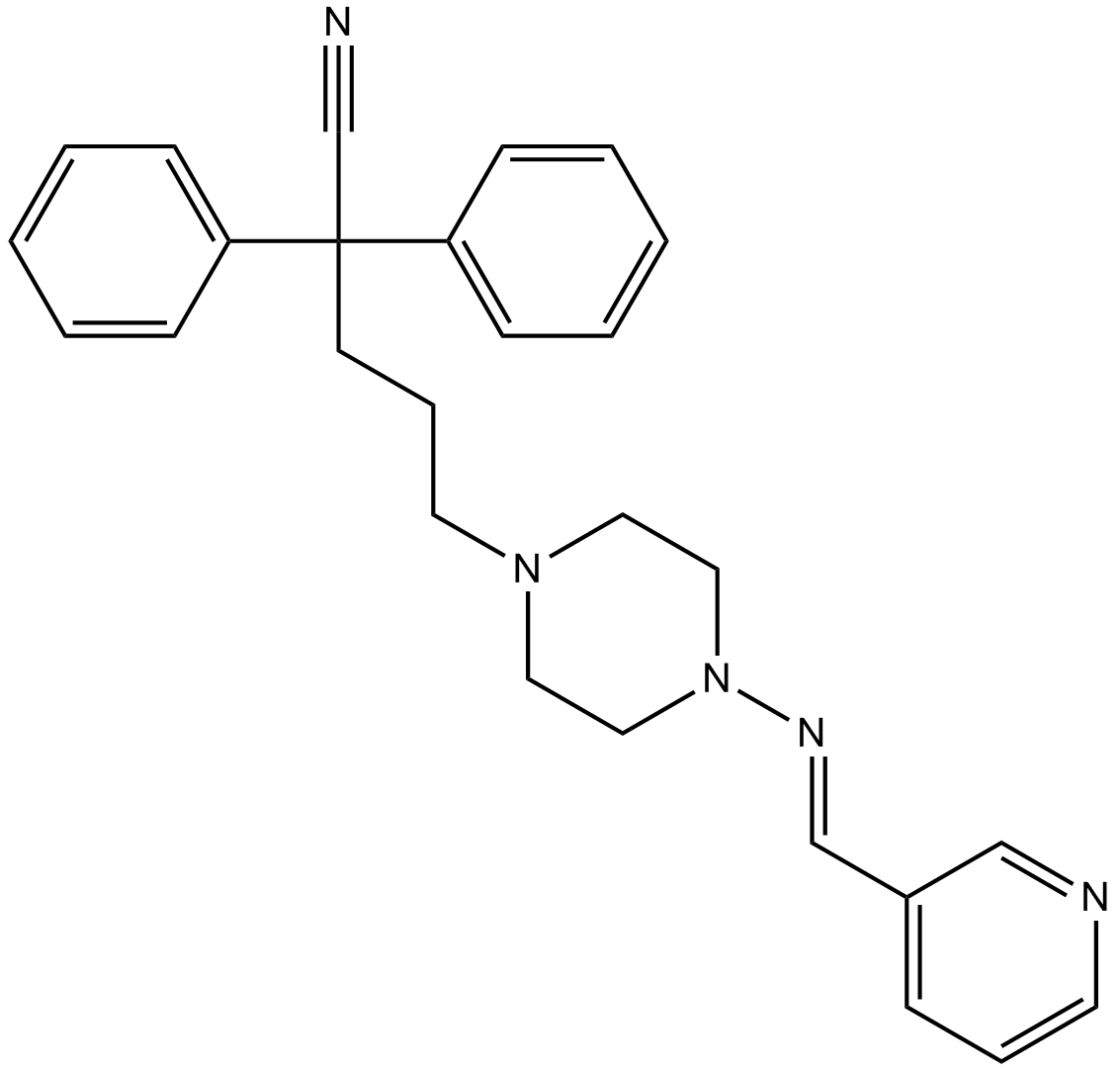 B7608 SC 26196Summary: Δ6 desaturase inhibitor
B7608 SC 26196Summary: Δ6 desaturase inhibitor -
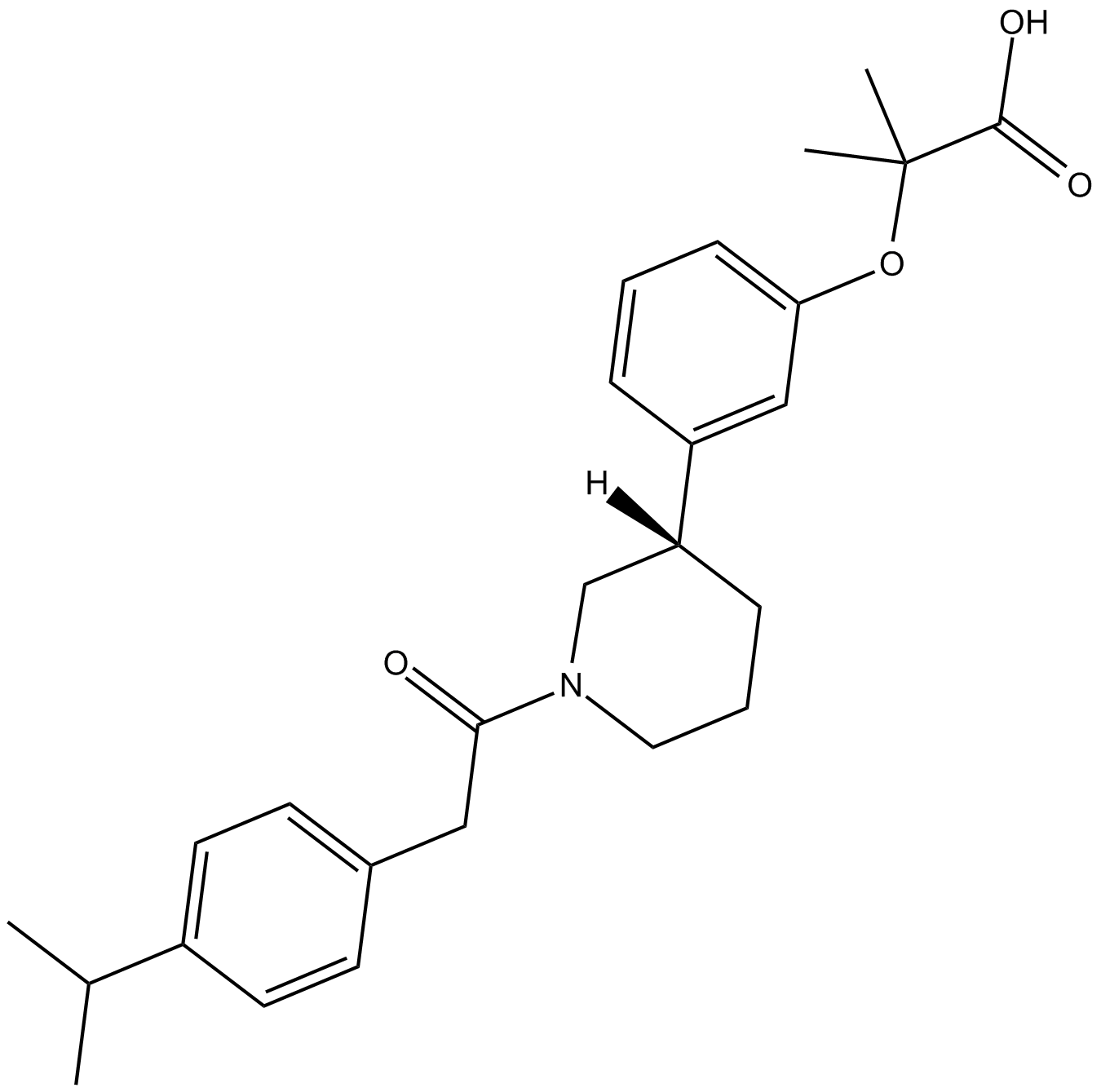 B7609 CP 775146Summary: PPARα agonist
B7609 CP 775146Summary: PPARα agonist -
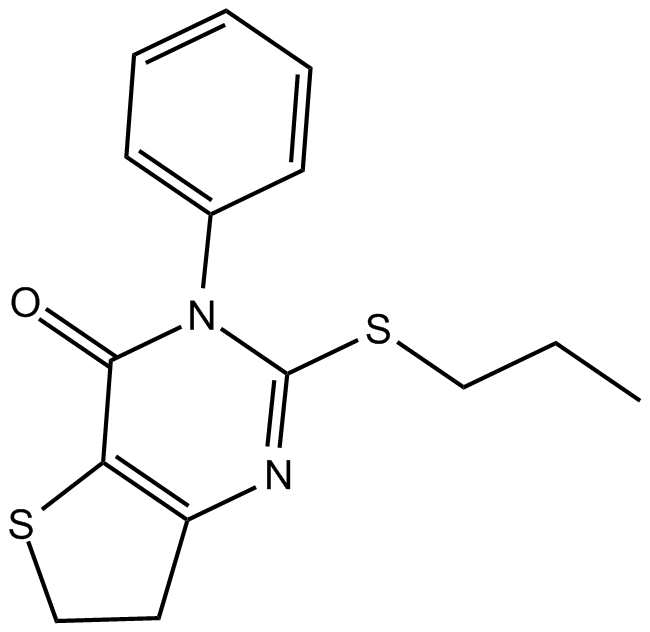 B7673 BC 11-38Summary: Selective PDE11 inhibitor
B7673 BC 11-38Summary: Selective PDE11 inhibitor -
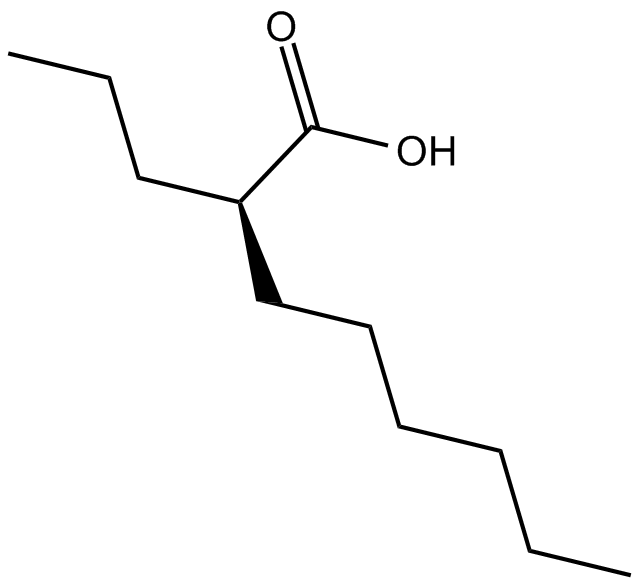 B7676 ONO 2506Summary: exhibits neuroprotective effects
B7676 ONO 2506Summary: exhibits neuroprotective effects -
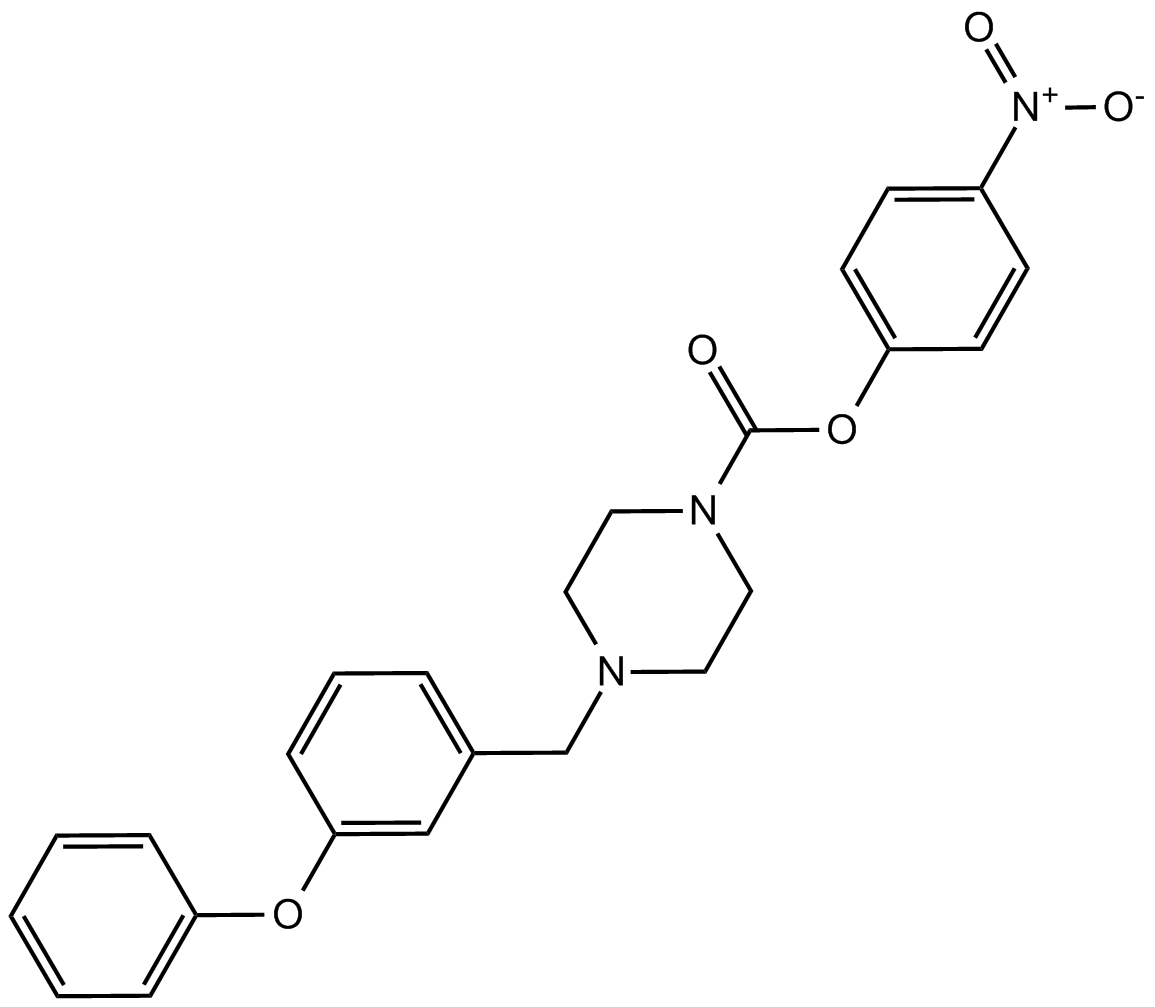 B7701 JZL 195Summary: Dual inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL)
B7701 JZL 195Summary: Dual inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL)

