Metabolism
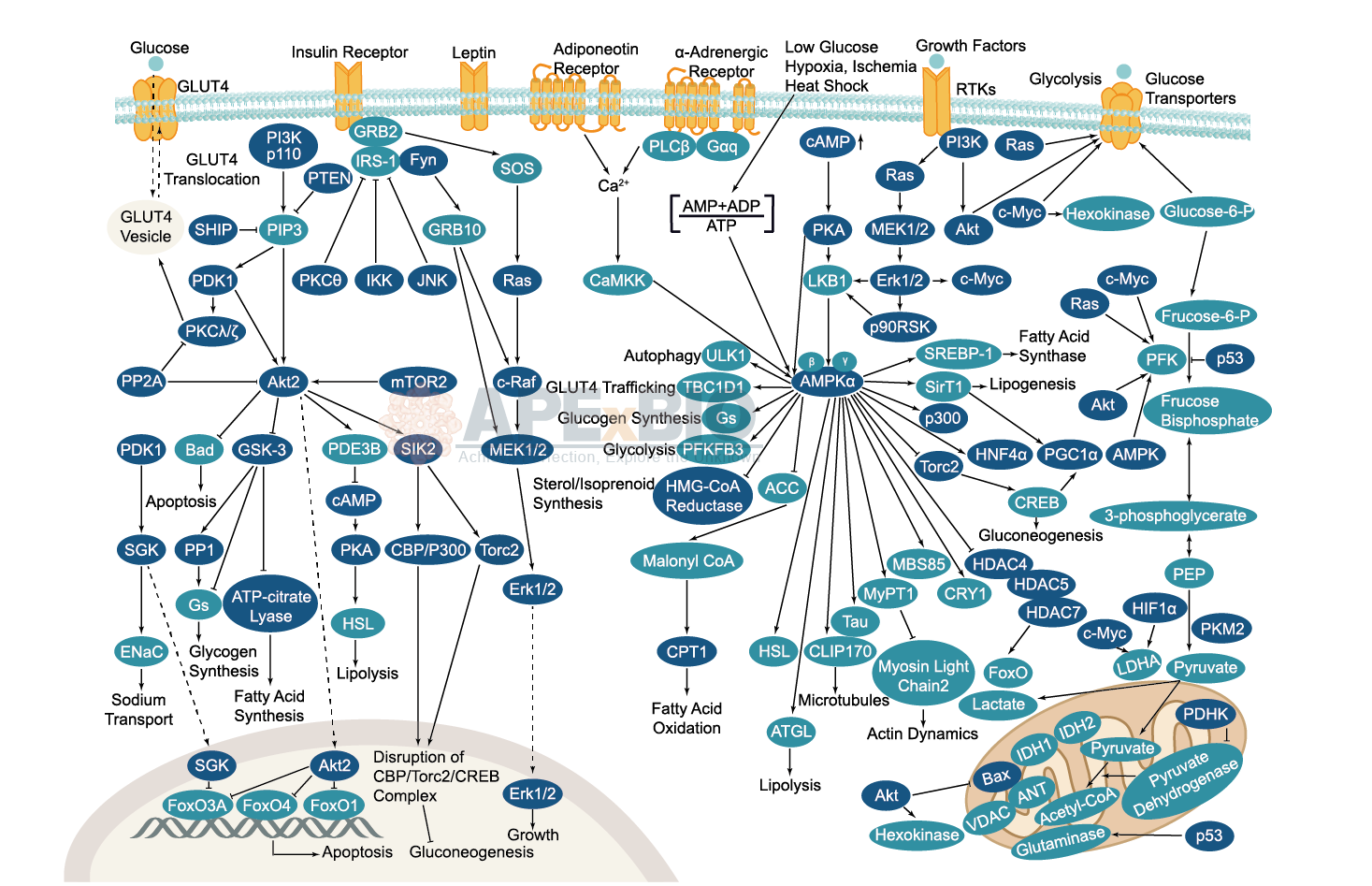
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
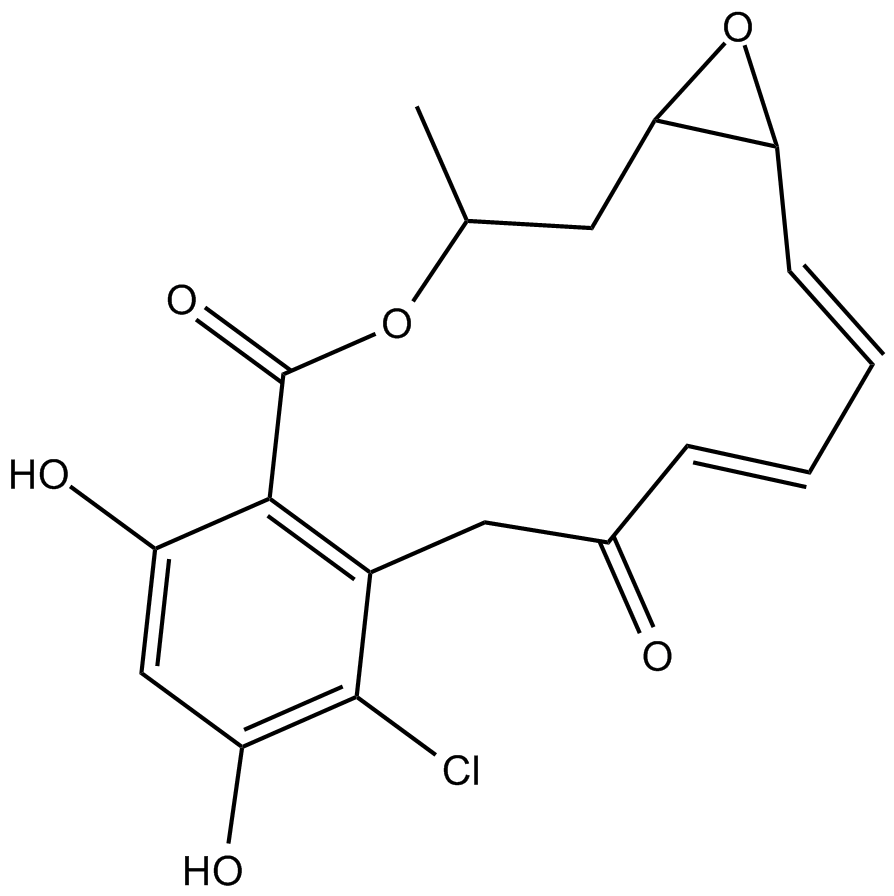 A4067 RadicicolSummary: ATPase/kinase inhibitor
A4067 RadicicolSummary: ATPase/kinase inhibitor -
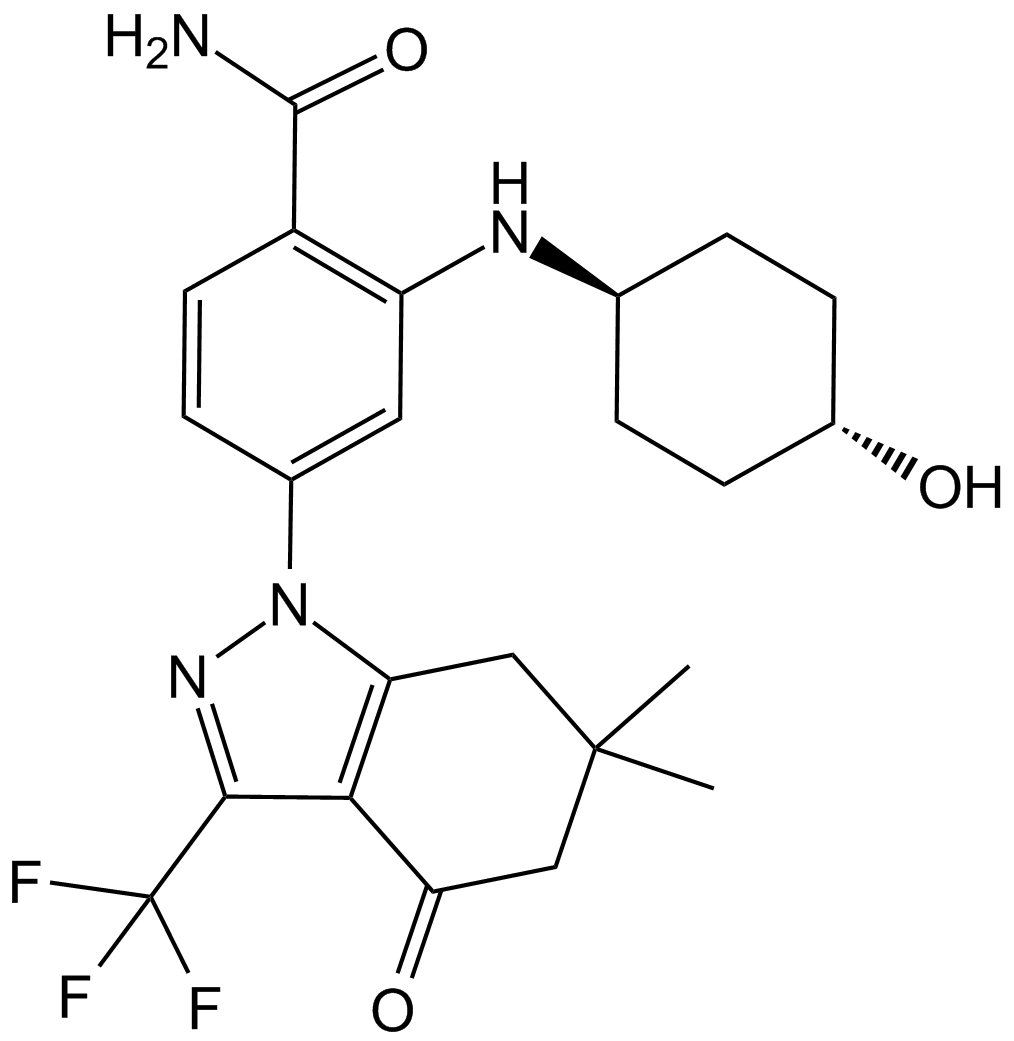 A4068 SNX-21121 CitationSummary: Hsp90 inhibitor,ATP-competitve,potent and selective
A4068 SNX-21121 CitationSummary: Hsp90 inhibitor,ATP-competitve,potent and selective -
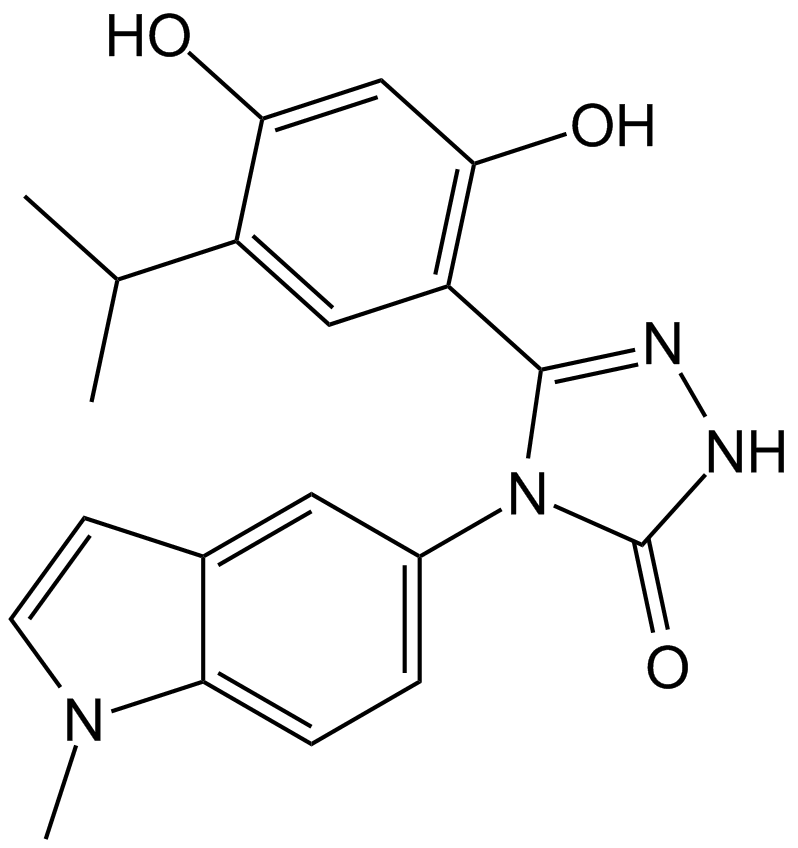 A4385 Ganetespib (STA-9090)3 CitationSummary: Hsp90 inhibitor,non-geldanamycin
A4385 Ganetespib (STA-9090)3 CitationSummary: Hsp90 inhibitor,non-geldanamycin -
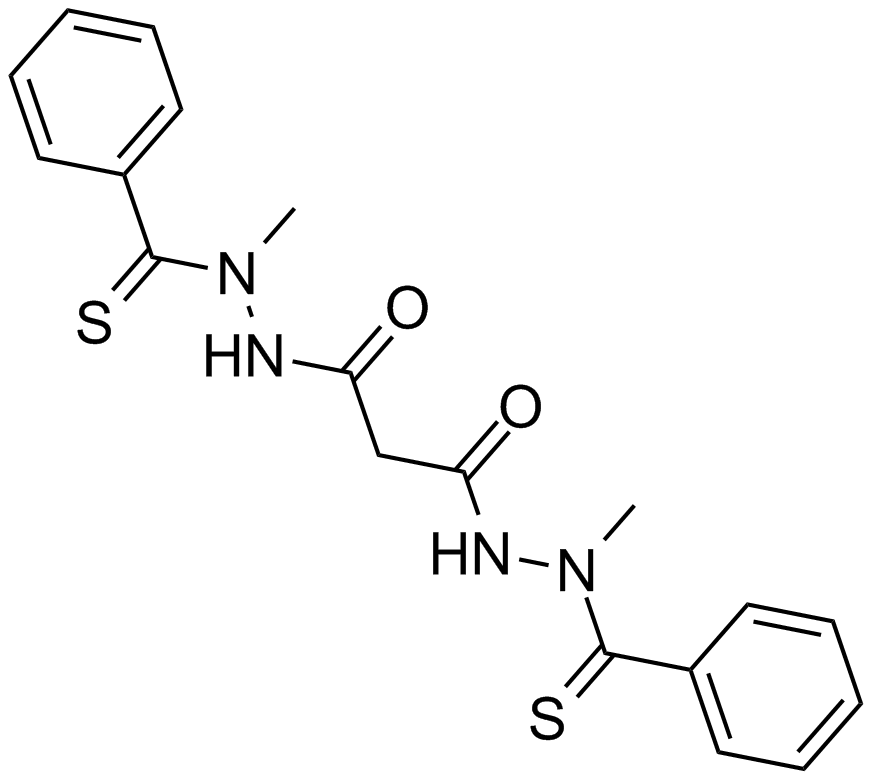 A4386 Elesclomol (STA-4783)3 CitationSummary: Oxidative stress/apoptosis inducer,potent and novel
A4386 Elesclomol (STA-4783)3 CitationSummary: Oxidative stress/apoptosis inducer,potent and novel -
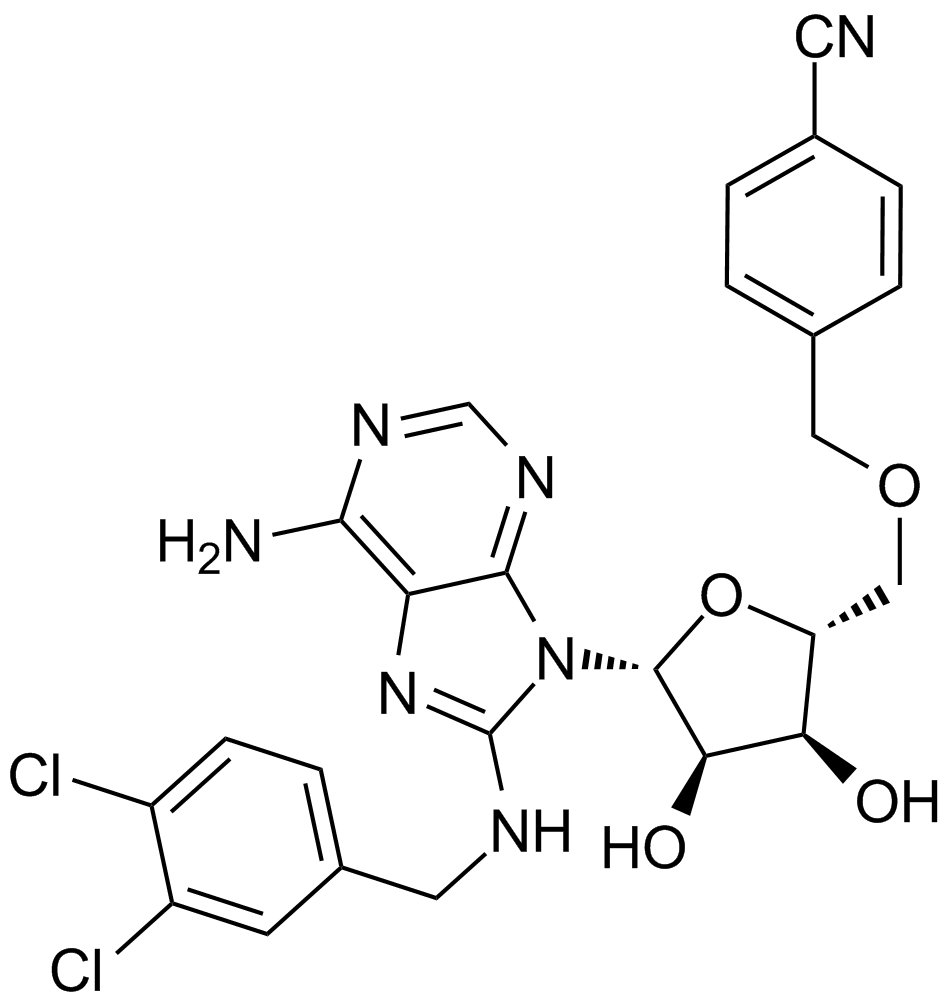 A4387 VER 1550084 CitationSummary: HSP 70 inhibitor,adenosine-derived
A4387 VER 1550084 CitationSummary: HSP 70 inhibitor,adenosine-derived -
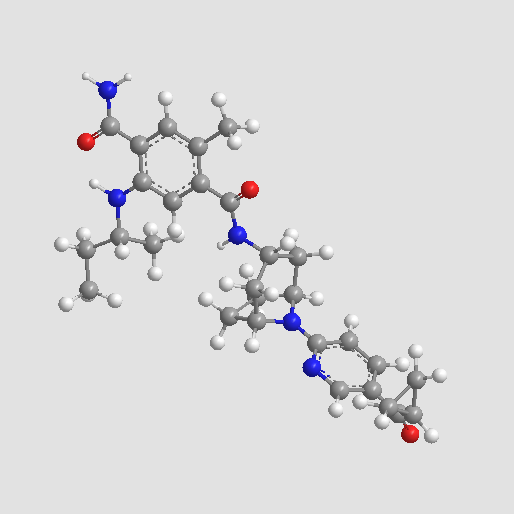 A4388 XL-8881 CitationTarget: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor
A4388 XL-8881 CitationTarget: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor -
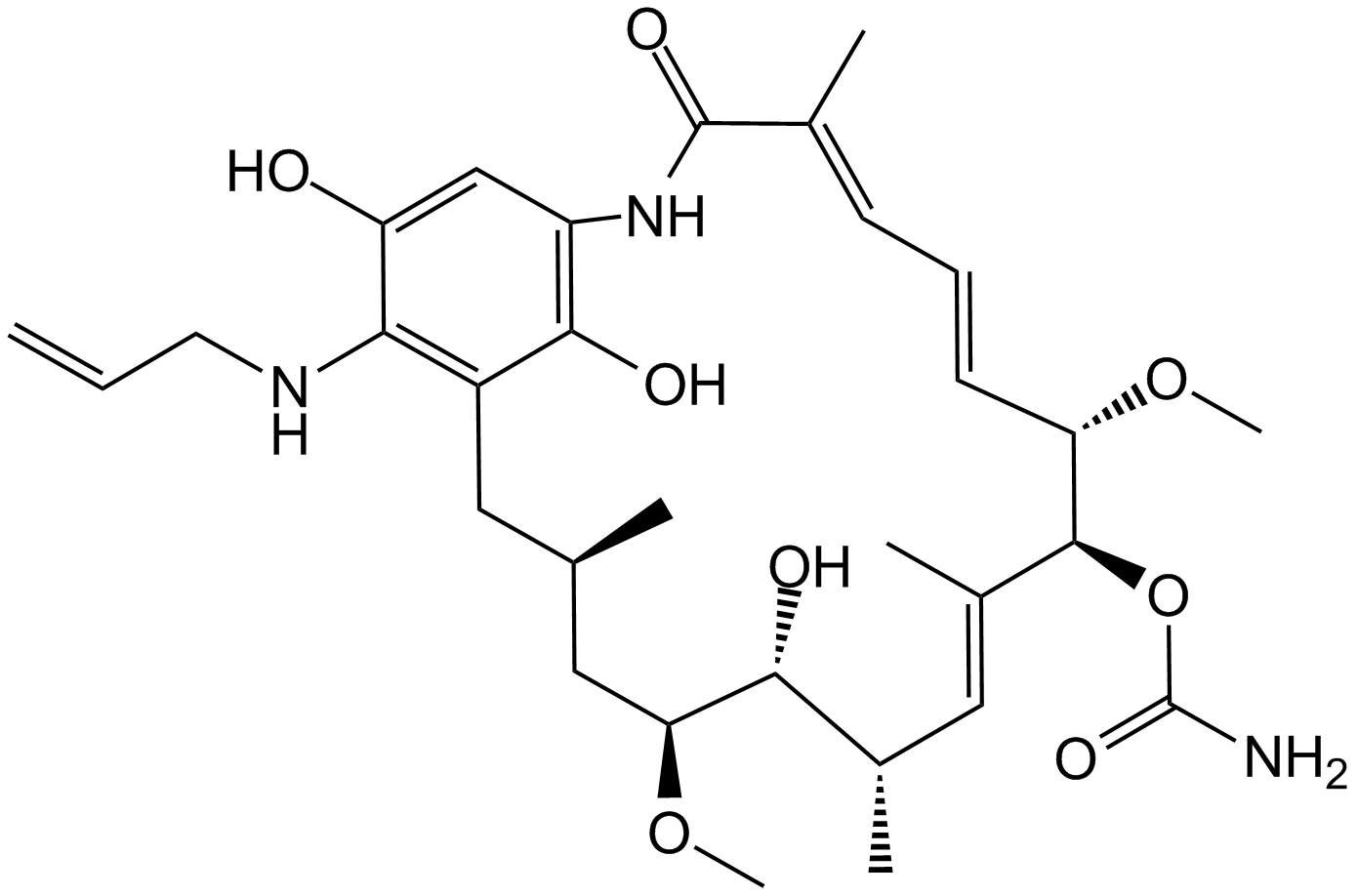 A3756 RetaspimycinSummary: HSP90 inhibitor,antiproliferative and antineoplastic
A3756 RetaspimycinSummary: HSP90 inhibitor,antiproliferative and antineoplastic -
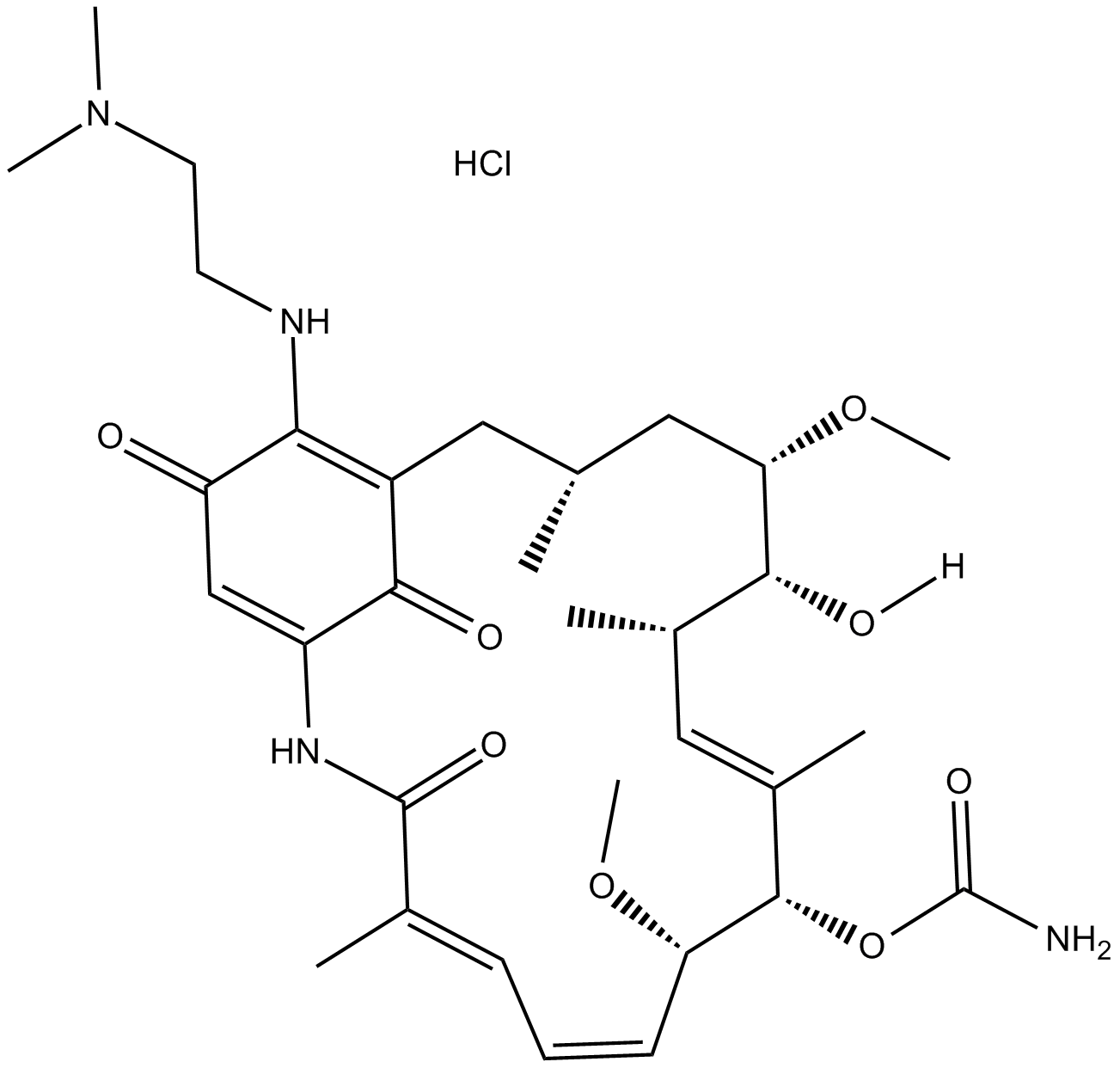 A2213 17-DMAG (Alvespimycin) HCl1 CitationTarget: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor
A2213 17-DMAG (Alvespimycin) HCl1 CitationTarget: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor -
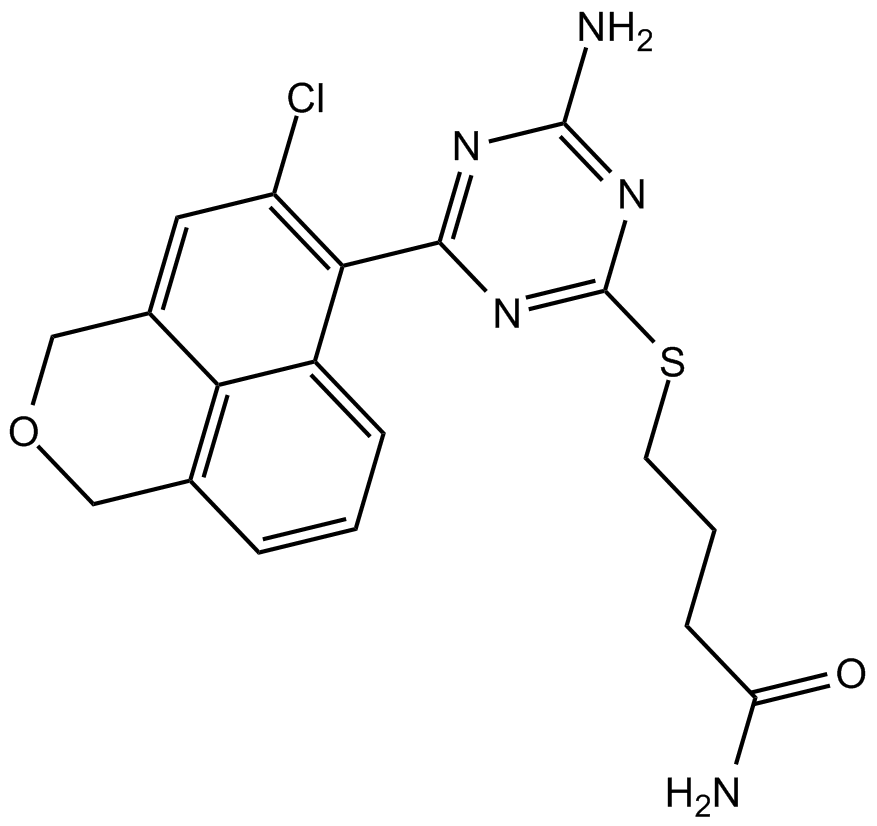 B4571 CH5138303Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, orally available
B4571 CH5138303Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, orally available -
 C3212 CCT018159Summary: inhibitor of the ATPase activity of Hsp90
C3212 CCT018159Summary: inhibitor of the ATPase activity of Hsp90

