Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
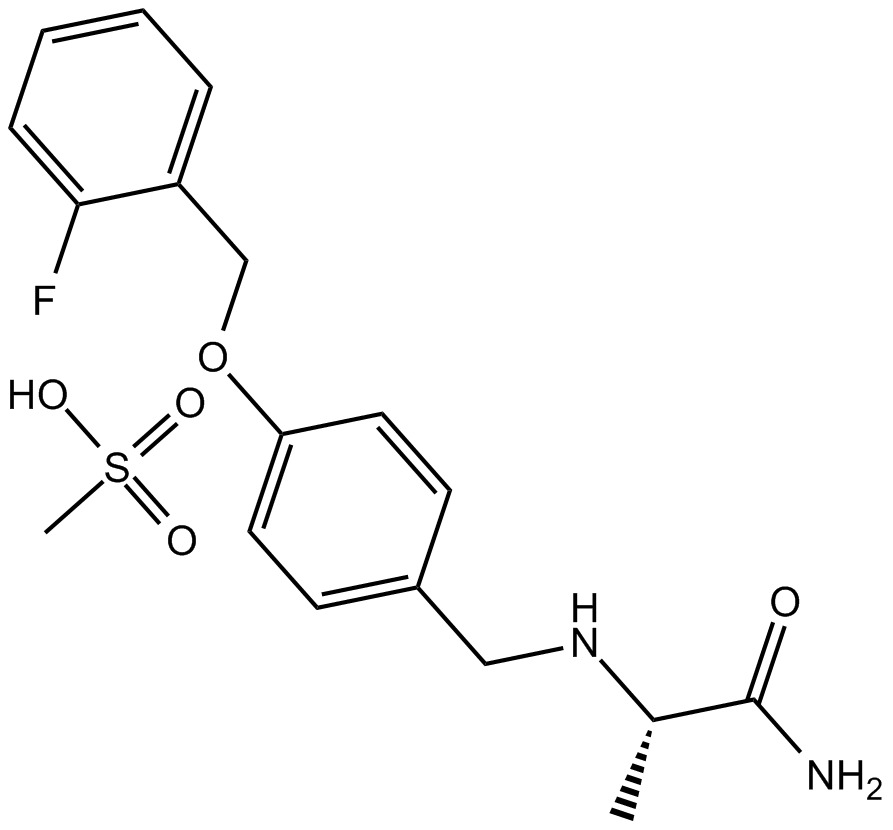 B7569 Ralfinamide mesylateSummary: Sodium channel blocker
B7569 Ralfinamide mesylateSummary: Sodium channel blocker -
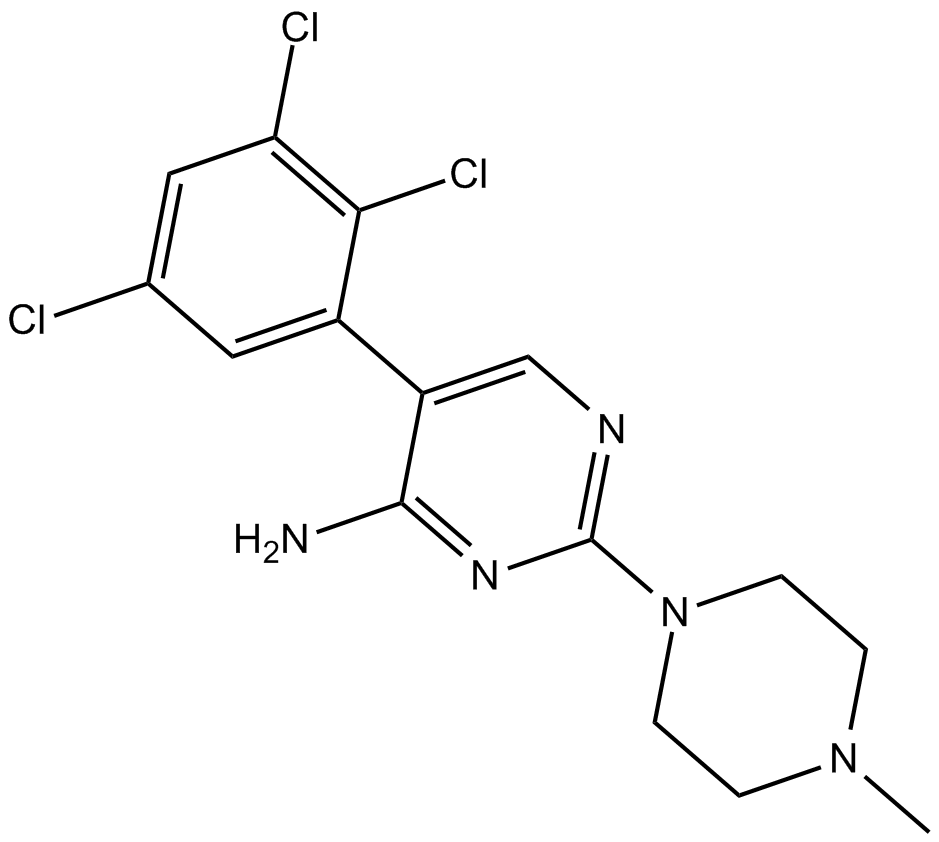 B7573 SipatrigineSummary: voltage-dependent sodium channels (NaV) blocker
B7573 SipatrigineSummary: voltage-dependent sodium channels (NaV) blocker -
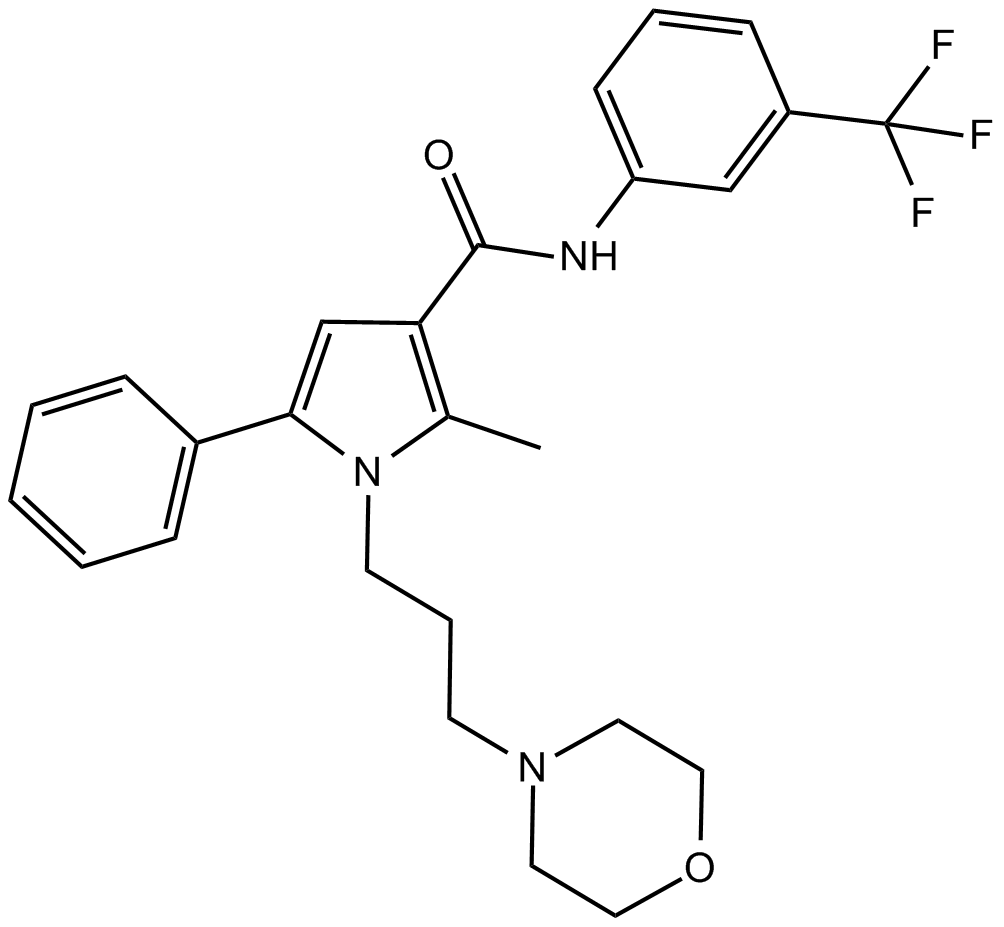 B7588 HC 067047Summary: TRPV4 antagonist
B7588 HC 067047Summary: TRPV4 antagonist -
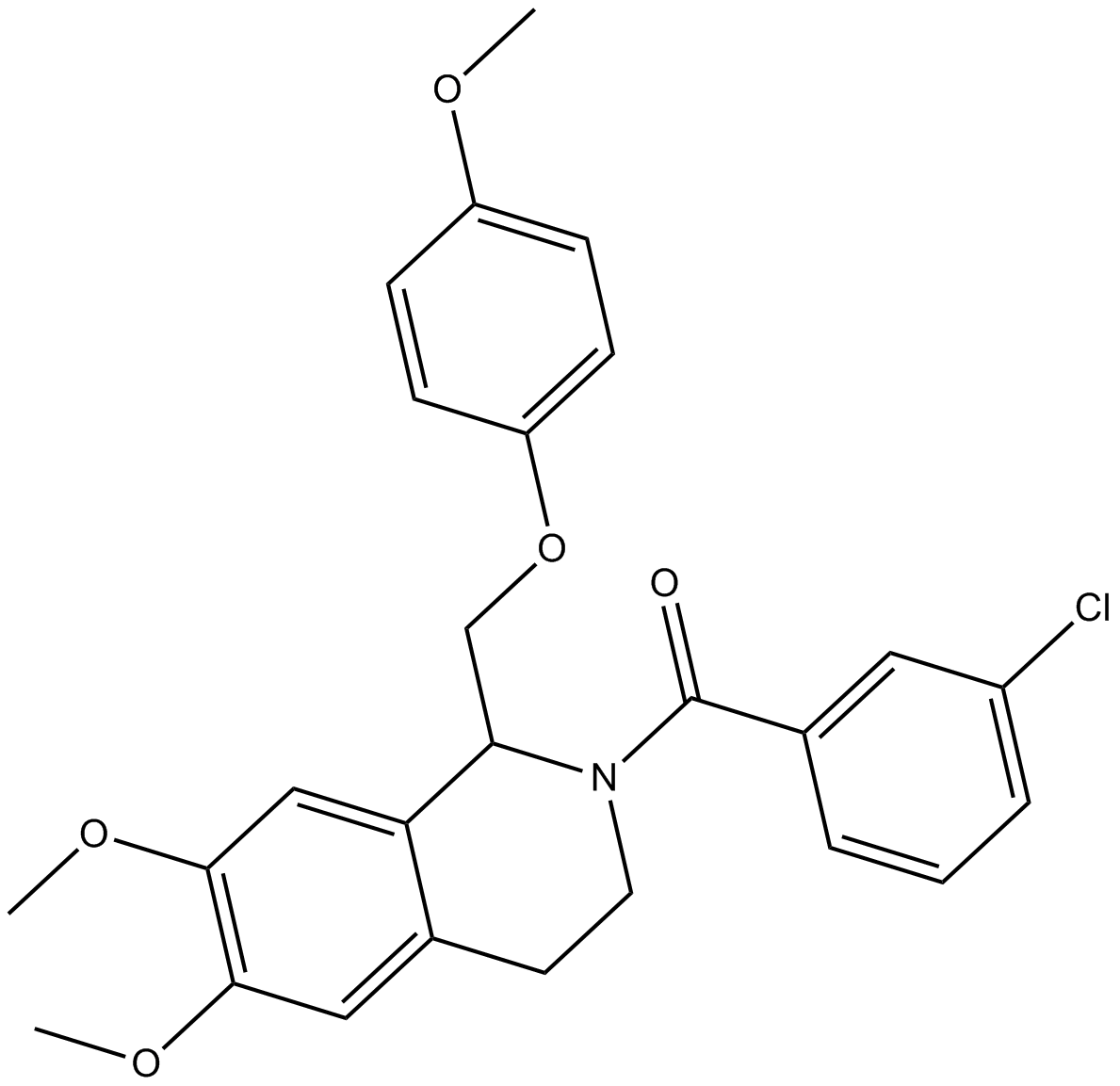 B7589 CIQSummary: NMDA receptor potentiator
B7589 CIQSummary: NMDA receptor potentiator -
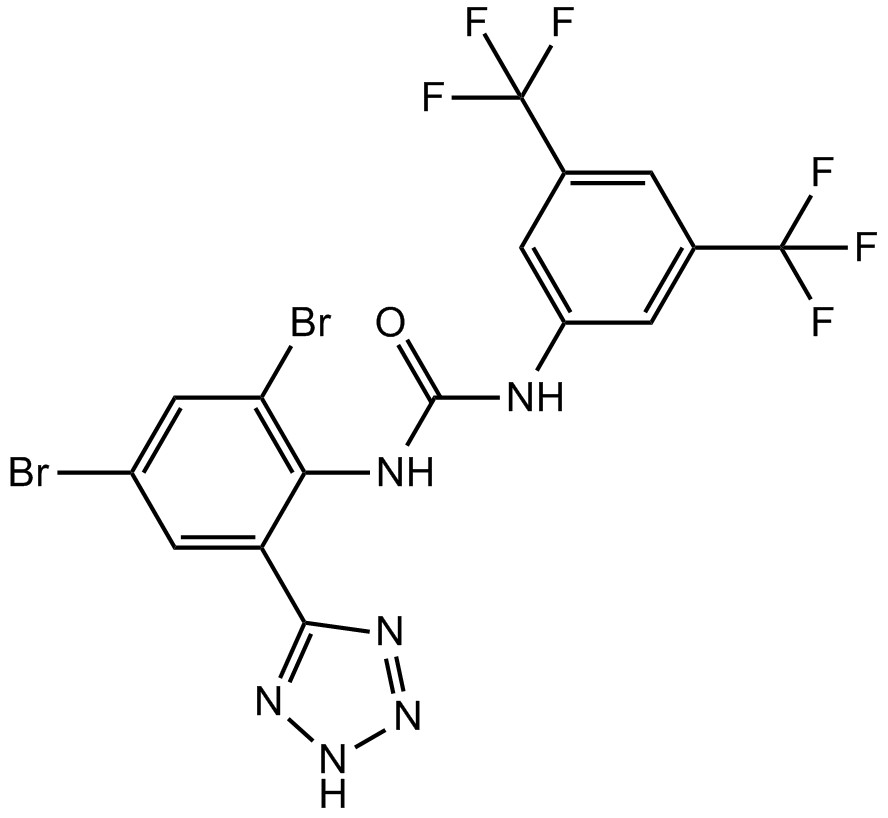 B7600 NS 5806Summary: KV4.3 channel activator
B7600 NS 5806Summary: KV4.3 channel activator -
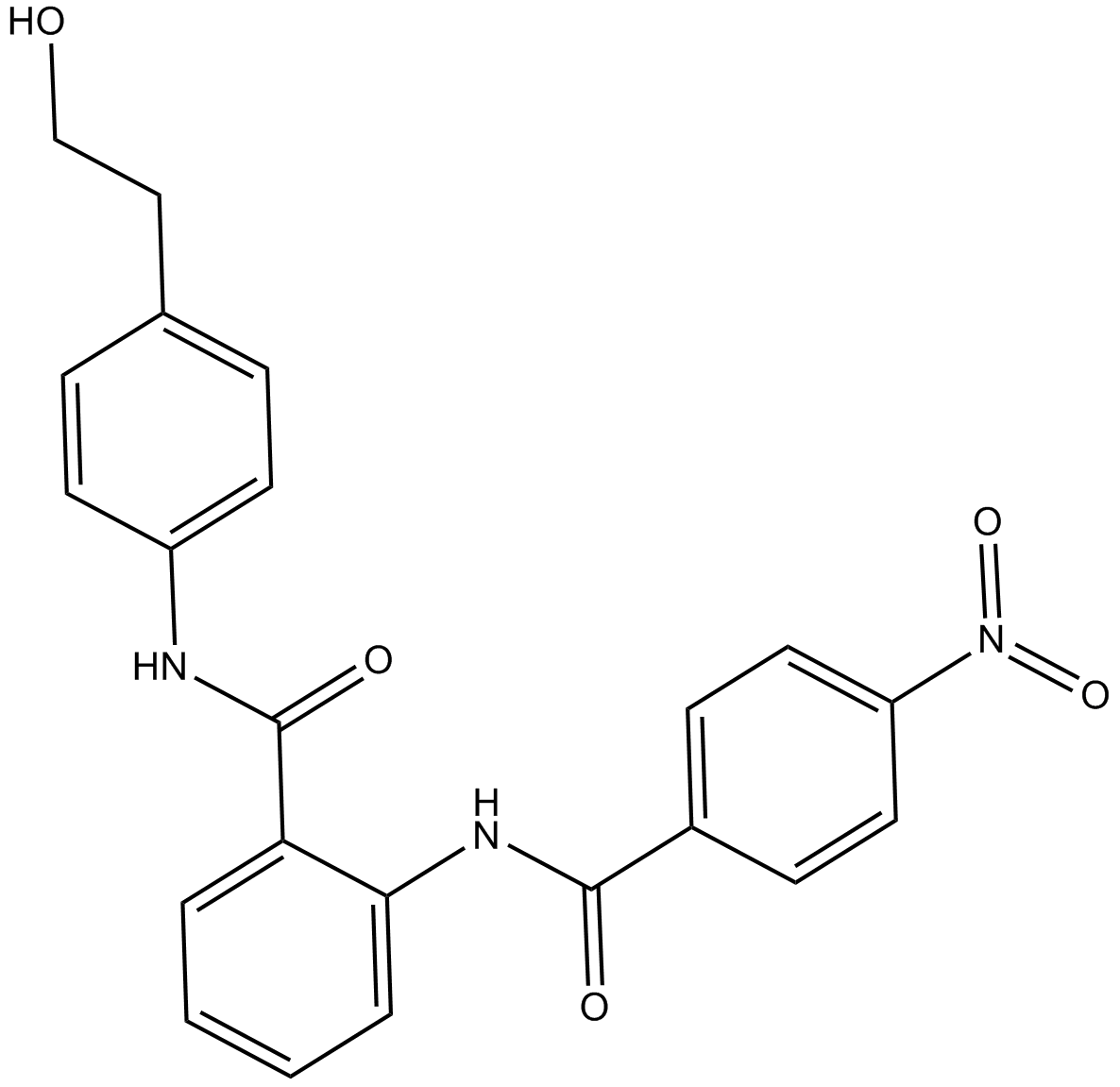 B7602 KS 176Summary: inhibitor of the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) multidrug transporter
B7602 KS 176Summary: inhibitor of the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) multidrug transporter -
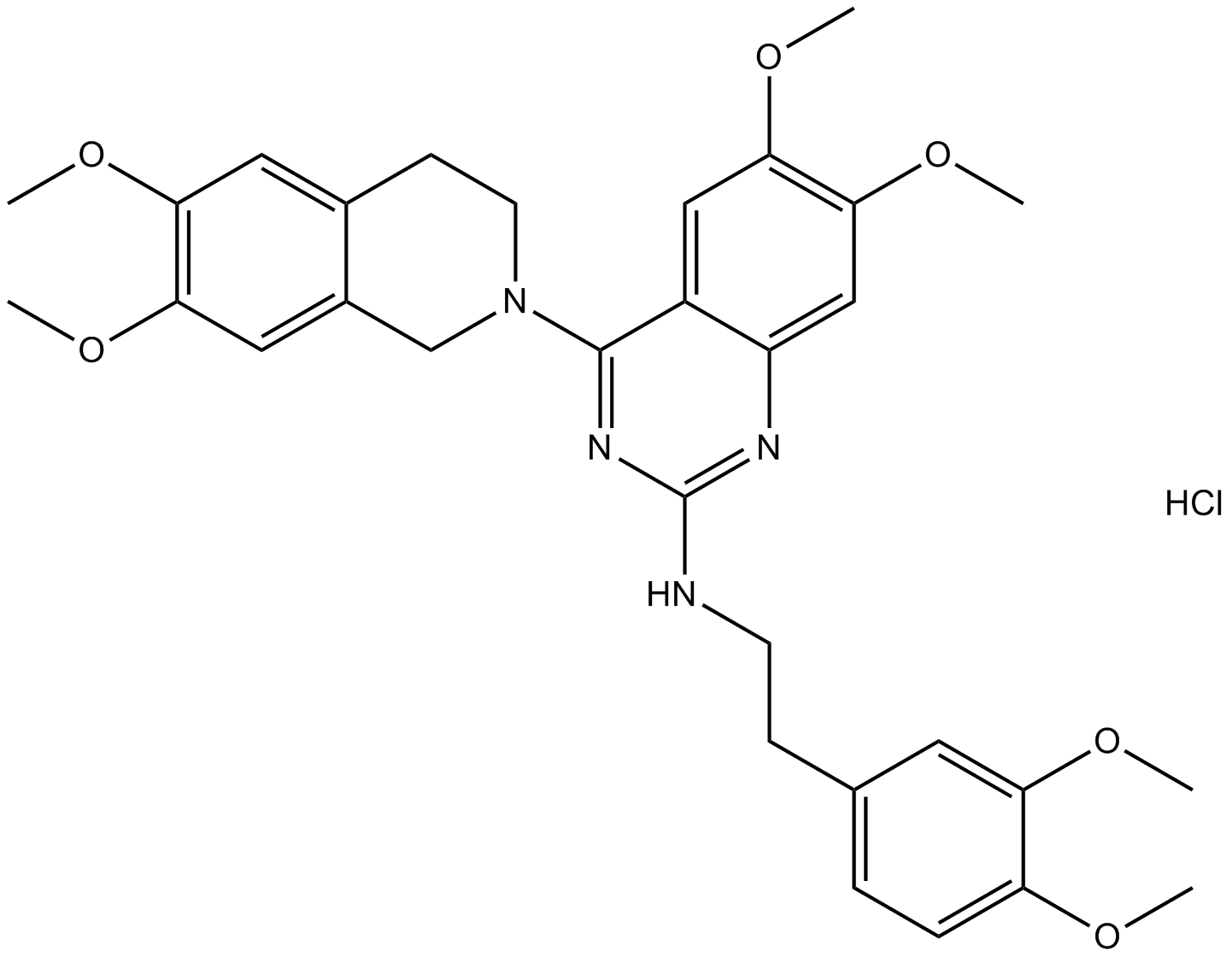 B7610 CP 100356 hydrochlorideSummary: P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor
B7610 CP 100356 hydrochlorideSummary: P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor -
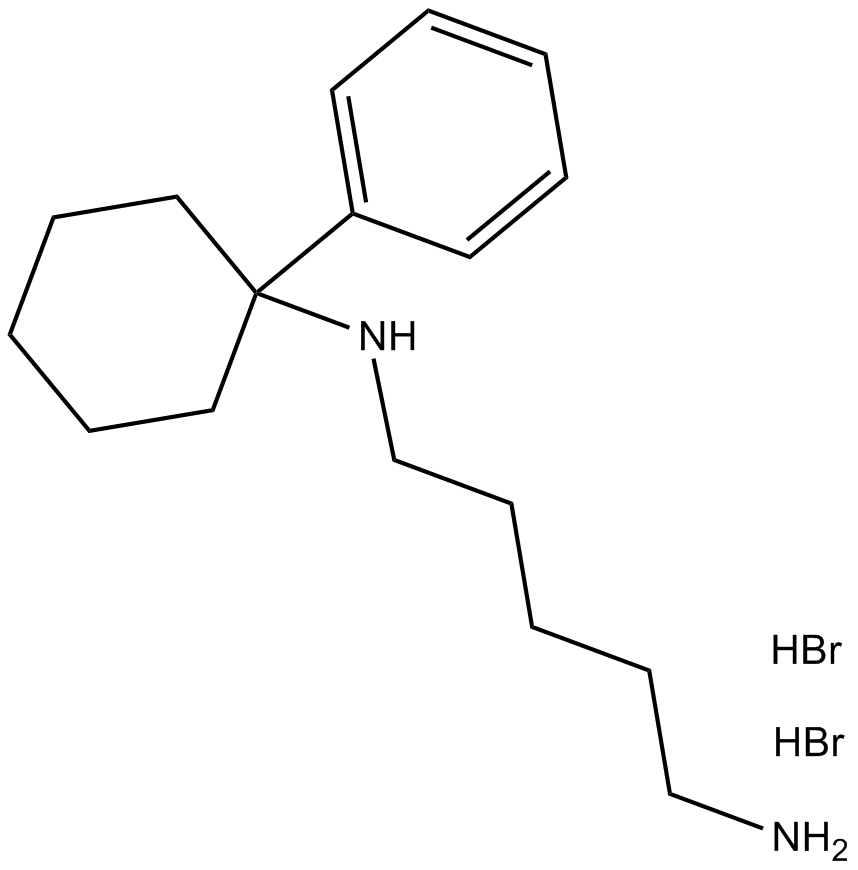 B7613 IEM 1925 dihydrobromideSummary: AMPA receptor antagonist
B7613 IEM 1925 dihydrobromideSummary: AMPA receptor antagonist -
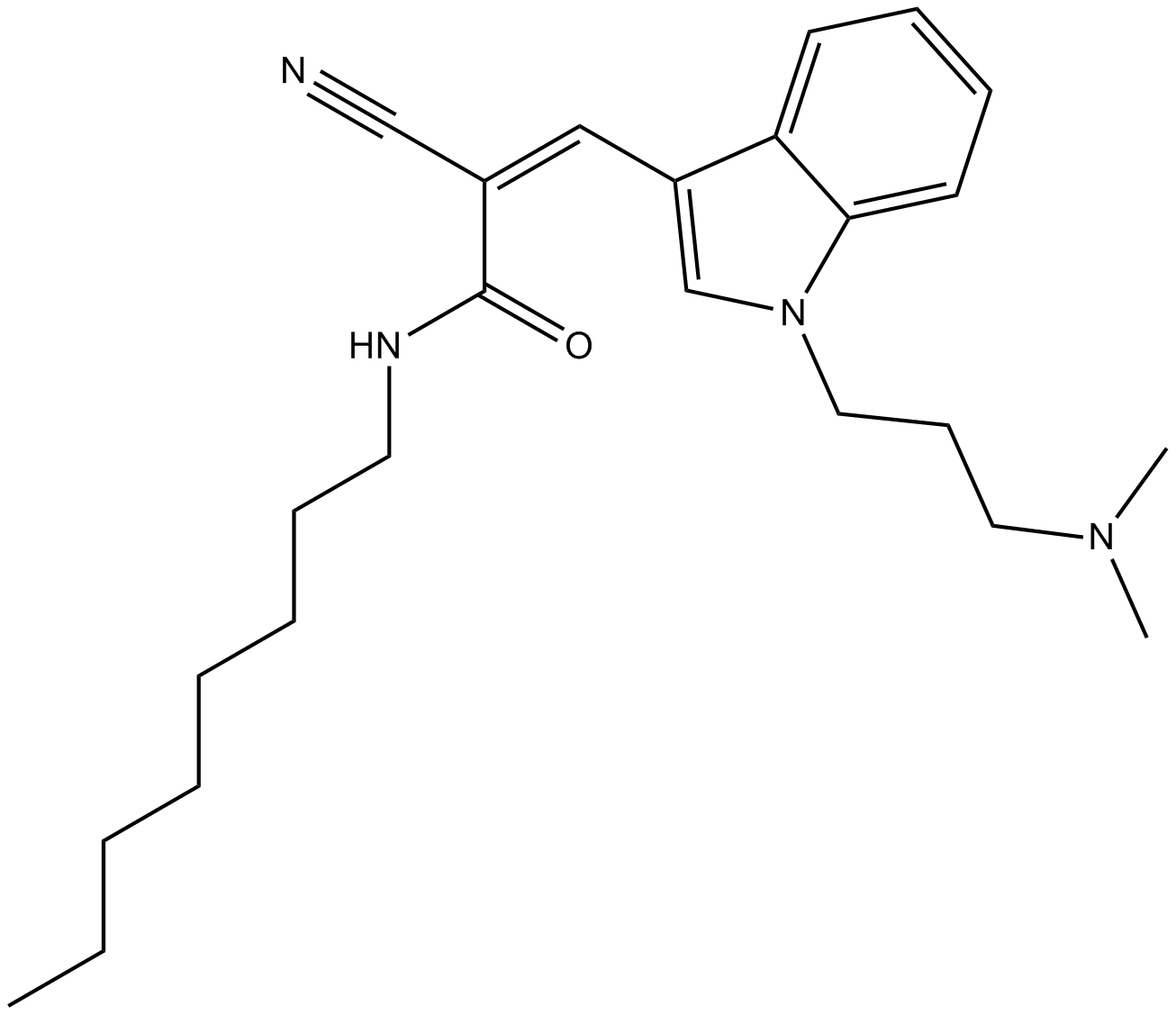 B7619 Dynole 34-2Summary: Dynamin I inhibitor
B7619 Dynole 34-2Summary: Dynamin I inhibitor -
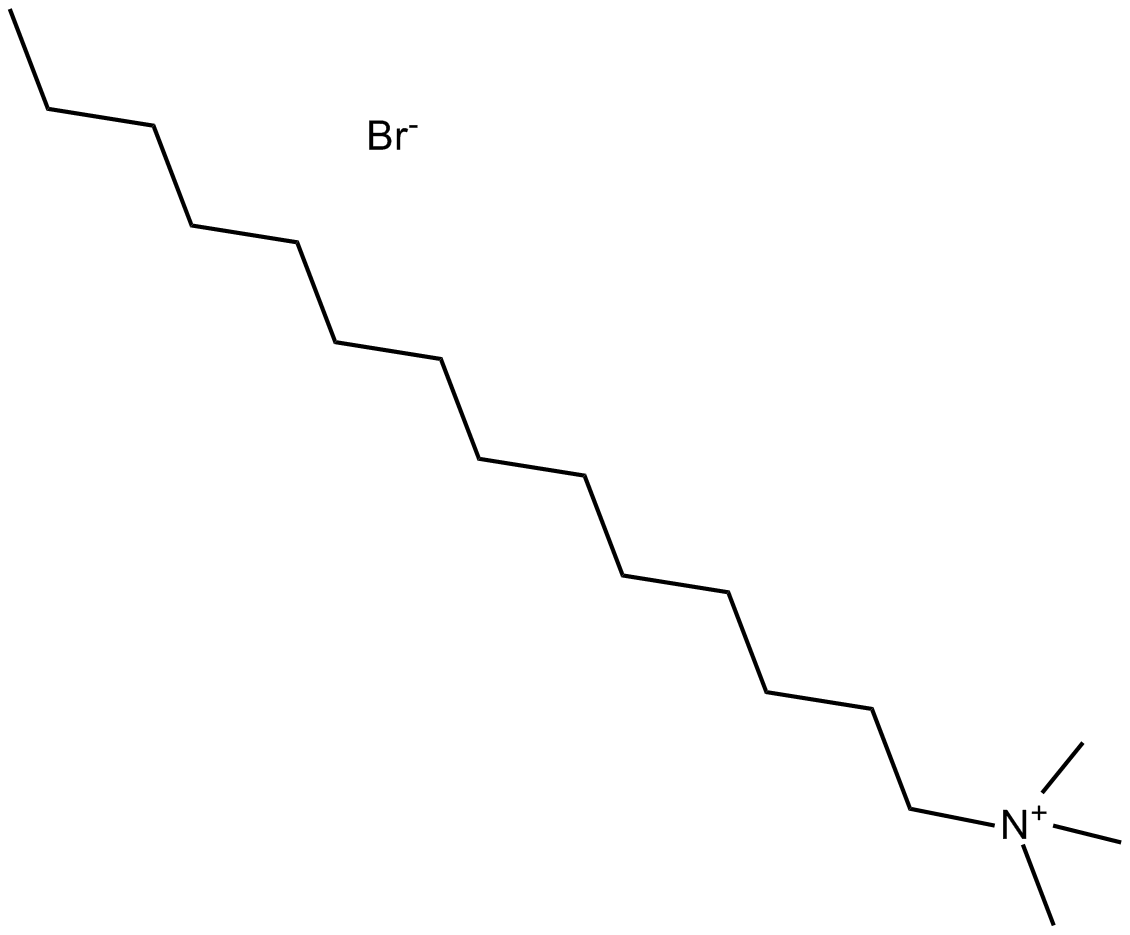 B7620 MitMABSummary: Dynamin GTPase activity inhibitor
B7620 MitMABSummary: Dynamin GTPase activity inhibitor

