Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
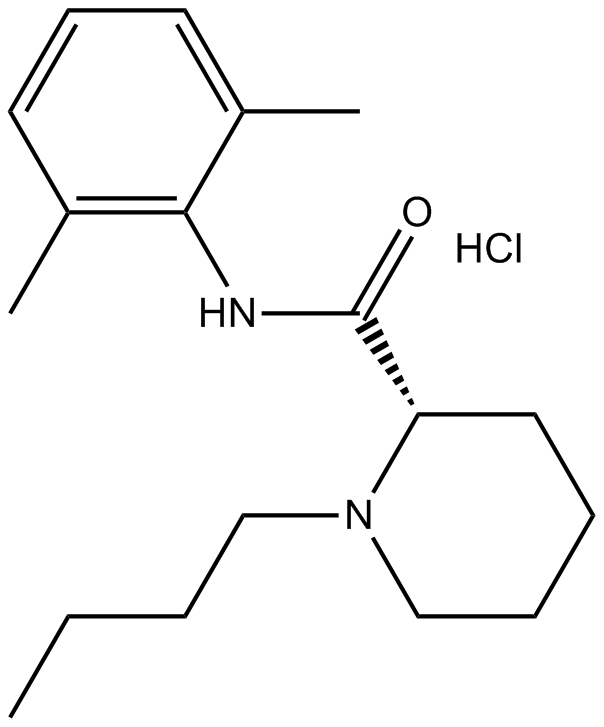 B1420 Bupivacaine HClTarget: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: Anaesthetic drug
B1420 Bupivacaine HClTarget: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: Anaesthetic drug -
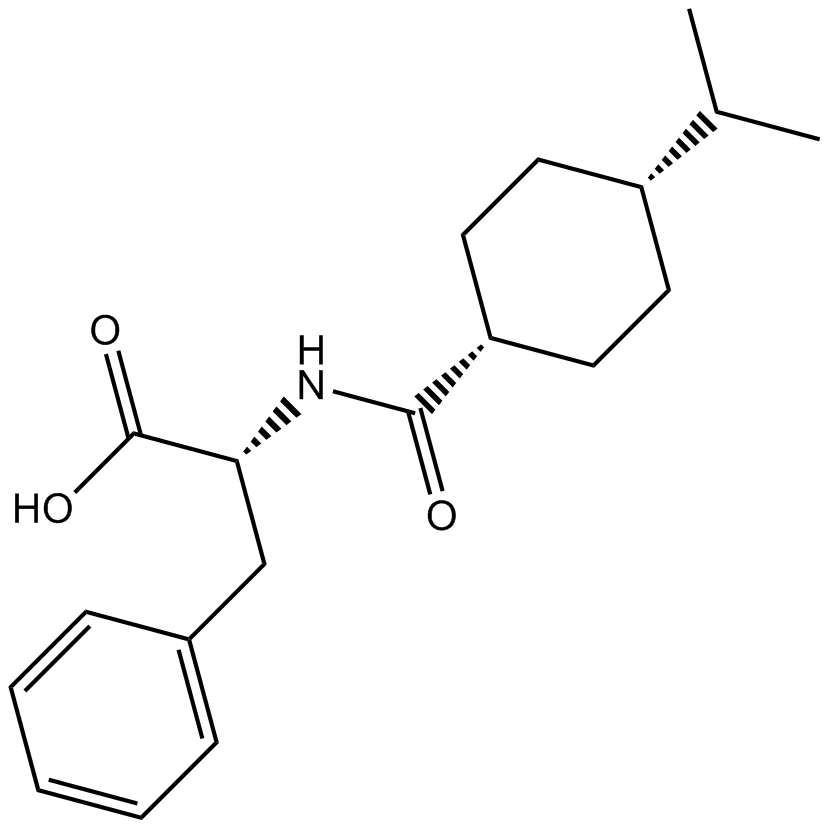 B2198 NateglinideTarget: Inward Rectifier Potassium (Kir) ChannelsSummary: Insulin secretagog agent
B2198 NateglinideTarget: Inward Rectifier Potassium (Kir) ChannelsSummary: Insulin secretagog agent -
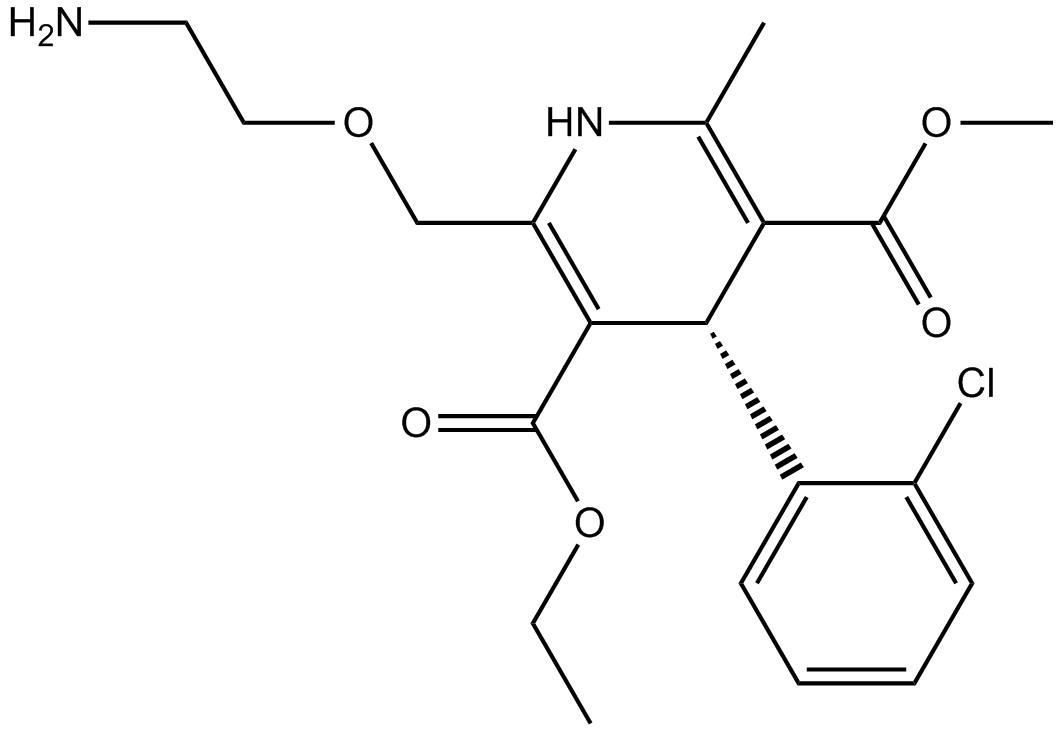 B1410 AmlodipineTarget: Voltage-gated Calcium Channels (CaV)Summary: Calcium channel blocker
B1410 AmlodipineTarget: Voltage-gated Calcium Channels (CaV)Summary: Calcium channel blocker -
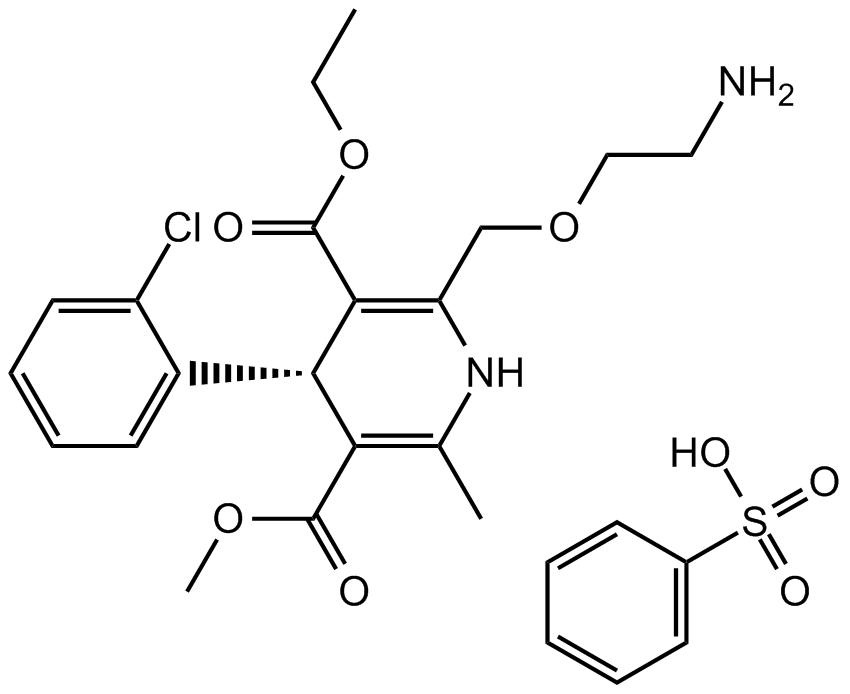 B1411 Amlodipine BesylateSummary: Block of L-type calcium channel
B1411 Amlodipine BesylateSummary: Block of L-type calcium channel -
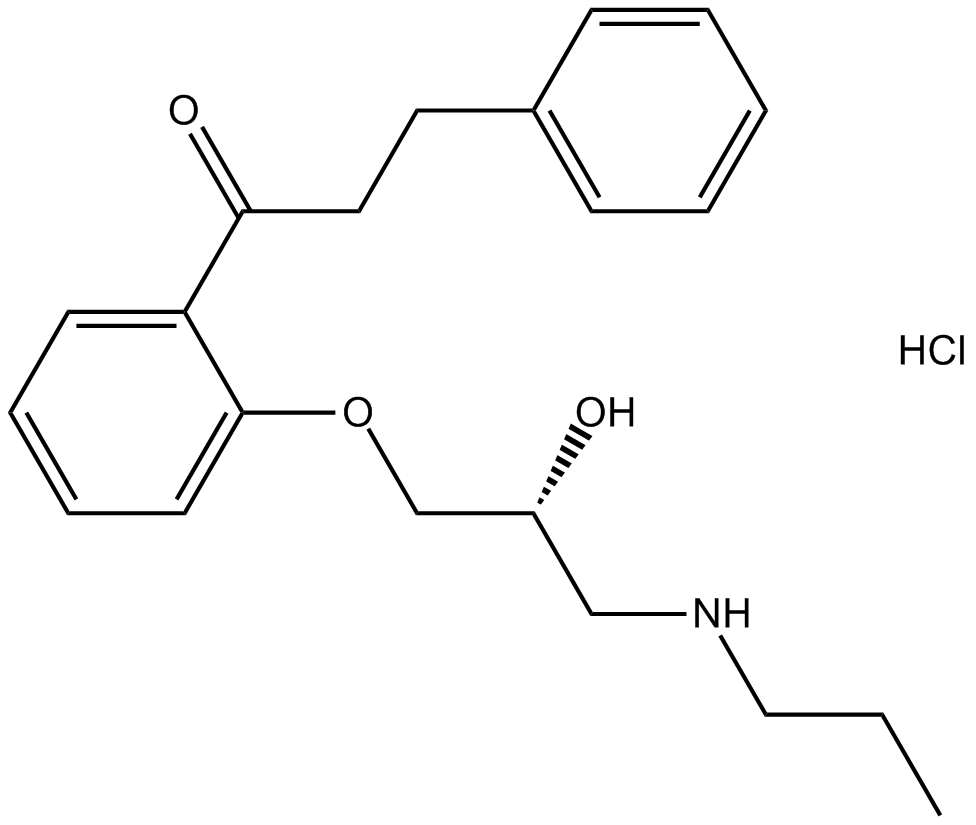 B2281 Propafenone HClSummary: classic anti-arrhythmic medication
B2281 Propafenone HClSummary: classic anti-arrhythmic medication -
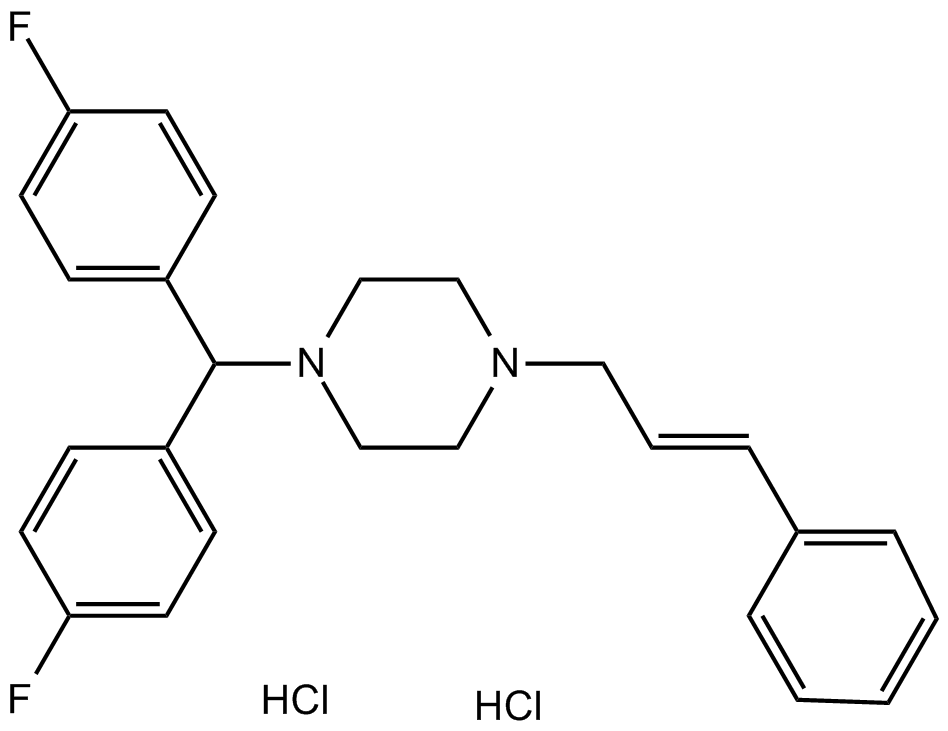 B1412 Flunarizine 2HClSummary: Calcium entry blocker
B1412 Flunarizine 2HClSummary: Calcium entry blocker -
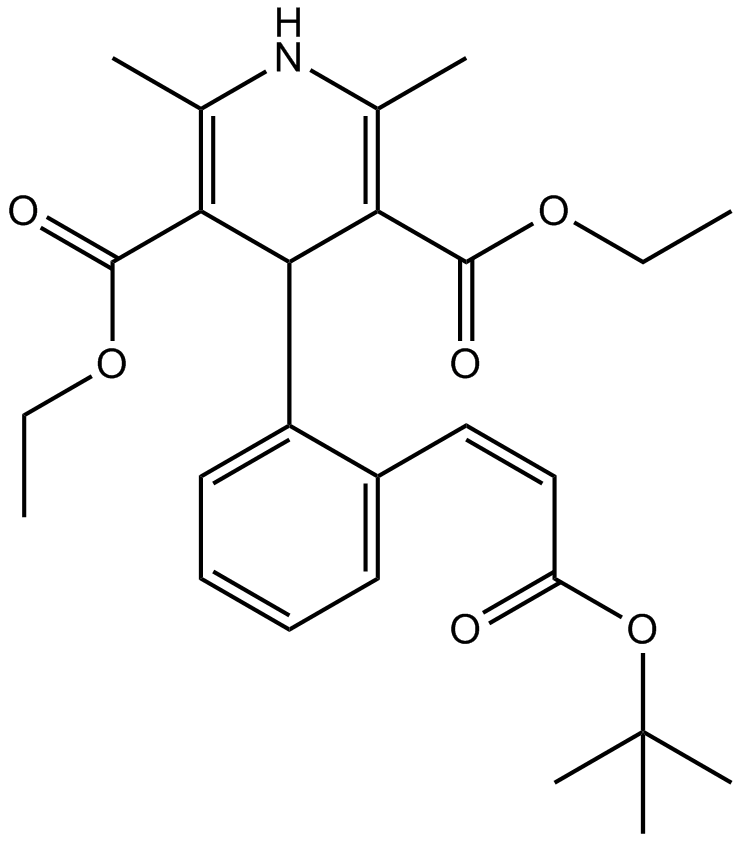 B1417 LacidipineSummary: L-type calcium channel blocker
B1417 LacidipineSummary: L-type calcium channel blocker -
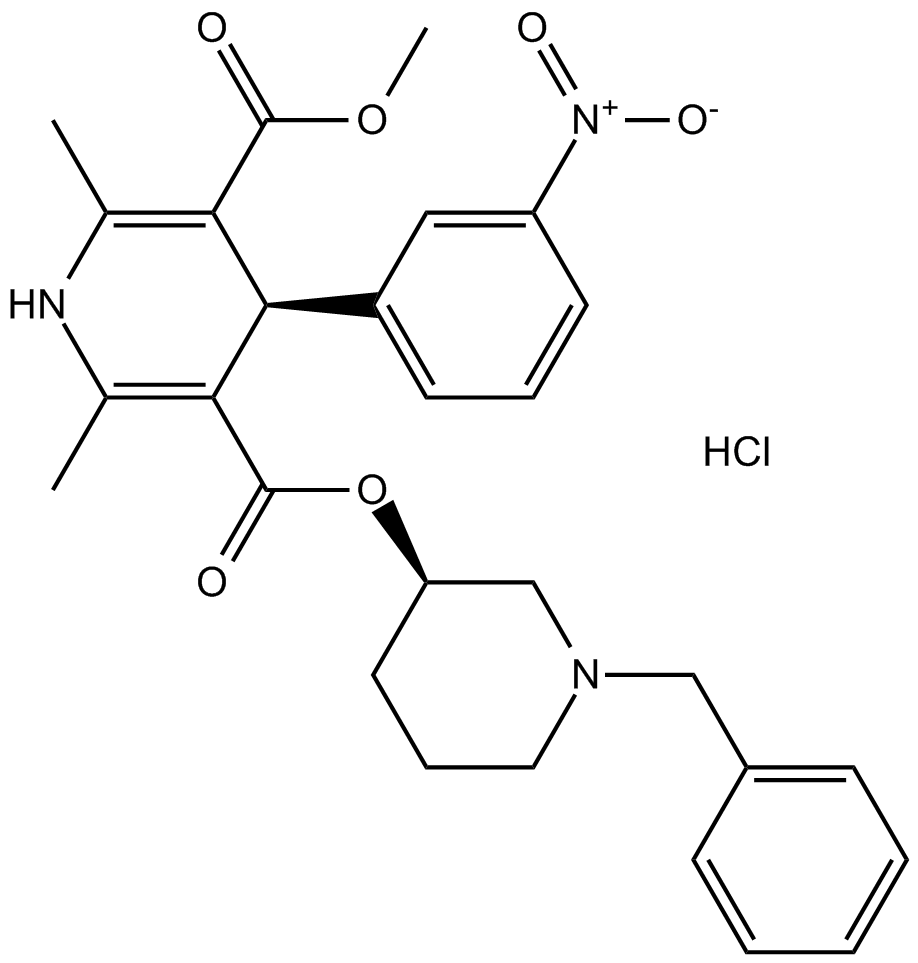 B1409 Benidipine HClSummary: Calcium channel blocker
B1409 Benidipine HClSummary: Calcium channel blocker -
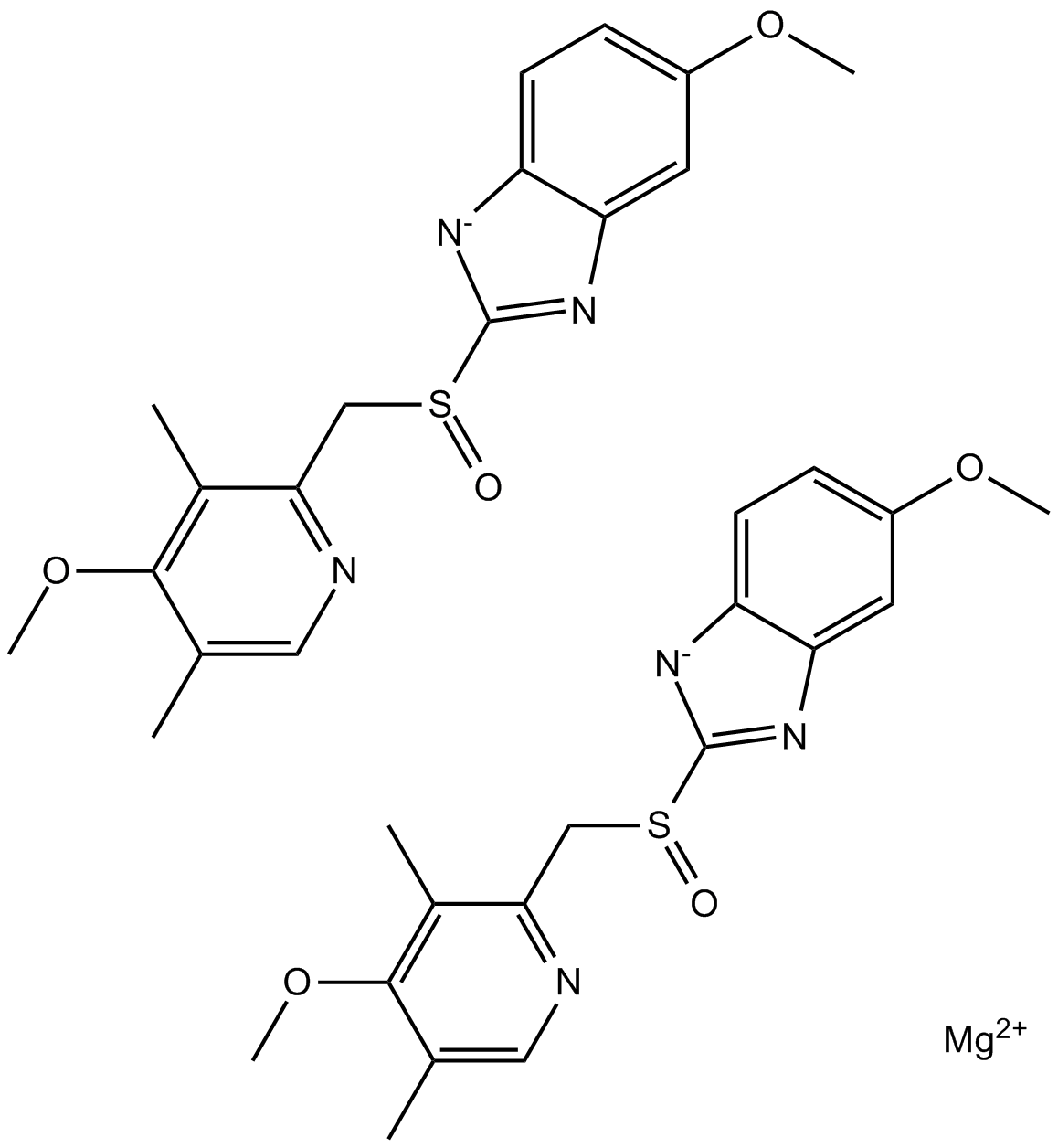 B2200 Esomeprazole MagnesiumSummary: Proton pump inhibitor
B2200 Esomeprazole MagnesiumSummary: Proton pump inhibitor -
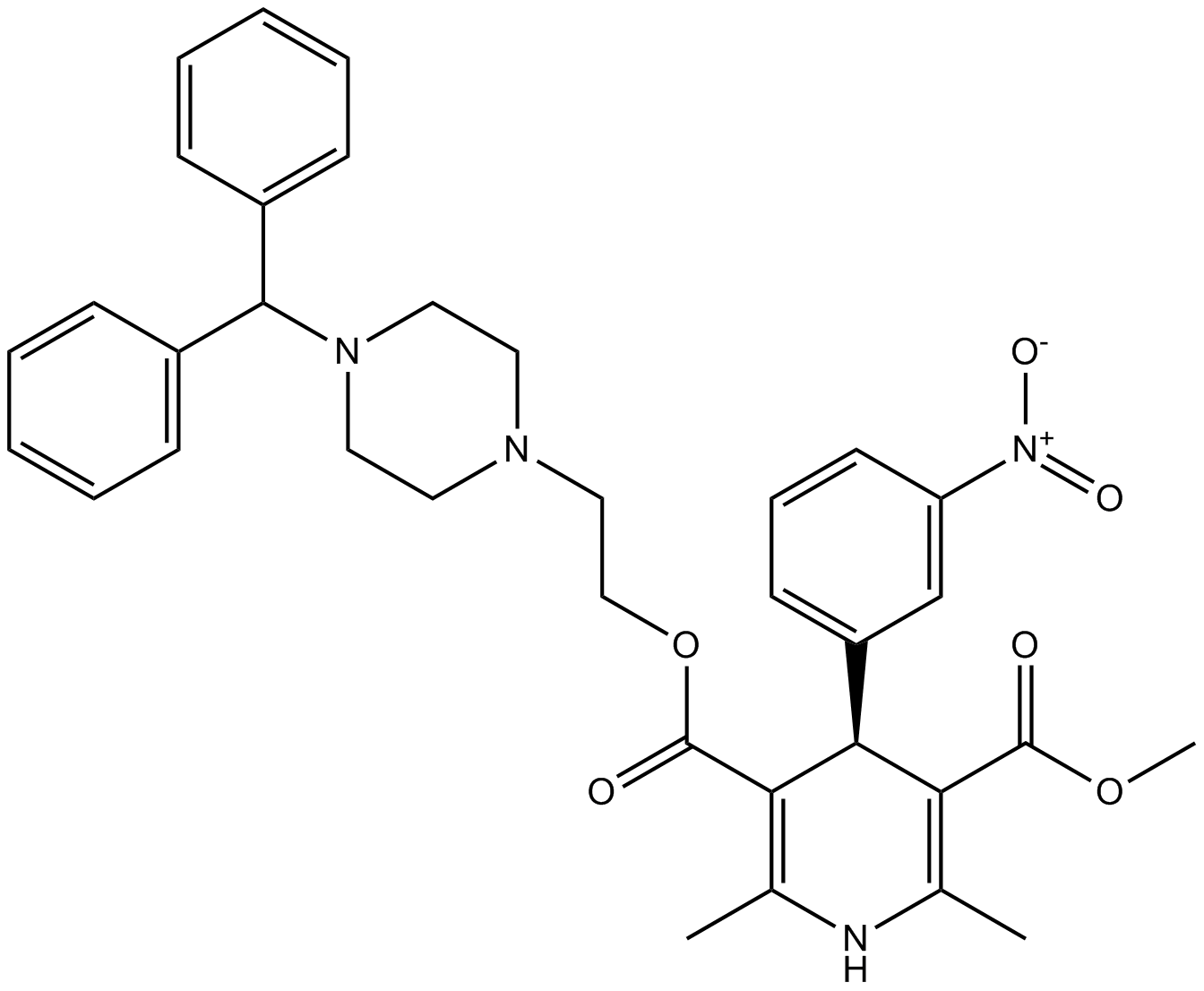 B1418 ManidipineSummary: Calcium channel blocker
B1418 ManidipineSummary: Calcium channel blocker

