Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
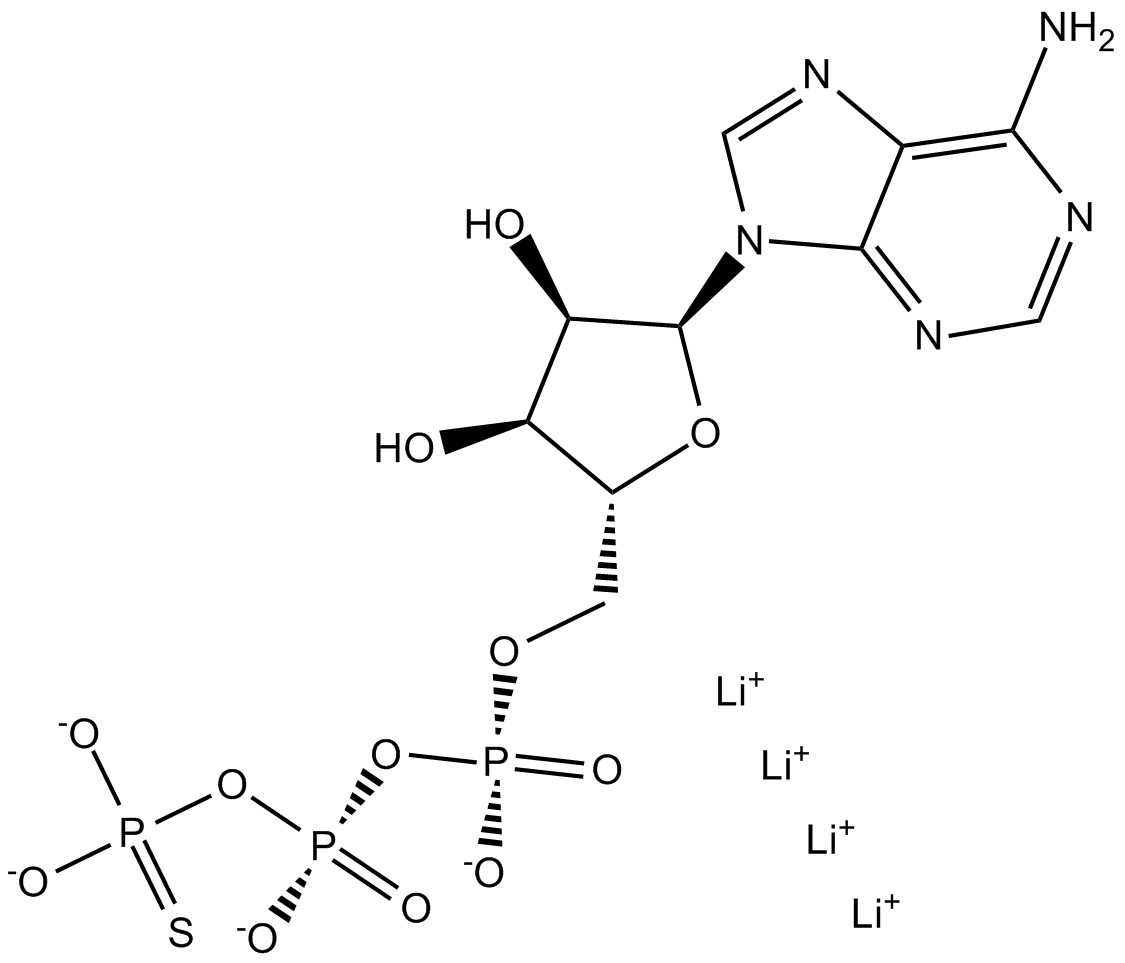 B7582 ATPγS tetralithium saltSummary: P2 purinergic receptor agonist
B7582 ATPγS tetralithium saltSummary: P2 purinergic receptor agonist -
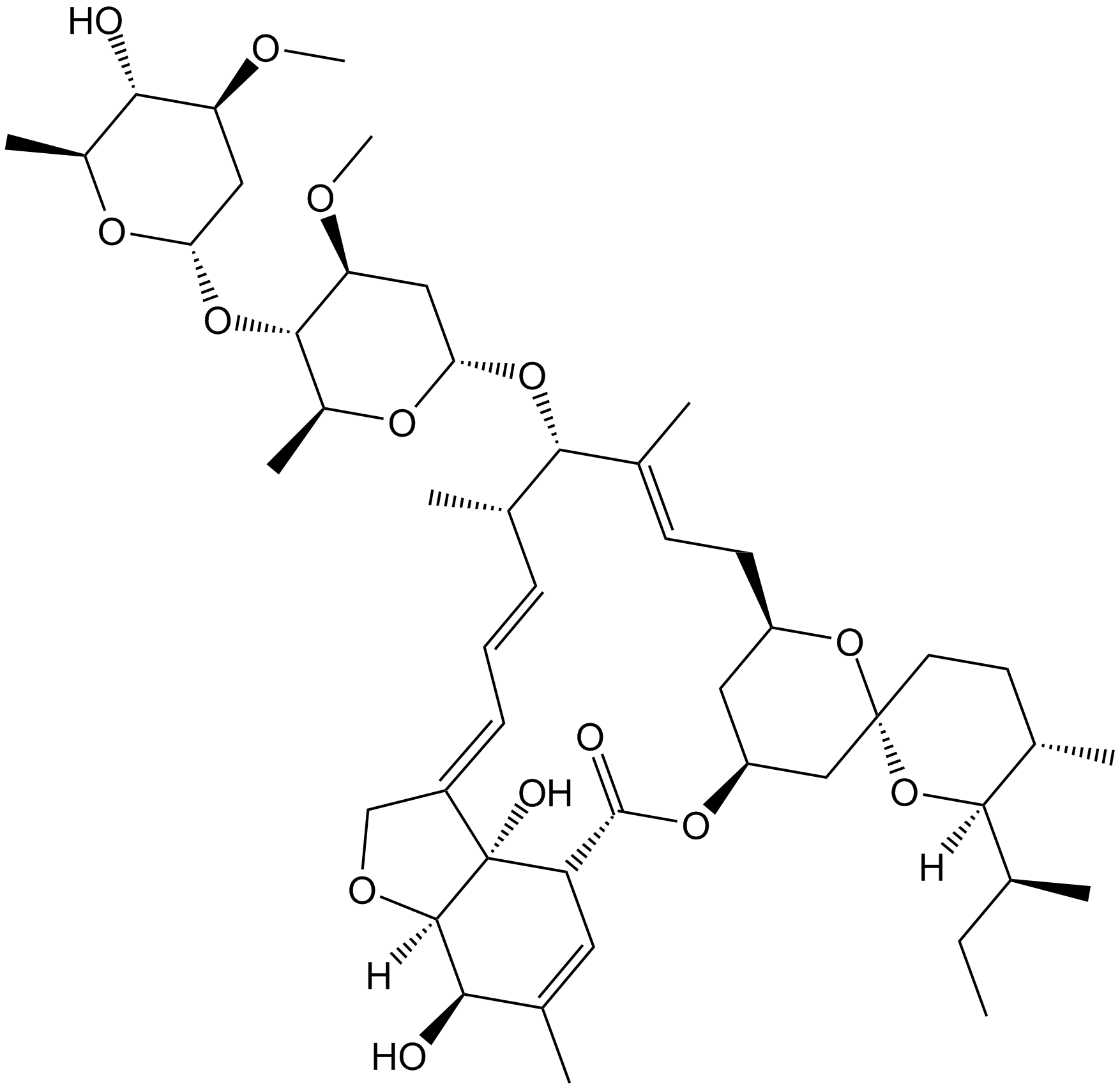 A2813 IvermectinSummary: NAChR/purinergic P2X4 receptor modulator
A2813 IvermectinSummary: NAChR/purinergic P2X4 receptor modulator -
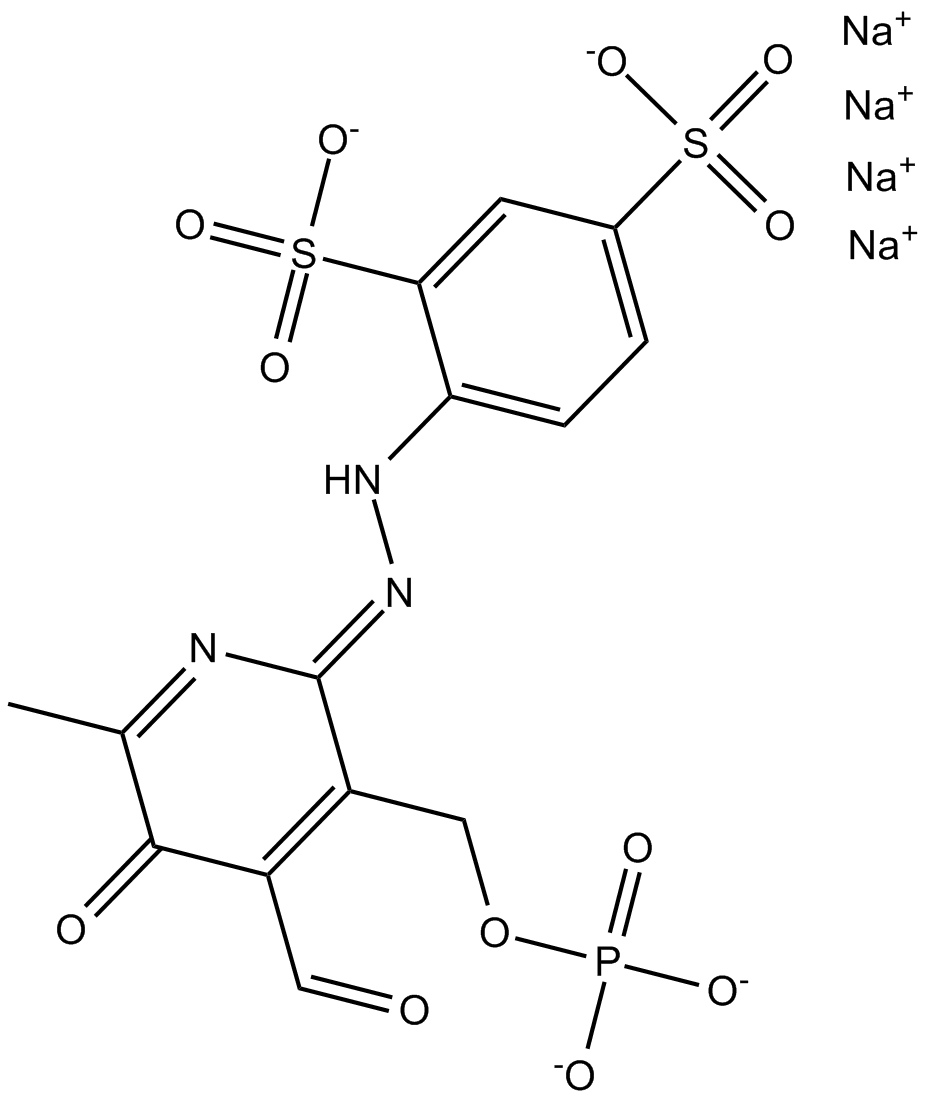 B6381 PPADS tetrasodium saltSummary: P2 purinergic antagonist
B6381 PPADS tetrasodium saltSummary: P2 purinergic antagonist -
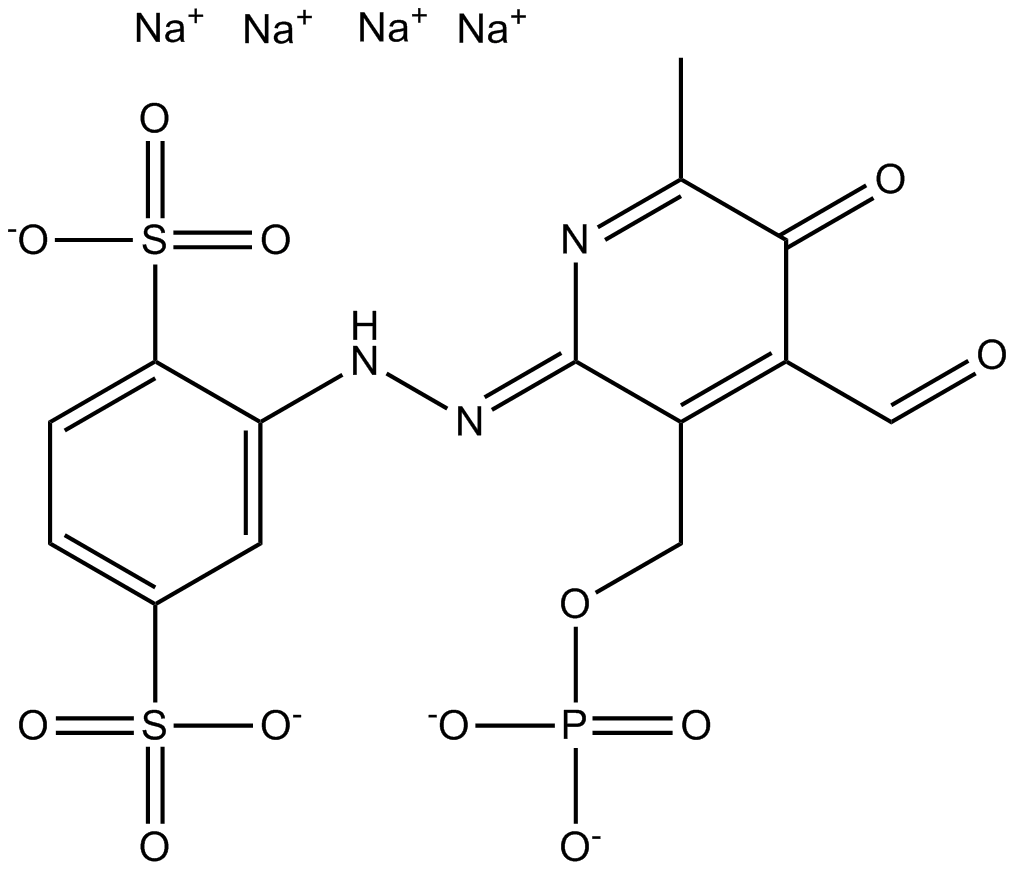 B6405 iso-PPADS tetrasodium saltSummary: P2 purinoceptors antagonist, specific
B6405 iso-PPADS tetrasodium saltSummary: P2 purinoceptors antagonist, specific -
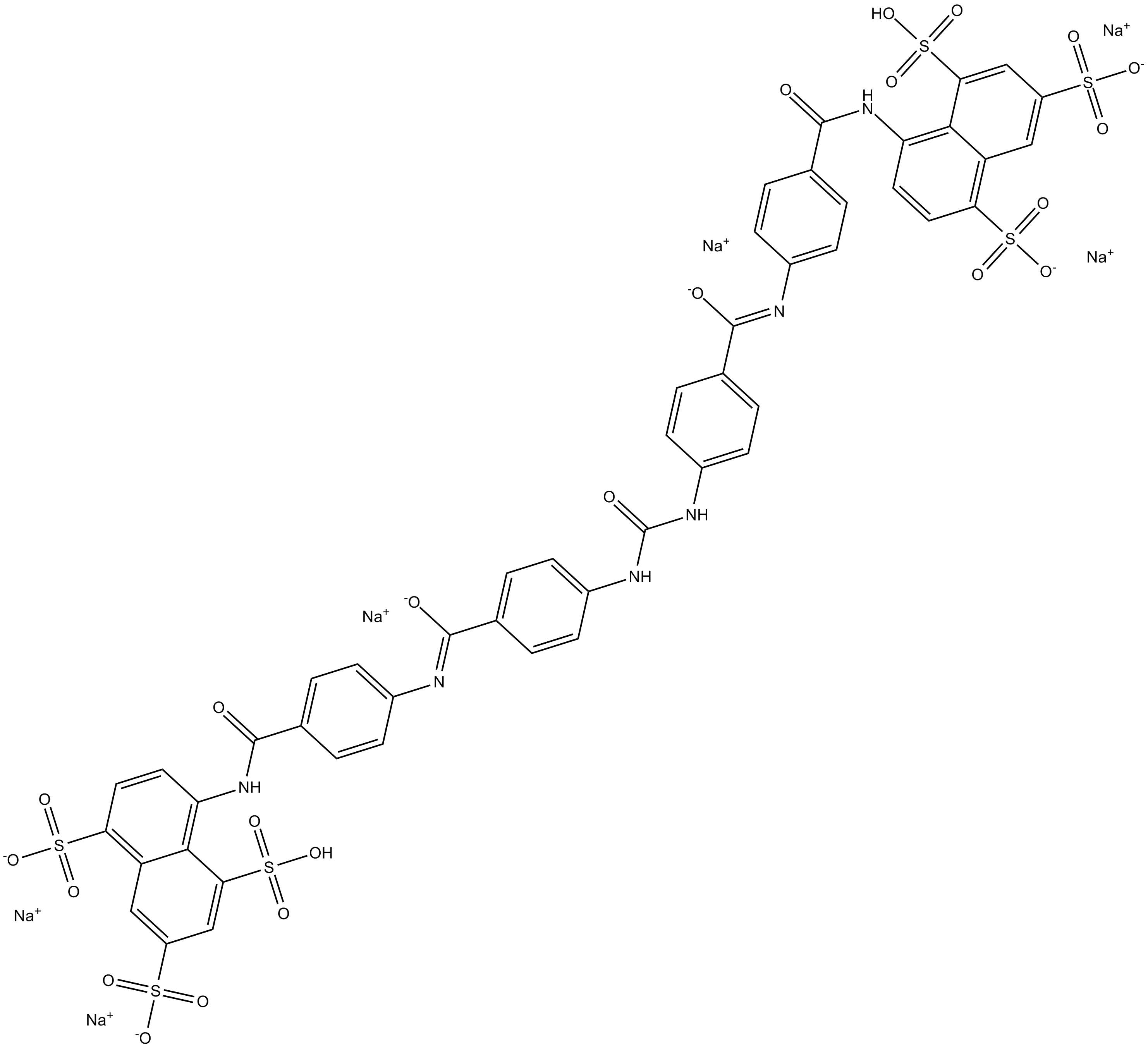 B6629 NF 279Summary: P2X1 antagonist
B6629 NF 279Summary: P2X1 antagonist -
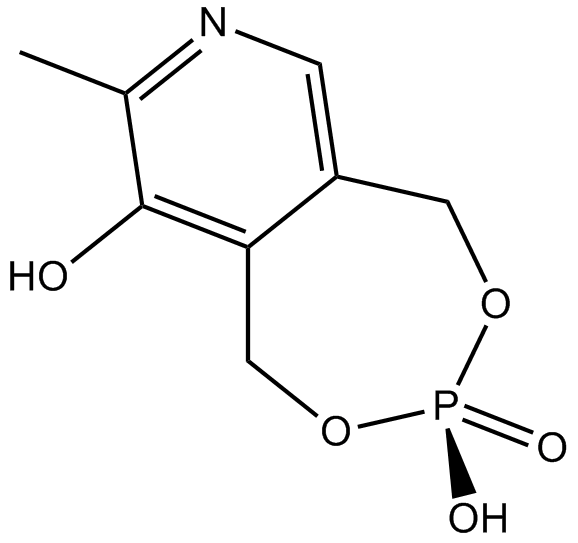 B6631 MRS 2219Summary: P2X1 receptor potentiator
B6631 MRS 2219Summary: P2X1 receptor potentiator -
 B6651 NF 023Summary: P2X1 receptor antagonist
B6651 NF 023Summary: P2X1 receptor antagonist -
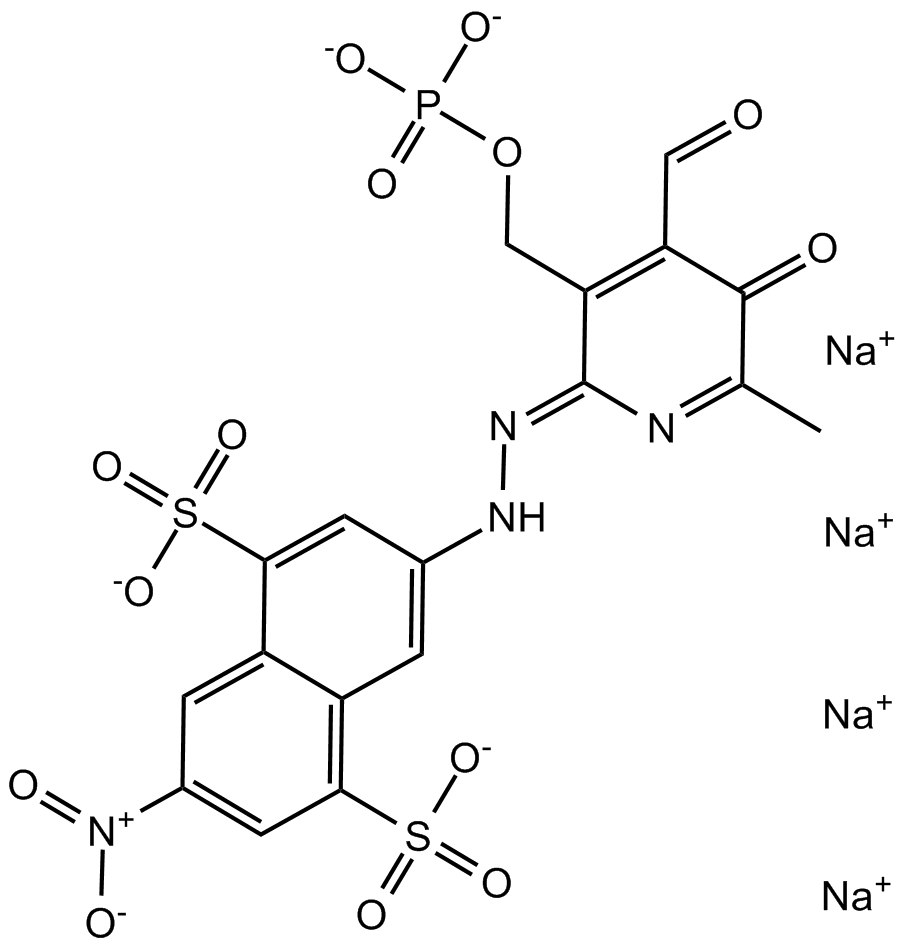 B6682 PPNDSSummary: P2X1 receptor antagonist
B6682 PPNDSSummary: P2X1 receptor antagonist -
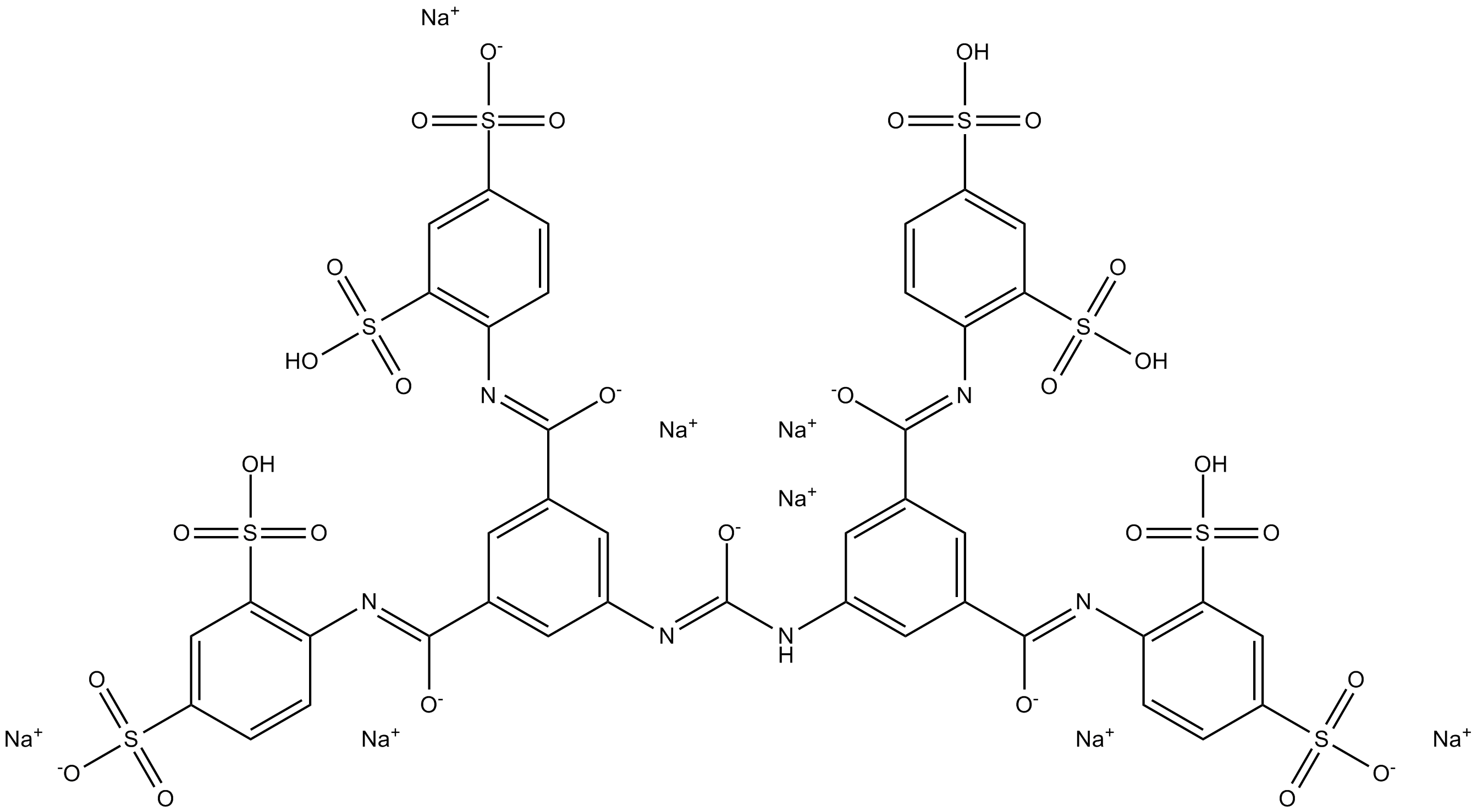 B6716 NF 449Summary: purinergic receptor antagonist
B6716 NF 449Summary: purinergic receptor antagonist -
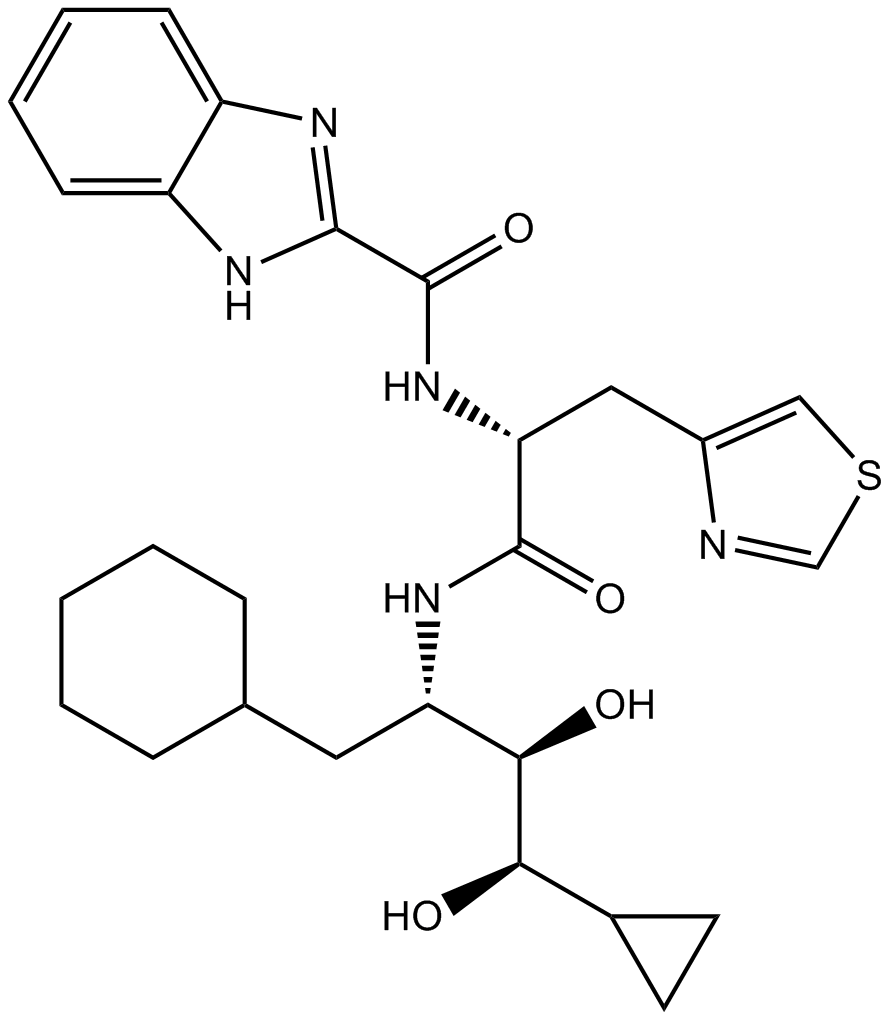 B6964 Ro 0437626Summary: P2X1 purinergic receptor antagonist
B6964 Ro 0437626Summary: P2X1 purinergic receptor antagonist

