MAPK Signaling

Activated MAPKs transduce the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs), e.g. RSK, MSK, or MNK family, and MK2/3/5. There are three main MAPK families, signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (Erk1/2 or p44/42), the c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1-3 (JNK1-3)/ stress activated protein kinases (SAPK1A, 1B, 1C), the p38 isoforms (p38α, β, γ, and δ). ERK signaling is involved in cell division, migration and survival. p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK pathways are activated by cellular stress. The p38 MAPK pathway regulates cell motility, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. JNK/SAPK signaling affects apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MAPK pathway results in tumorgenesis and other pathological conditions.
-
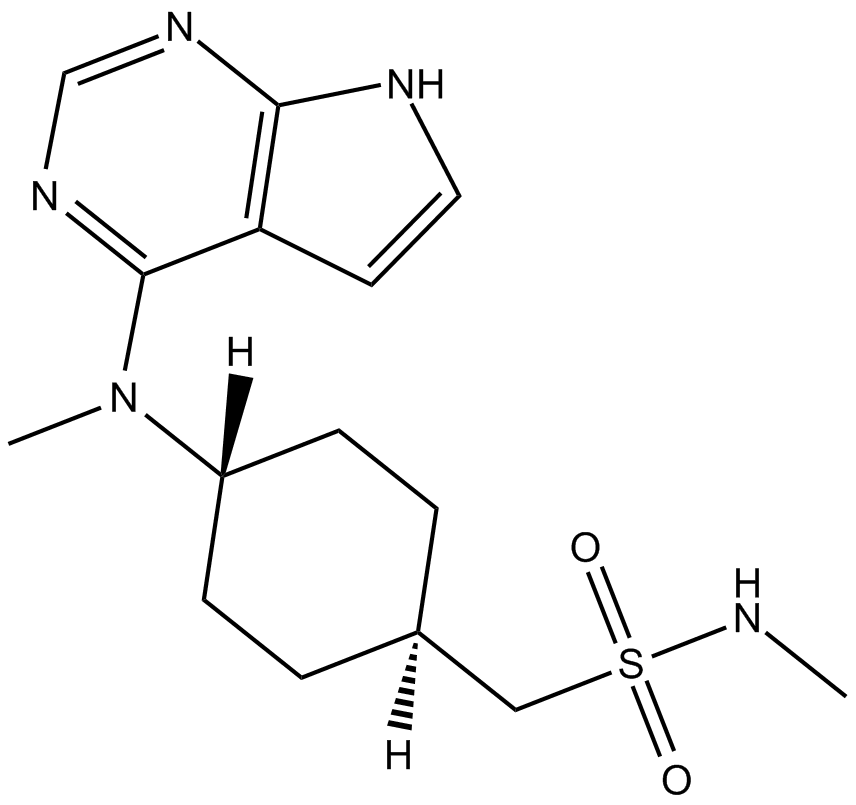 B5960 PF-03394197(Oclacitinib)Summary: Novel Janus kinase inhibitor
B5960 PF-03394197(Oclacitinib)Summary: Novel Janus kinase inhibitor -
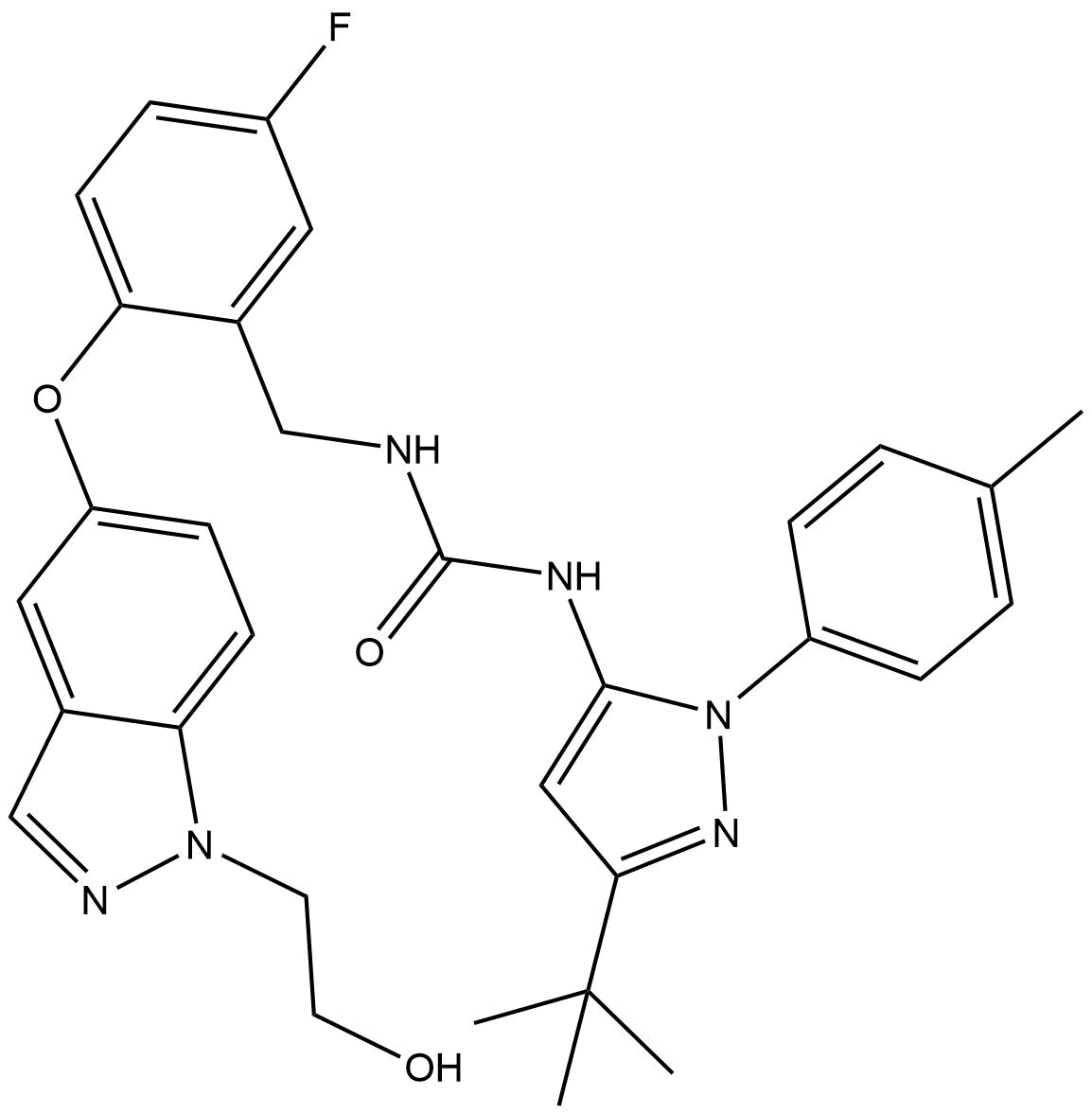 B6012 Pexmetinib (ARRY-614)Target: p38|Tie-2Summary: dual inhibitor of p38 MAPK and Tie2/Tek receptor tyrosine kinase
B6012 Pexmetinib (ARRY-614)Target: p38|Tie-2Summary: dual inhibitor of p38 MAPK and Tie2/Tek receptor tyrosine kinase -
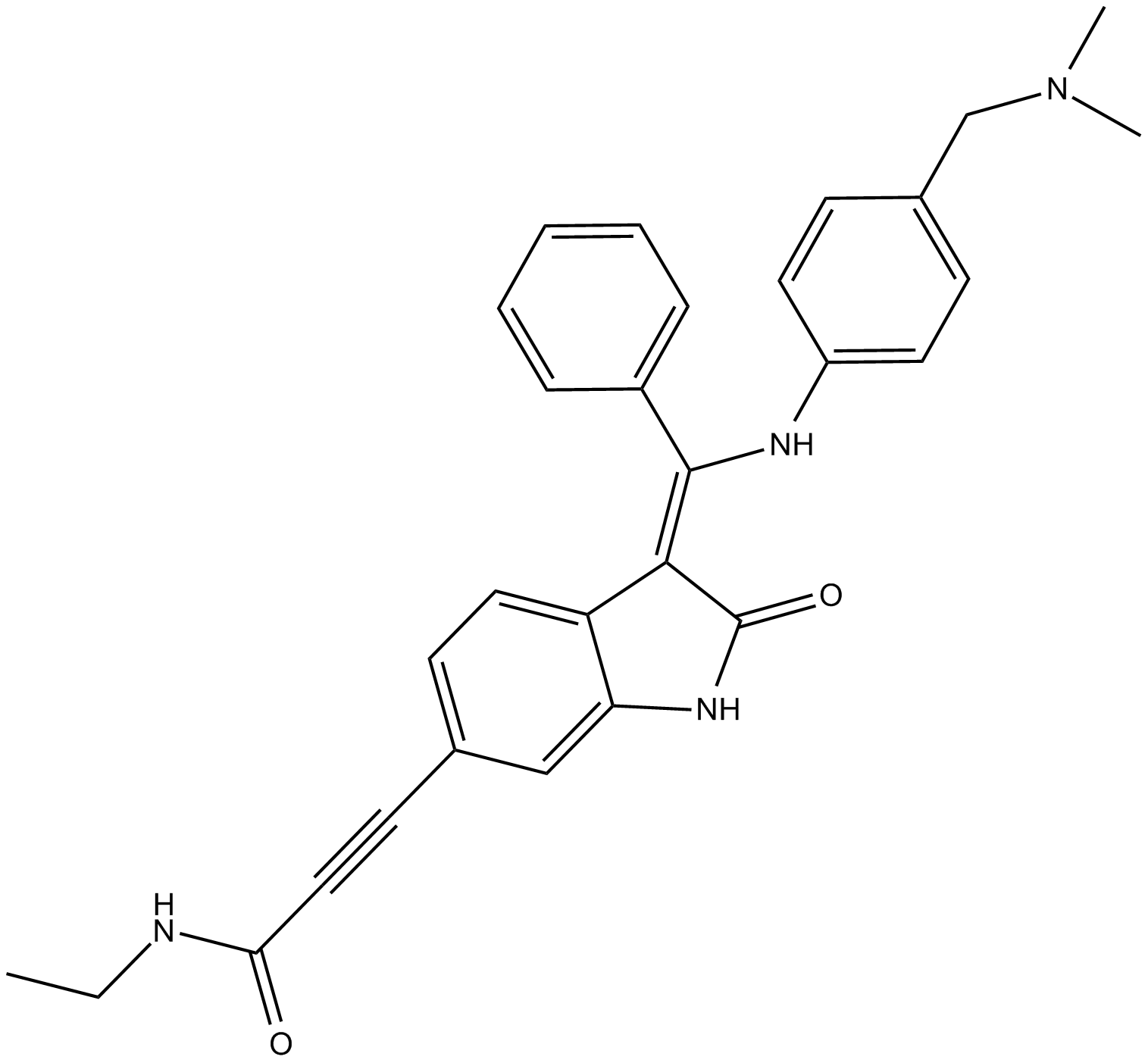 B6014 BI-847325Summary: dual inhibitor of MEK and Aurora kinases
B6014 BI-847325Summary: dual inhibitor of MEK and Aurora kinases -
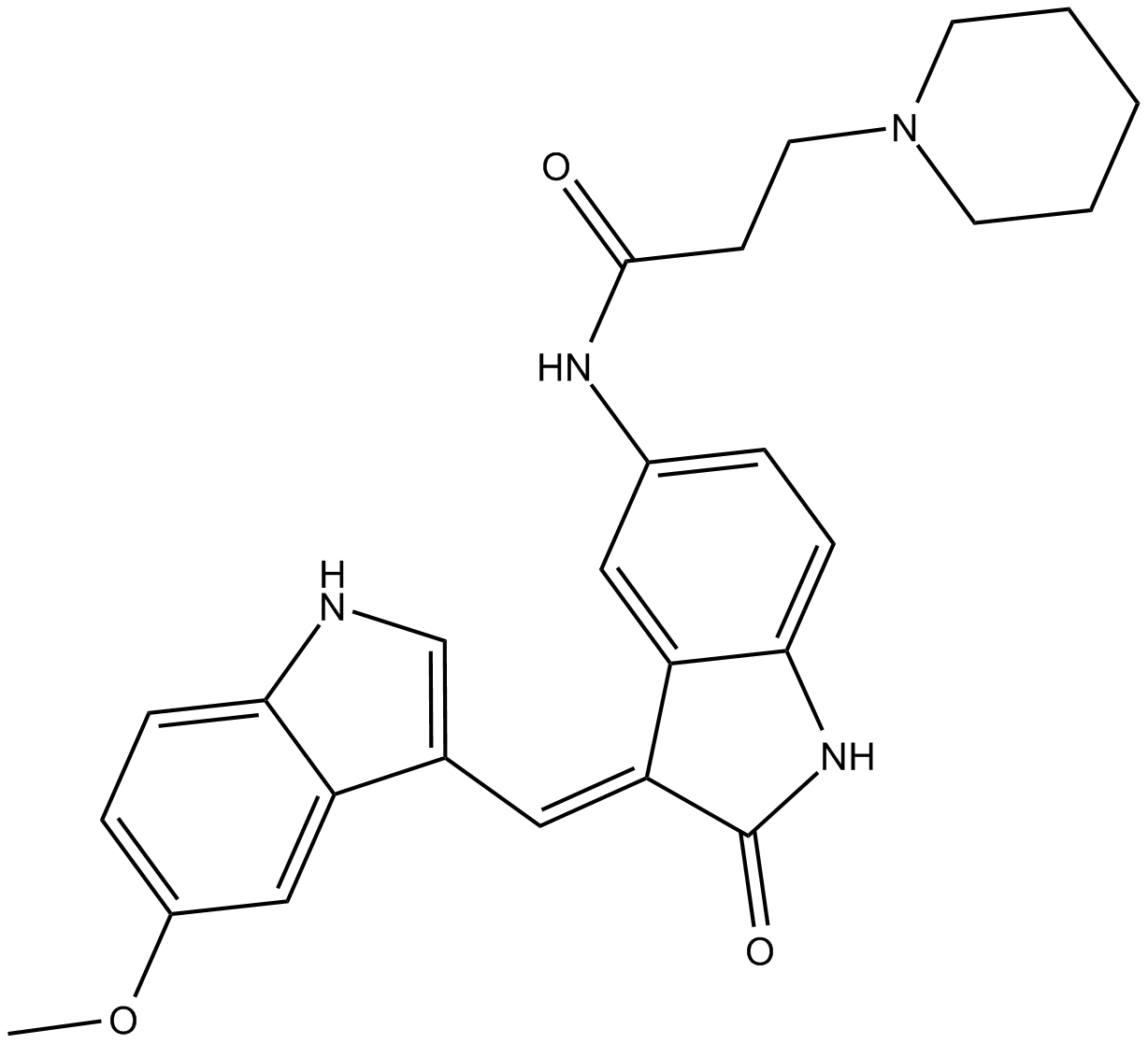 B6024 DEL-22379Summary: inhibitor of the dimerization of ERK
B6024 DEL-22379Summary: inhibitor of the dimerization of ERK -
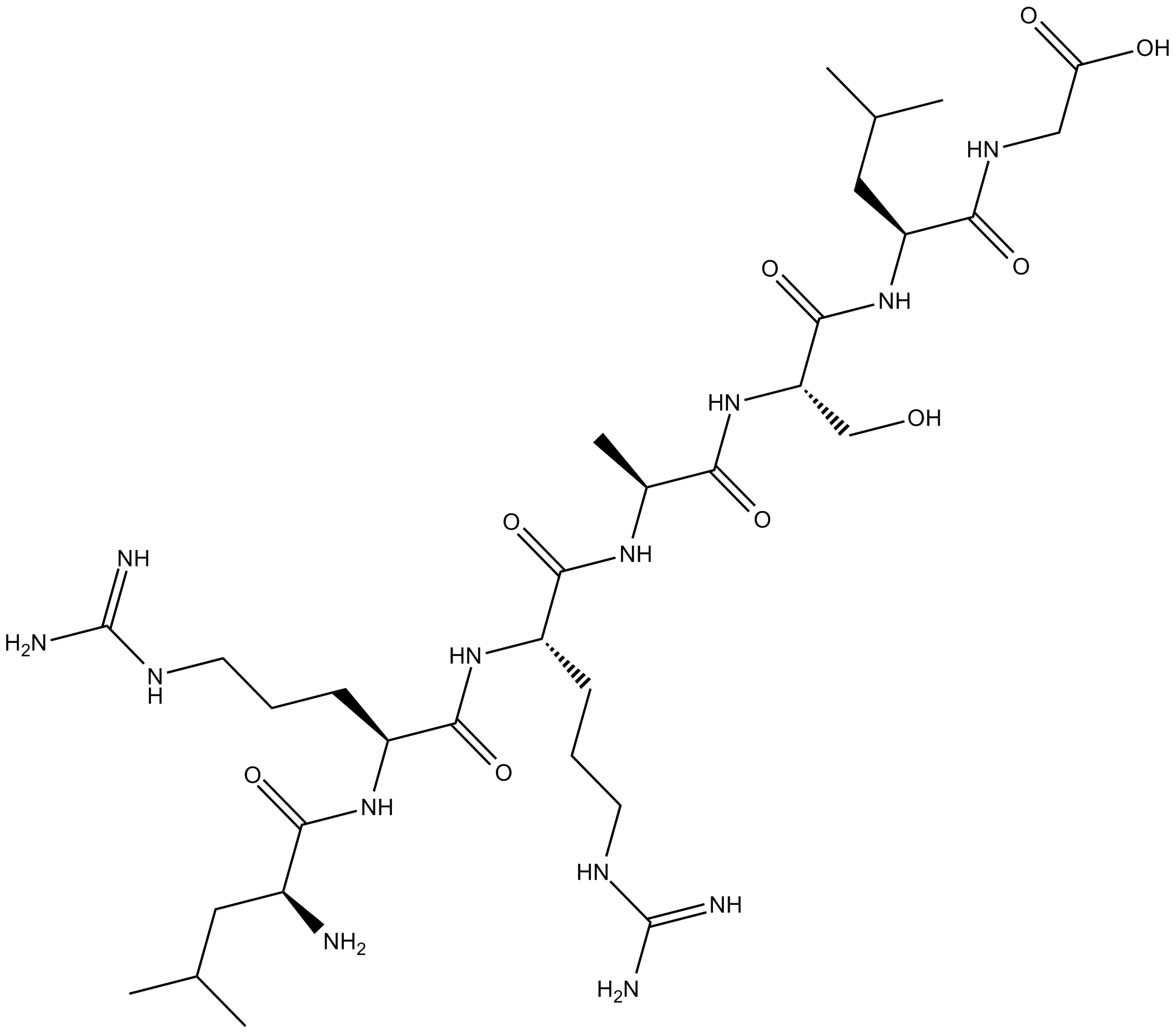 C4308 KemptideSummary: substrate for cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)
C4308 KemptideSummary: substrate for cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) -
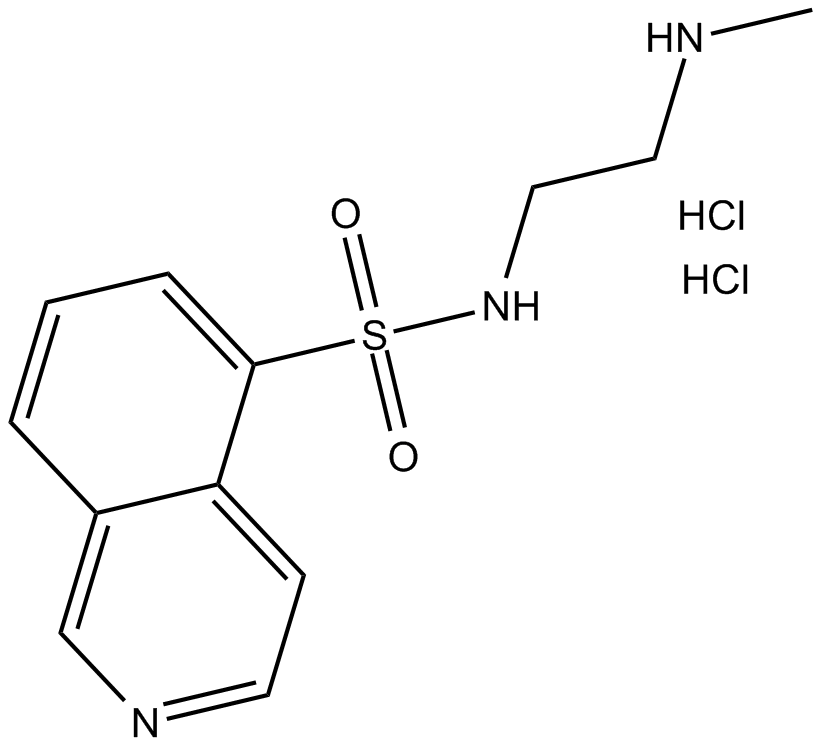 C4683 H-8 (hydrochloride)Summary: potent inhibitor of PKA and PKG
C4683 H-8 (hydrochloride)Summary: potent inhibitor of PKA and PKG -
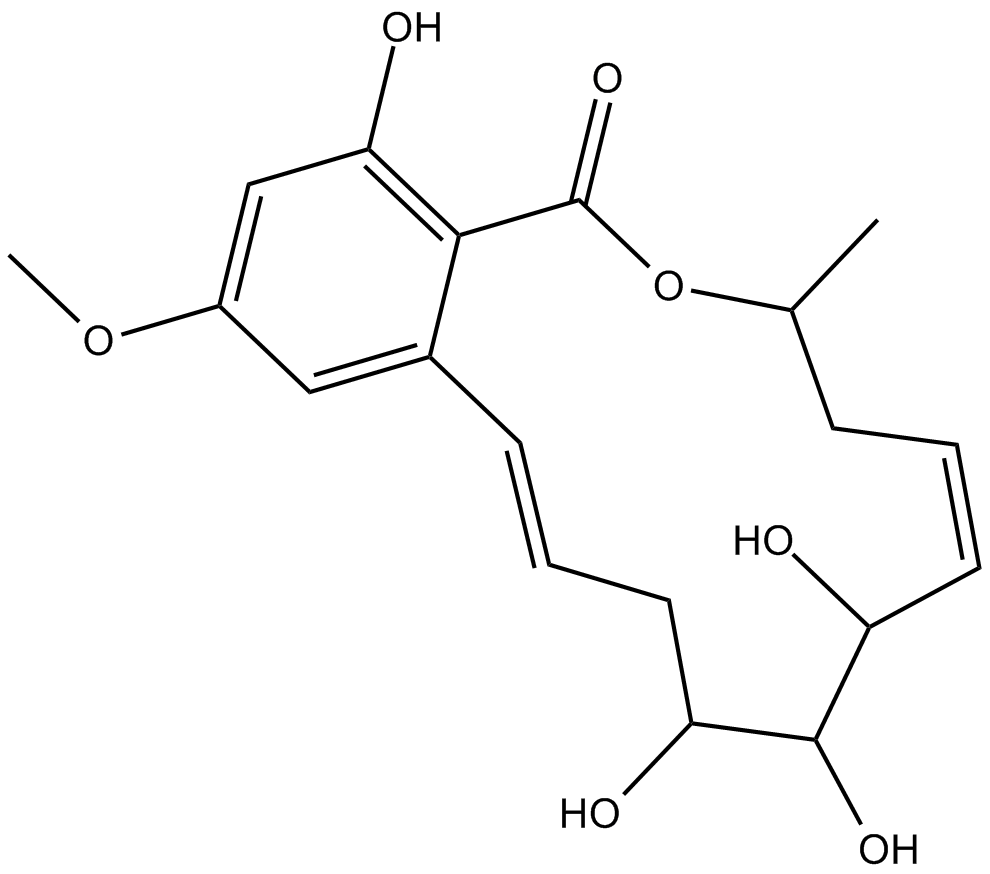 C5106 LL-Z 1640-4Summary: A signal-specific JNK/p38 pathway and TAK 1 inhibitor
C5106 LL-Z 1640-4Summary: A signal-specific JNK/p38 pathway and TAK 1 inhibitor -
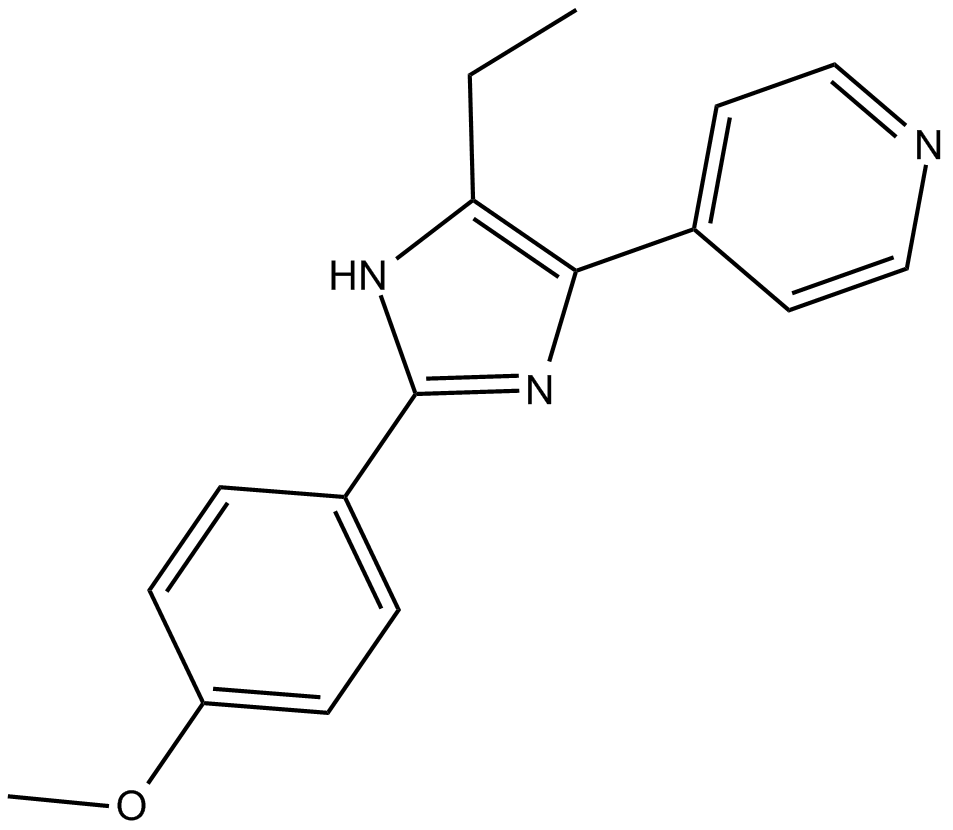 C4949 SB 202474Summary: a negative control in studies of p38 inhibition
C4949 SB 202474Summary: a negative control in studies of p38 inhibition -
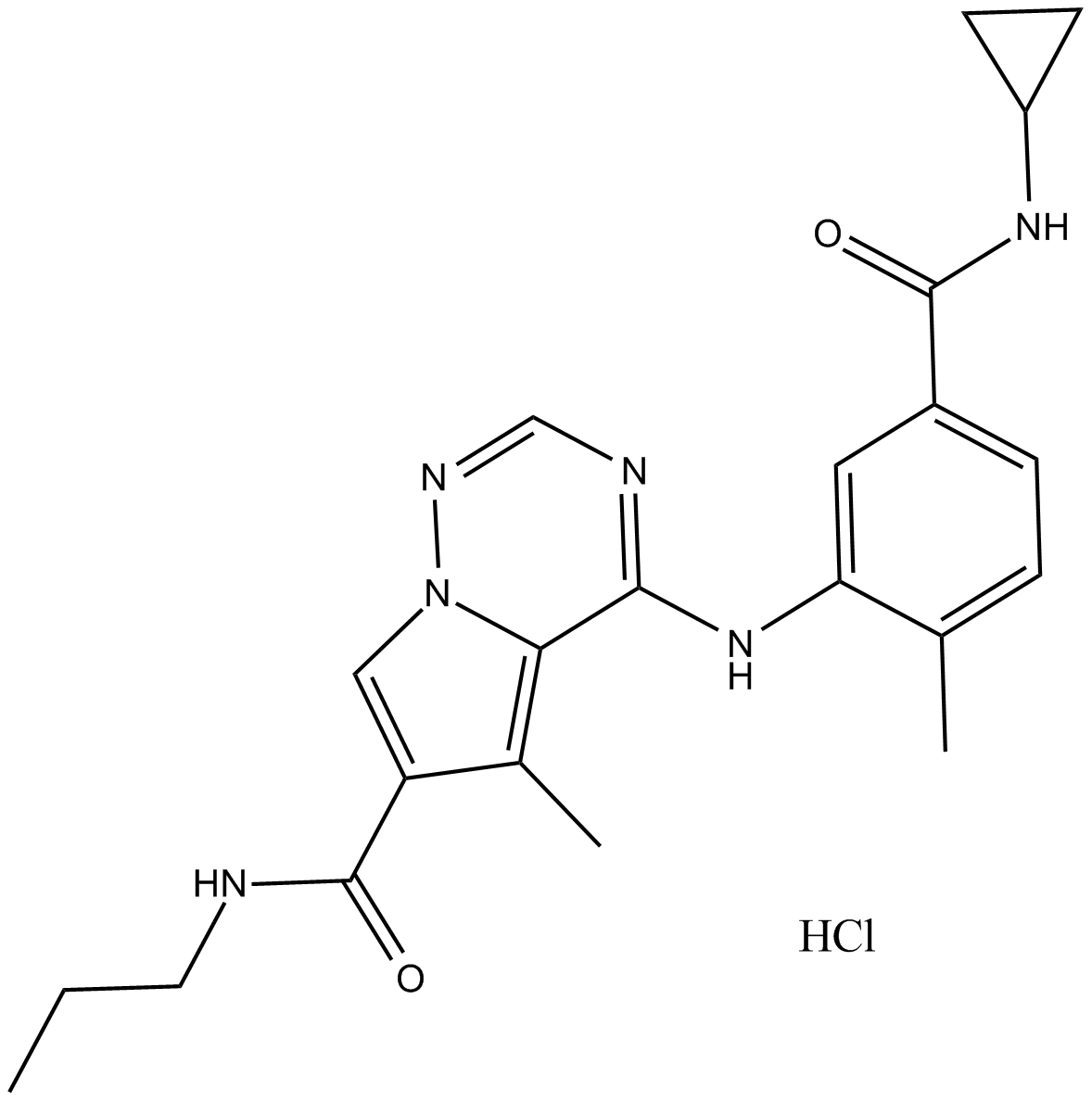 B7850 BMS-582949 hydrochlorideSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor
B7850 BMS-582949 hydrochlorideSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor -
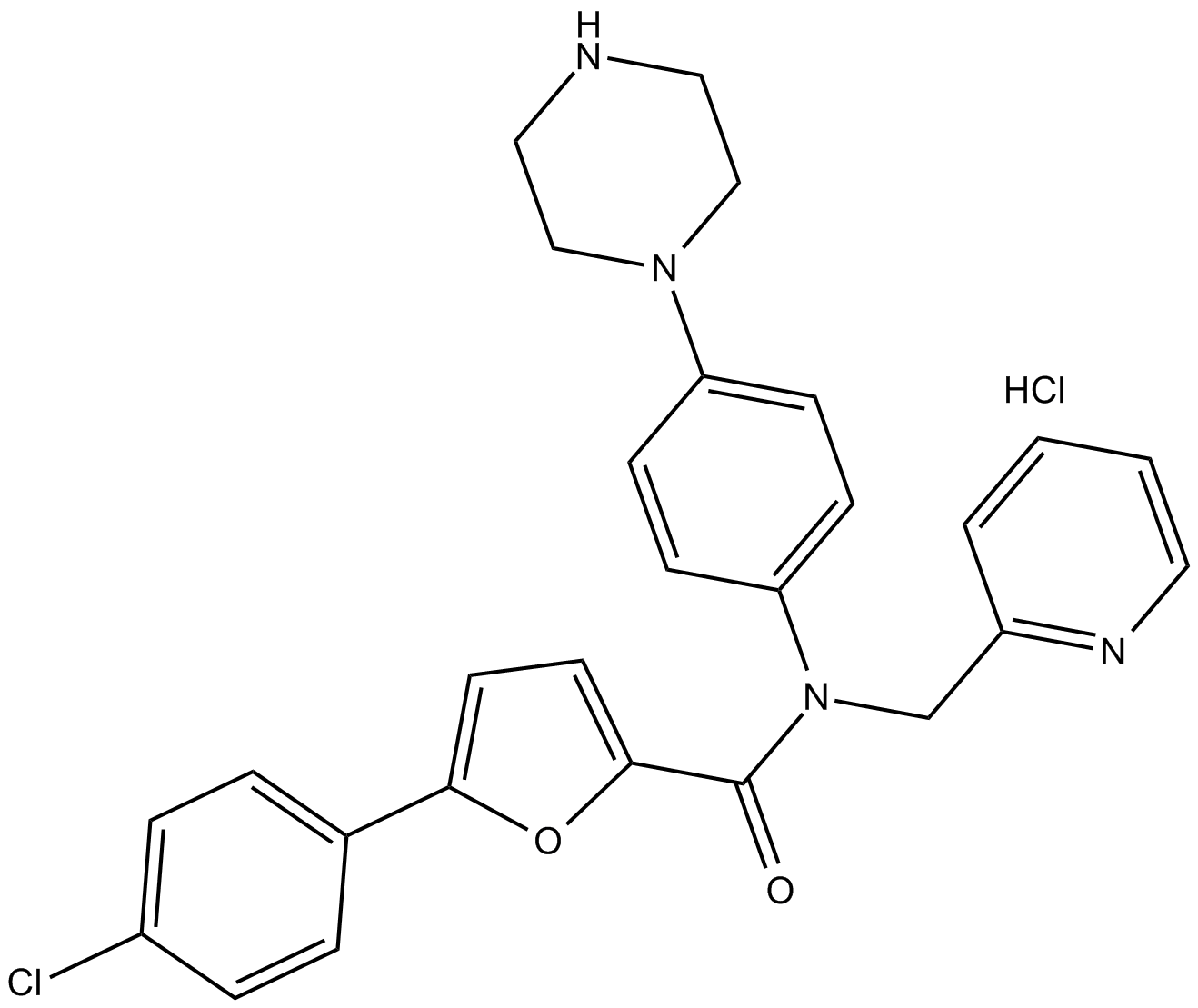 C5545 MK2 Inhibitor IVTarget: MK2Summary: highly selective, non-ATP competitive MK2 inhibitor
C5545 MK2 Inhibitor IVTarget: MK2Summary: highly selective, non-ATP competitive MK2 inhibitor

