GPCR/G protein
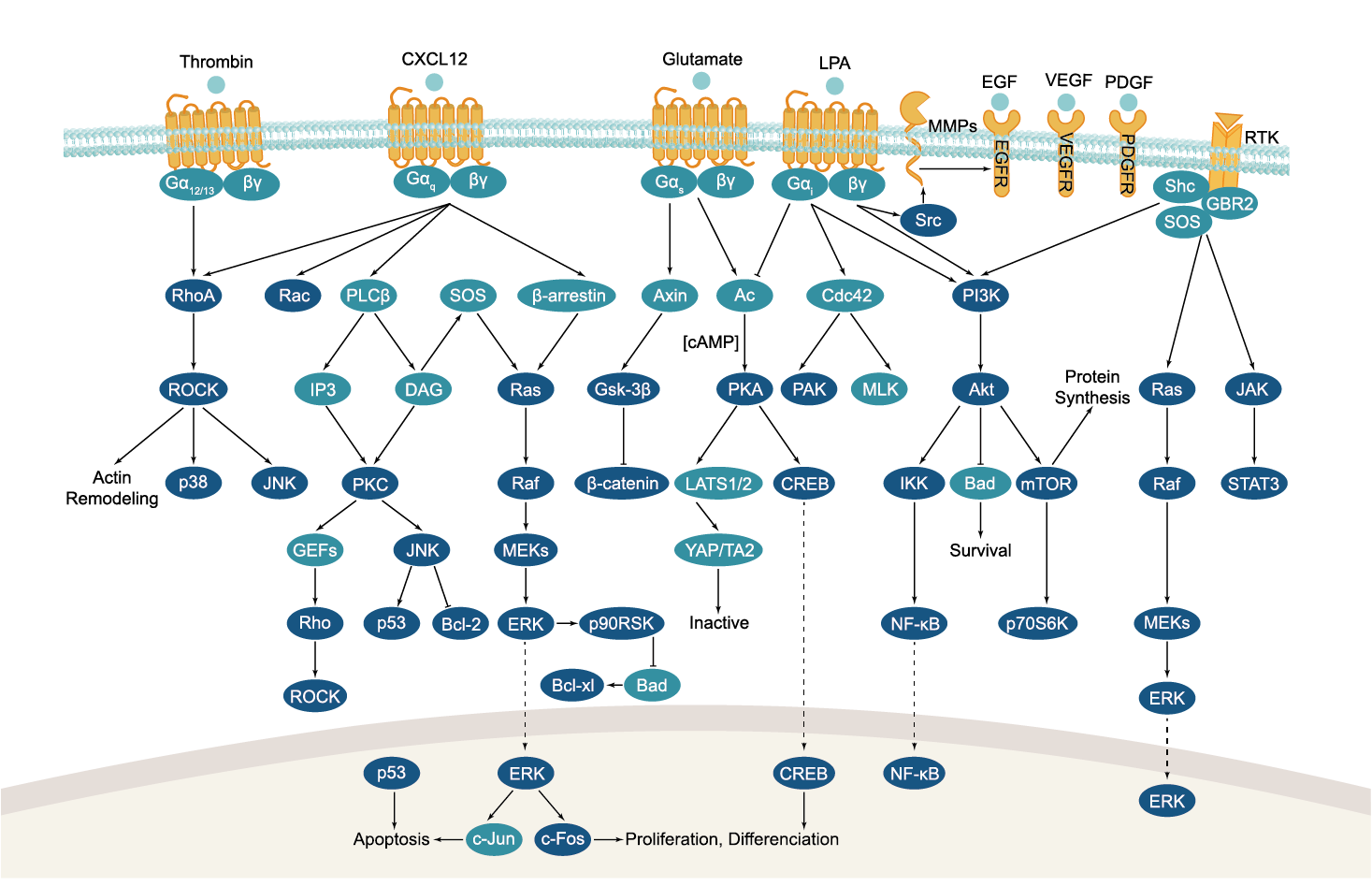
All GPCRs share a common seven trans-membrane structure. GPCRs are associated with heterotrimeric G-proteins which are GTP-binding proteins made of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. When a ligand binds to GPCR, it activates the attached G-protein, the GDP is replaced with GTP. The activated G-protein then dissociates into an alpha and a beta-gamma complex which activates downstream signaling pathways. These intracellular signaling pathways include cAMP/PKA, calcium/NFAT, phospholipase C, protein tyrosine kinases, MAP kinases, PI-3-kinase, nitric oxide/cGMP, Rho, and JAK/STAT.
GPCRs are one of the most important therapeutic targets for various diseases, over 30% of all modern medicinal drugs target this family. Aberrant GPCR functions are involved in pathological conditions such as neurological, immunological and hormonal disorders. A large number of GPCRs have been identified, but whose ligands are not known, are classified as orphan receptors.
-
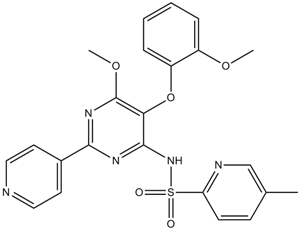 A3208 AvosentanSummary: ETA receptor antagonist
A3208 AvosentanSummary: ETA receptor antagonist -
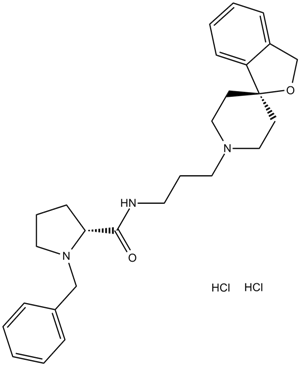 A3219 BAN ORL 24Summary: NOP receptor antagonist, potent and selective
A3219 BAN ORL 24Summary: NOP receptor antagonist, potent and selective -
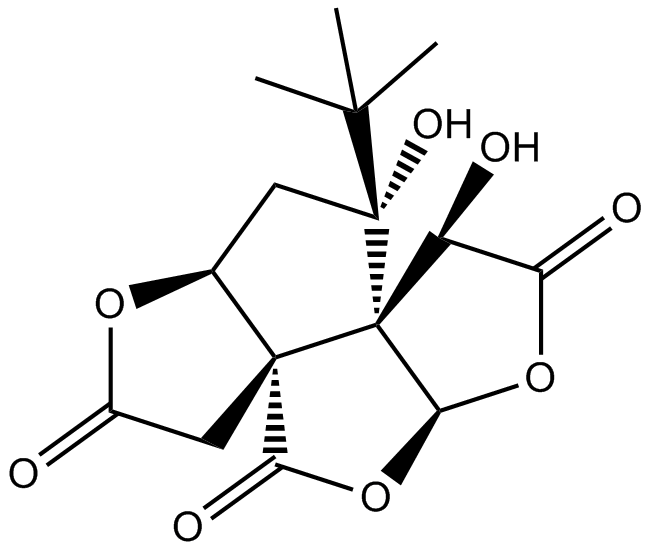 A3241 BilobalideSummary: Neuroprotective agent
A3241 BilobalideSummary: Neuroprotective agent -
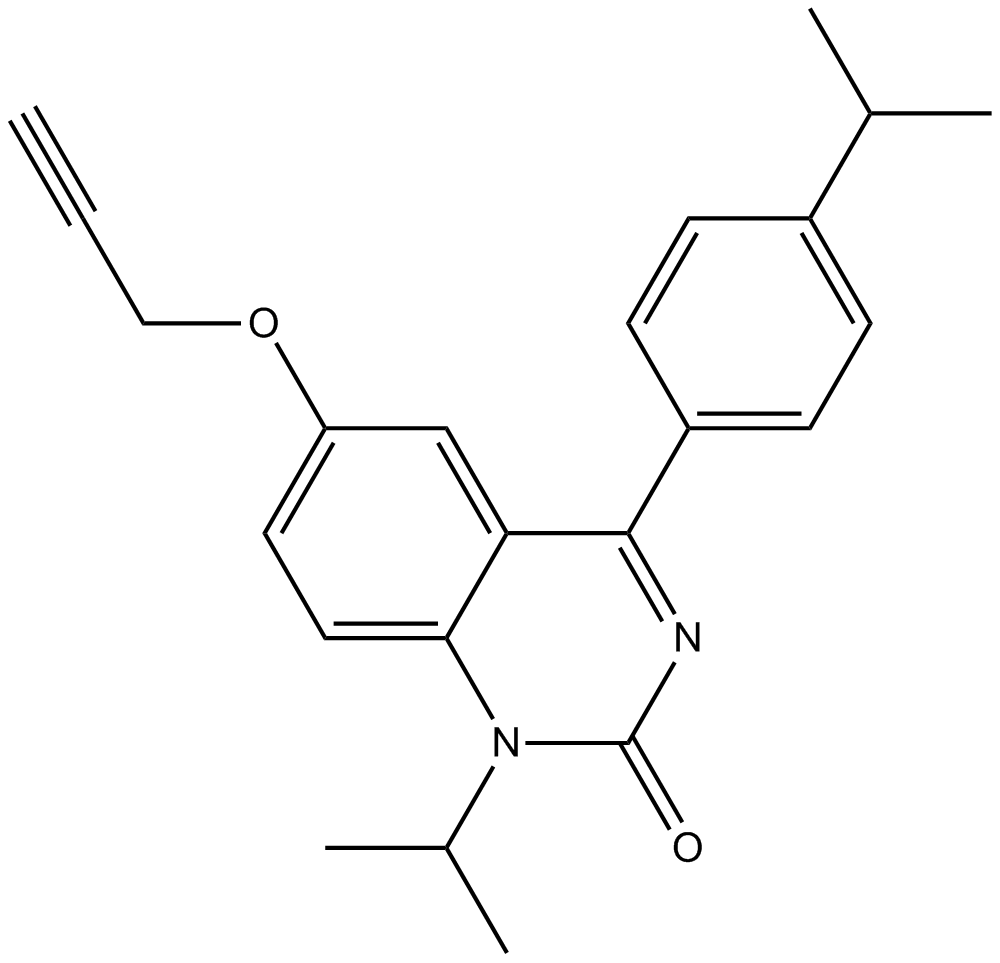 A3275 Calcium-Sensing Receptor Antagonists ISummary: CaSR antagonist
A3275 Calcium-Sensing Receptor Antagonists ISummary: CaSR antagonist -
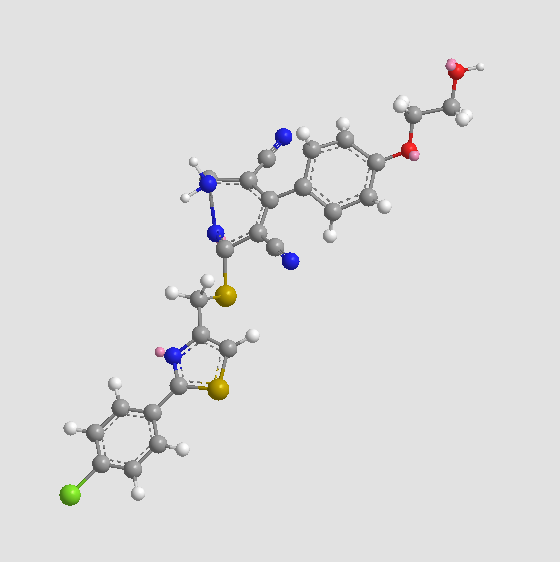 A3277 CapadenosonSummary: Adenosine A1 receptor agonist
A3277 CapadenosonSummary: Adenosine A1 receptor agonist -
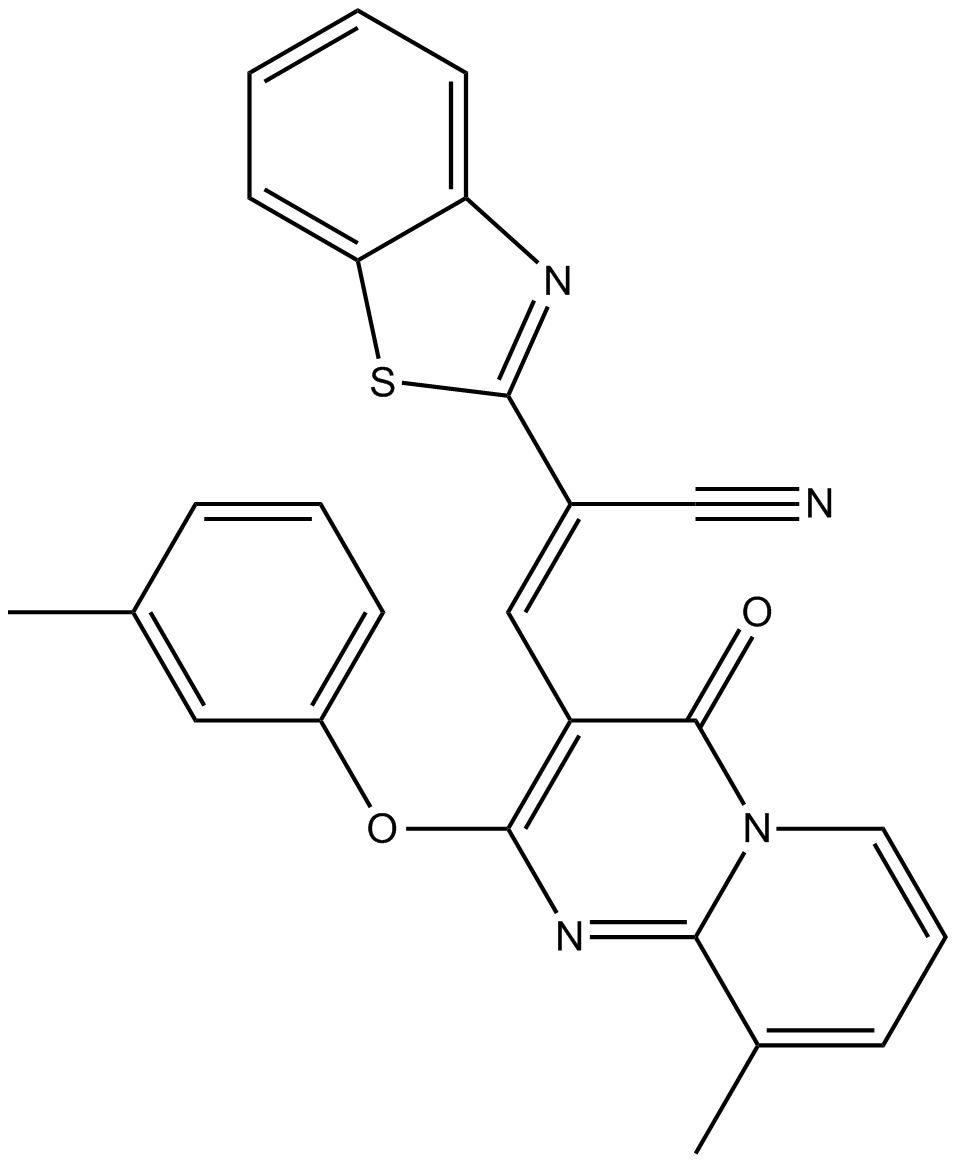 A3289 CCG-63802Summary: RGS protein inhibitor
A3289 CCG-63802Summary: RGS protein inhibitor -
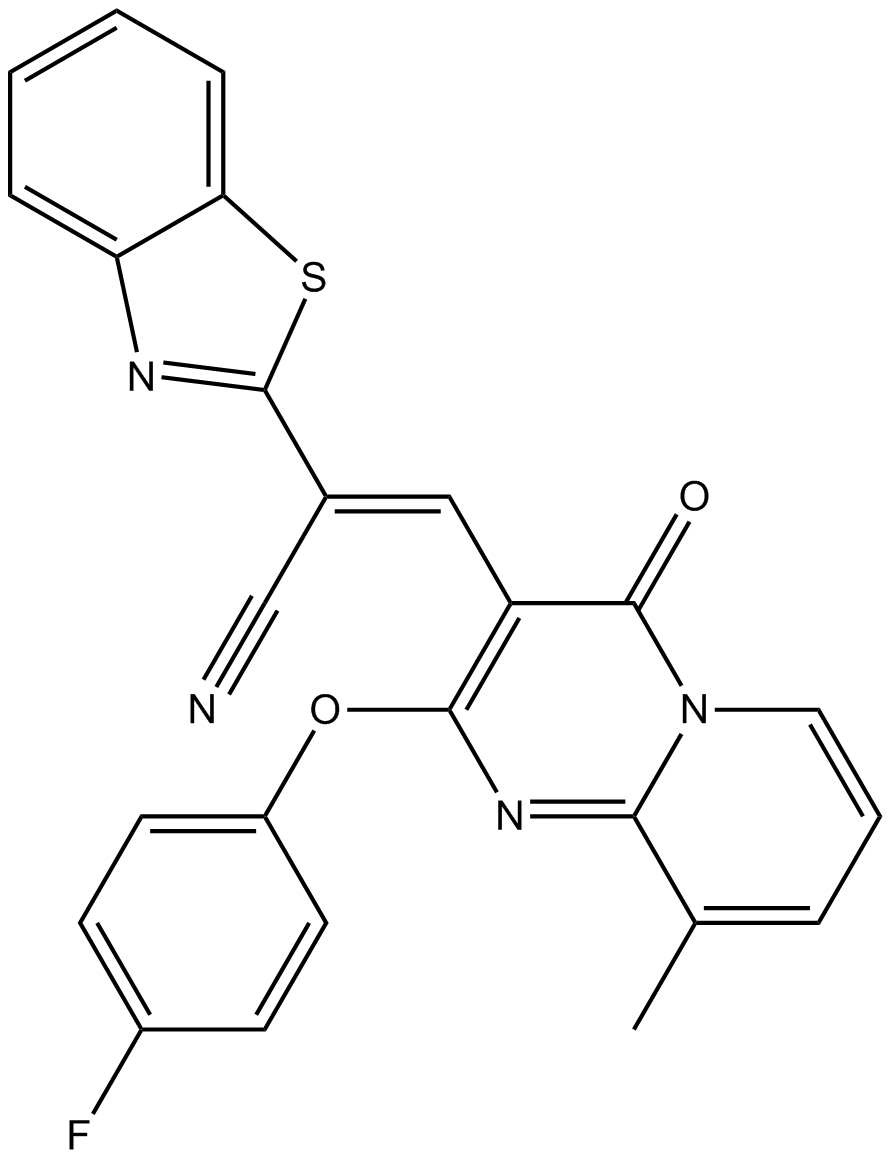 A3290 CCG-63808Summary: Reversible RGS inhibitor
A3290 CCG-63808Summary: Reversible RGS inhibitor -
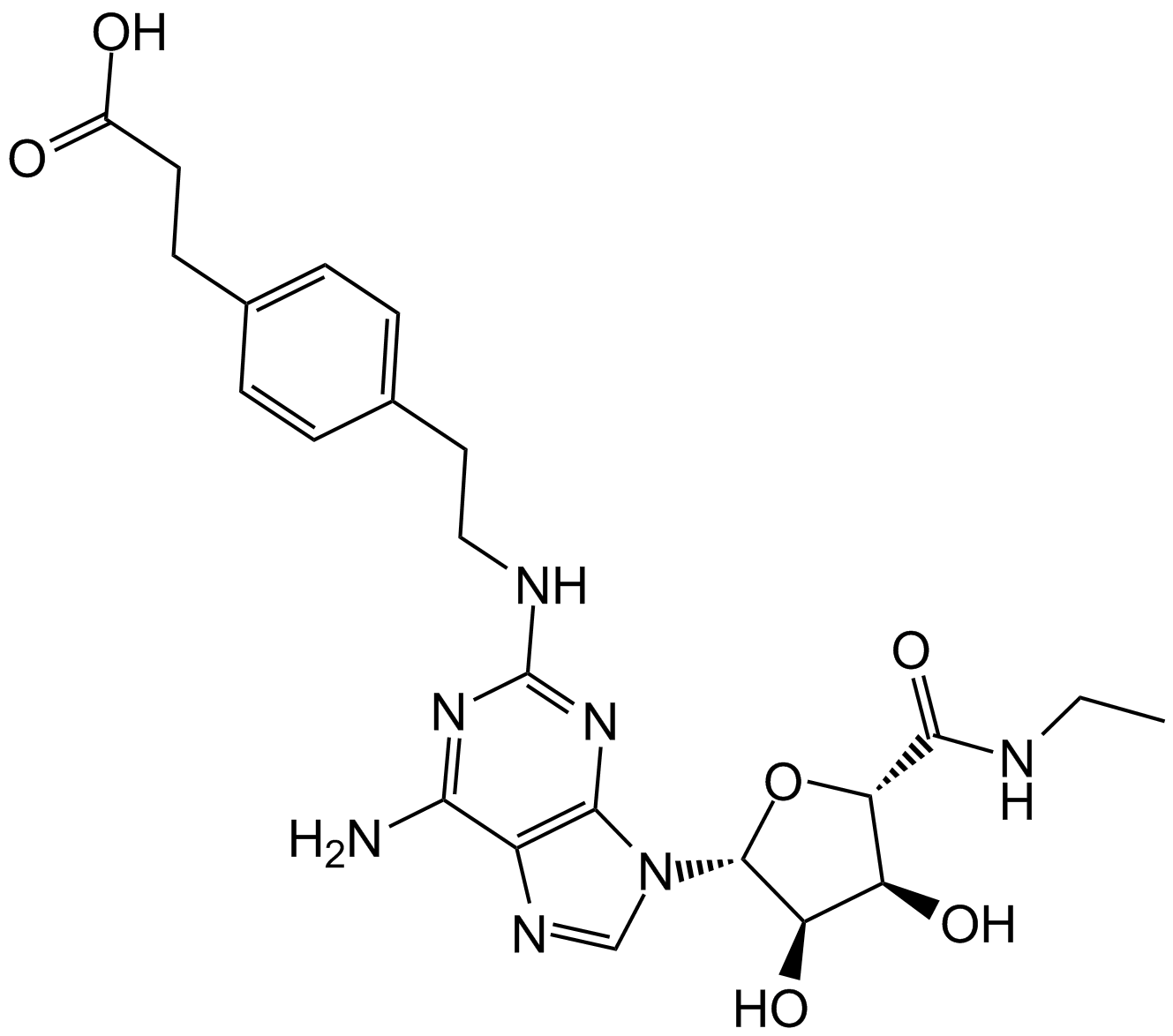 A3304 CGS 21680Summary: Adenosine A2 receptor agonists,potent and selective
A3304 CGS 21680Summary: Adenosine A2 receptor agonists,potent and selective -
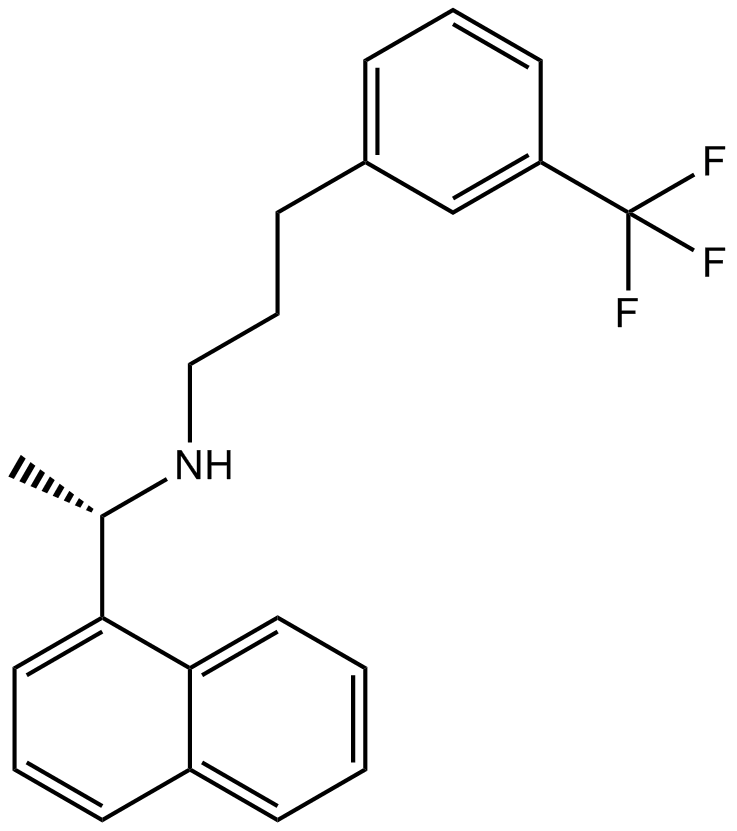 A3313 CinacalcetSummary: Calcimimetic agent,orally active
A3313 CinacalcetSummary: Calcimimetic agent,orally active -
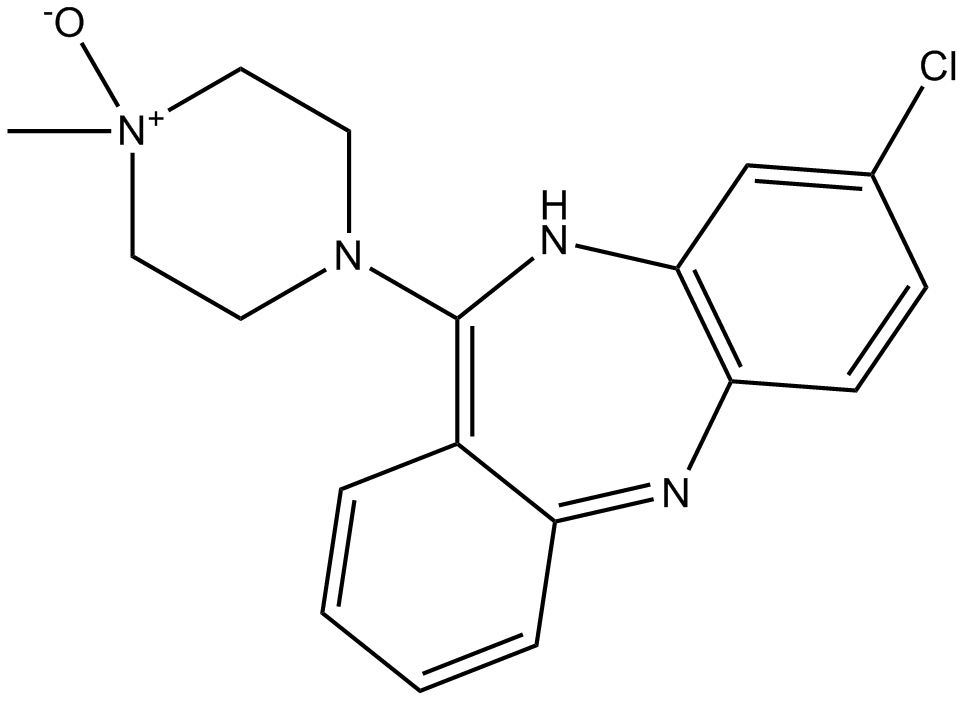 A3317 Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)32 CitationTarget: DREADD LigandsSummary: Metabolite of clozapine
A3317 Clozapine N-oxide (CNO)32 CitationTarget: DREADD LigandsSummary: Metabolite of clozapine

