Endocrinology and Hormones
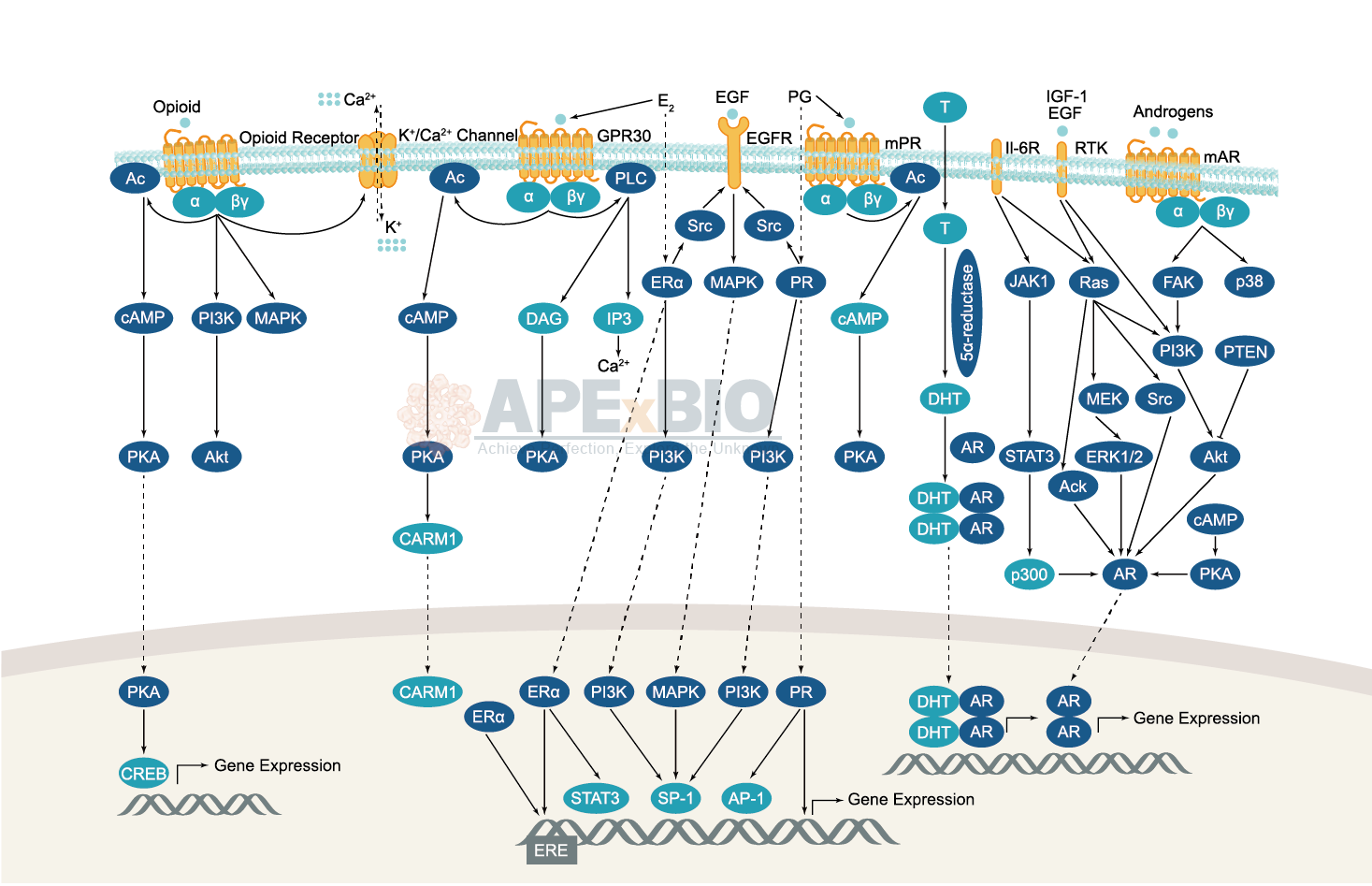
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
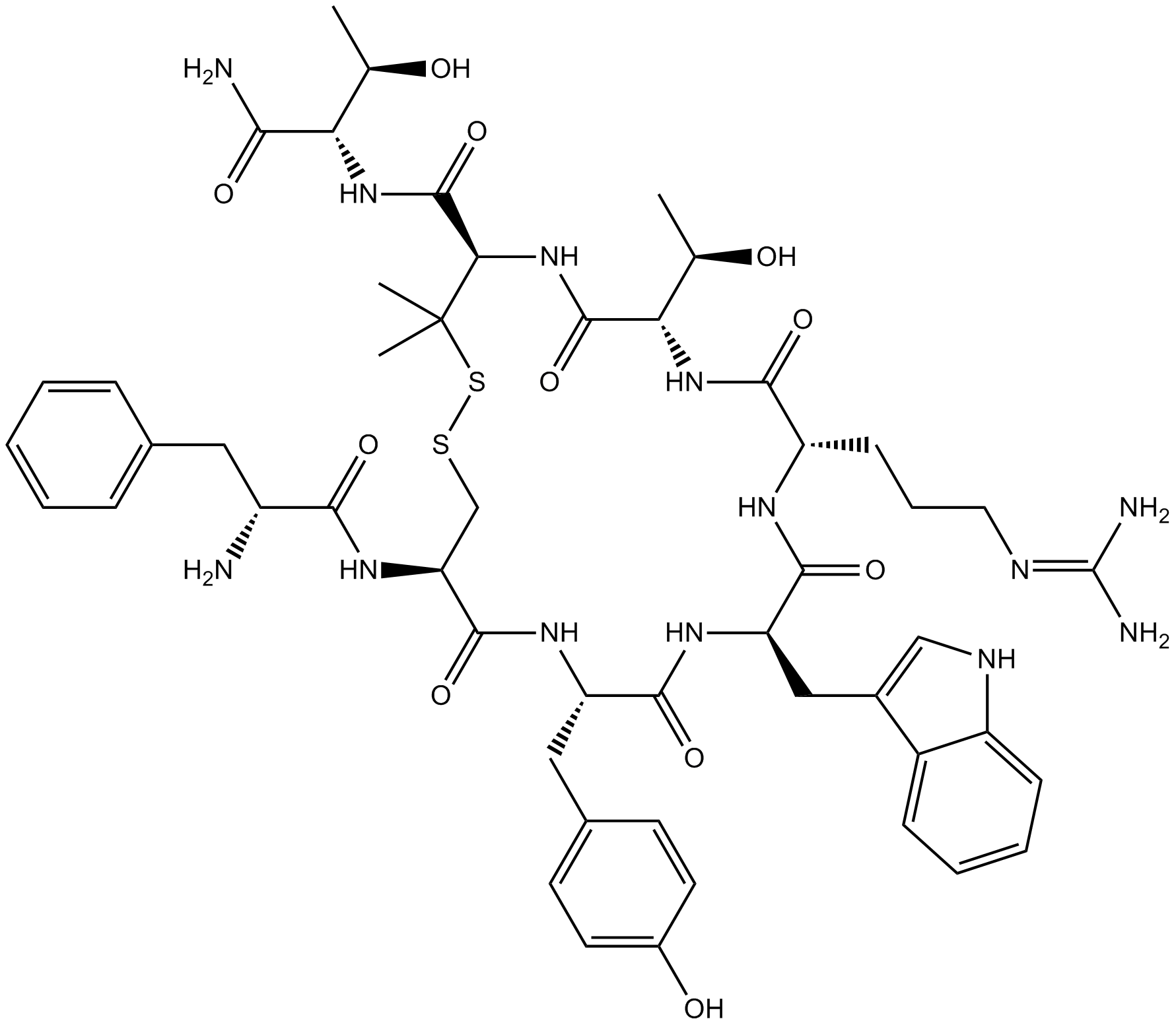 B5129 CTAPSummary: Potent and selective μ opioid receptor antagonist
B5129 CTAPSummary: Potent and selective μ opioid receptor antagonist -
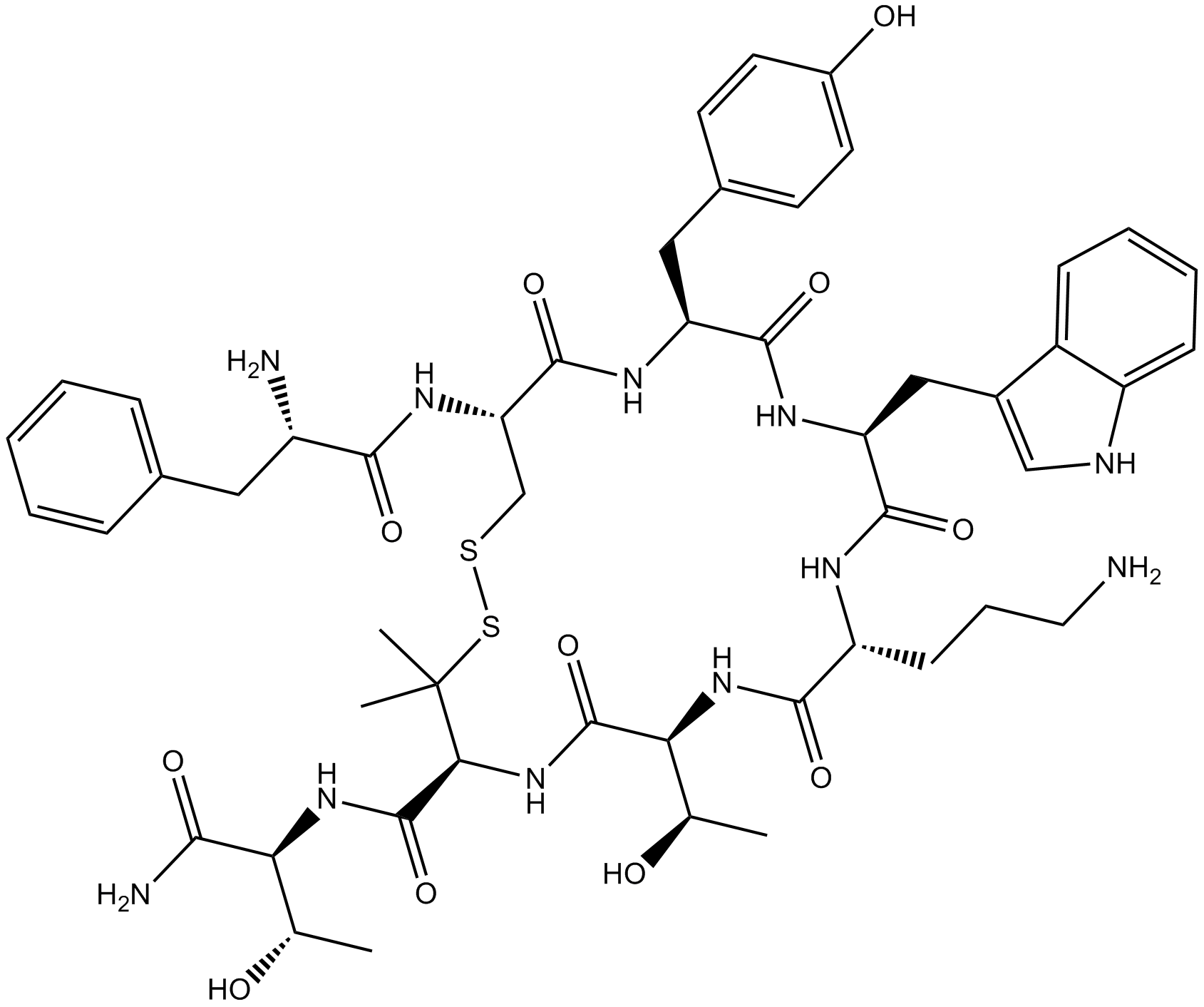 B5135 CTOPSummary: Potent and selective μ opioid receptor antagonist
B5135 CTOPSummary: Potent and selective μ opioid receptor antagonist -
 B5155 BAM 22PSummary: Potent endogenous agonist peptide for the newly identified sensory neuron specific receptor (SNSR);
B5155 BAM 22PSummary: Potent endogenous agonist peptide for the newly identified sensory neuron specific receptor (SNSR); -
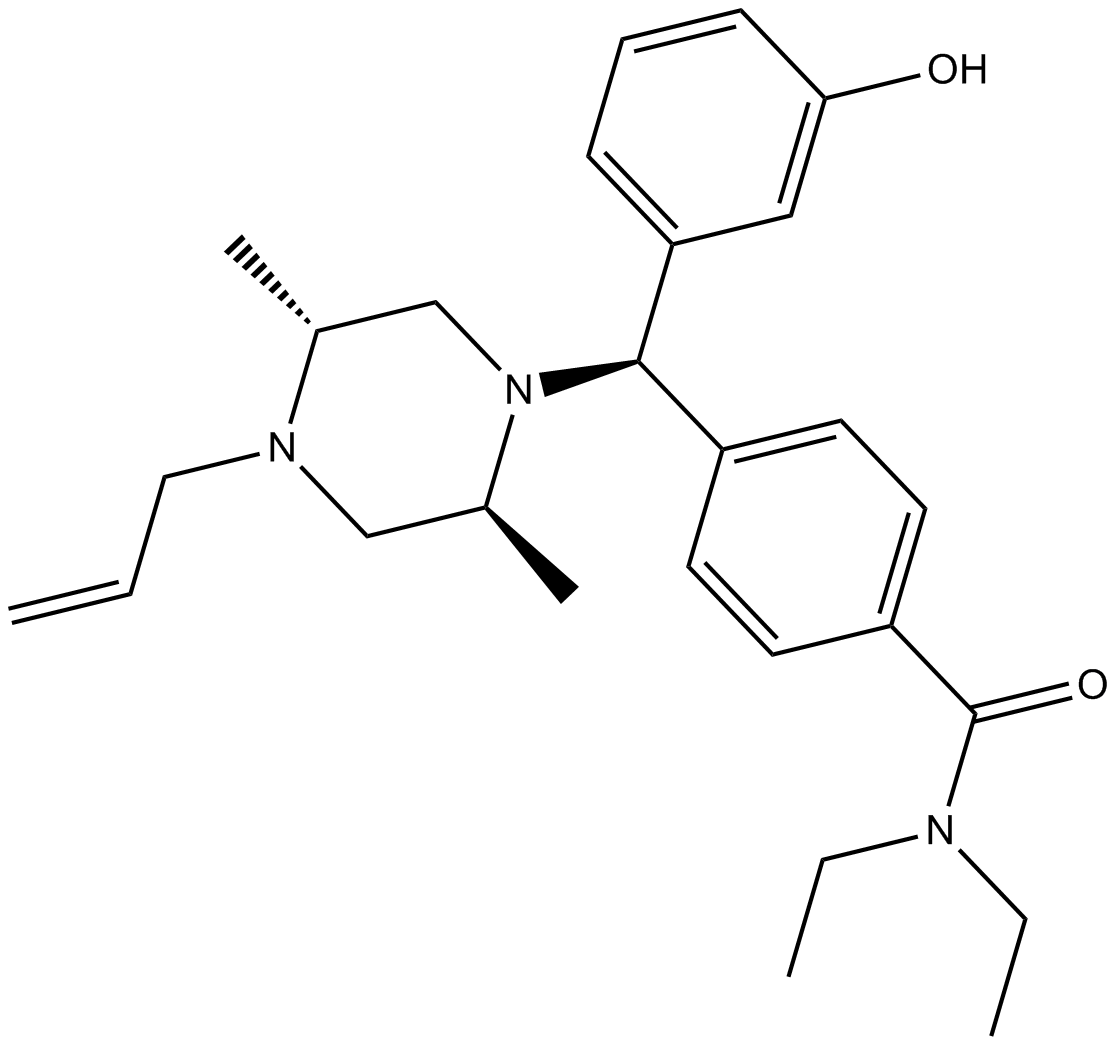 B5157 BW 373U86Summary: Non-peptide delta agonist,potent and selective
B5157 BW 373U86Summary: Non-peptide delta agonist,potent and selective -
![[Leu5]-Enkephalin](/pub/media/prod_images/b/5/b5214.png) B5214 [Leu5]-EnkephalinSummary: An endogenous pentapeptide that acts as an agonist at opioid receptors
B5214 [Leu5]-EnkephalinSummary: An endogenous pentapeptide that acts as an agonist at opioid receptors -
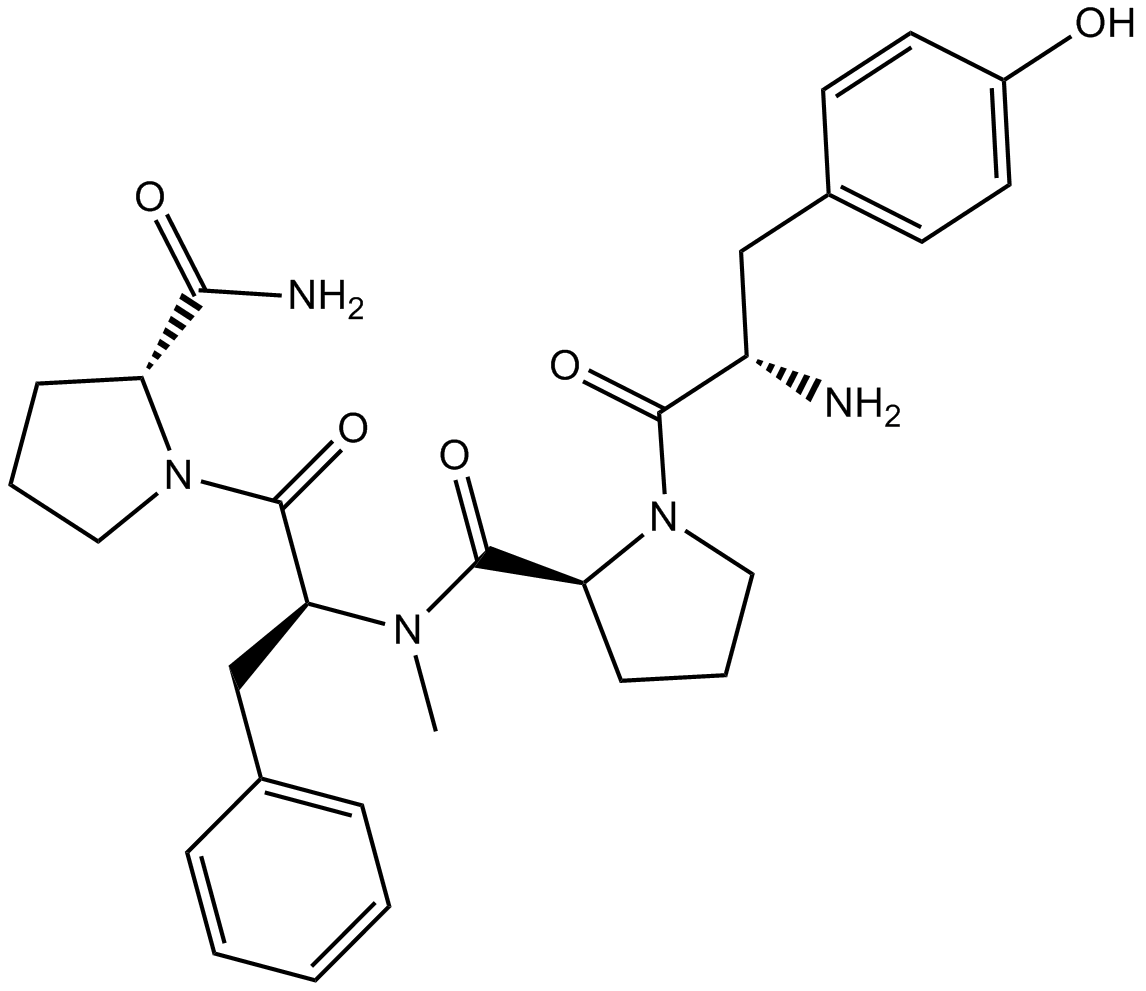 B5249 PL 017Summary: Selective μ opioid receptor agonist
B5249 PL 017Summary: Selective μ opioid receptor agonist -
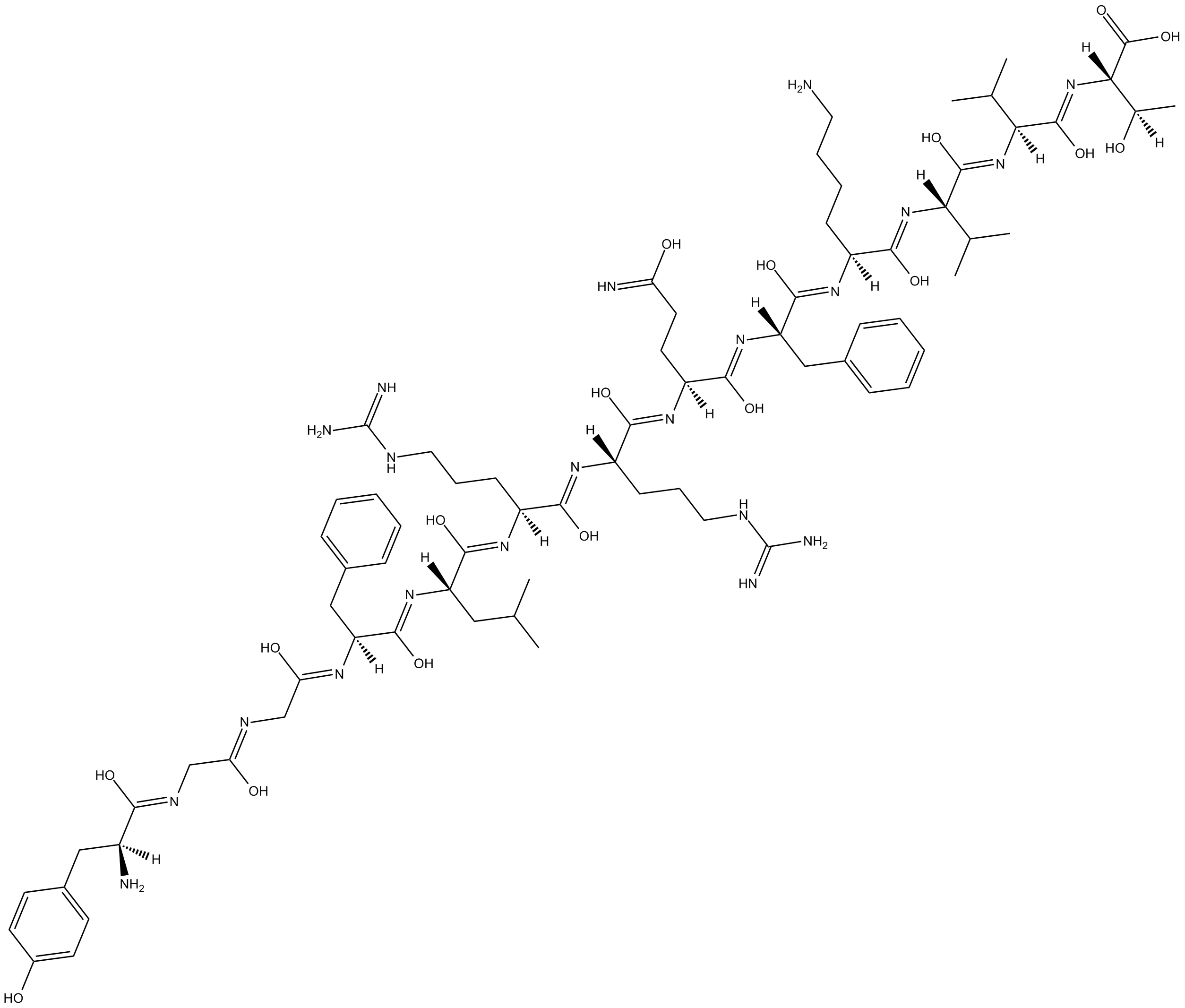 B5390 Dynorphin BSummary: endogenous agonist for the kappa opioid receptor
B5390 Dynorphin BSummary: endogenous agonist for the kappa opioid receptor -
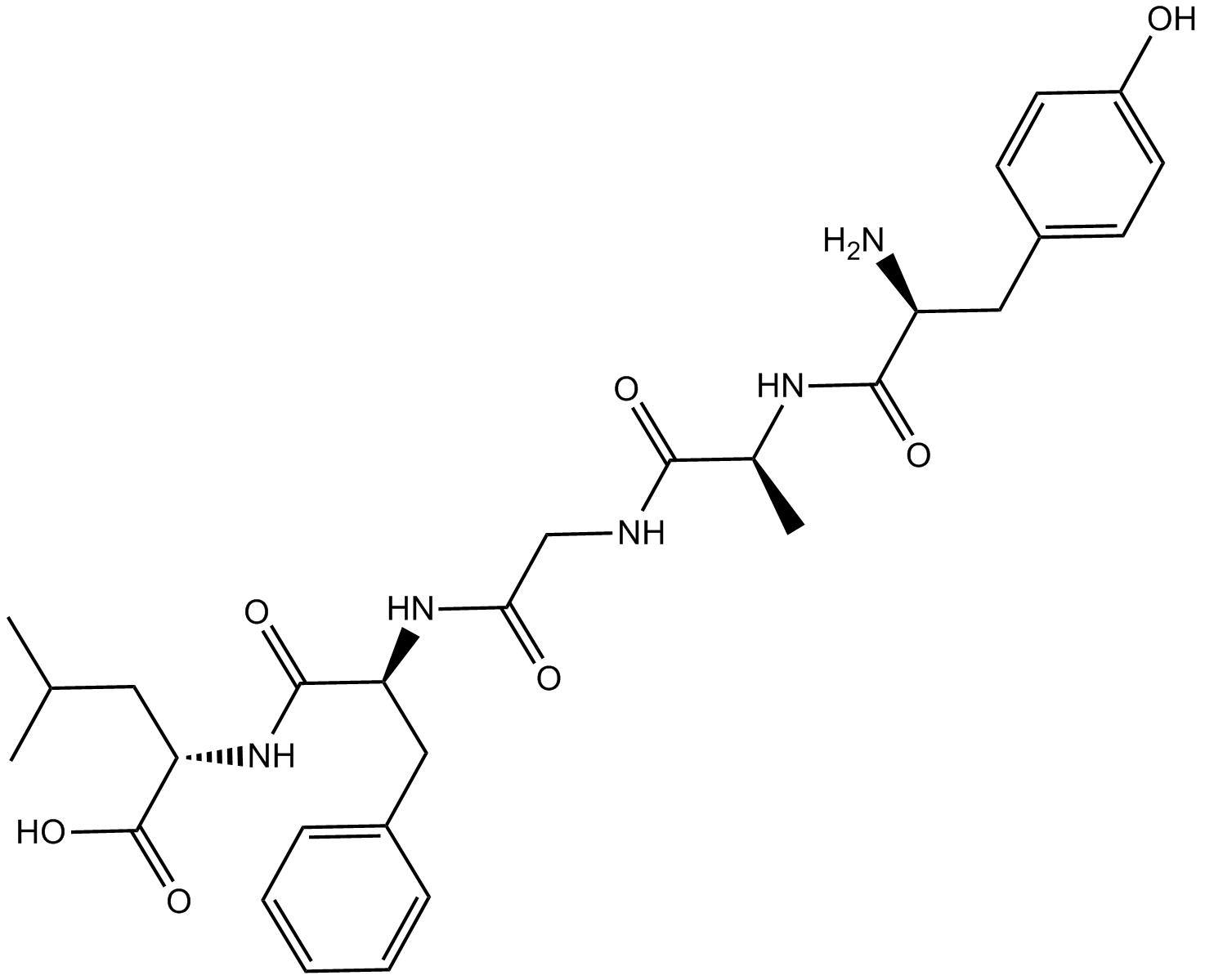 B5475 DADLESummary: δ-opioid receptor agonist
B5475 DADLESummary: δ-opioid receptor agonist -
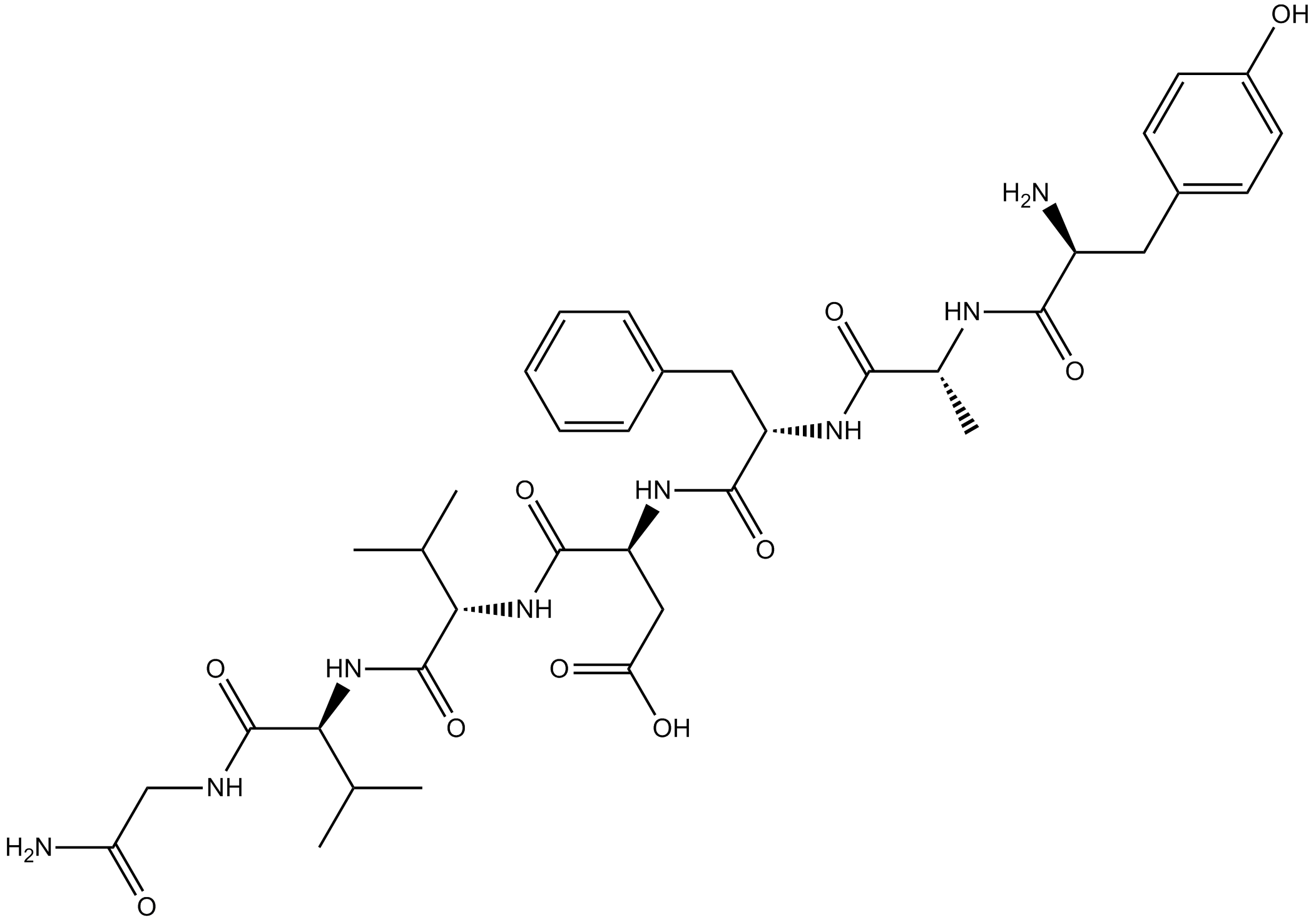 B5649 Deltorphin ISummary: δ-opioid receptor agonist
B5649 Deltorphin ISummary: δ-opioid receptor agonist -
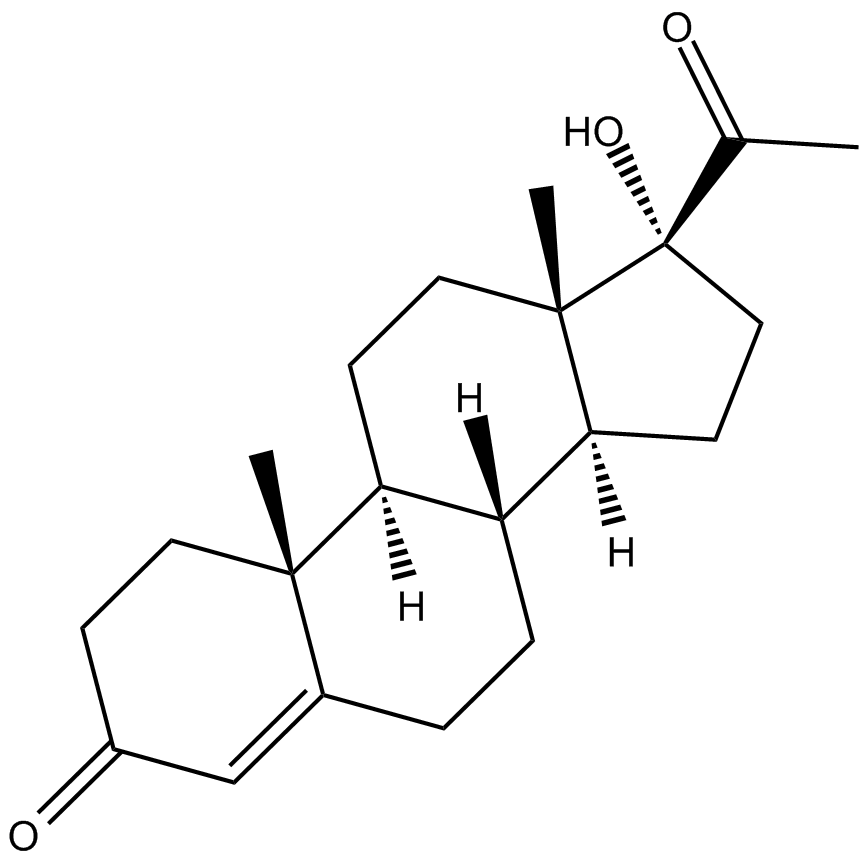 B6126 17-HydroxyprogesteroneSummary: endogenous progestogen as well as chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of other steroid hormones
B6126 17-HydroxyprogesteroneSummary: endogenous progestogen as well as chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of other steroid hormones

