Endocrinology and Hormones
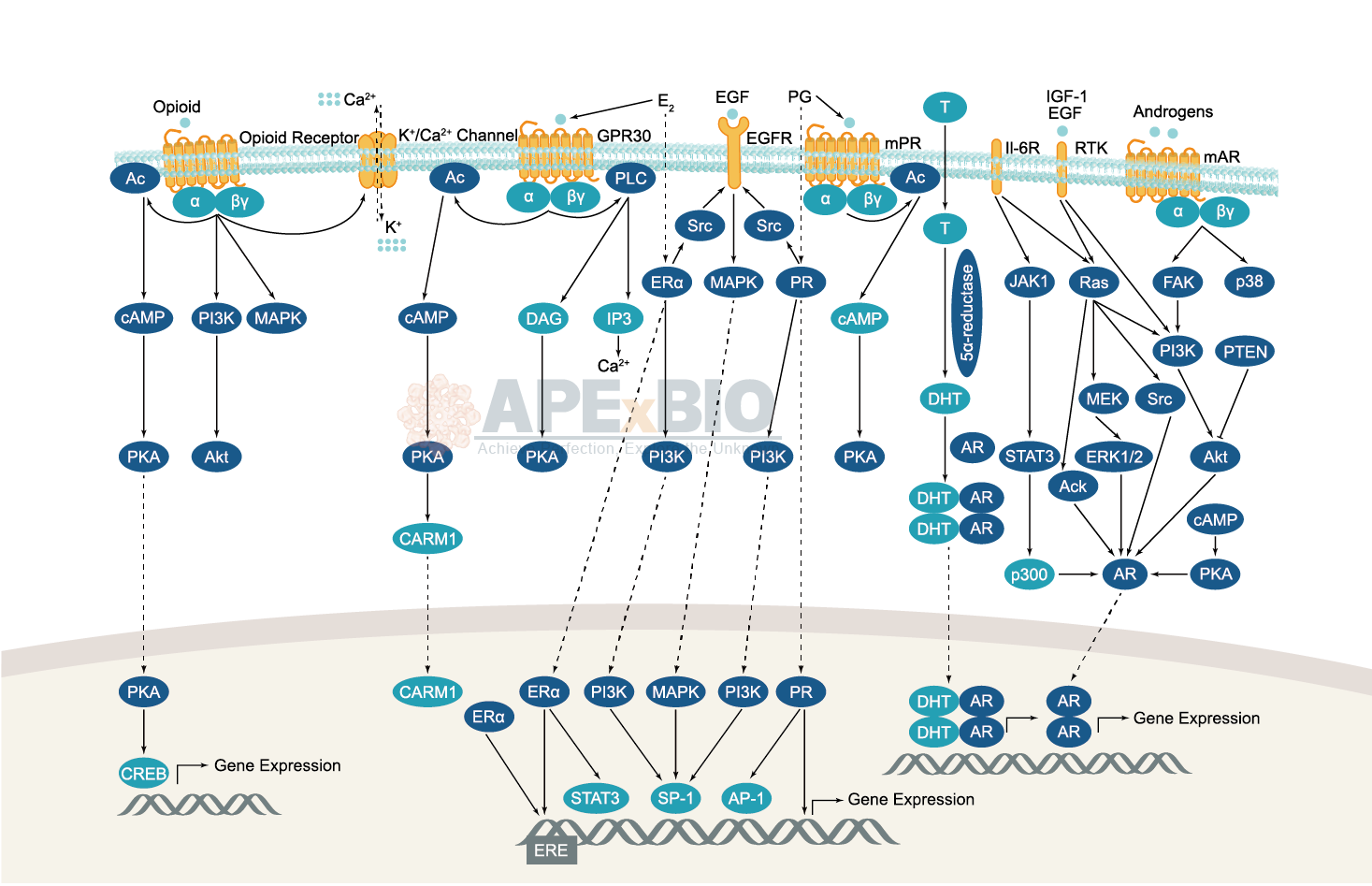
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
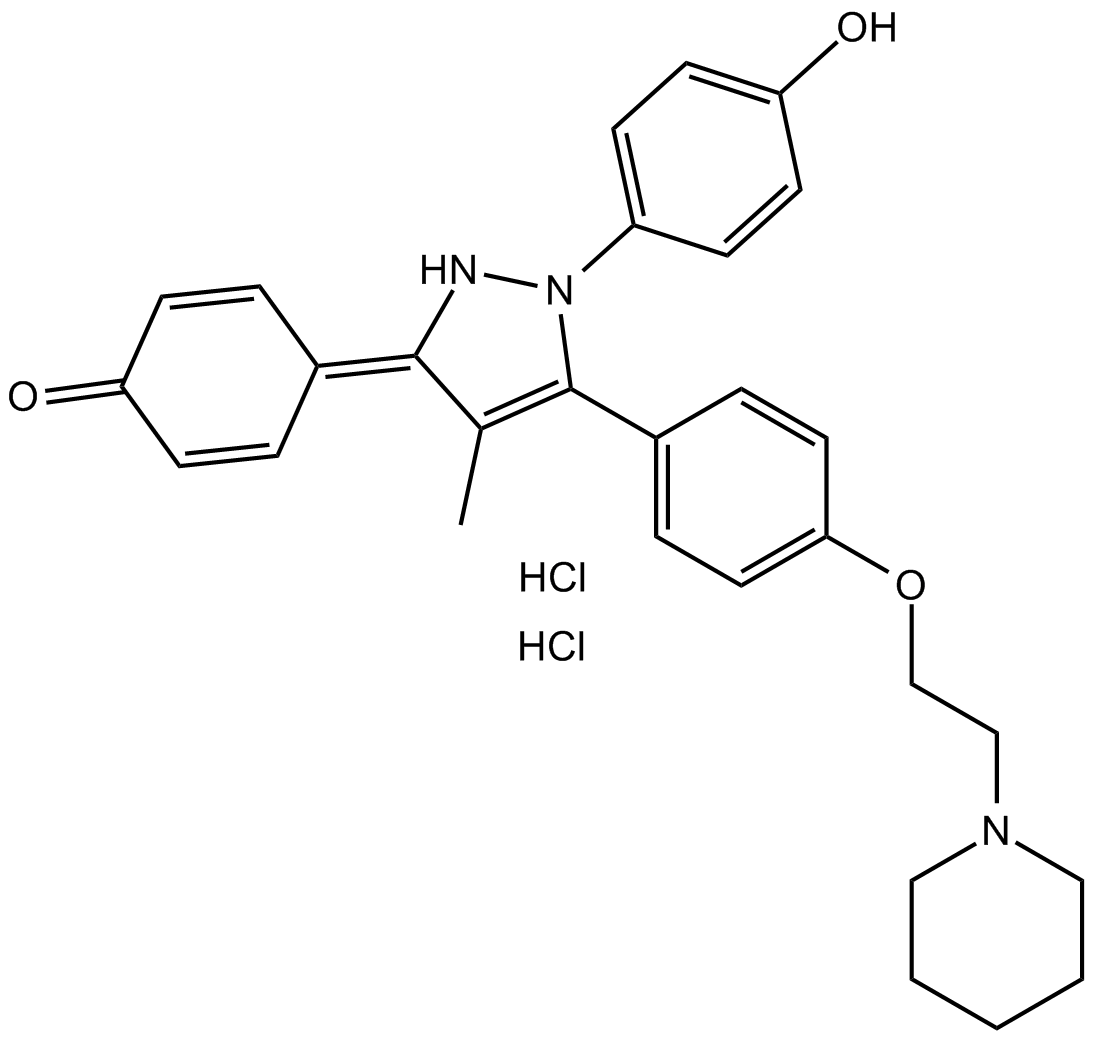 B6910 MPP dihydrochlorideSummary: ERα receptors silent antagonist
B6910 MPP dihydrochlorideSummary: ERα receptors silent antagonist -
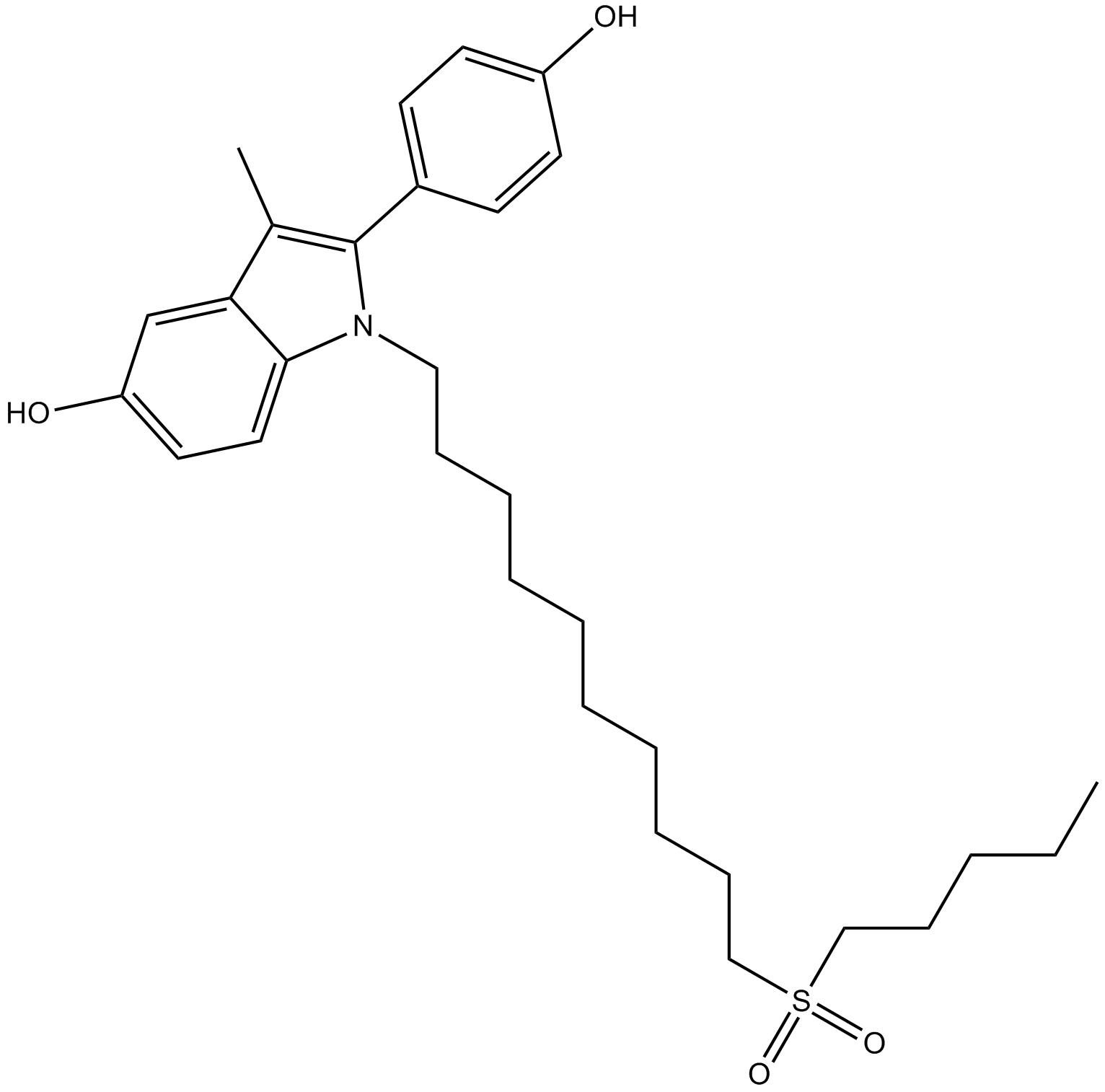 B6960 ZK 164015Summary: estrogen receptor silent antagonist
B6960 ZK 164015Summary: estrogen receptor silent antagonist -
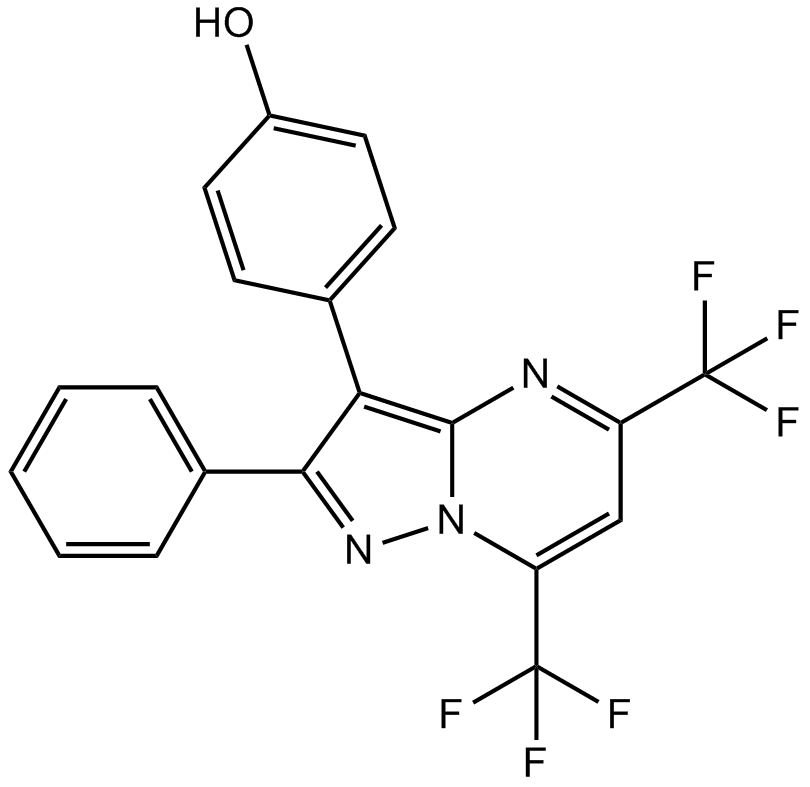 B7144 PHTPPSummary: estrogen ERβ receptor antagonist
B7144 PHTPPSummary: estrogen ERβ receptor antagonist -
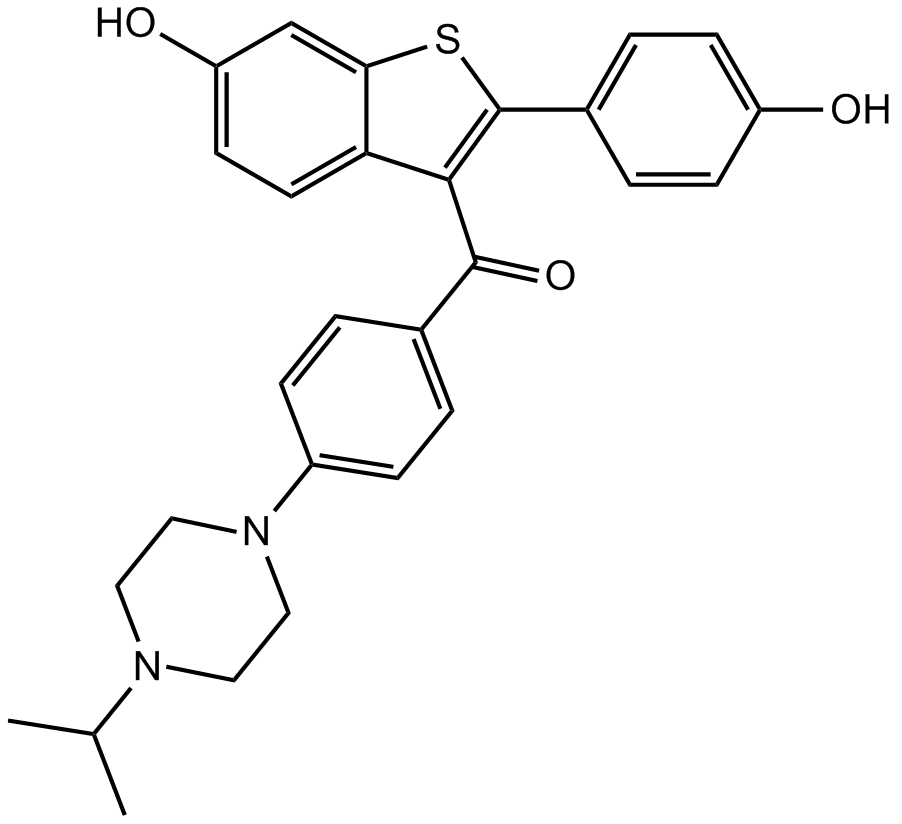 B7149 Y 134Summary: estrogen receptor modulator
B7149 Y 134Summary: estrogen receptor modulator -
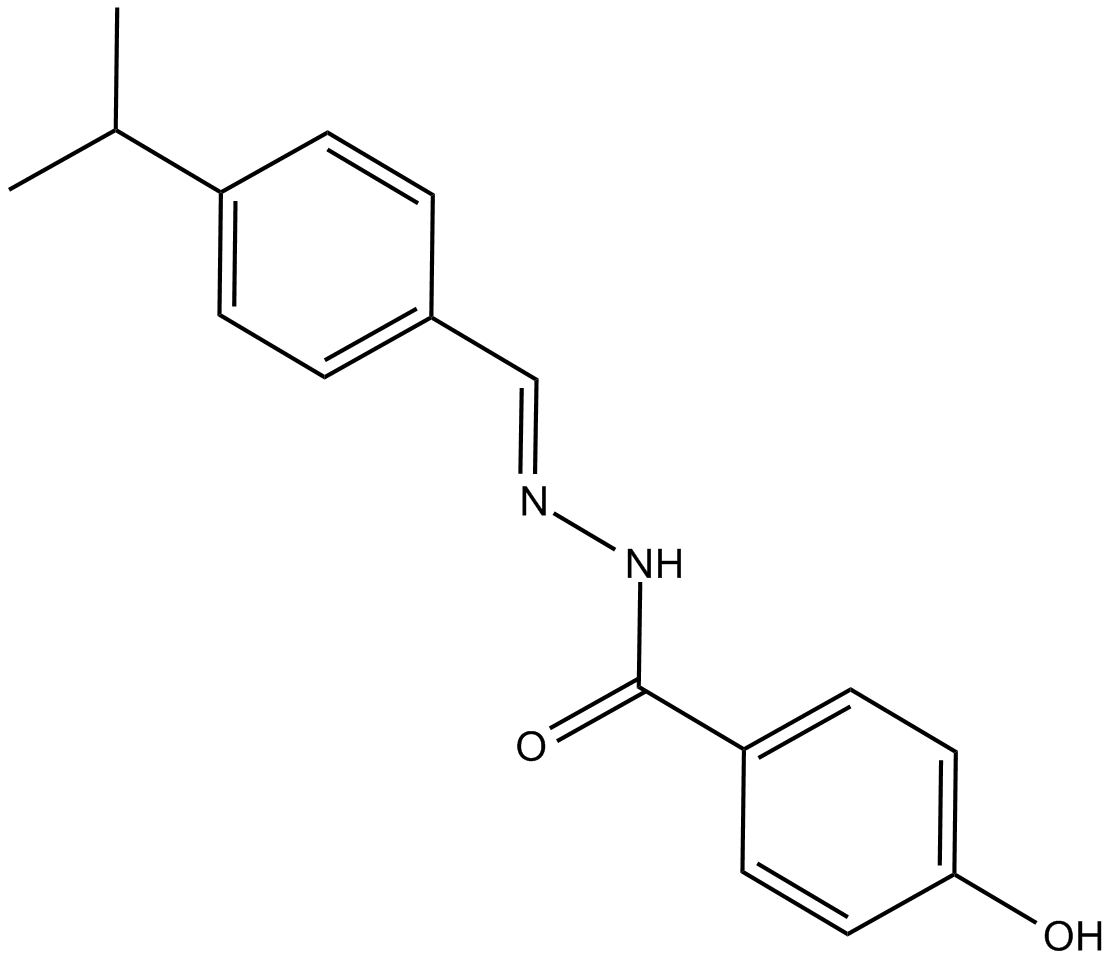 B7265 GSK 4716Summary: estrogen-related receptors ERRβ and ERRγ agonist
B7265 GSK 4716Summary: estrogen-related receptors ERRβ and ERRγ agonist -
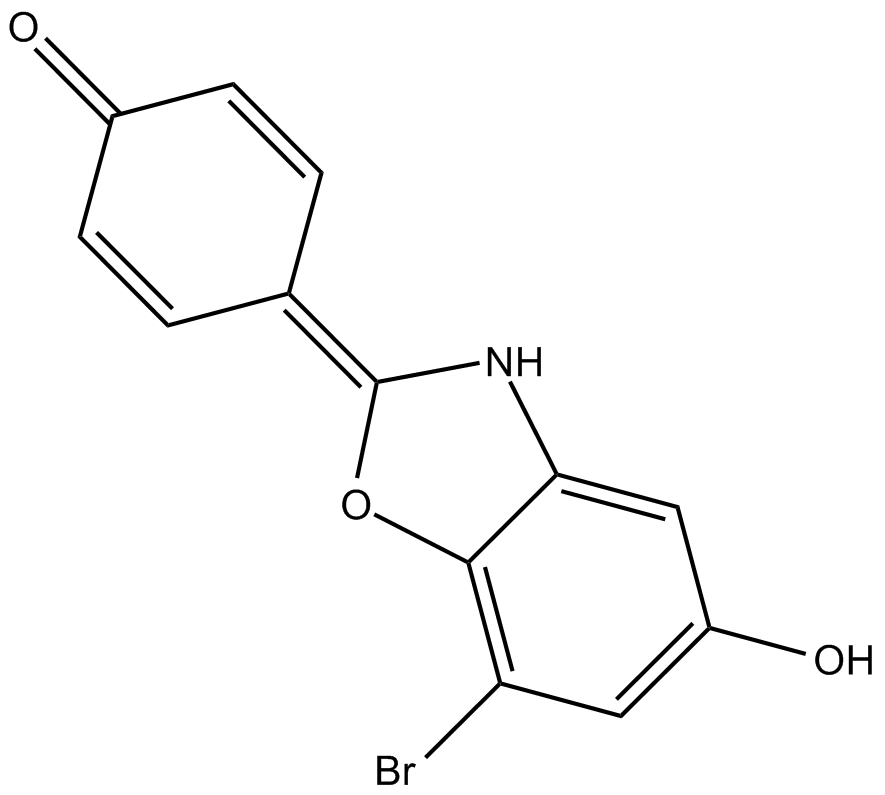 B7386 WAY 200070Summary: ERβ receptor agonist
B7386 WAY 200070Summary: ERβ receptor agonist -
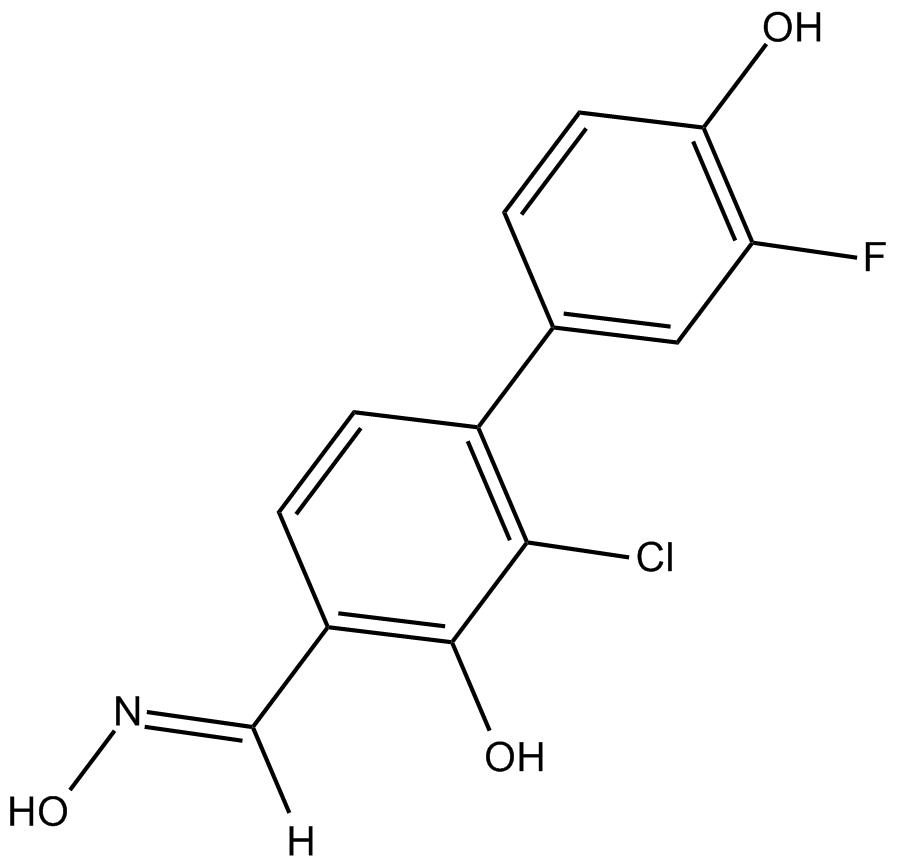 B7419 FERb 033Summary: ERβ receptor agonist
B7419 FERb 033Summary: ERβ receptor agonist -
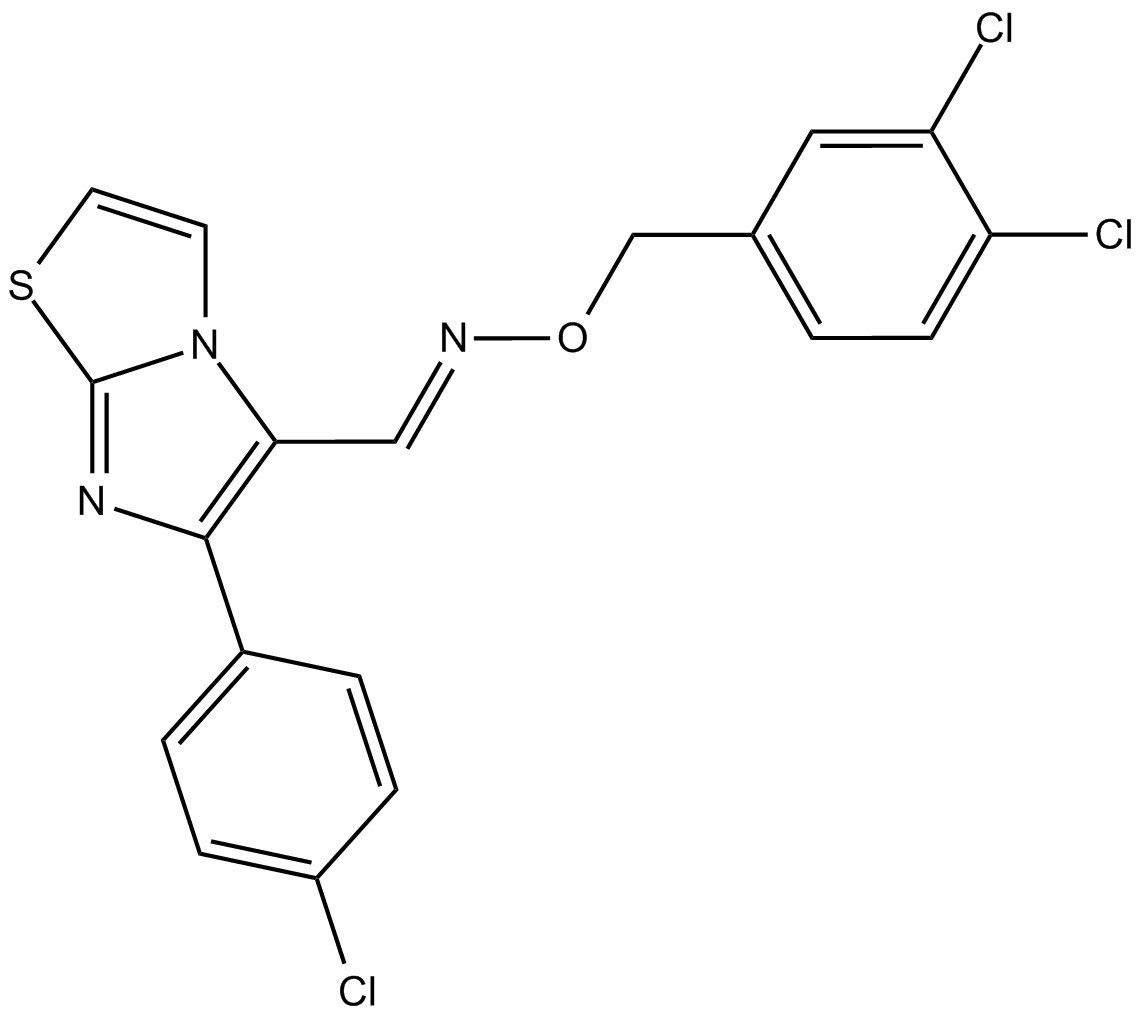 B7468 CITCO1 CitationTarget: constitutive androstane receptor (CAR)Summary: A selective constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) agonist
B7468 CITCO1 CitationTarget: constitutive androstane receptor (CAR)Summary: A selective constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) agonist -
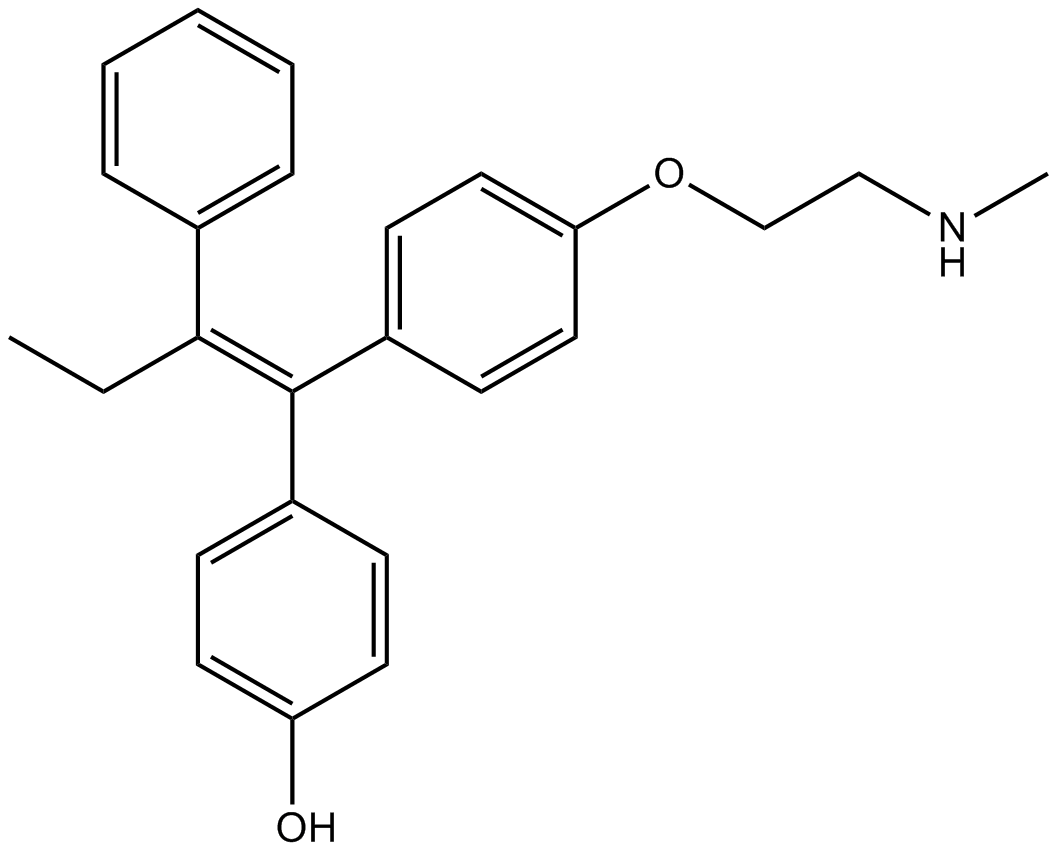 B7481 EndoxifenSummary: Estrogen receptor α (ERα) ligand
B7481 EndoxifenSummary: Estrogen receptor α (ERα) ligand -
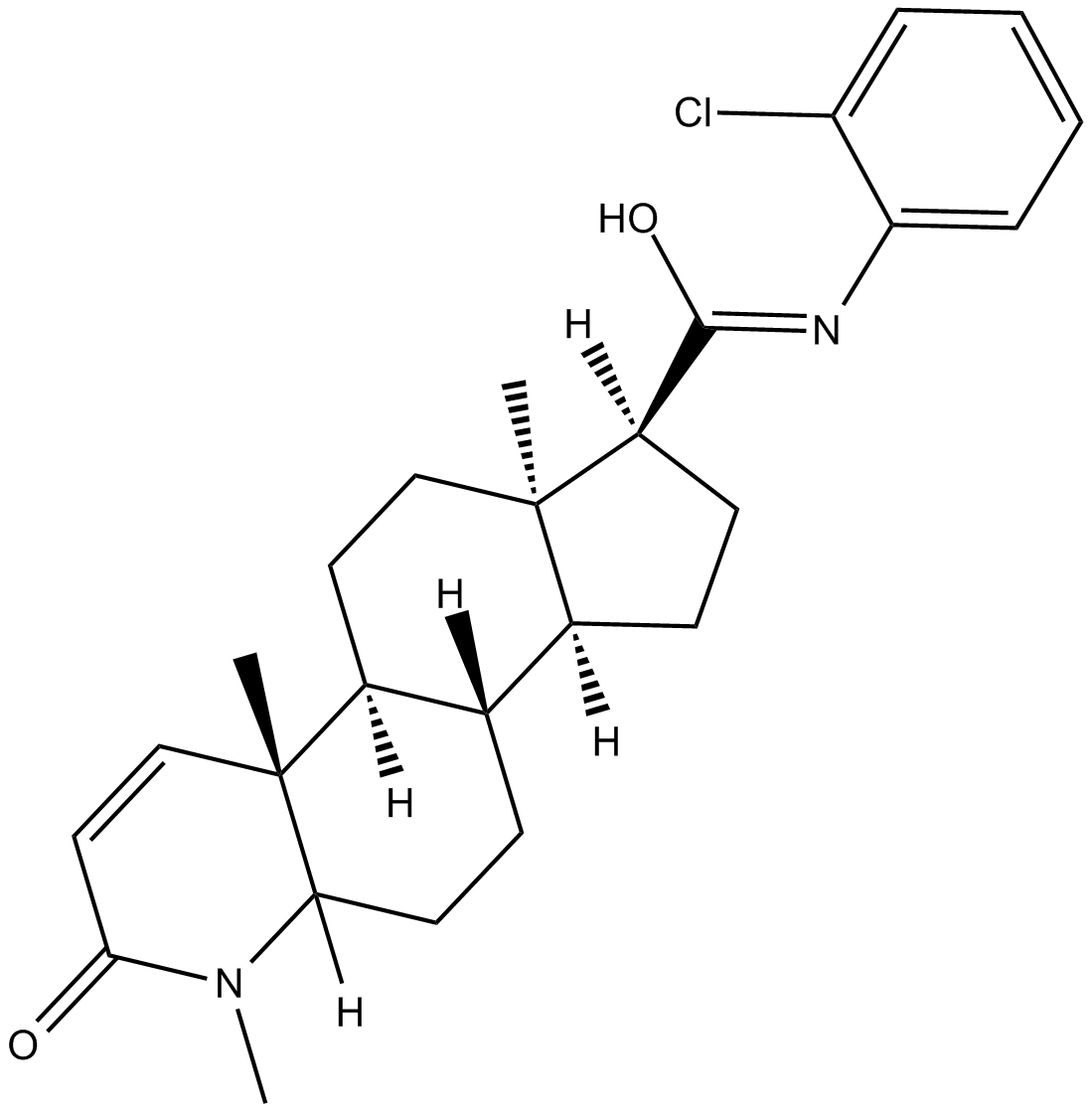 B7503 Cl-4AS-1Summary: steroidal androgen receptor agonist
B7503 Cl-4AS-1Summary: steroidal androgen receptor agonist

