Endocrinology and Hormones
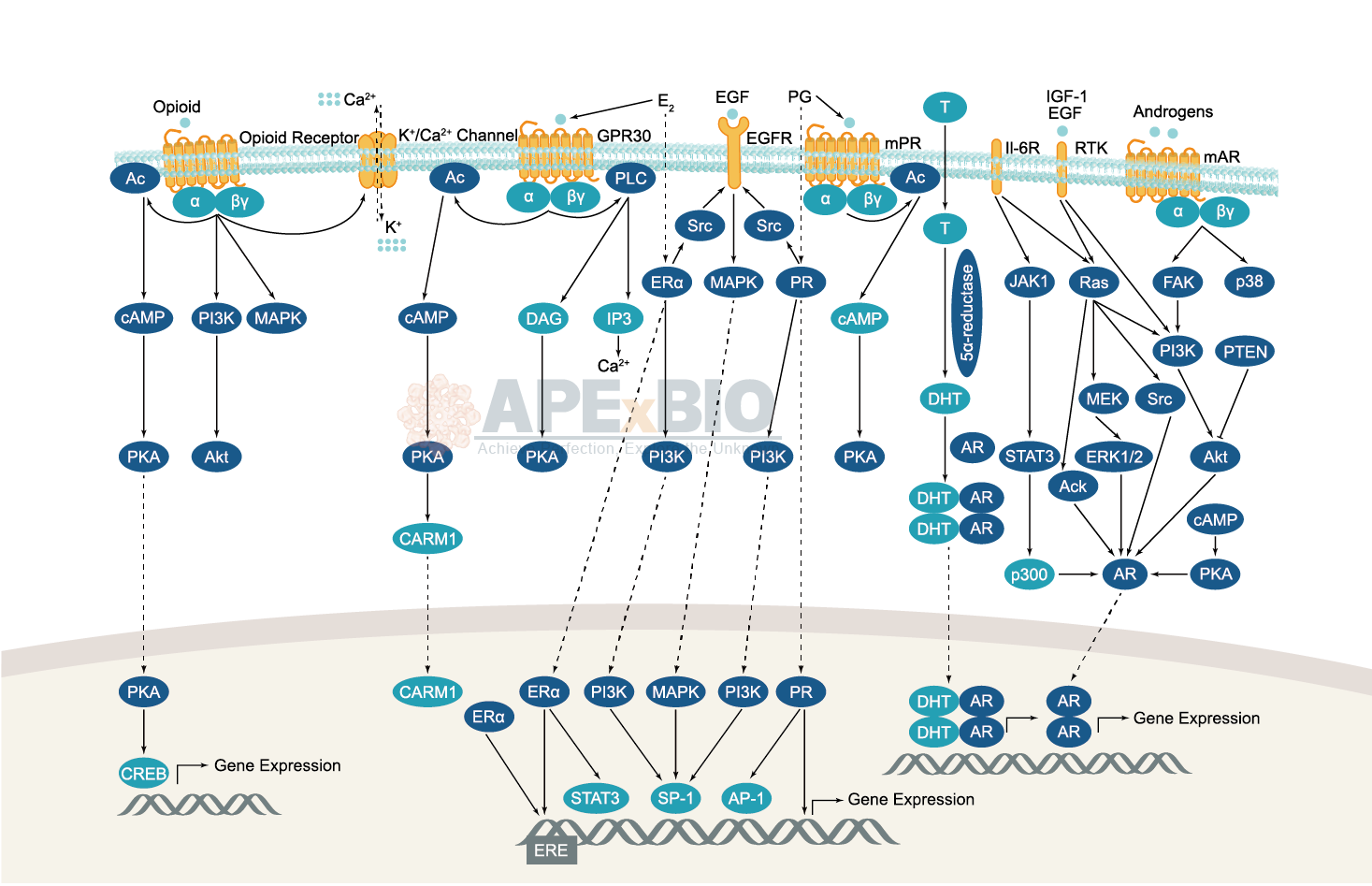
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
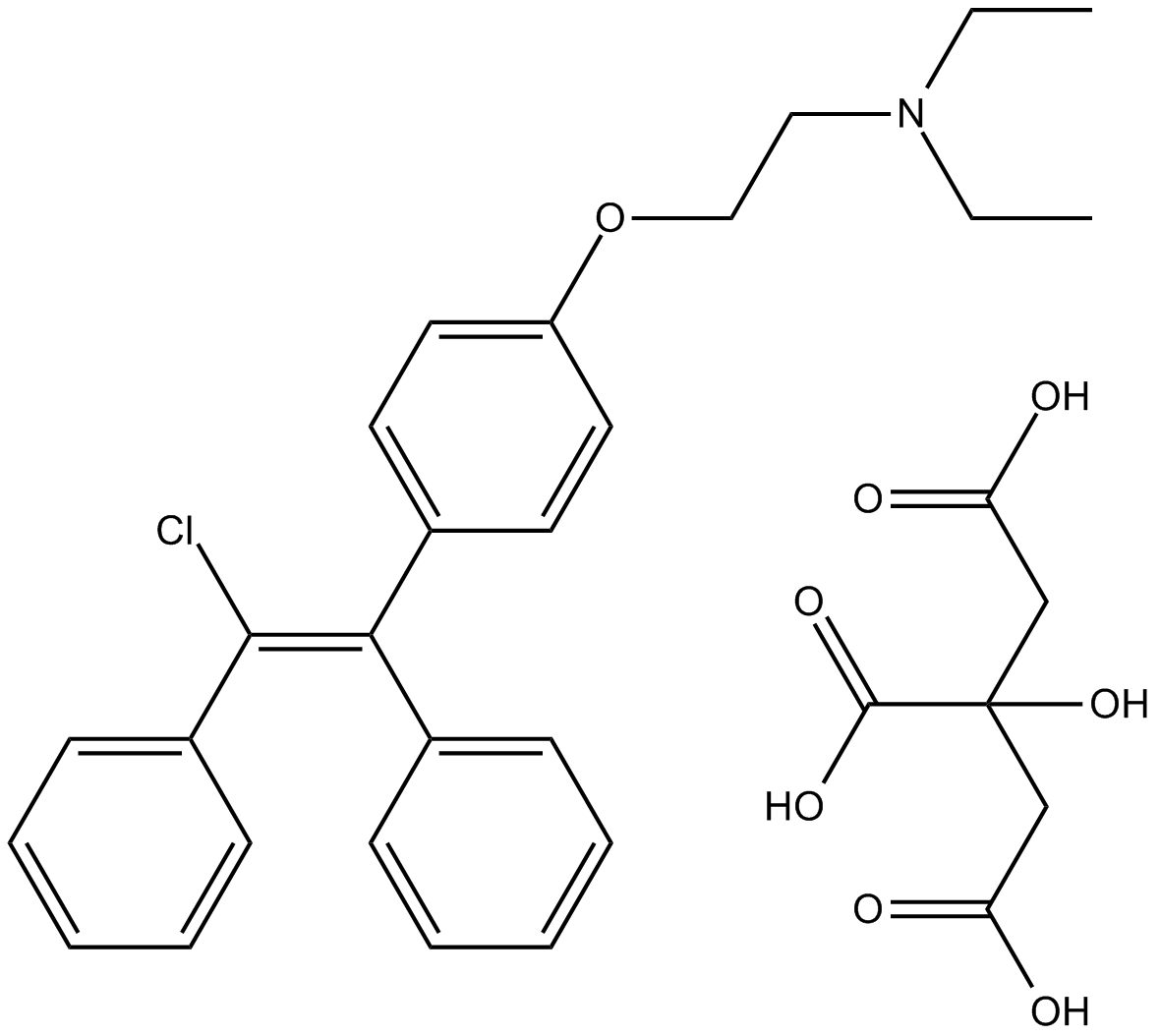 B1504 Clomiphene citrateSummary: Selective estrogen receptor modulator
B1504 Clomiphene citrateSummary: Selective estrogen receptor modulator -
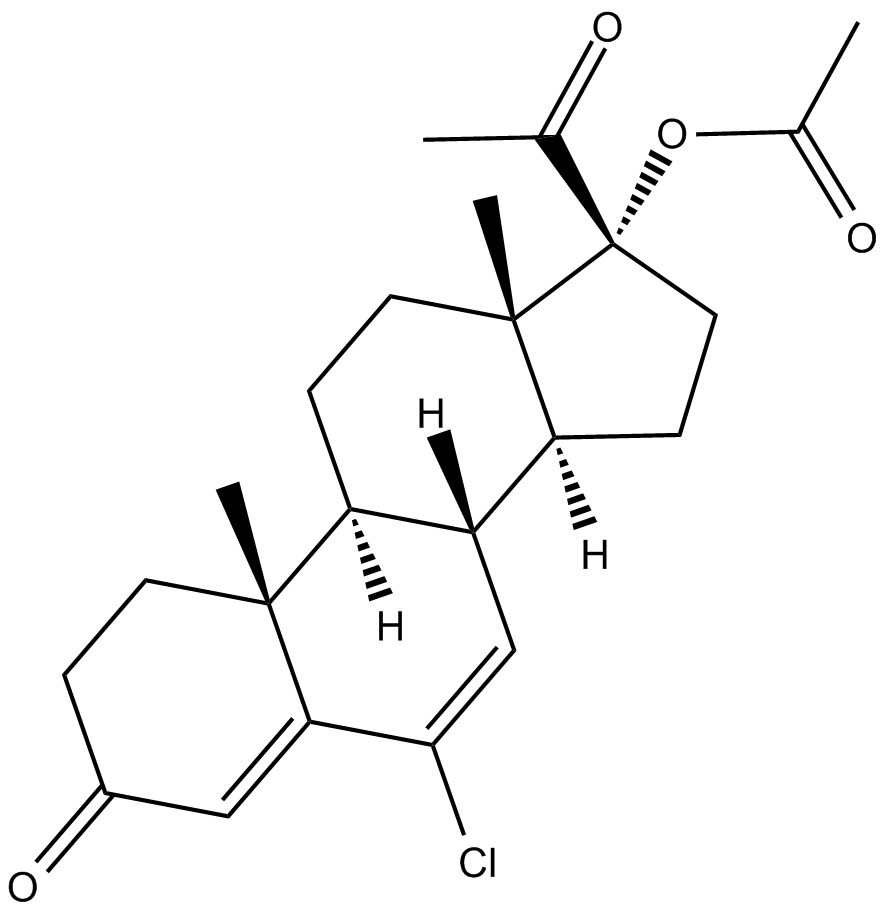 B6136 Chlormadinone acetateSummary: steroidal progestin with additional antiandrogen and antigonadotropic effects
B6136 Chlormadinone acetateSummary: steroidal progestin with additional antiandrogen and antigonadotropic effects -
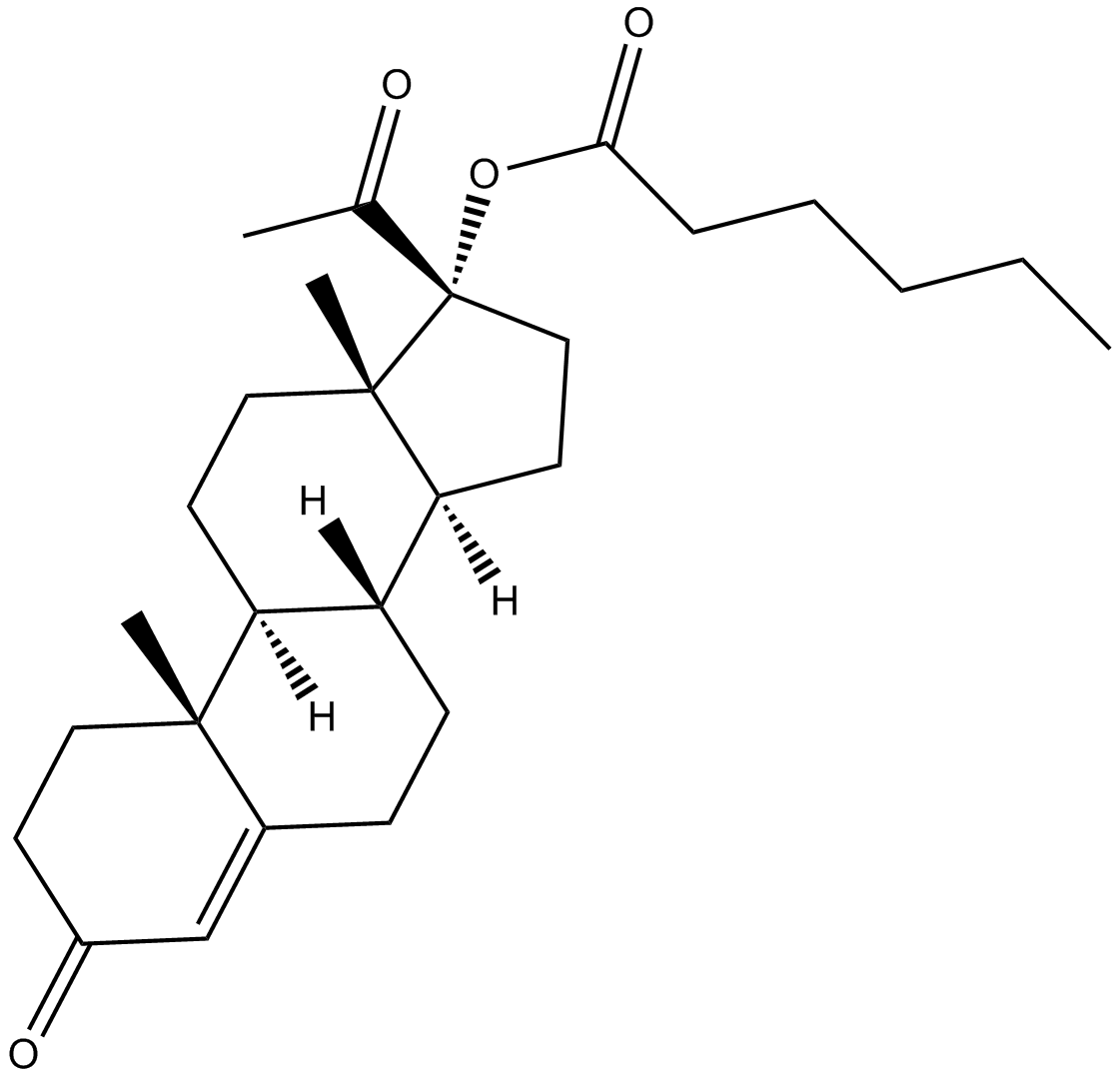 B6143 Hydroxyprogesterone caproateSummary: synthetic progestational agent
B6143 Hydroxyprogesterone caproateSummary: synthetic progestational agent -
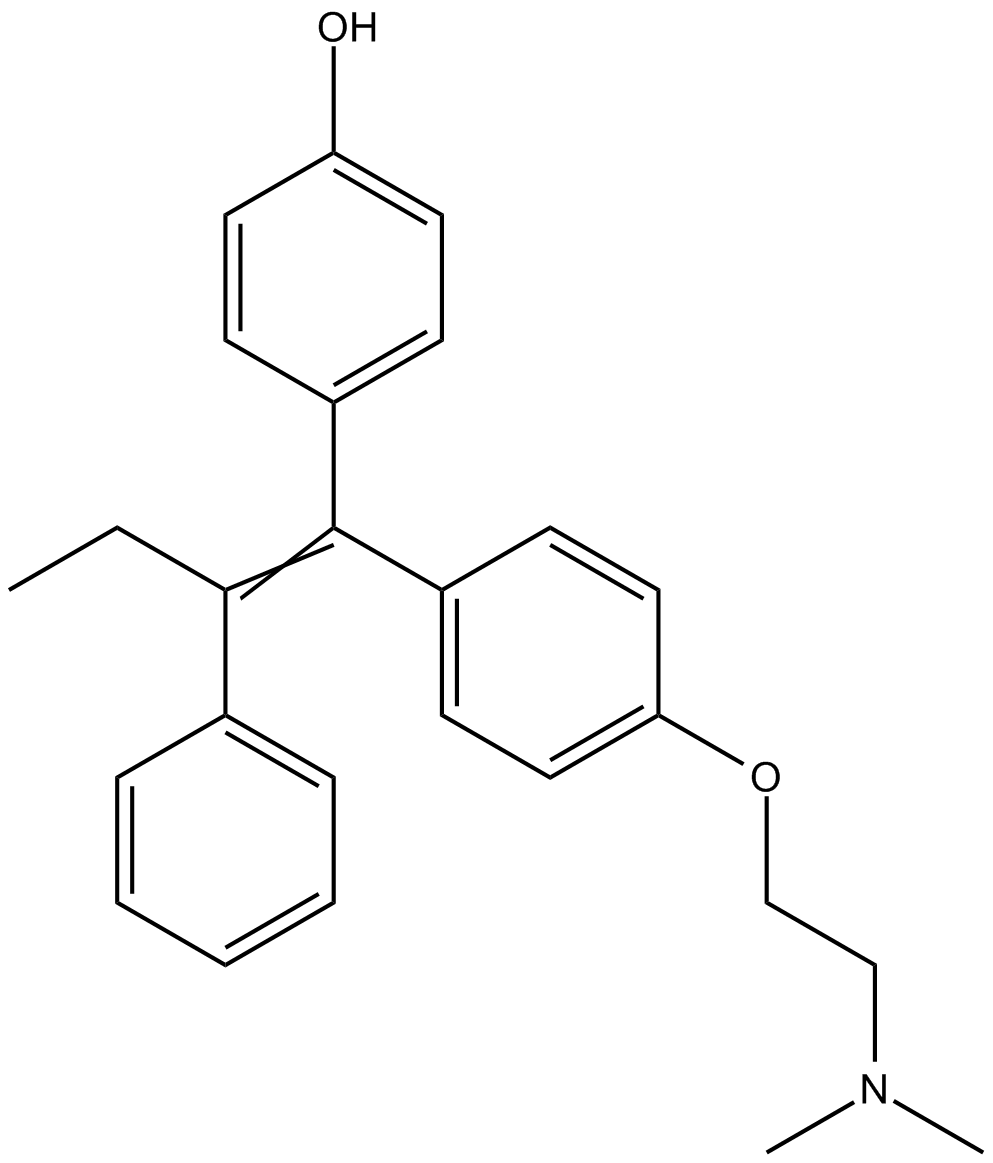 B6167 4-HydroxytamoxifenSummary: estrogen receptor modulator
B6167 4-HydroxytamoxifenSummary: estrogen receptor modulator -
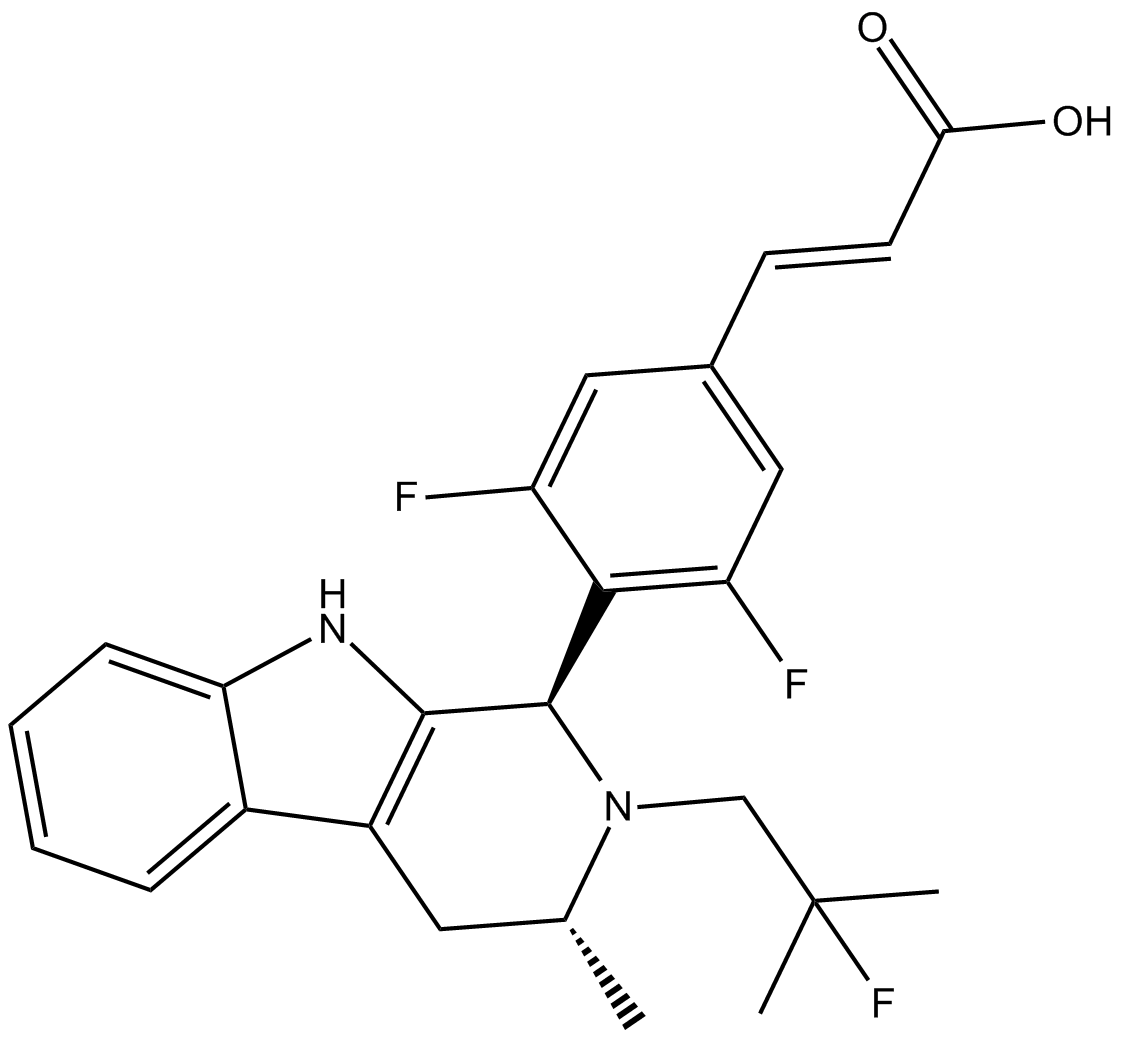 B7821 AZD9496Summary: estrogen receptor inhibitor, orally active
B7821 AZD9496Summary: estrogen receptor inhibitor, orally active -
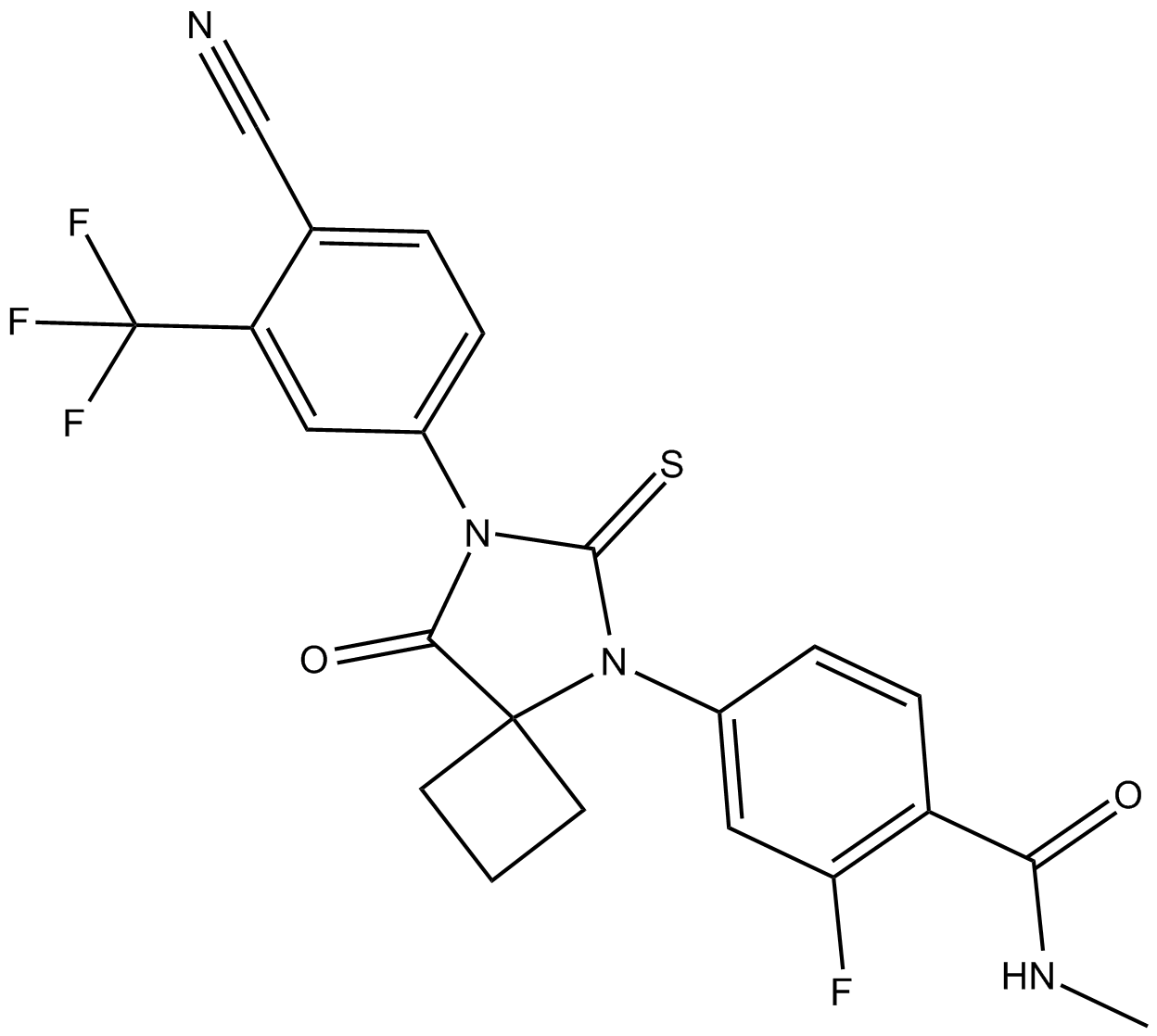 C3186 RD162Summary: androgen receptor (AR) antagonist
C3186 RD162Summary: androgen receptor (AR) antagonist -
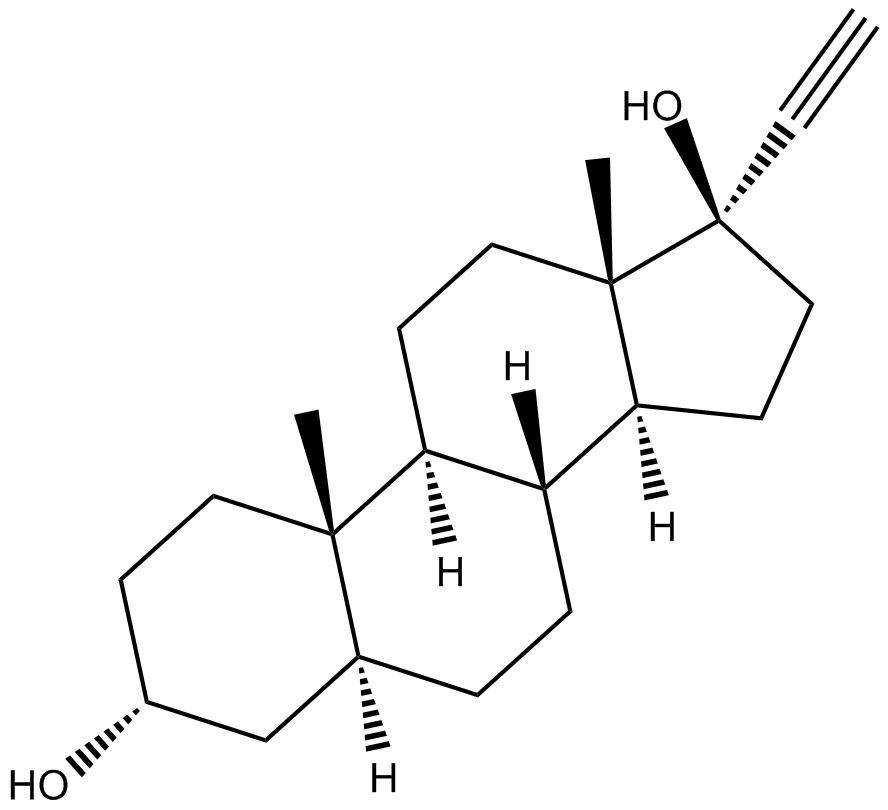 C3546 HE-3235Summary: androgen receptor antagonist
C3546 HE-3235Summary: androgen receptor antagonist -
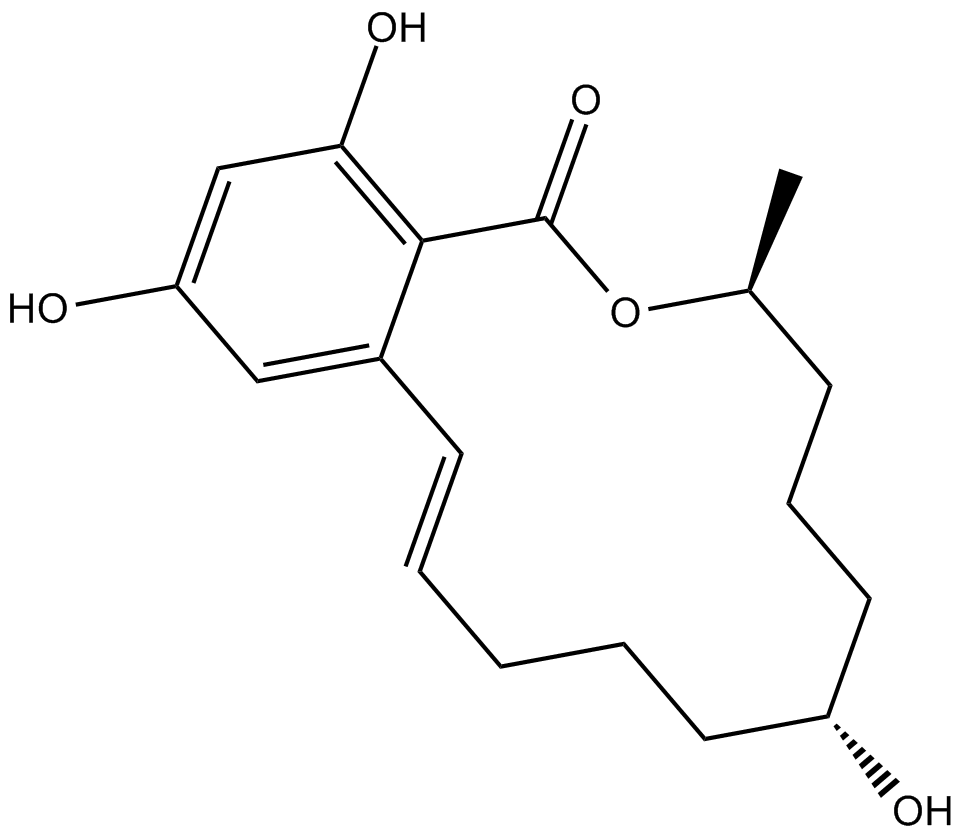 C3405 α-ZearalenolSummary: estrogen receptor agonist
C3405 α-ZearalenolSummary: estrogen receptor agonist -
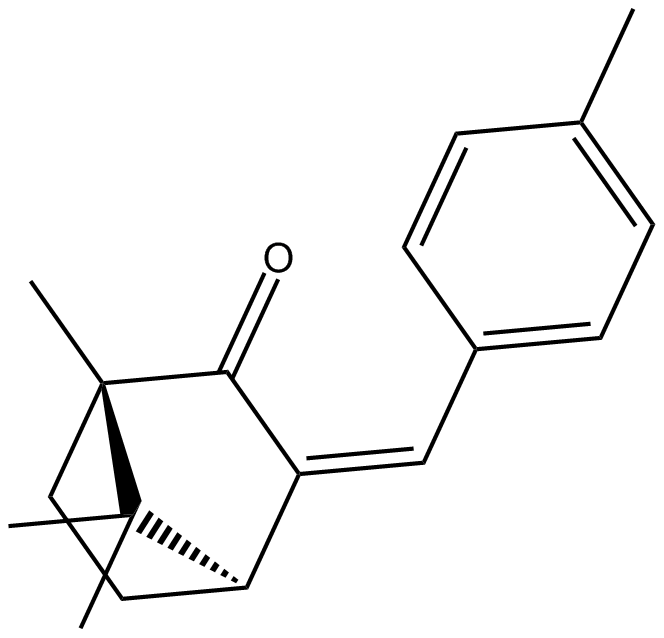 C3558 4-Methylbenzylidene camphorSummary: ultraviolet light blocker used in cosmetics and sunscreen preparations that also has estrogenic activities.
C3558 4-Methylbenzylidene camphorSummary: ultraviolet light blocker used in cosmetics and sunscreen preparations that also has estrogenic activities. -
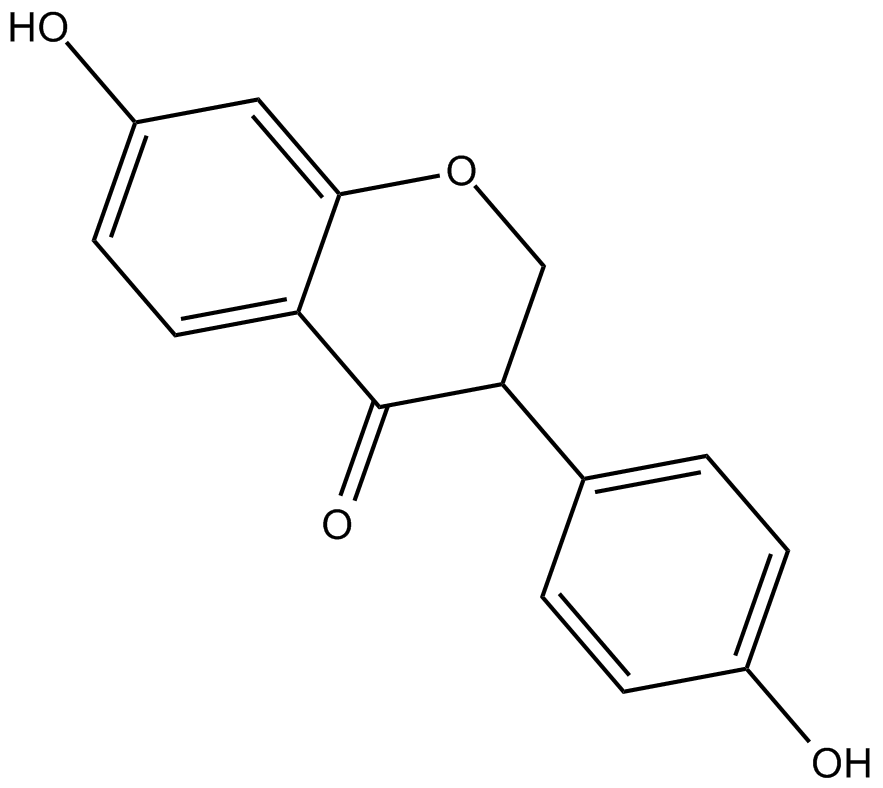 C4020 DihydrodaidzeinSummary: estrogen receptor agonist
C4020 DihydrodaidzeinSummary: estrogen receptor agonist

