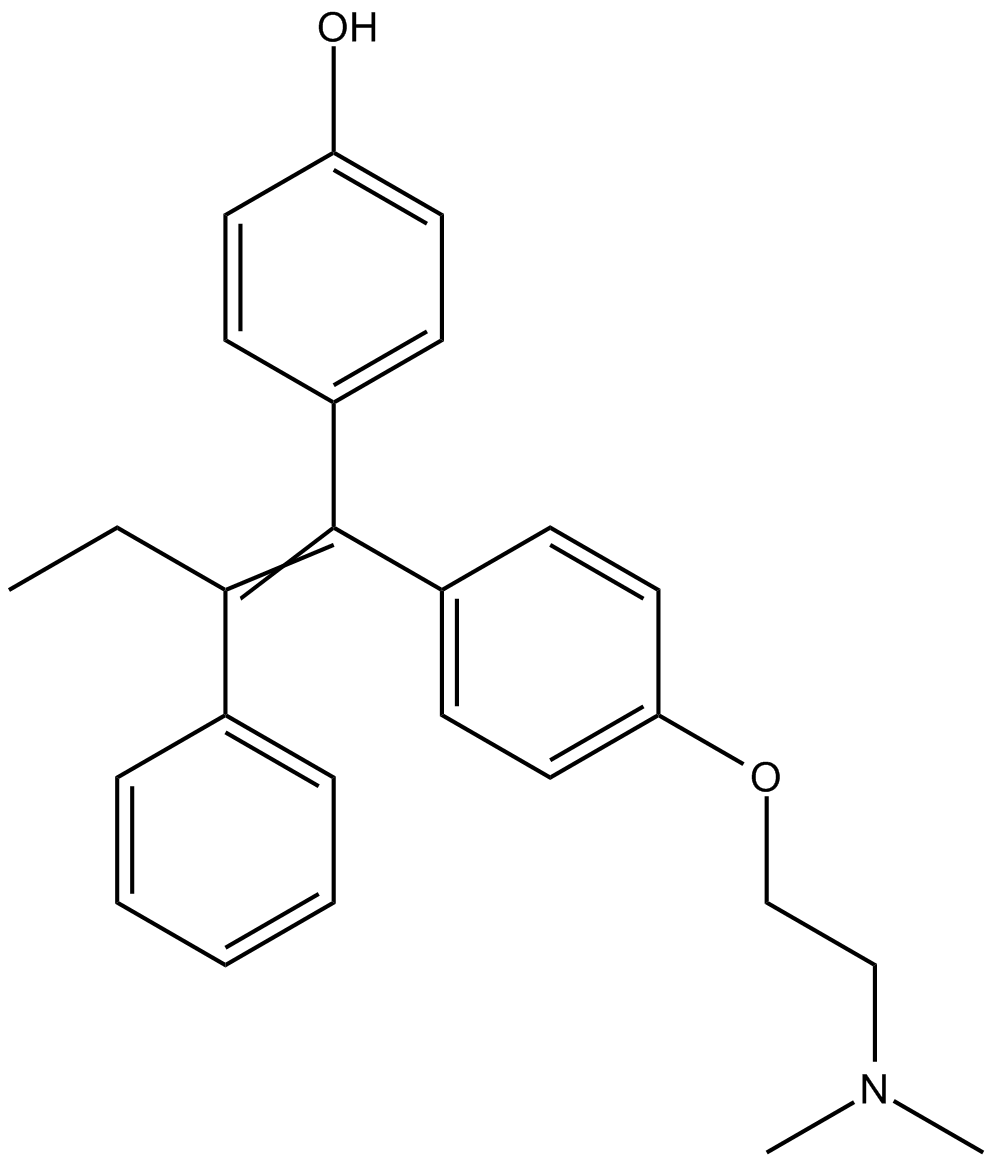
4-Hydroxytamoxifen
IC50: 27 and 18 μM for MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation
4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an estrogen receptor modulator.
Estrogen receptor can be selectively stimulated or inhibited, providing promising therapeutic opportunities for auto-immune diseases, prostate and breast cancer, as well as depression.
In vitro: Previous study was conducted to evaluate the effects of tamoxifen and its active metabolite 4-hydroxytamoxifen on isolated rat cardiac myocyte mechanical function and calcium handling. Results showed that myocytes treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen had similarly to tamoxifen-treated cells to both calcium handling and contractility [1].
In vivo: Previous animal study compared the extent of DNA adduct formation in SD rats treated with seven tamoxifen or 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Results showed that the liver weights and microsomal rates were not changed by tamoxifen or 4-hydroxytamoxifen treatment. Moreover, the uterine weights were significantly decreased and uterine peroxidase activity was marginally decreased in tamoxifen or 4-hydroxytamoxifen treated rats. In addition, hepatic DNA adduct levels in rats treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen did not differ from control rats. Similaryly, the adduct levels in uterus DNA from rats treated with tamoxifen or 4-hydroxytamoxifen were not different from those in control rats [2].
Clinical trial: Previous clinical study showed that the antiproliferative effect of 4-hydroxytamoxifen gel to breast skin was similar to that of oral tamoxifen, but the effects on endocrine and coagulation parameters decreased [3].
References:
[1] Asp ML,Martindale JJ,Metzger JM. Direct, differential effects of tamoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and raloxifene on cardiac myocyte contractility and calcium handling. PLoS One.2013 Oct 24;8(10):e78768.
[2] Beland FA,McDaniel LP,Marques MM. Comparison of the DNA adducts formed by tamoxifen and 4-hydroxytamoxifen in vivo. Carcinogenesis.1999 Mar;20(3):471-7.
[3] Lee O et al. A randomized phase II presurgical trial of transdermal 4-hydroxytamoxifen gel versus oral tamoxifen in women with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Clin Cancer Res.2014 Jul 15;20(14):3672-82.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 387.51 |
| Cas No. | 68392-35-8 |
| Formula | C26H29NO2 |
| Solubility | ≥42 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 4-(1-(4-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)-2-phenylbut-1-en-1-yl)phenol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(c1ccccc1)=C(c(cc1)ccc1O)c(cc1)ccc1OCCN(C)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Isolated rat cardiac myocytes |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0 ~ 10 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen |
|
Applications |
Myocytes treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen responded similarly to tamoxifen-treated cells with regard to both contractility and calcium handling, suggesting an estrogen-receptor independent mechanism is responsible for the effects. At 10 μM, both drugs had a time-dependent effect to abolish cellular contraction. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
C57BL/6 J mice, aged 6 weeks |
|
Dosage form |
6 μg/day Administered subcutaneously for 3 consecutive days |
|
Applications |
Three daily doses of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (6 μg/day) effectively attenuated methamphetamine-induced nigrostriatal dopamine depletions in both sexes of intact and gonadectomized C57BL/6 J mice. 4-OHT alone did not alter the dopamine content levels in the striatum. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Asp ML, Martindale JJ, Metzger JM. Direct, differential effects of tamoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and raloxifene on cardiac myocyte contractility and calcium handling. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e78768. 2. Kuo YM, Chen HH, Shieh CC, et al. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen attenuates methamphetamine-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic toxicity in intact and gonadetomized mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 2003, 87(6): 1436-1443. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure