DNA Damage/DNA Repair
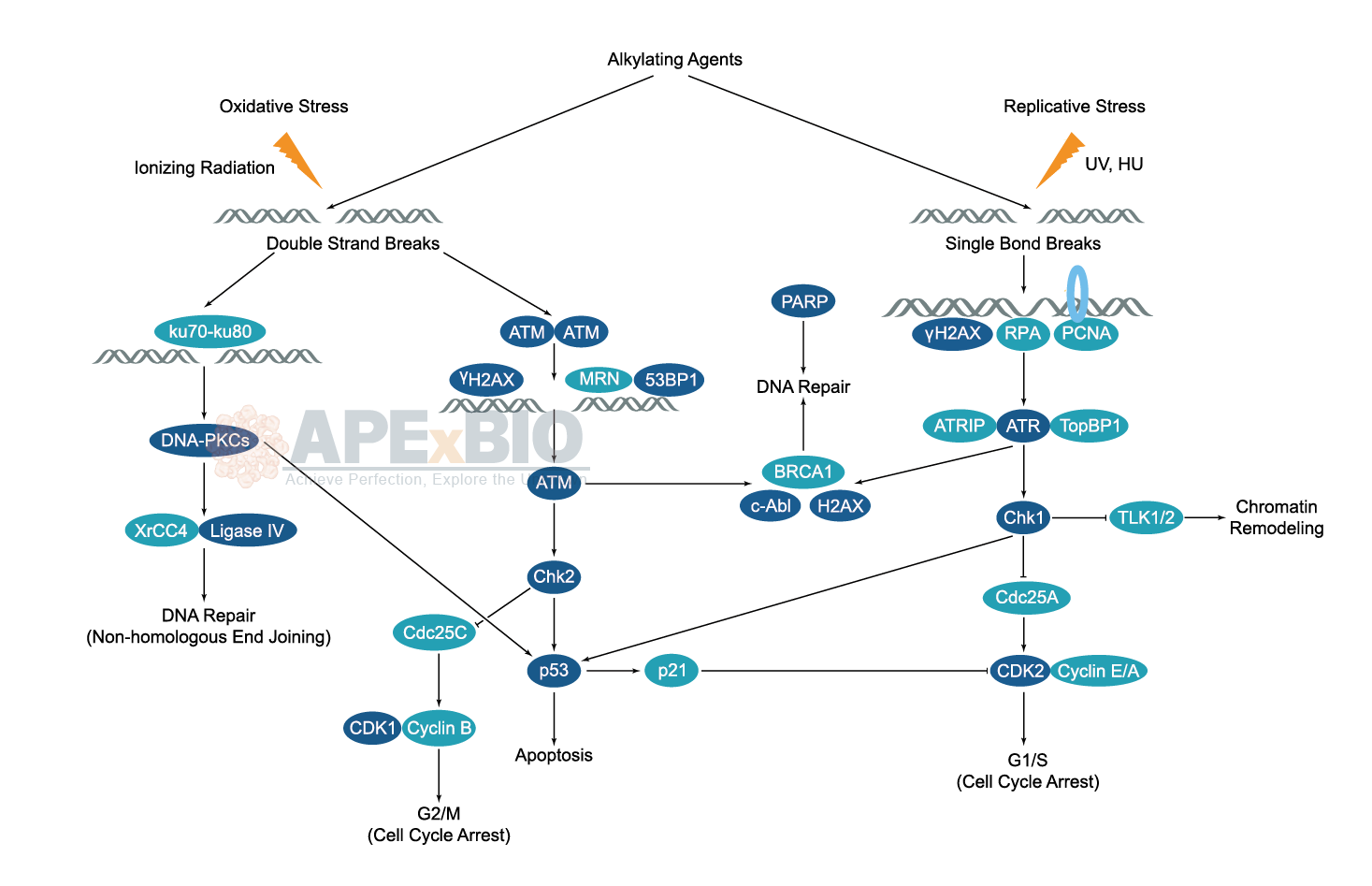
The DNA in a human cell receives tens of thousands of damages per day due to both external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) stress. The exogenous damages are caused by chemical contamination, UV light, ionizing radiation and alkylation/methylation etc, while the endogenous damages are coming from oxidation, alkylation and hydrolysis of bases etc. Since single strand and double strand breaks of DNA will occur after the damage, unrepaired DNA damage leads to cell senescent, apoptosis and malignancies etc. To overcome this threat, cell has developed DNA damage response, to detect DNA damage and mediate its repair.
DNA repair involves multiple mechanisms such as mismatch, base excision, and nucleotide excision repair etc. A group of proteins and pathways are participated in those processes. ATM/ATR kinases and DNA-PK are crucial for the detection of the DNA damage. Chromatin remodelers regulate chromatin accessibility for the DNA repair factors to function. RPA, Rad51 and the fanconi anemia proteins act directly on repairing the DNA damage. p53 network, the RAS GTPase superfamily, and the ubiquitin system also play important part in the DNA damage response. Aberrant DNA damage response is linked to aging, cancer and immune diseases.
-
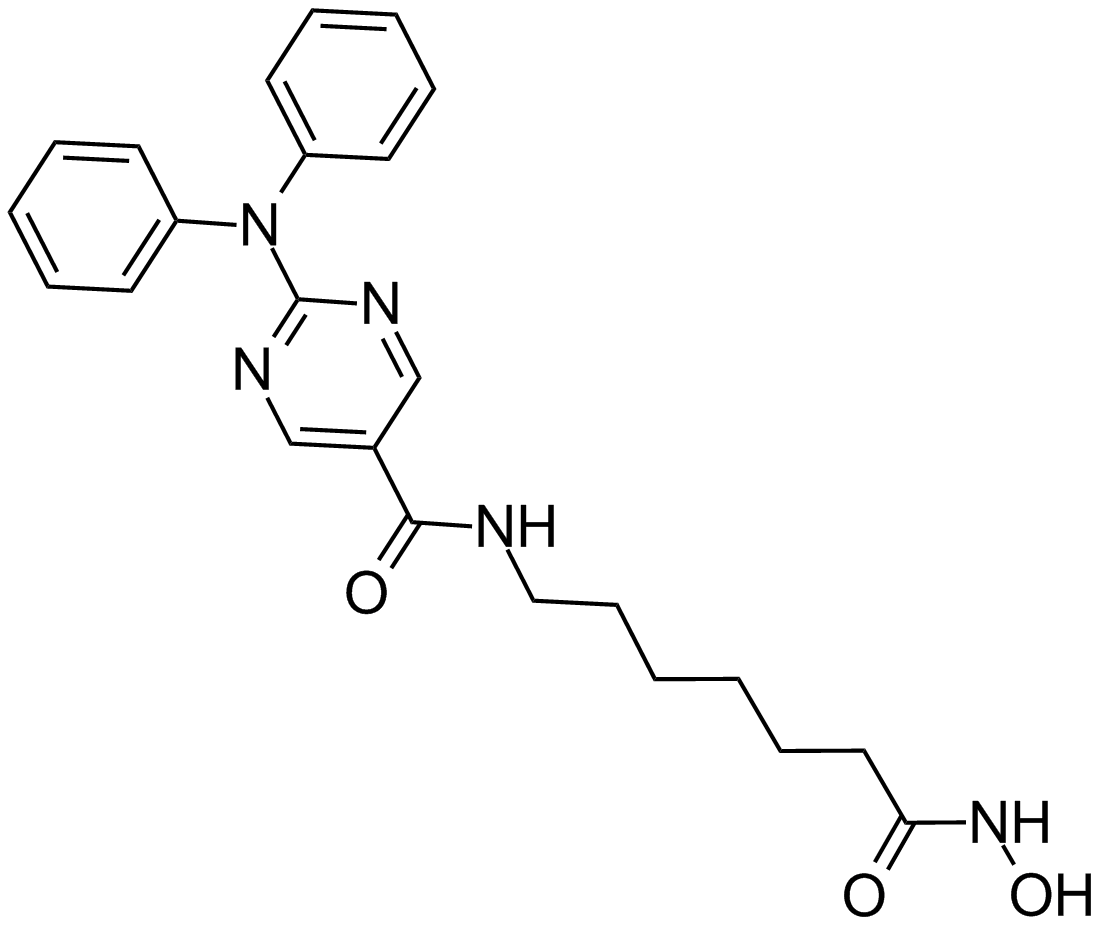 A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor
A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor -
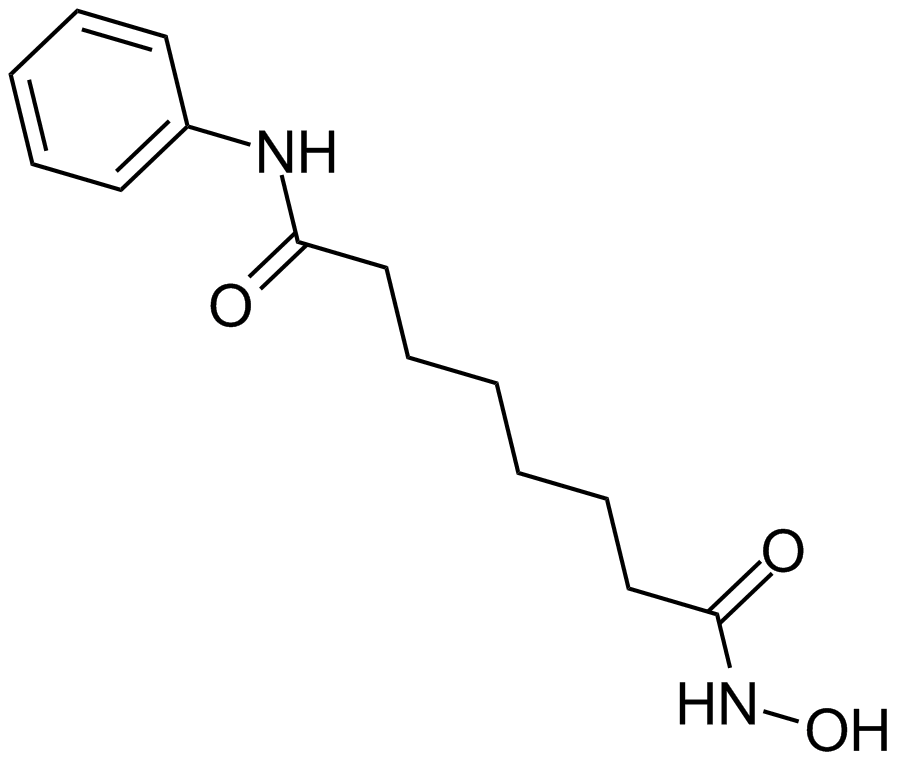 A4084 Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)9 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor
A4084 Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)9 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor -
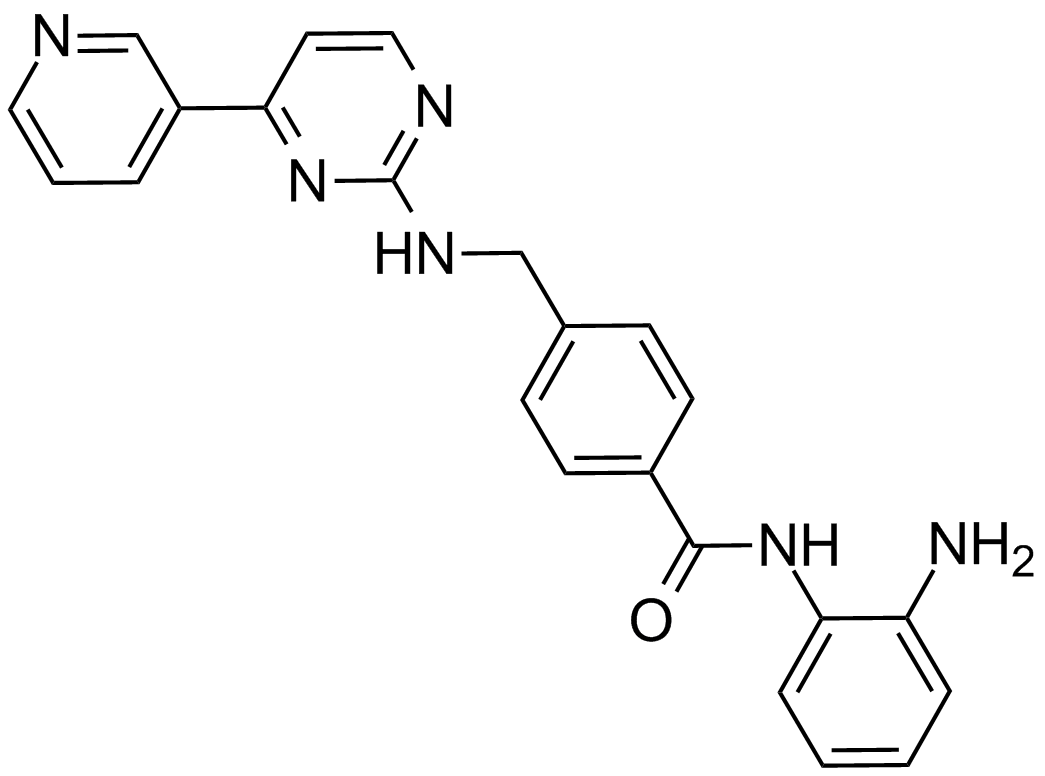 A4089 Mocetinostat (MGCD0103, MG0103)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor,isotype-selective and potent
A4089 Mocetinostat (MGCD0103, MG0103)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor,isotype-selective and potent -
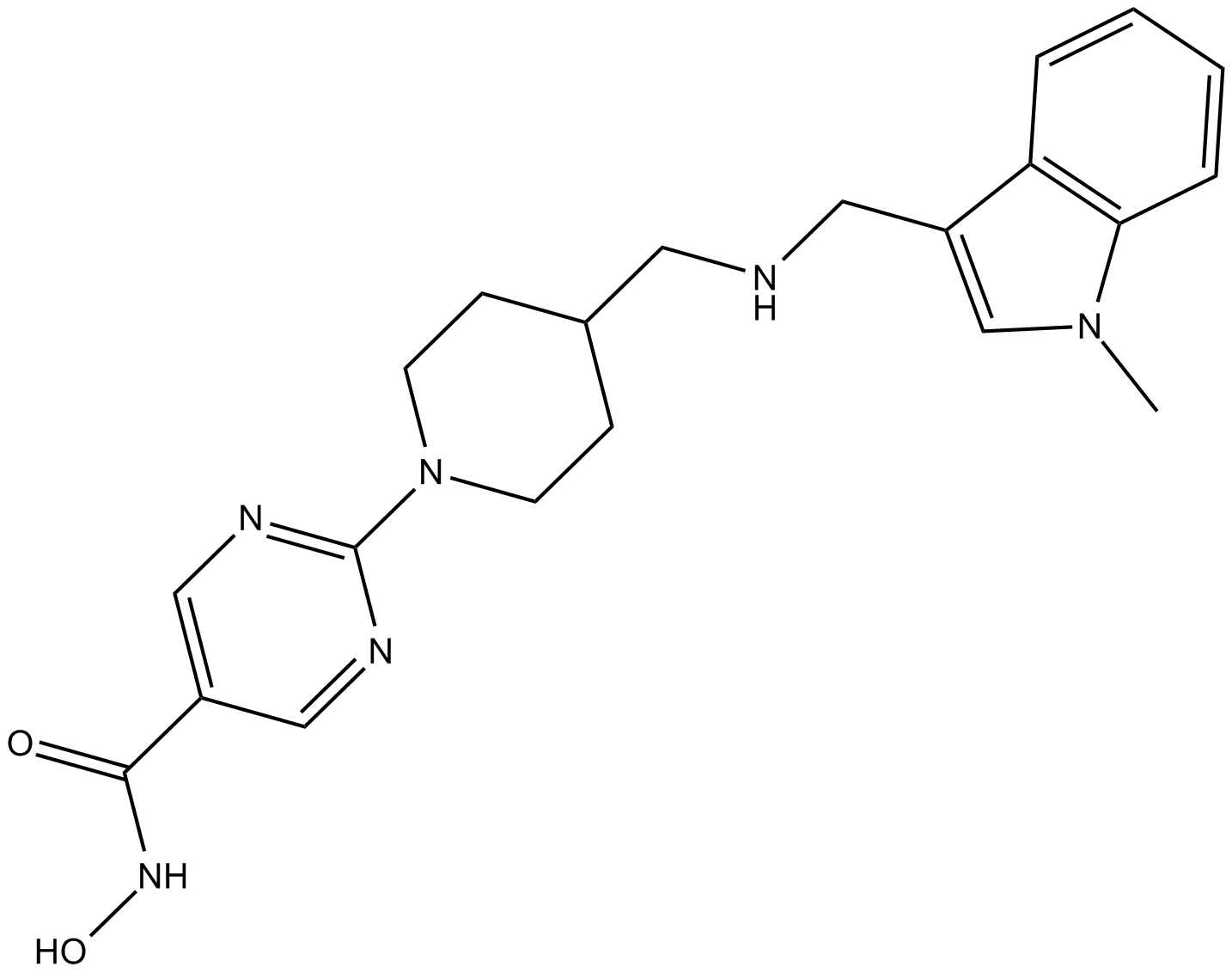 A4090 JNJ-264815853 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Potent HDAC inhibitor
A4090 JNJ-264815853 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Potent HDAC inhibitor -
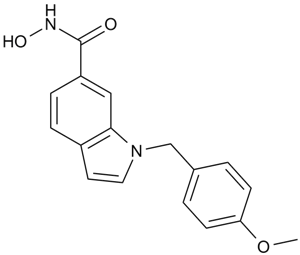 A4091 PCI-340511 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC8 inhibitor,potent and selective
A4091 PCI-340511 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC8 inhibitor,potent and selective -
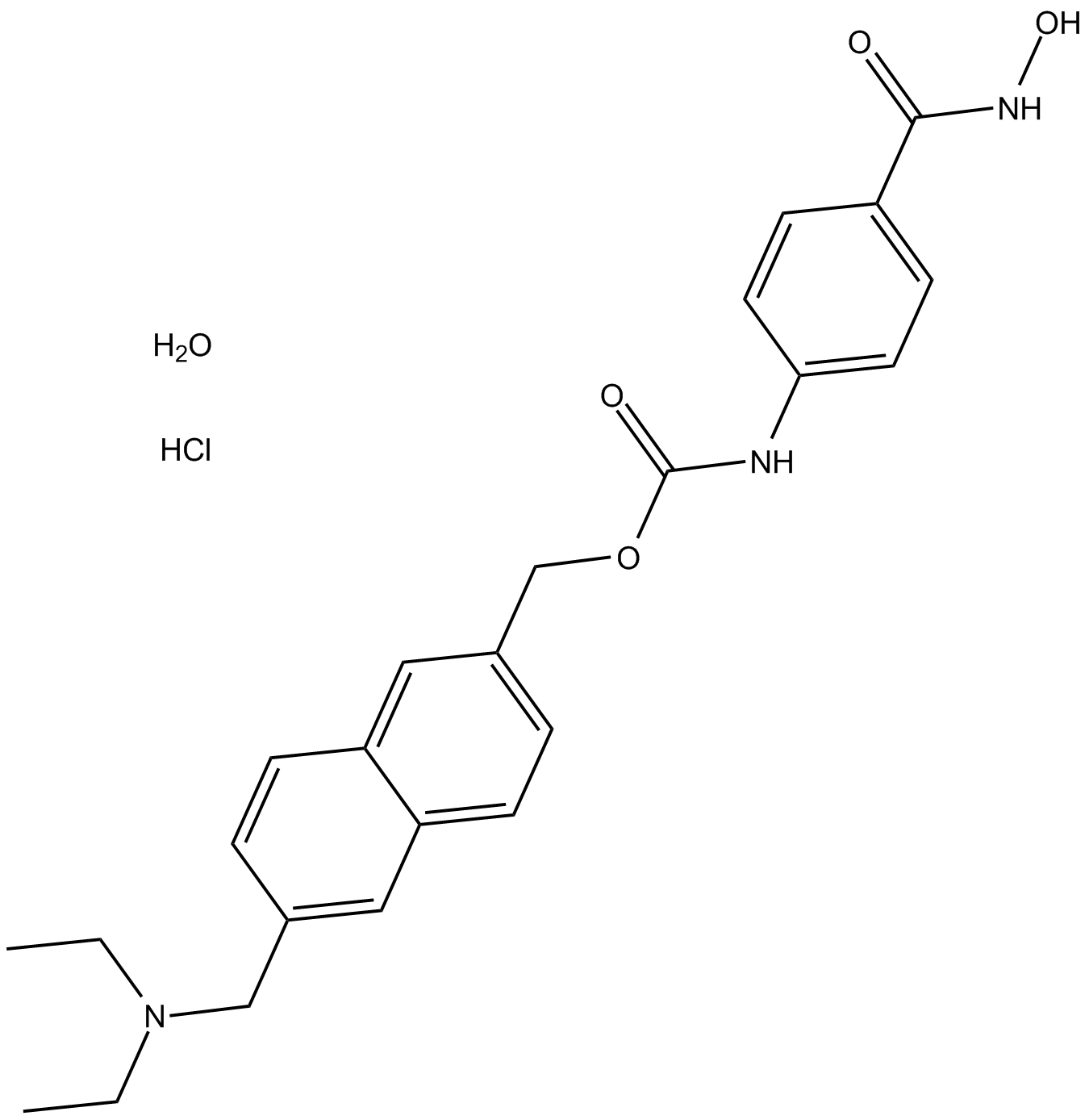 A4093 ITF2357 (Givinostat)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor
A4093 ITF2357 (Givinostat)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor -
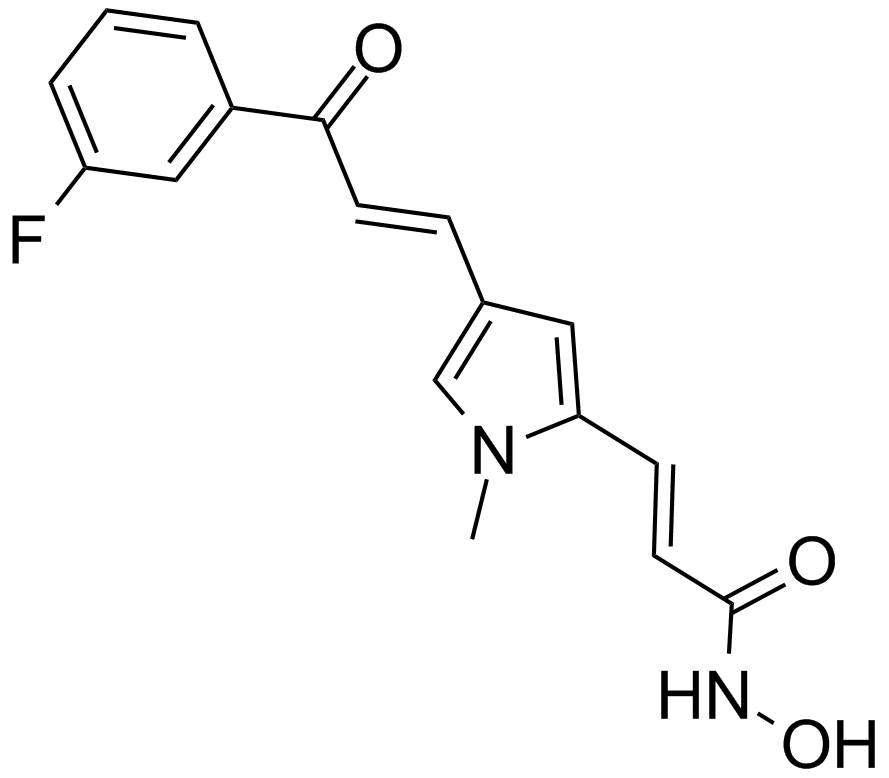 A4094 MC15683 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Class II HDAC inhibitor,potent and selective
A4094 MC15683 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Class II HDAC inhibitor,potent and selective -
 A4096 Belinostat (PXD101)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Hydroxamate-type HDAC inhibitor
A4096 Belinostat (PXD101)2 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Hydroxamate-type HDAC inhibitor -
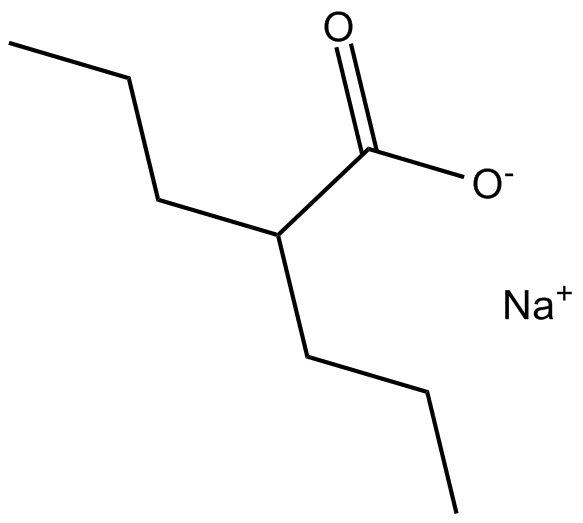 A4099 Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)Target: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor
A4099 Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)Target: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC inhibitor -
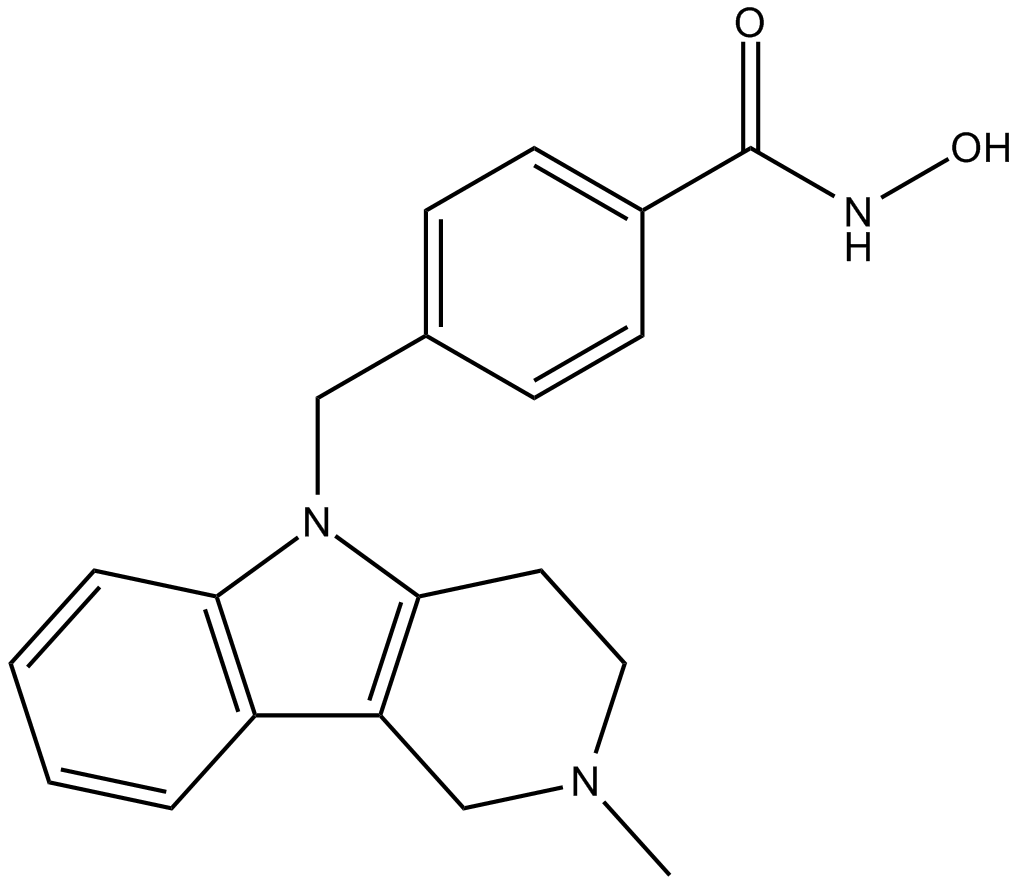 A4101 Tubastatin A6 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC6 inhibitor,potent and selective
A4101 Tubastatin A6 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: HDAC6 inhibitor,potent and selective

