Angiogenesis
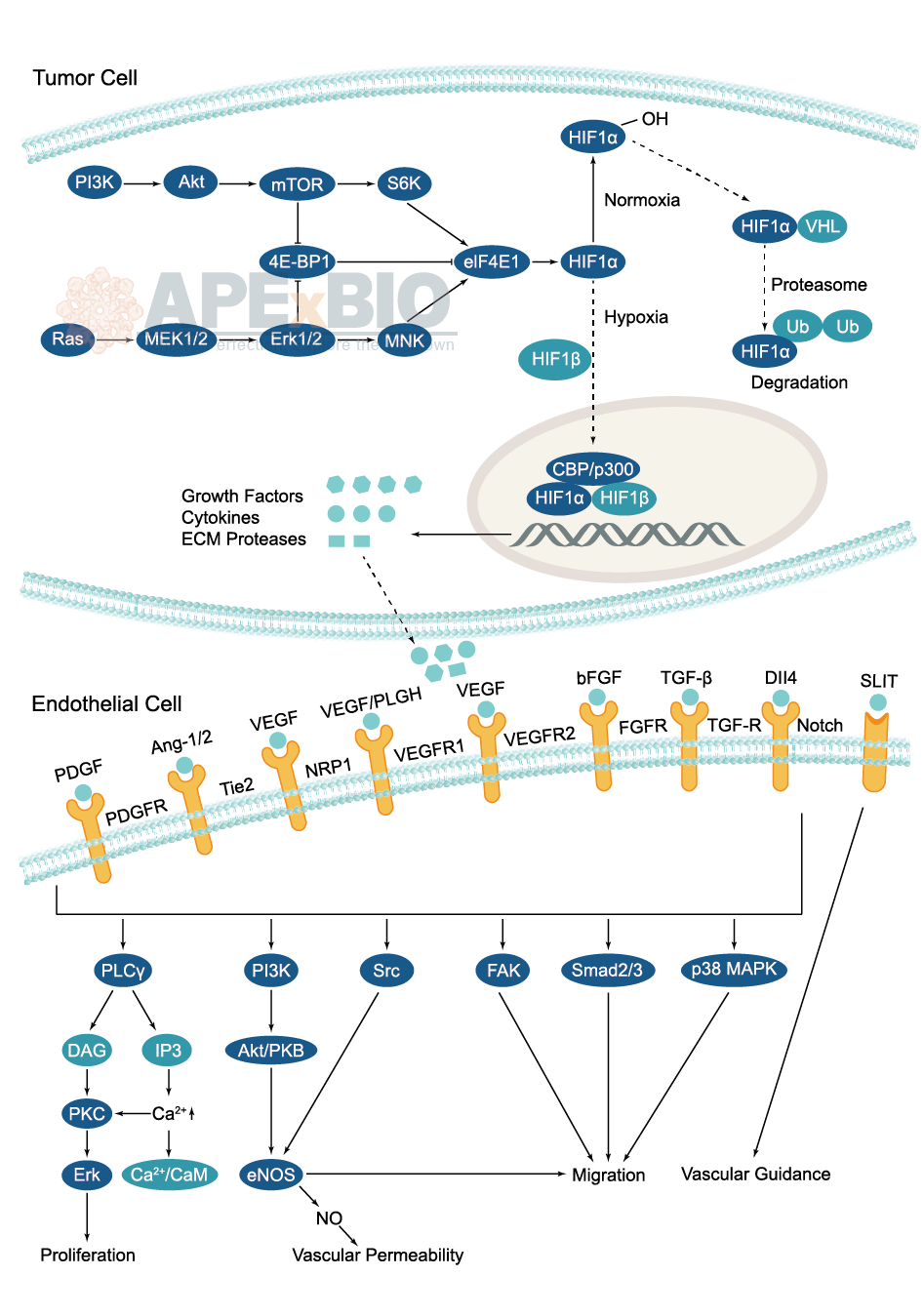
During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
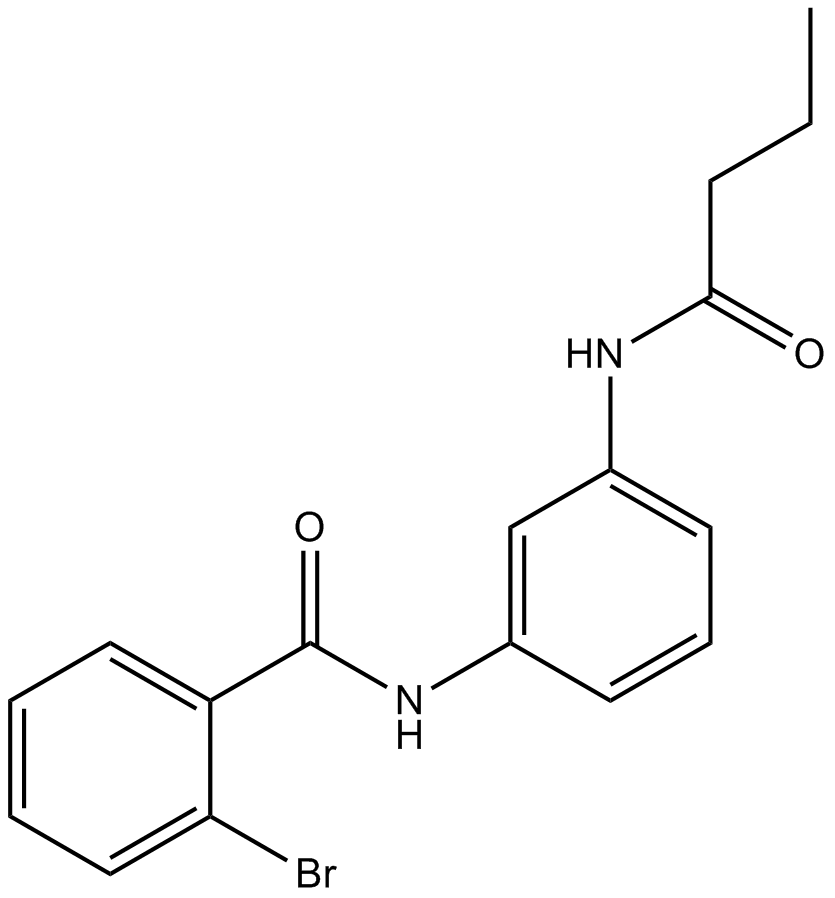 A8229 ML161Target: Protease-Activated ReceptorsSummary: PAR1 inhibitor
A8229 ML161Target: Protease-Activated ReceptorsSummary: PAR1 inhibitor -
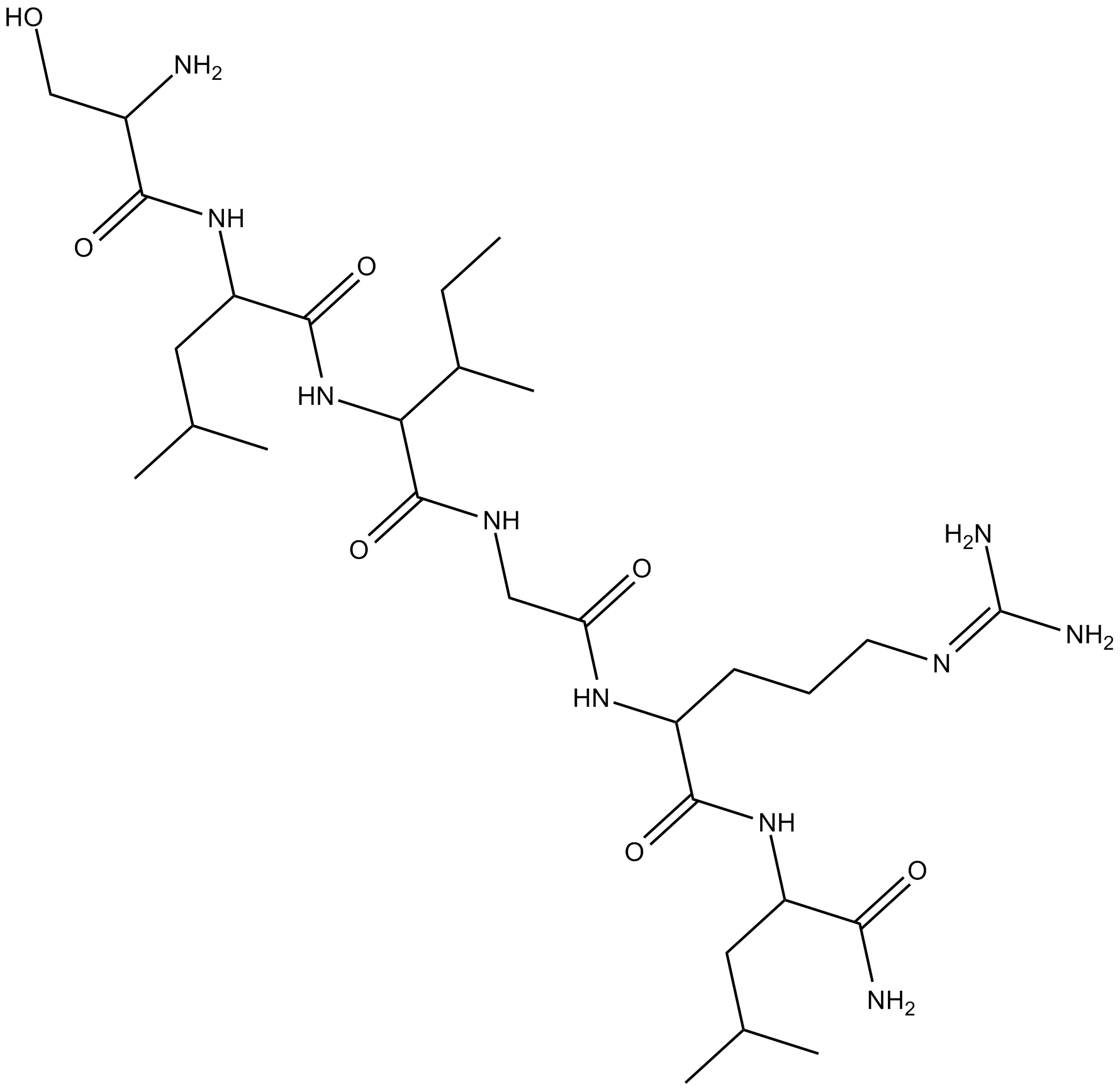 A8665 SLIGRL-NH2Summary: PAR2 activator
A8665 SLIGRL-NH2Summary: PAR2 activator -
 A8666 TFLLR-NH2Summary: PAR1 selective agonist
A8666 TFLLR-NH2Summary: PAR1 selective agonist -
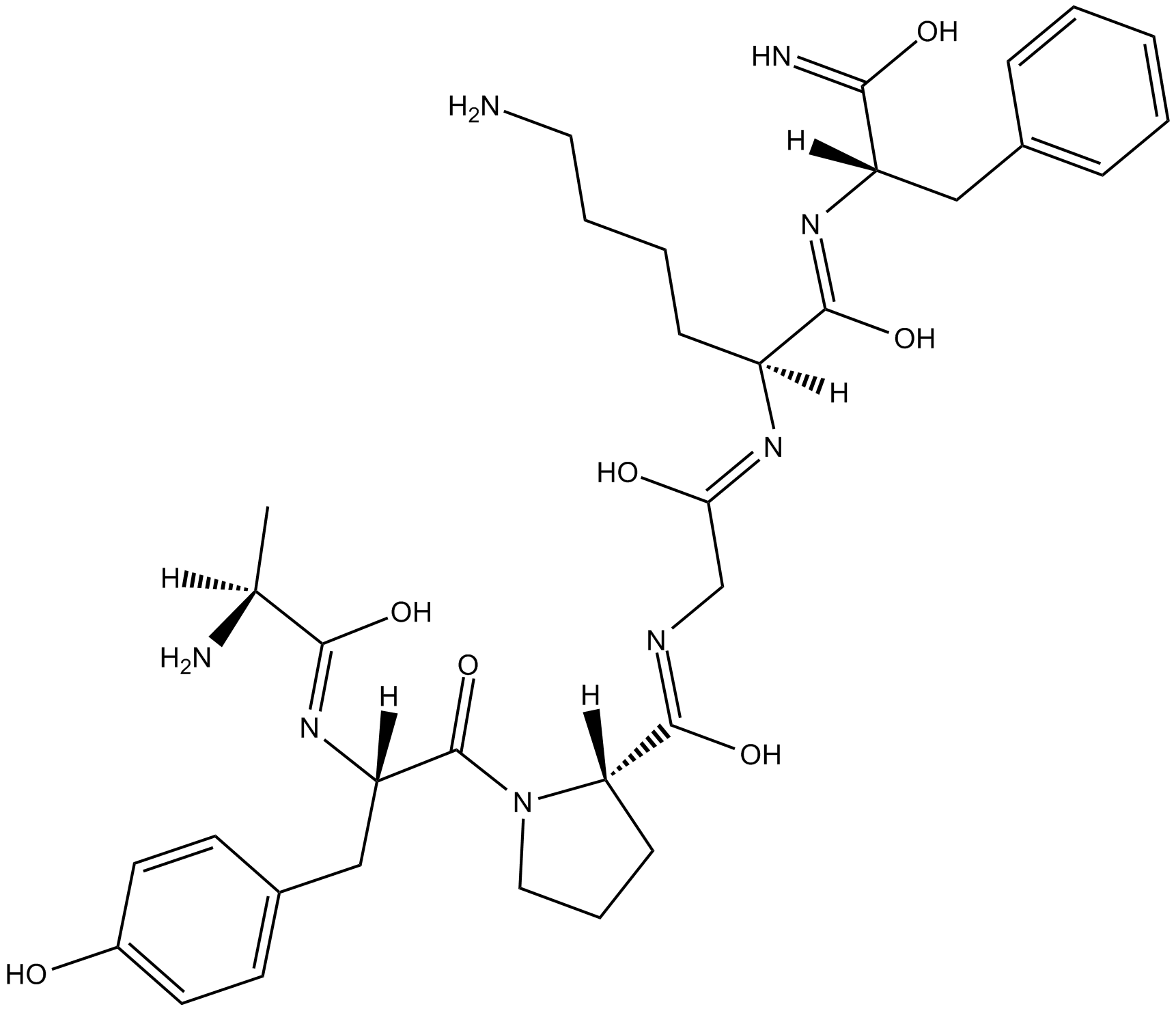 A8667 AY-NH2Summary: Selective PAR4 agonist
A8667 AY-NH2Summary: Selective PAR4 agonist -
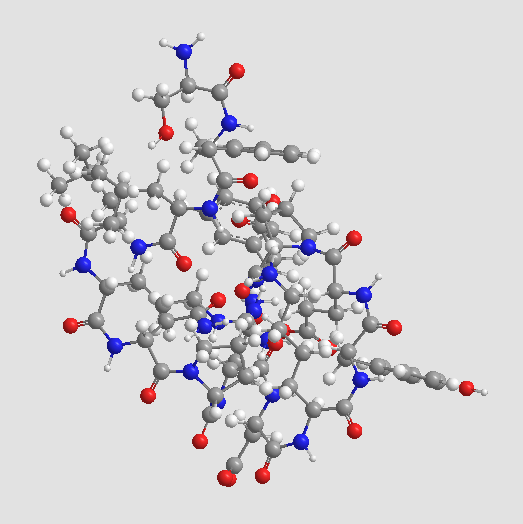 A8668 Thrombin Receptor Agonist PeptideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8668 Thrombin Receptor Agonist PeptideSummary: Protease-activated receptor agonist -
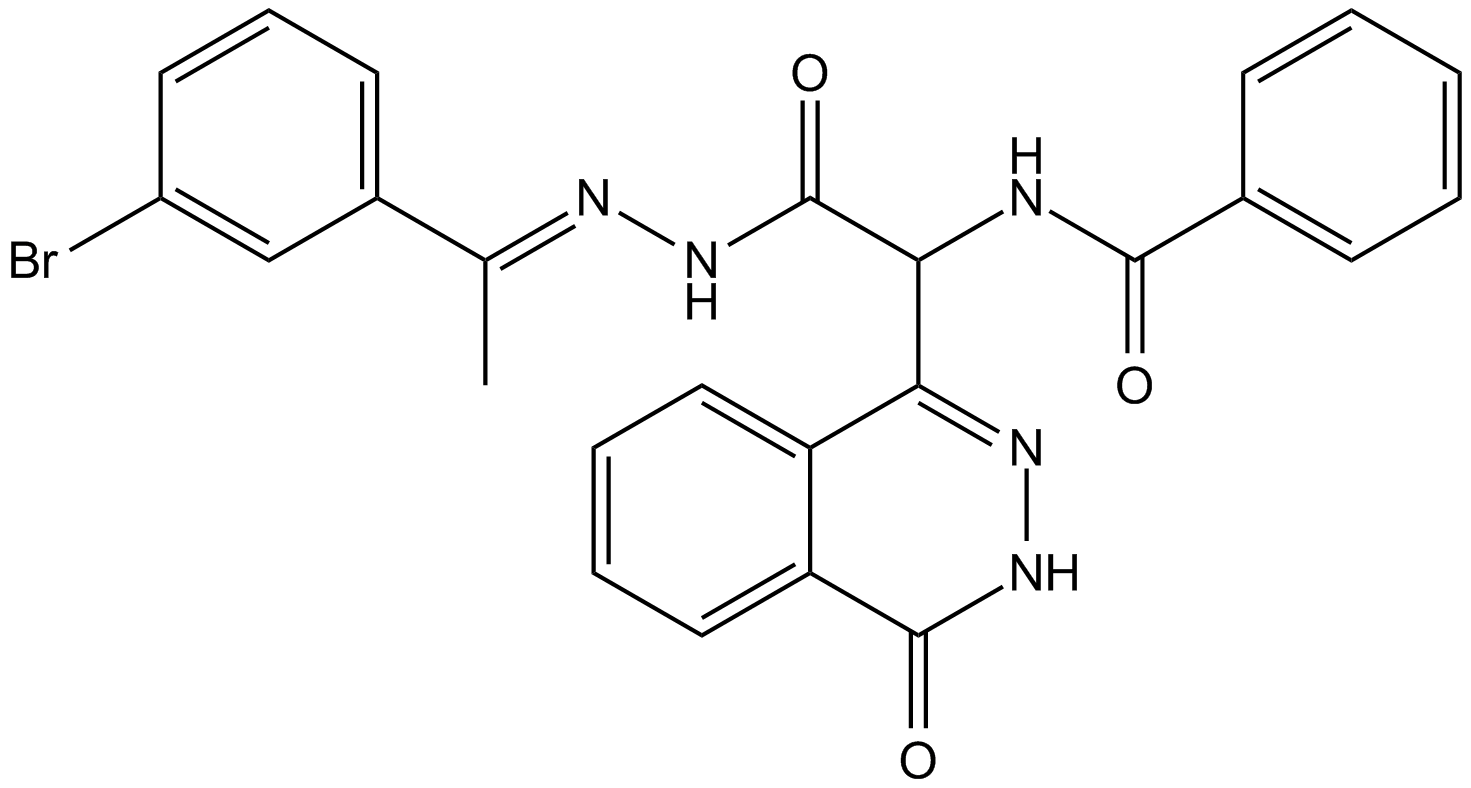 A8669 AC 55541Target: PARSummary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective
A8669 AC 55541Target: PARSummary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective -
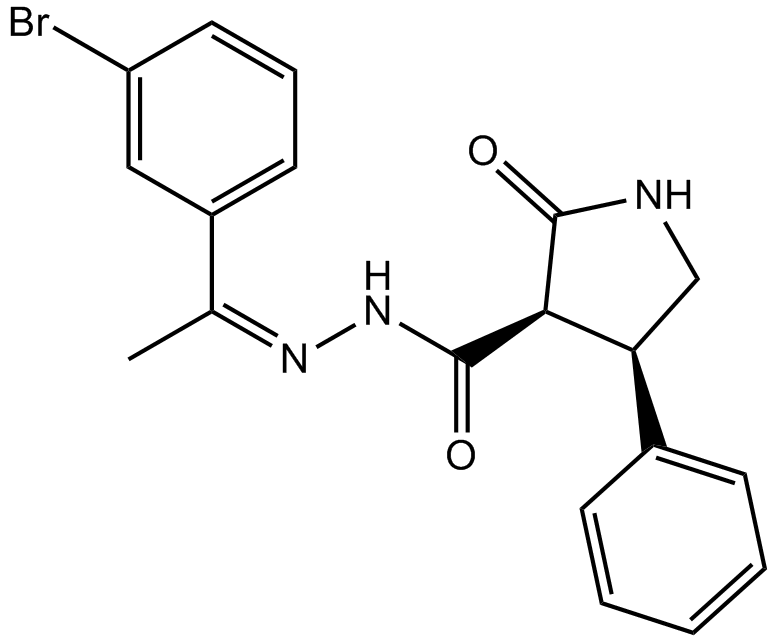 A8670 AC 264613Summary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective
A8670 AC 264613Summary: PAR2 agonist,potent and selective -
 A8671 VKGILS-NH2Summary: control peptide for SLIGKV-NH2, PAR1 agonist
A8671 VKGILS-NH2Summary: control peptide for SLIGKV-NH2, PAR1 agonist -
 A8672 RLLFT-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8672 RLLFT-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist -
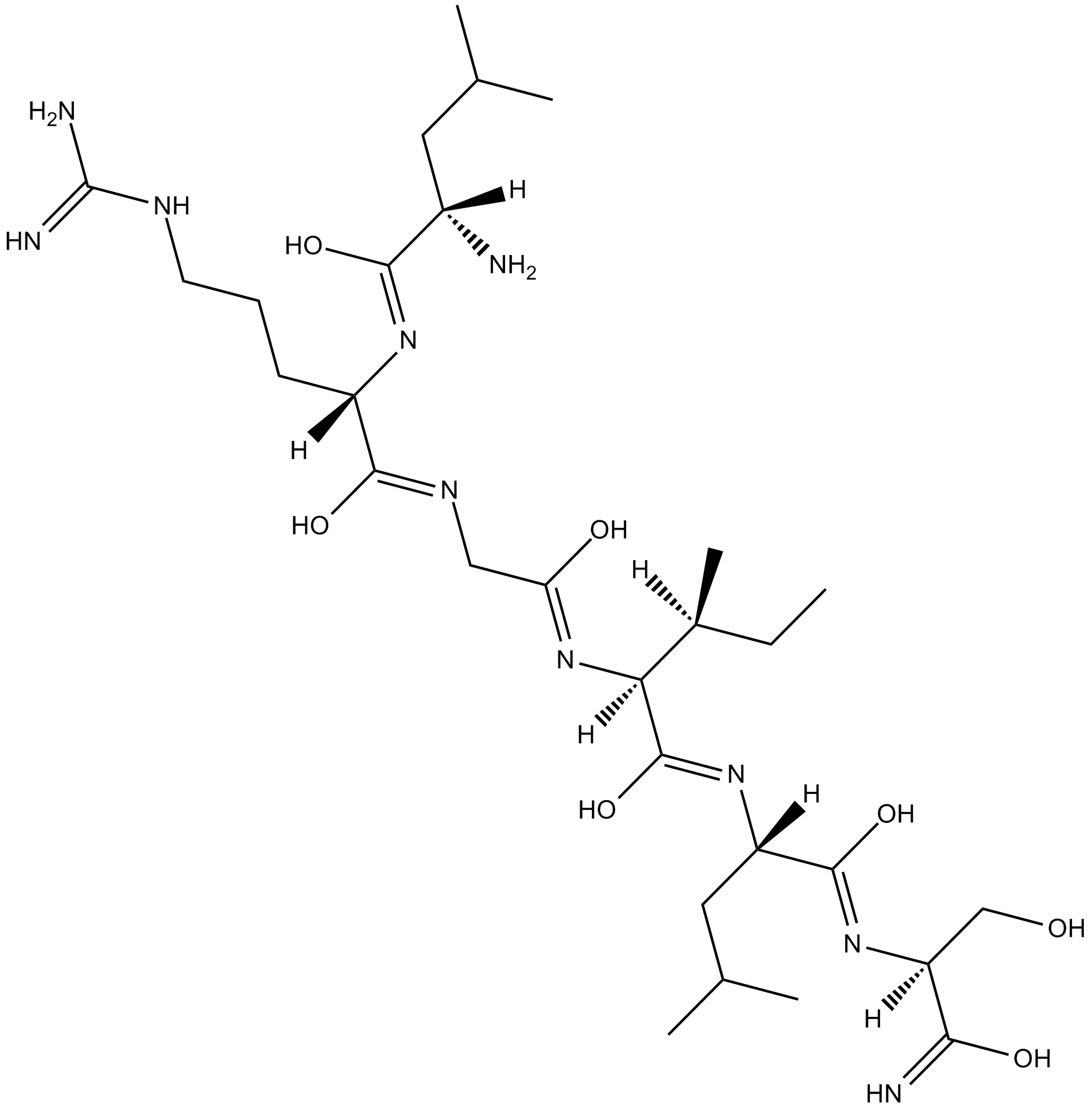 A8673 LRGILS-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist
A8673 LRGILS-NH2Summary: Protease-activated receptor agonist

