Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
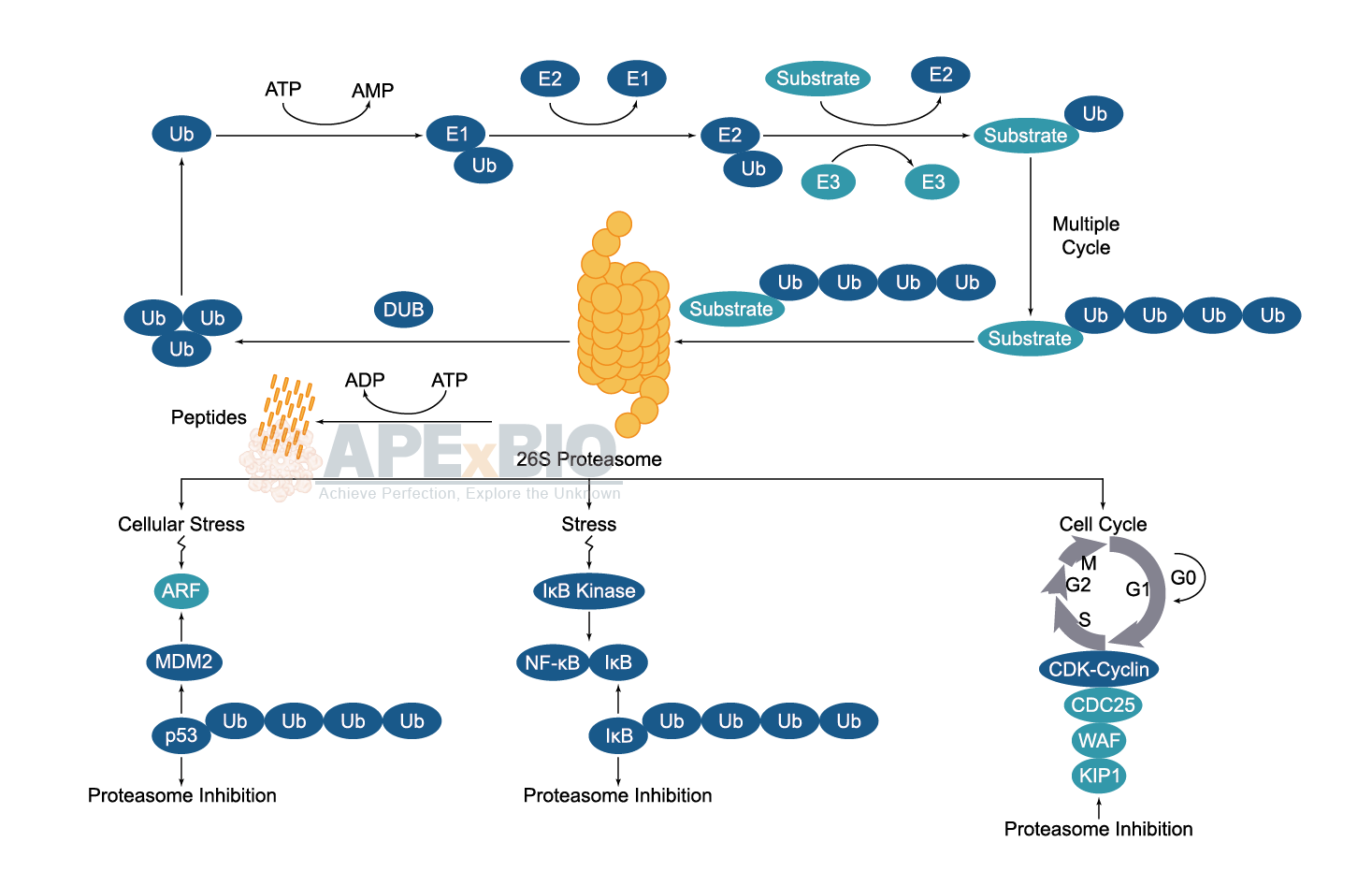
Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
 A8693 C527Target: USP1/USF1 complexSummary: Inhibitor of USP1/USF1 complex
A8693 C527Target: USP1/USF1 complexSummary: Inhibitor of USP1/USF1 complex -
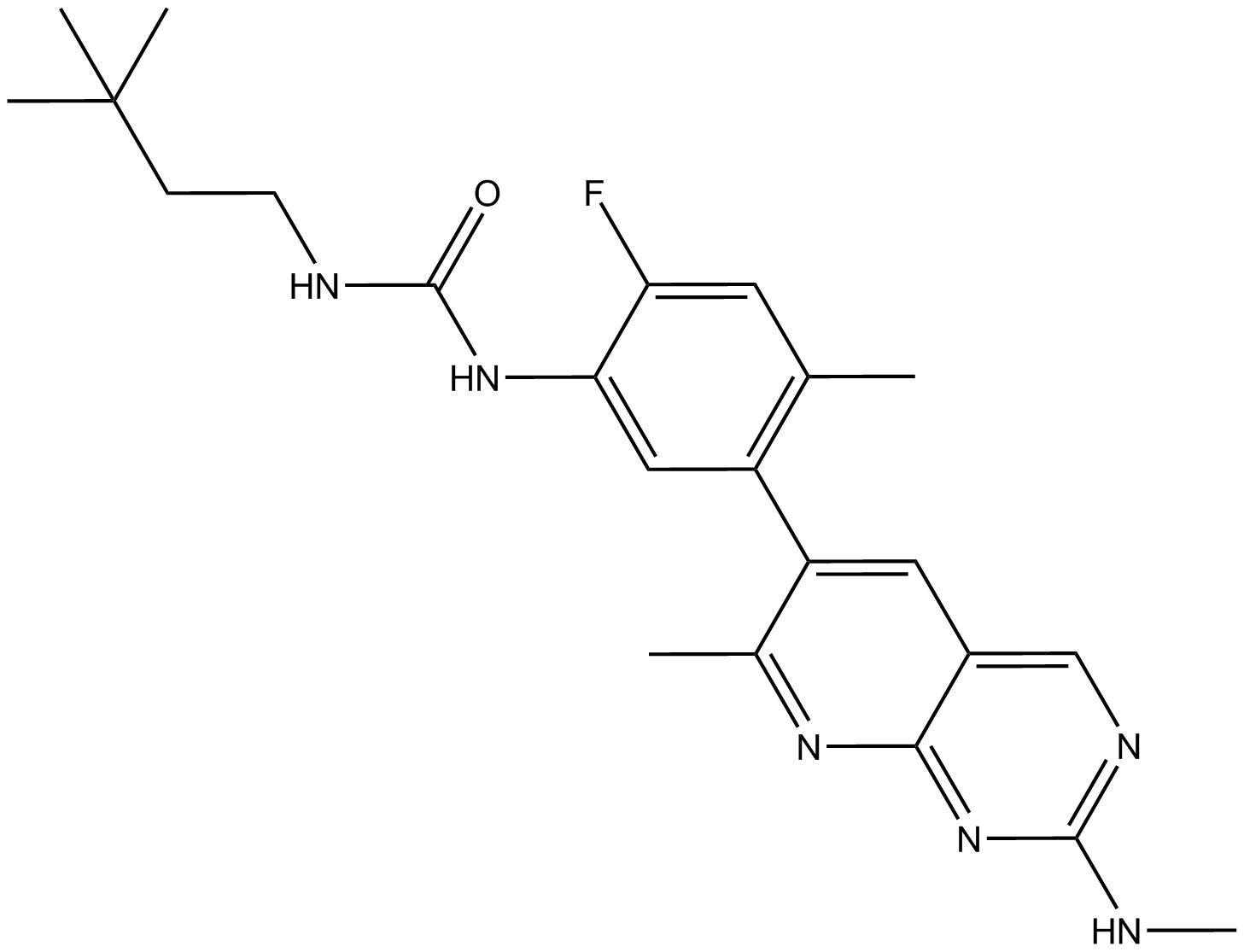 A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor
A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor -
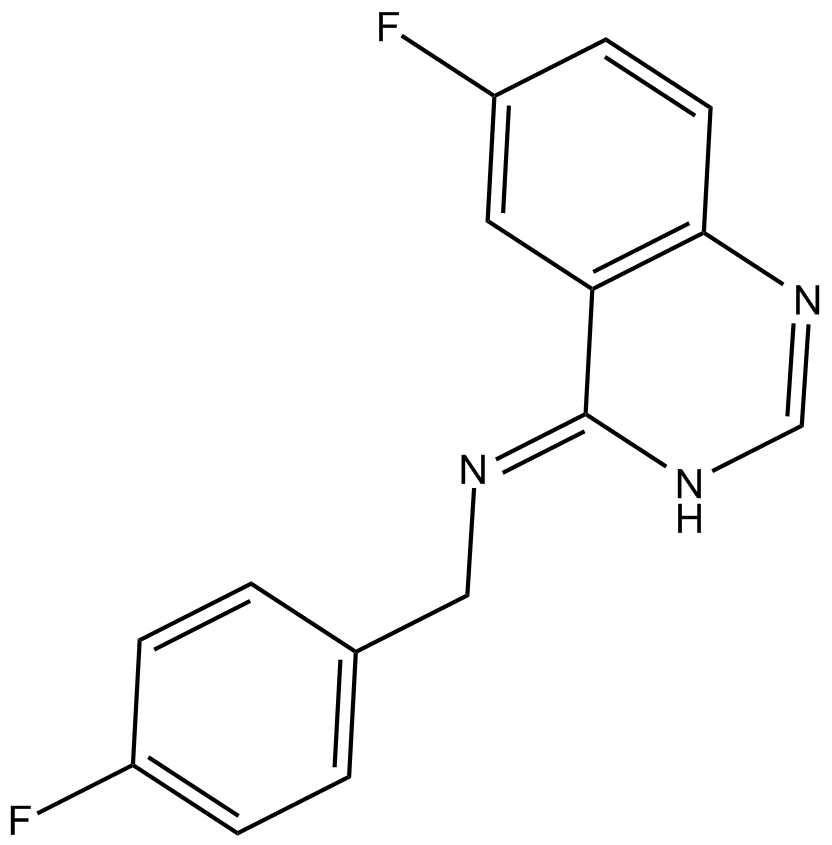 B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor
B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor -
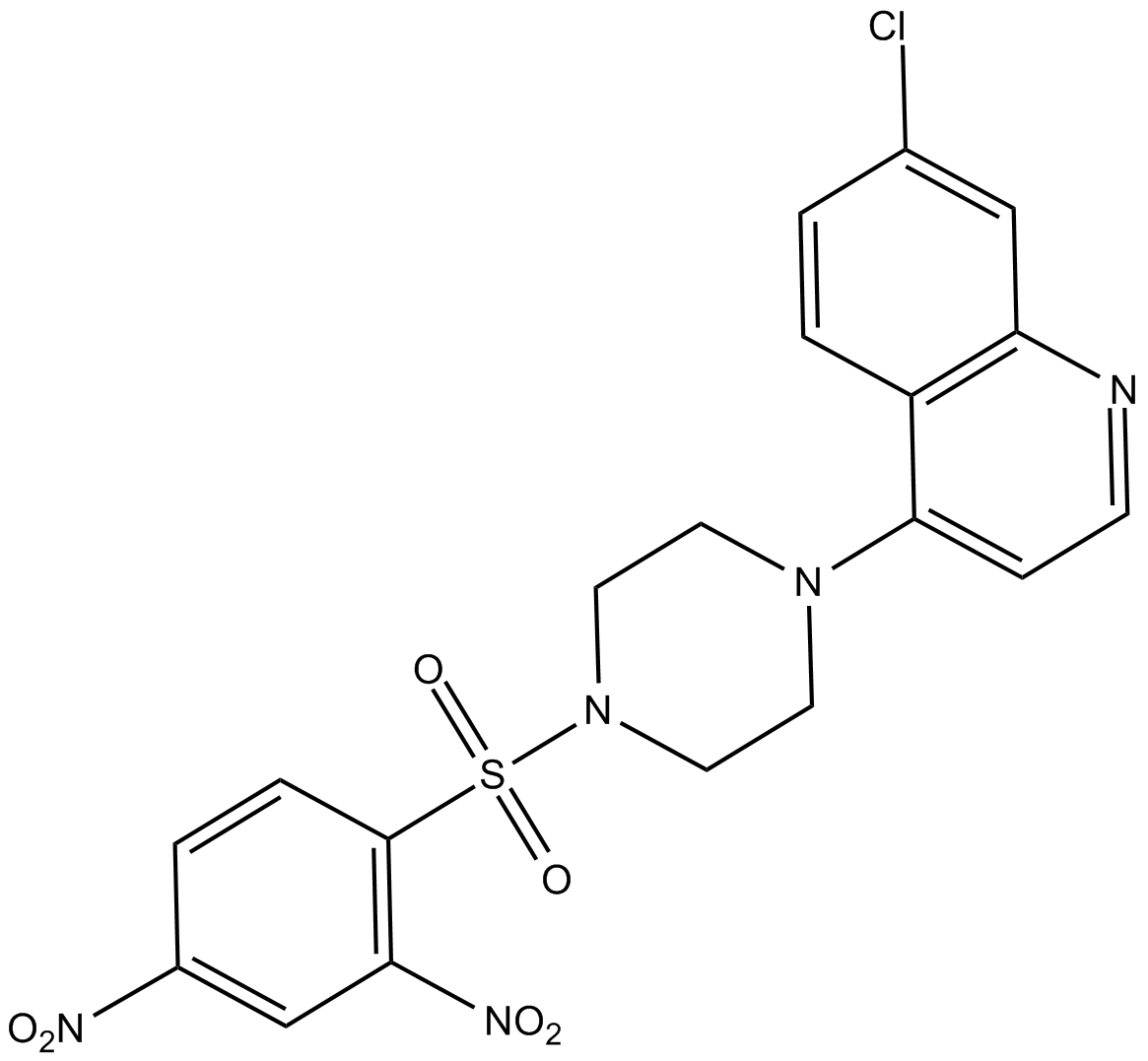 B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor
B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
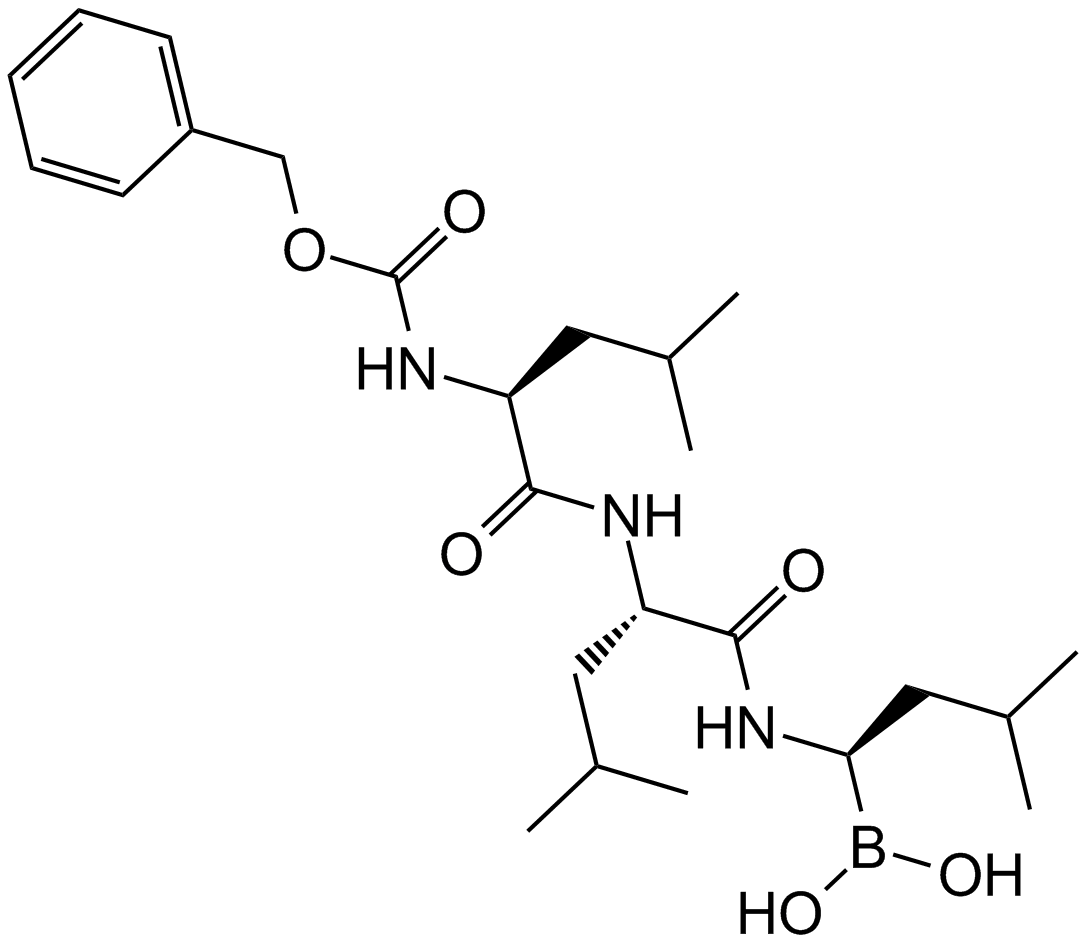 A8179 MG-2621 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor
A8179 MG-2621 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor -
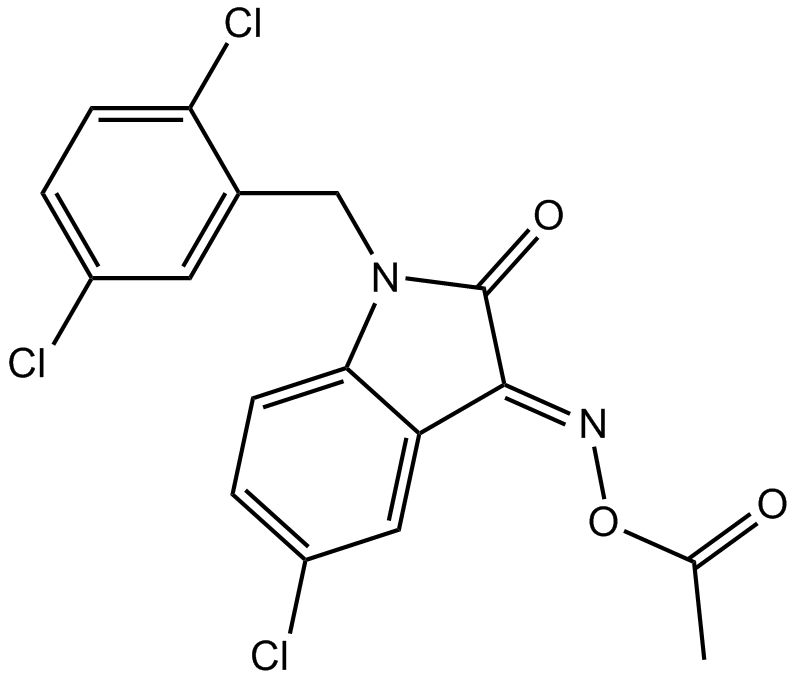 A4003 LDN 57444Target: UCHSummary: UCH-L1 inhibitor,reversible competitve
A4003 LDN 57444Target: UCHSummary: UCH-L1 inhibitor,reversible competitve -
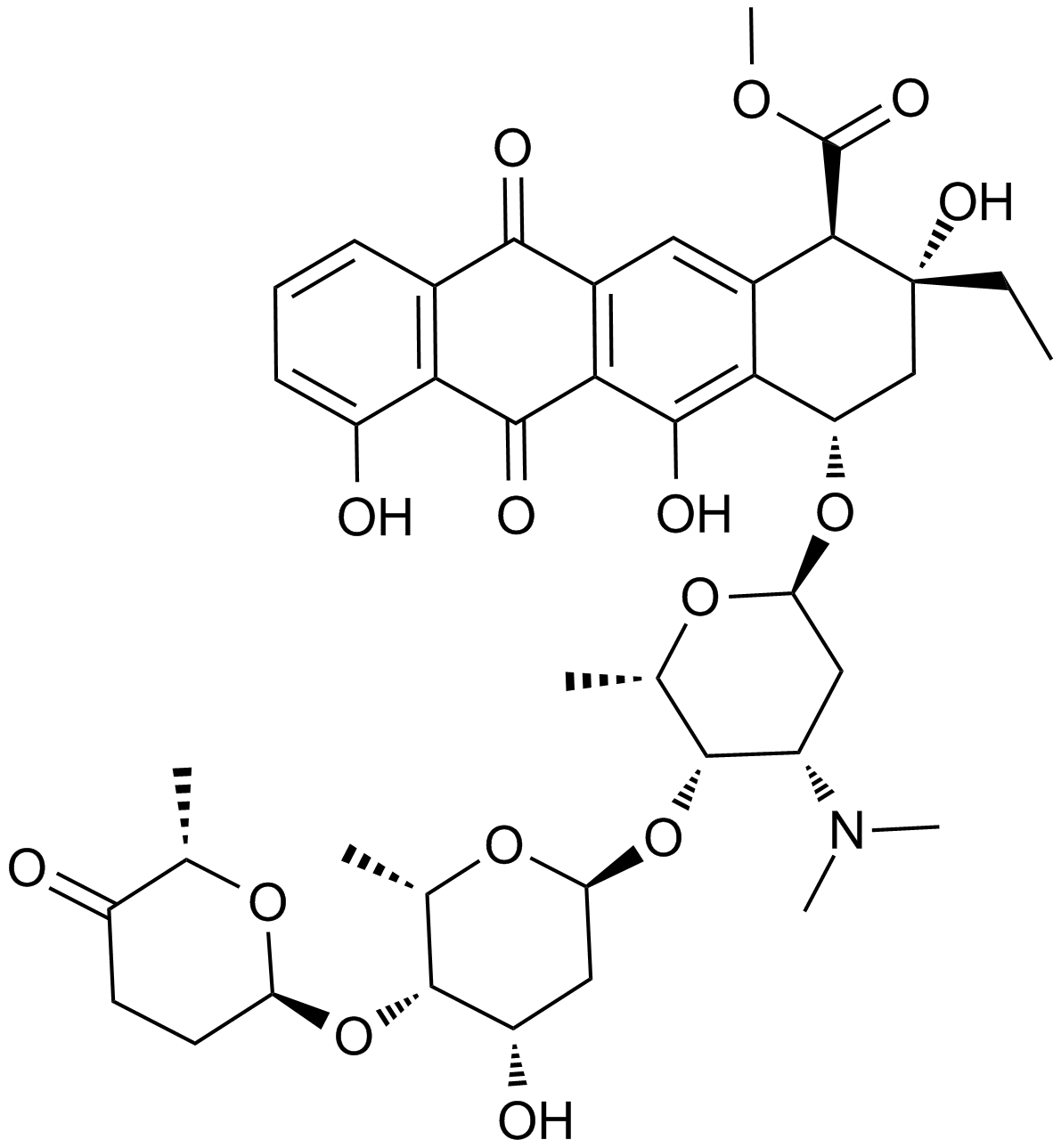 A2601 Aclacinomycin ATarget: TopoisomerasesSummary: Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor
A2601 Aclacinomycin ATarget: TopoisomerasesSummary: Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor -
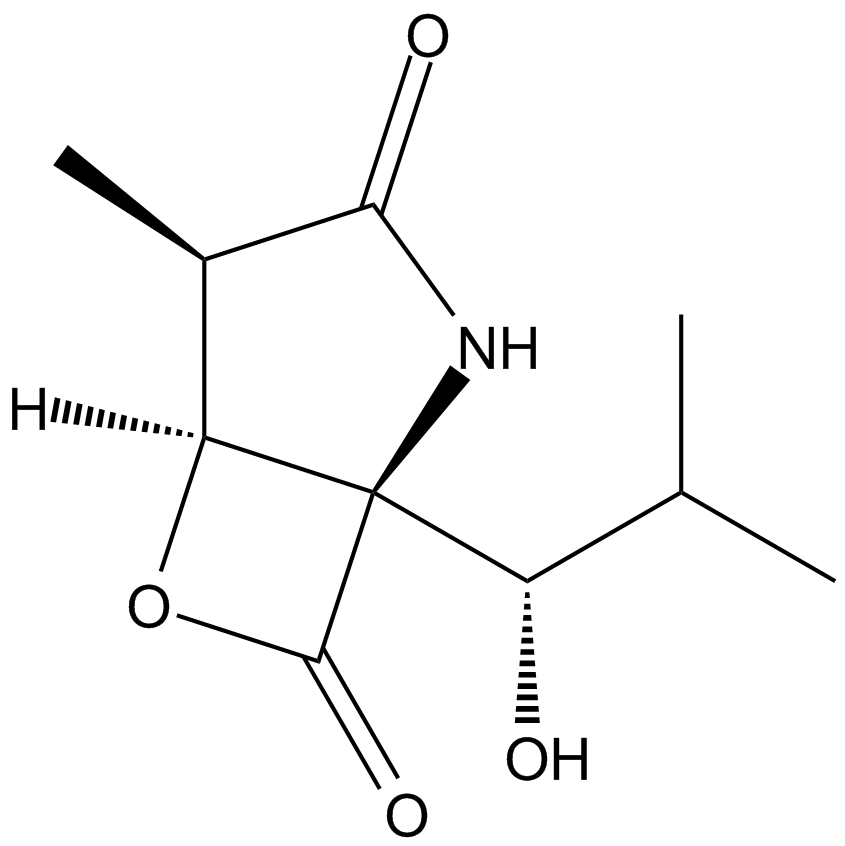 A2578 Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactoneTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor
A2578 Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactoneTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor -
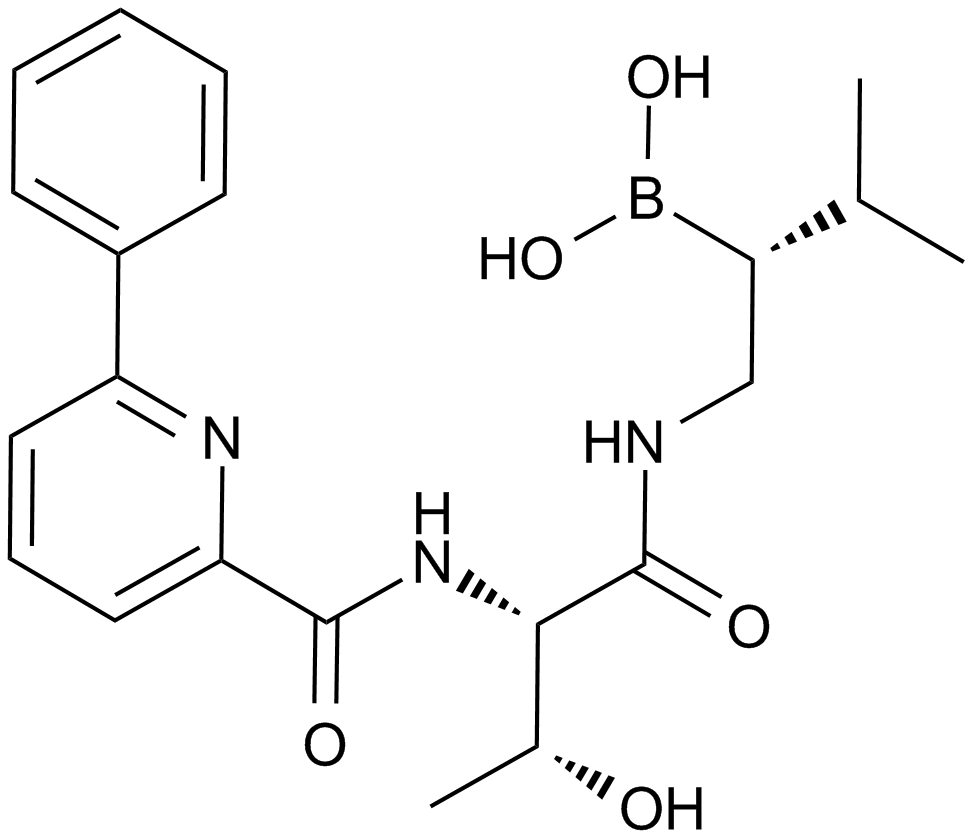 A4009 CEP-187701 CitationSummary: Proteasome inhibitor
A4009 CEP-187701 CitationSummary: Proteasome inhibitor -
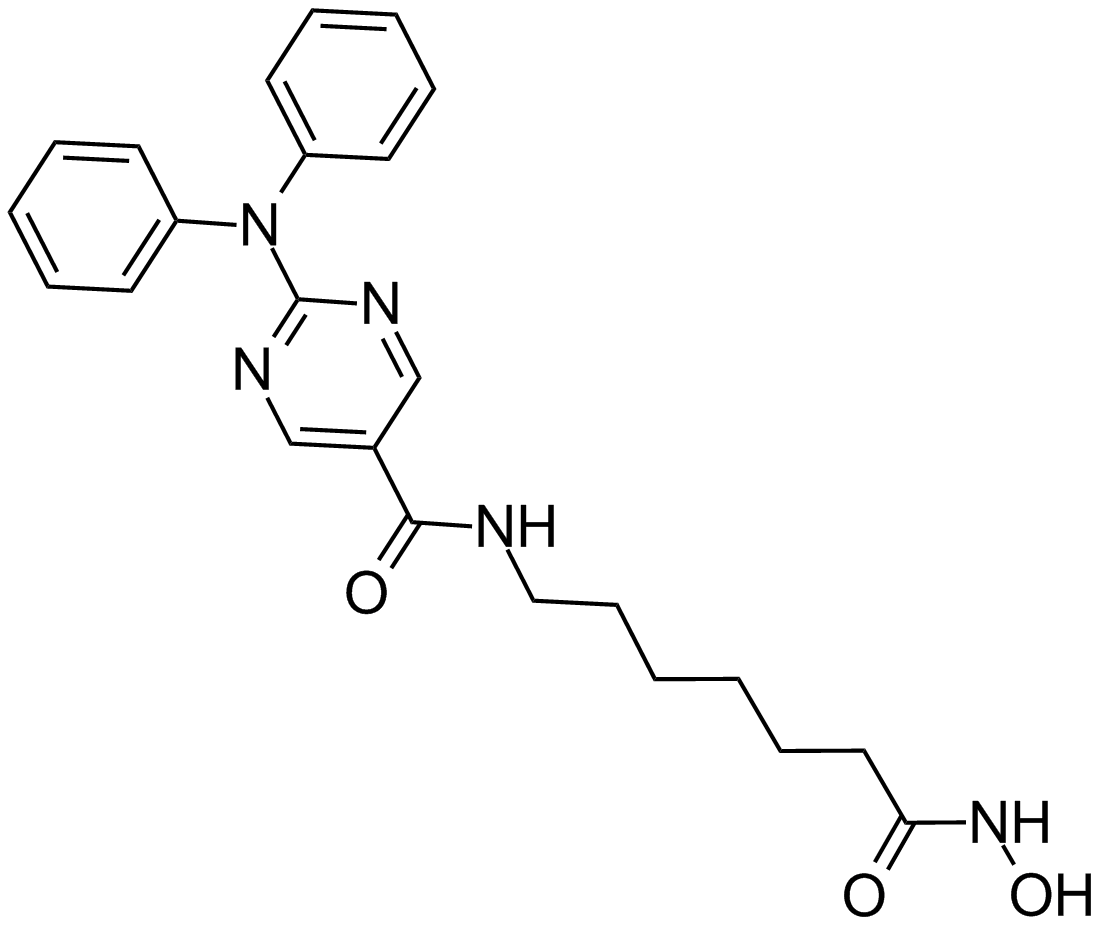 A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor
A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor

