Proteases
Proteases, also known as peptidases or proteolytic enzymes, consists of a large number of enzymes catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds and subsequently resulting in the degradation of protein substrates into amino acids. Proteases are involved in a wide range of human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Thus numerous proteases inhibitors (small molecules and proteins) have been identified to block activity of proteases. Proteases inhibitors can be classified into different types based on the class of proteases they inhibit through two general mechanisms, irreversible “trapping” reactions and reversible tight-binding reactions. Proteases inhibitors have been used as diagnostic or therapeutic agents for the treatment of proteases-related diseases.
-
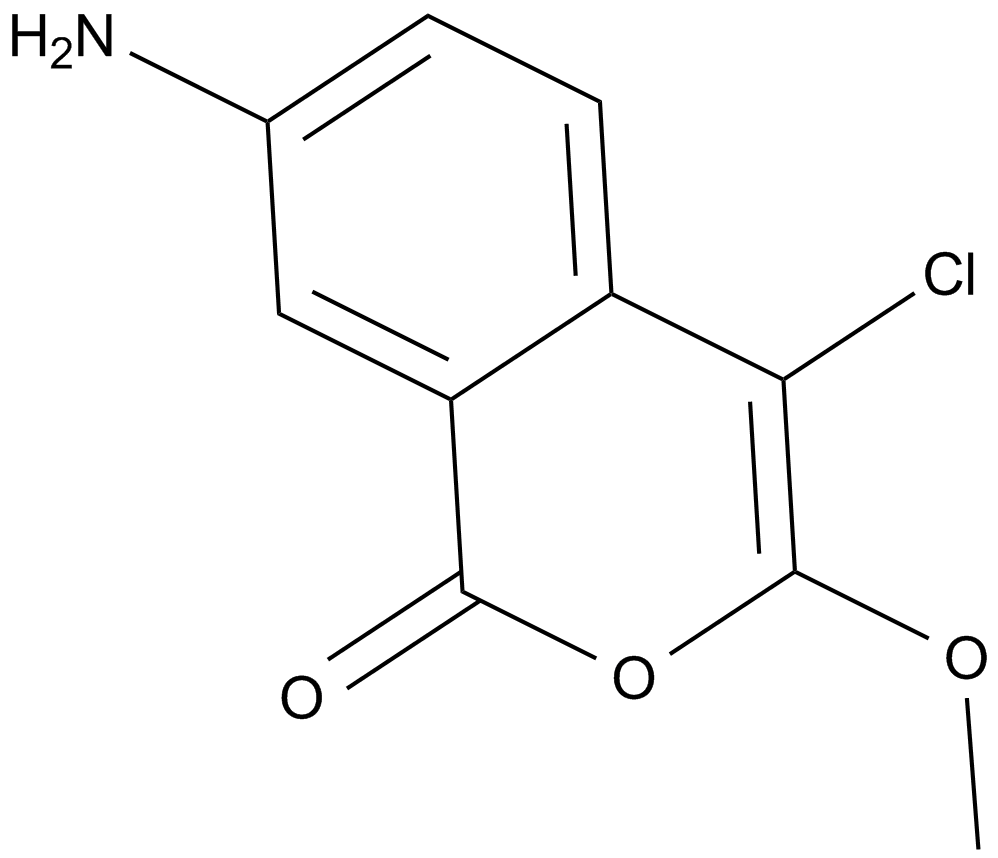 A4403 JLK 6Summary: γ-secretase inhibitor
A4403 JLK 6Summary: γ-secretase inhibitor -
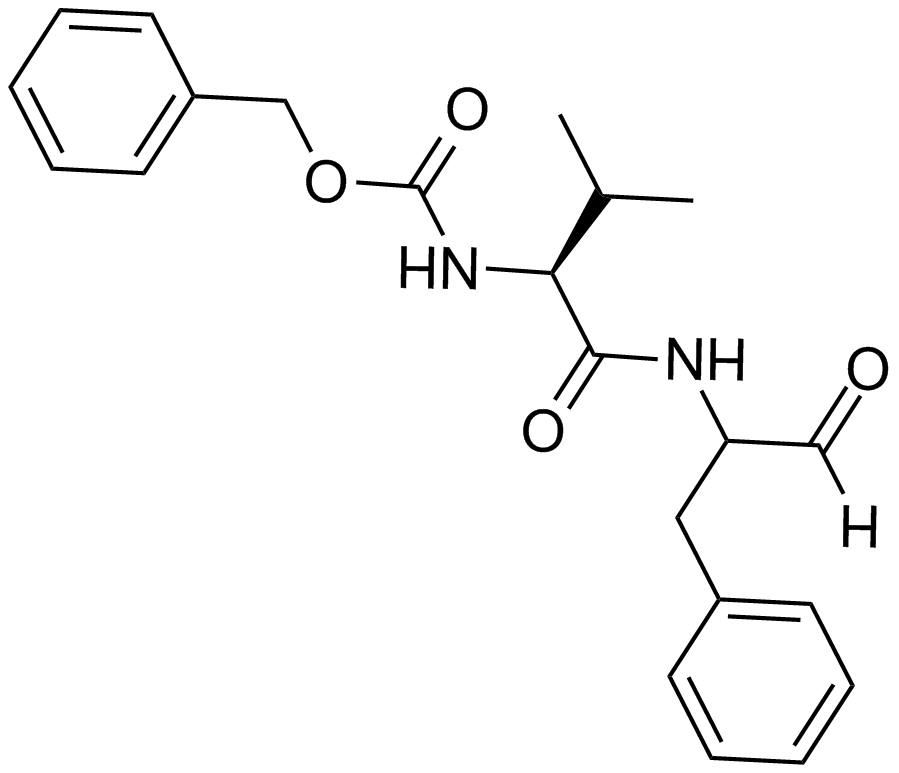 A4412 MDL 28170Target: Cathepsins|CalpainsSummary: Calpain and cathepsin B inhibitor, selective
A4412 MDL 28170Target: Cathepsins|CalpainsSummary: Calpain and cathepsin B inhibitor, selective -
 A4413 PD 150606Target: CalpainsSummary: Non-peptide calpain inhibitor
A4413 PD 150606Target: CalpainsSummary: Non-peptide calpain inhibitor -
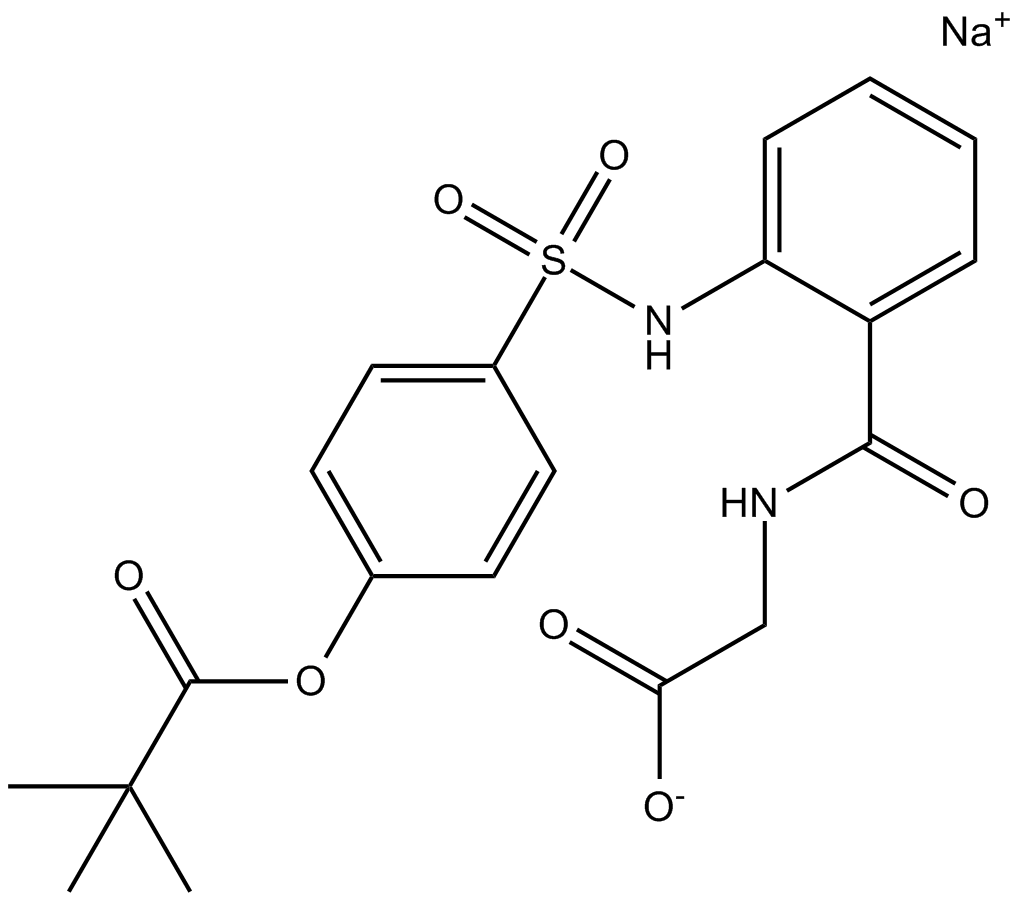 A4430 Sivelestat sodium saltTarget: ElastasesSummary: Leukocyte elastase inhibitor
A4430 Sivelestat sodium saltTarget: ElastasesSummary: Leukocyte elastase inhibitor -
 A4442 WAY 170523Target: MMPSummary: MMP-13 inhibitor,potent and selective
A4442 WAY 170523Target: MMPSummary: MMP-13 inhibitor,potent and selective -
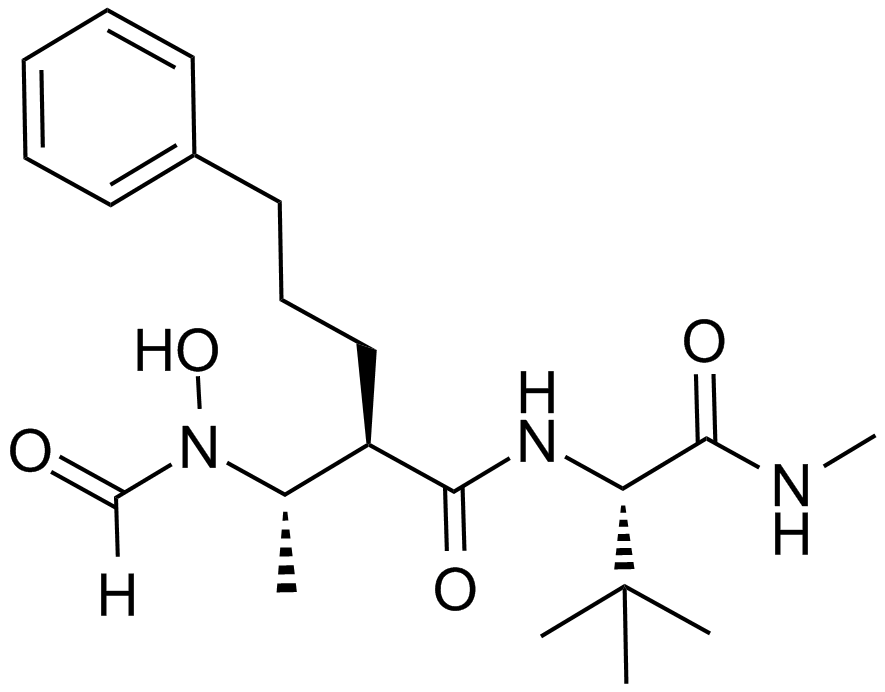 A4436 GI 254023X2 CitationTarget: ADAMsSummary: Selective inhibitor of ADAM10 metalloprotease
A4436 GI 254023X2 CitationTarget: ADAMsSummary: Selective inhibitor of ADAM10 metalloprotease -
 A8239 CA-074 Me7 CitationTarget: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin B inhibitor
A8239 CA-074 Me7 CitationTarget: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin B inhibitor -
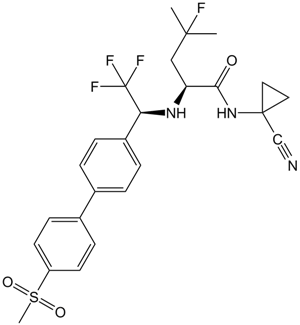 A2487 Odanacatib (MK-0822)Target: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin K,potent and selective
A2487 Odanacatib (MK-0822)Target: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin K,potent and selective -
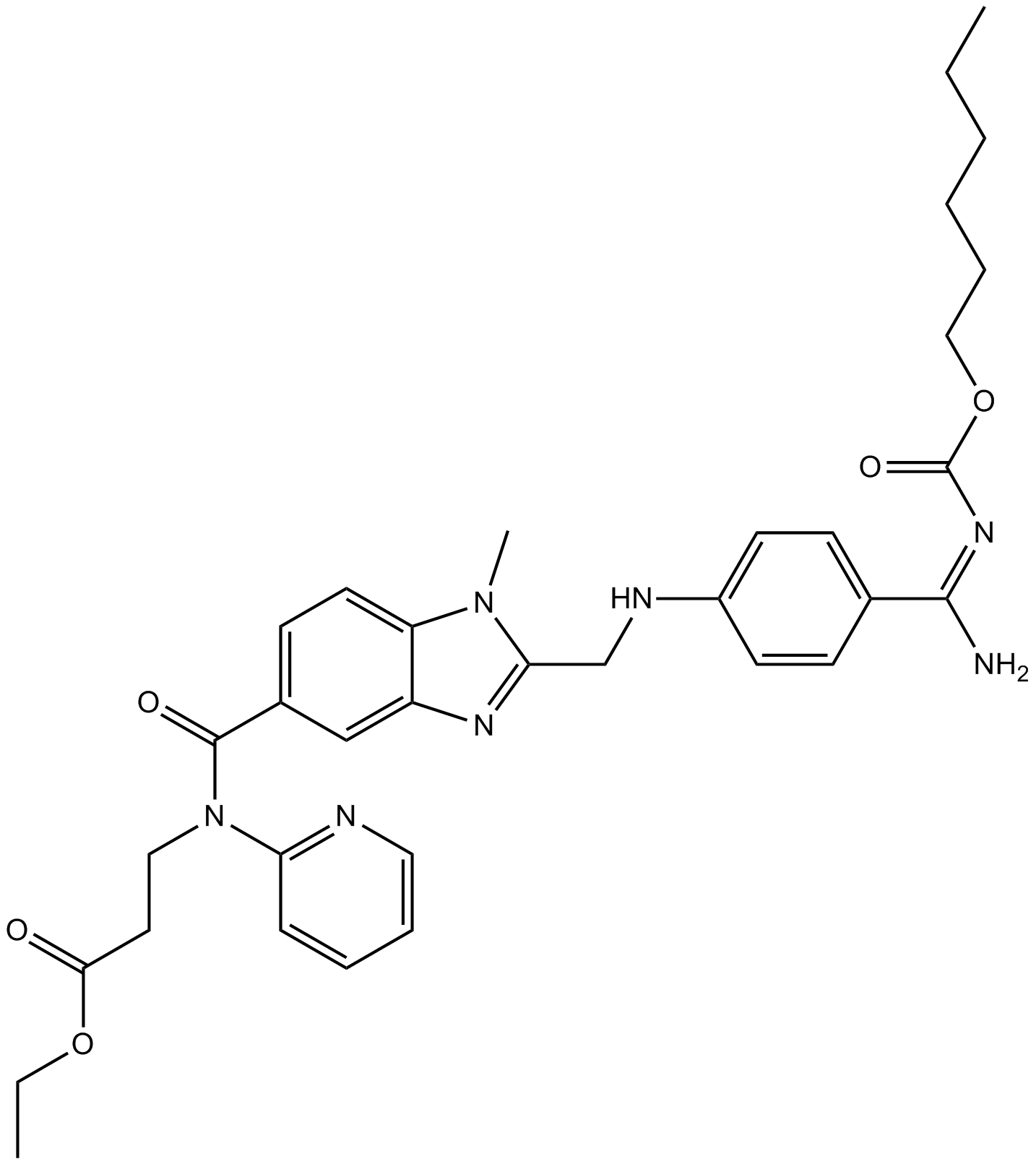 A8381 BIBR-1048Summary: Thrombin inhibitor
A8381 BIBR-1048Summary: Thrombin inhibitor -
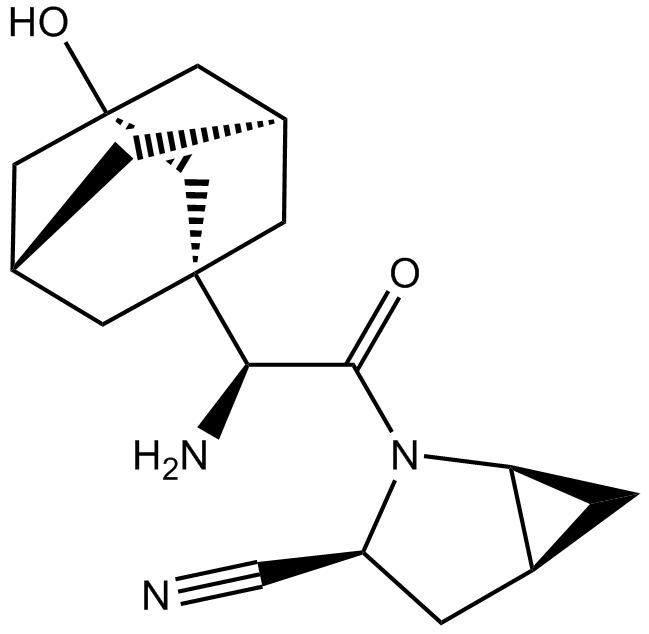 A8650 SaxagliptinTarget: DPP-4Summary: Selective DPP4 inhibitor
A8650 SaxagliptinTarget: DPP-4Summary: Selective DPP4 inhibitor

