PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling
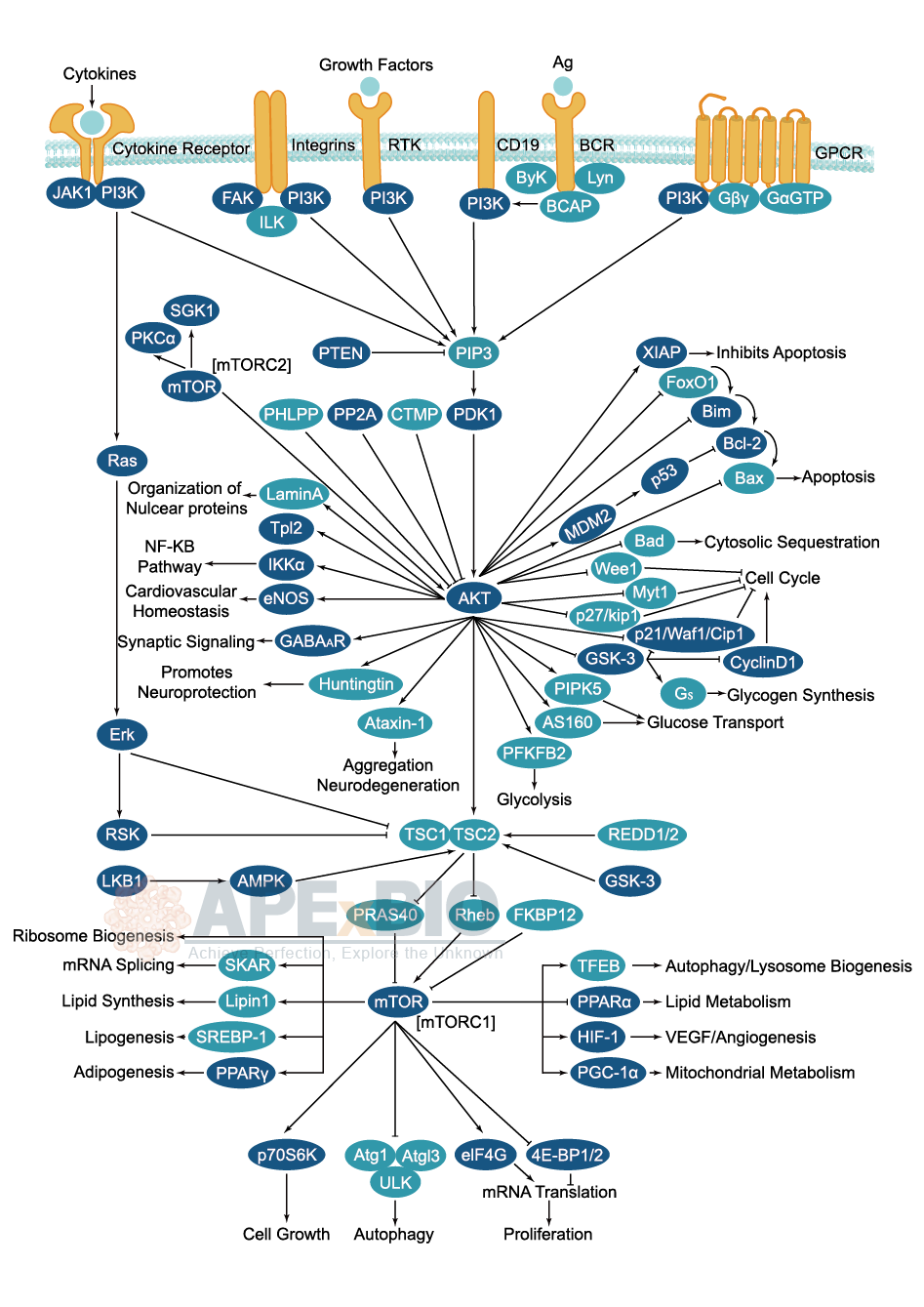
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is a key regulator in growth, survival, cell cycle proliferation, protein synthesis and glucose metabolism. Growth factors, hormones, and cytokines can activate this pathway by binding their cognate receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), cytokine receptor, or GPCR, resulting in the activation of lipid kinase PI3K which produces PIP3 at the plasma membrane.
The binding of PIP3 translocates Akt to cell membranes, enables Akt activation through phosphorylation at Thr308 mediated by phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1 (PDK1). In addition, Akt is phosphorylated at Ser473 by the mTOR-rictor complex, mTORC2. PTEN is a negative regulator of Akt signaling that reverses the function of PI3K by removing 3’-phosphate groups. Akt activity is also negatively regulated by the phosphatases PP2A and PHLPP. Akt propagates its signal to affect DNA transcription, cell cycle and apoptosis. Akt can activate mTOR directly by phosphorylation or indirectly, by phosphorylation and inactivation of mTOR inhibitor TSC2 and PRAS40. Together these mechanisms stimulate cell growth and G1 cell cycle progression through signaling via p70 S6 Kinase and inhibition of 4E-BP1. Defects in PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling are implicated in cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular disease etc.
-
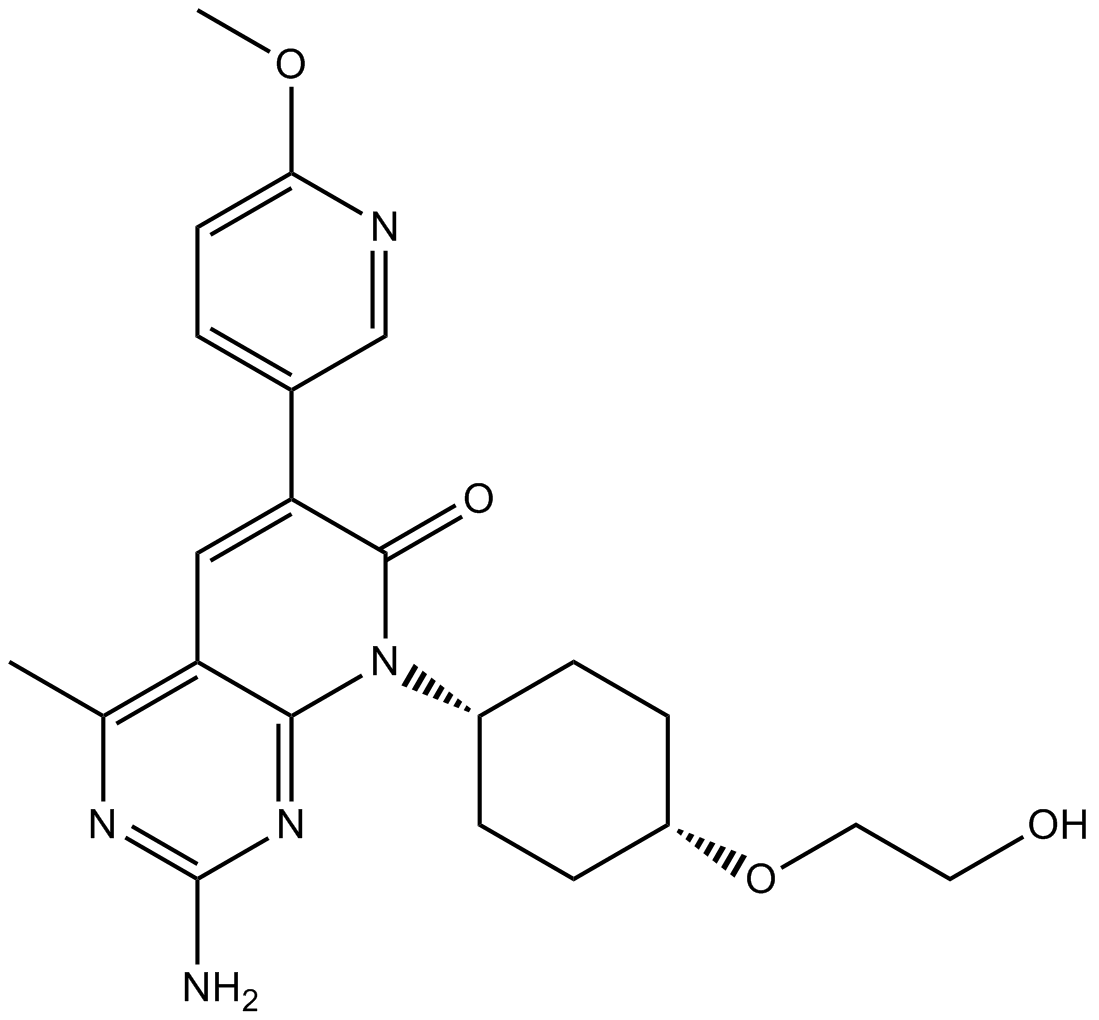 A8499 PF-04691502Target: Akt|PI3K|mTORSummary: PI3K/mTOR (FRAP) inhibitor
A8499 PF-04691502Target: Akt|PI3K|mTORSummary: PI3K/mTOR (FRAP) inhibitor -
 A8505 PKI-402Summary: PI3K inhibitor,selective, reversible and ATP-competitive
A8505 PKI-402Summary: PI3K inhibitor,selective, reversible and ATP-competitive -
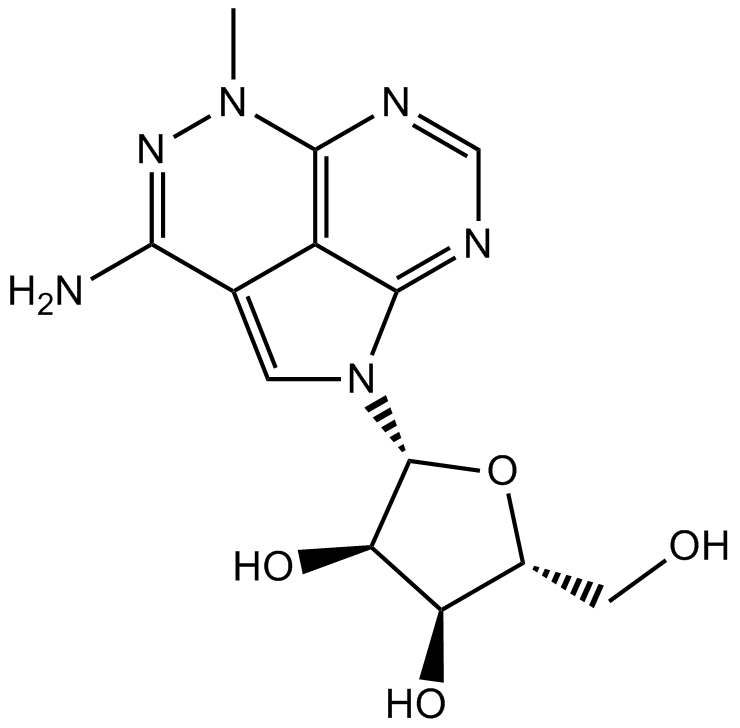 A8541 Triciribine5 CitationSummary: Akt inhibitor,highly selective
A8541 Triciribine5 CitationSummary: Akt inhibitor,highly selective -
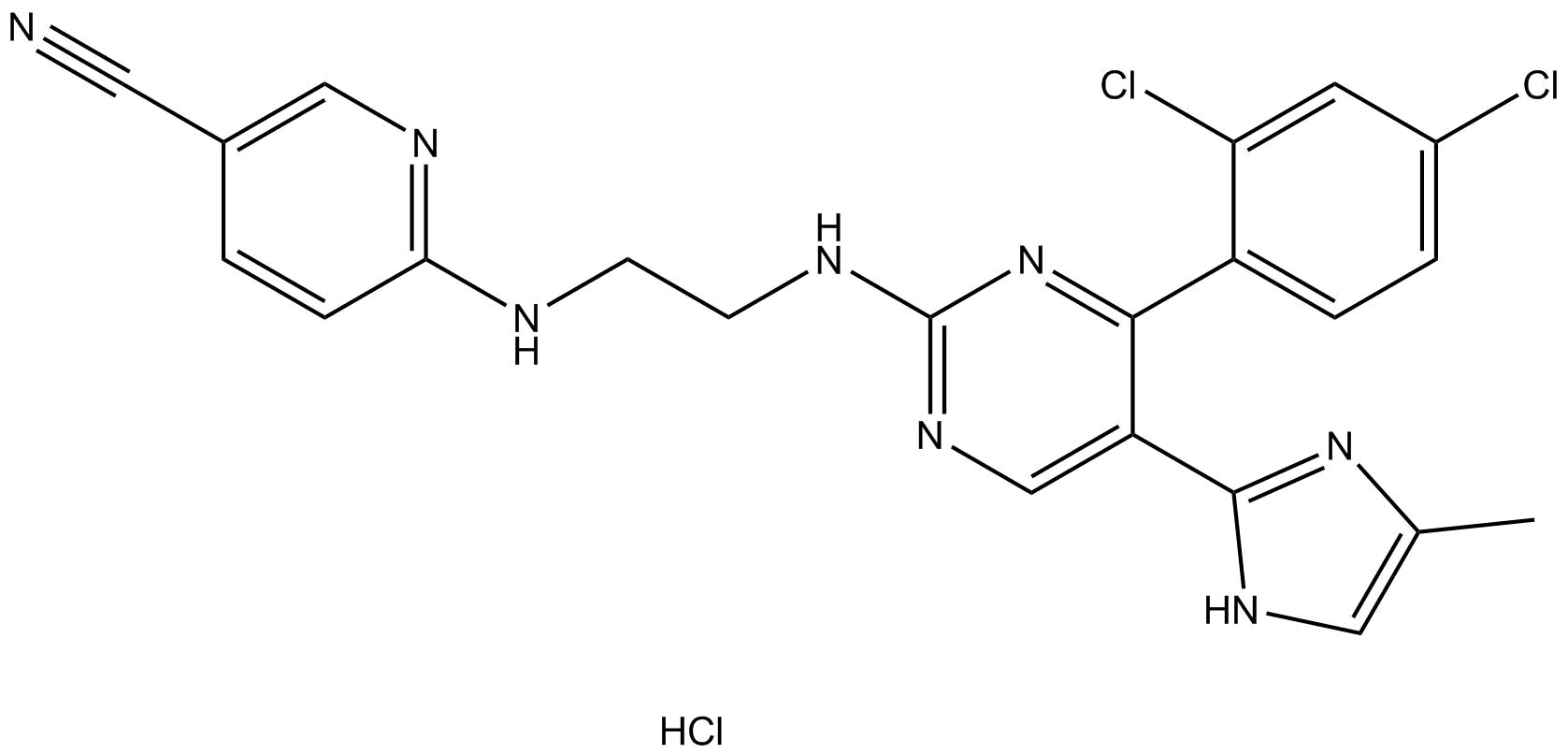 A8396 CHIR-99021 (CT99021) HClTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK-3α/β inhibitor
A8396 CHIR-99021 (CT99021) HClTarget: GSK-3Summary: GSK-3α/β inhibitor -
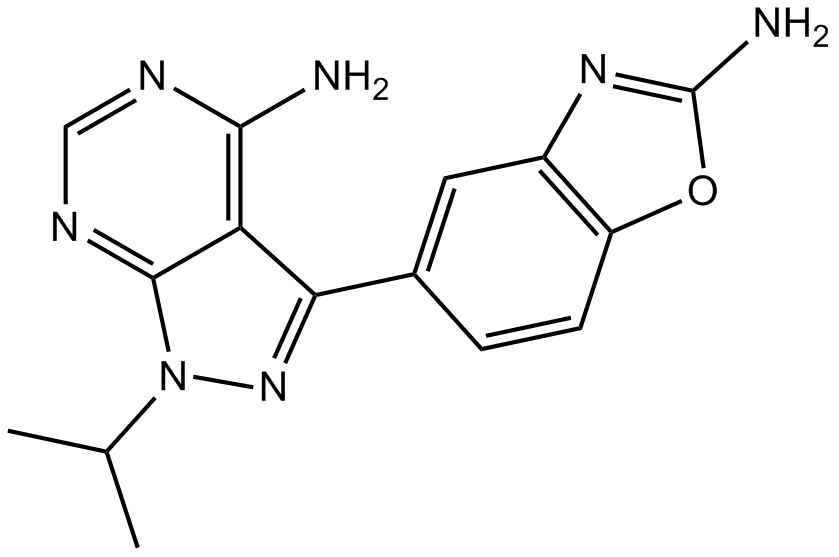 A8551 INK 128 (MLN0128)4 CitationTarget: mTORSummary: MTOR(TORC-1/-2) inhibitor,potent and selective
A8551 INK 128 (MLN0128)4 CitationTarget: mTORSummary: MTOR(TORC-1/-2) inhibitor,potent and selective -
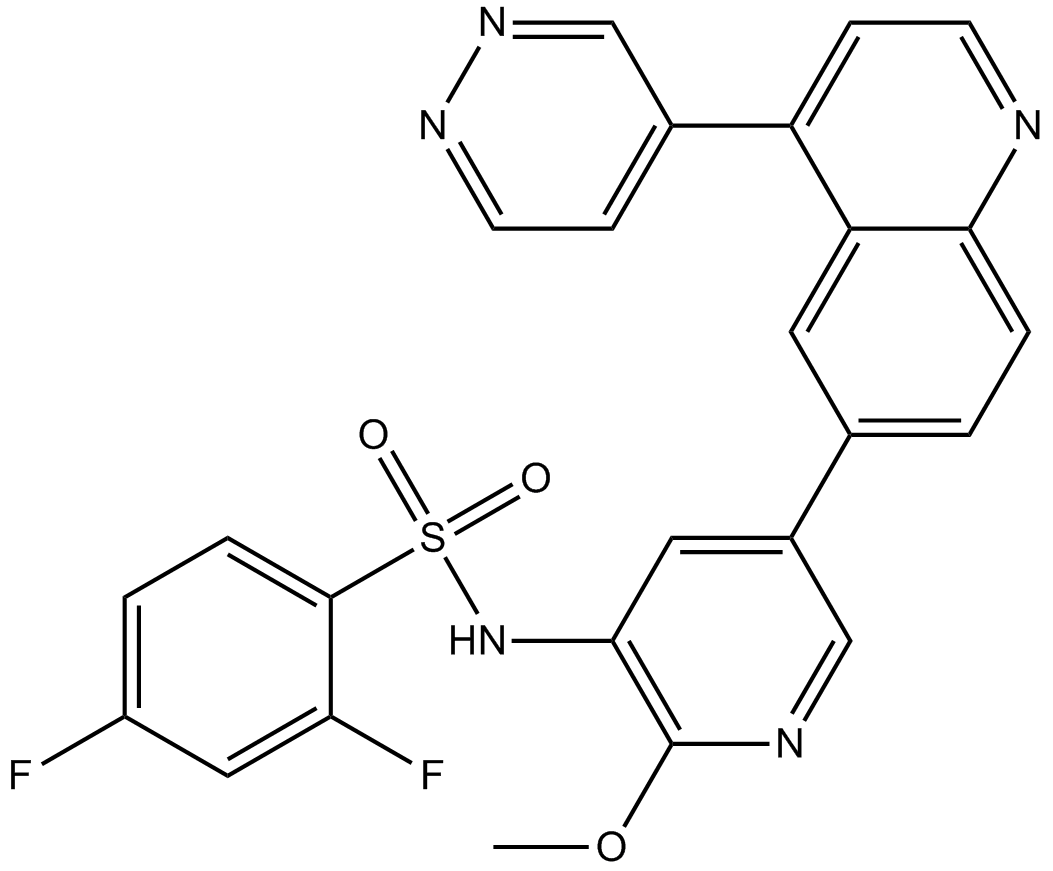 A8556 GSK21264581 CitationTarget: PI3K|mTORSummary: PI3K/mTOR inhibitor
A8556 GSK21264581 CitationTarget: PI3K|mTORSummary: PI3K/mTOR inhibitor -
 A8616 A-674563Target: Cyclin-Dependent Kinases|Akt|GSK-3|ERK|PKC|PKA|RSKSummary: Akt1/PKA/CDK2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A8616 A-674563Target: Cyclin-Dependent Kinases|Akt|GSK-3|ERK|PKC|PKA|RSKSummary: Akt1/PKA/CDK2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
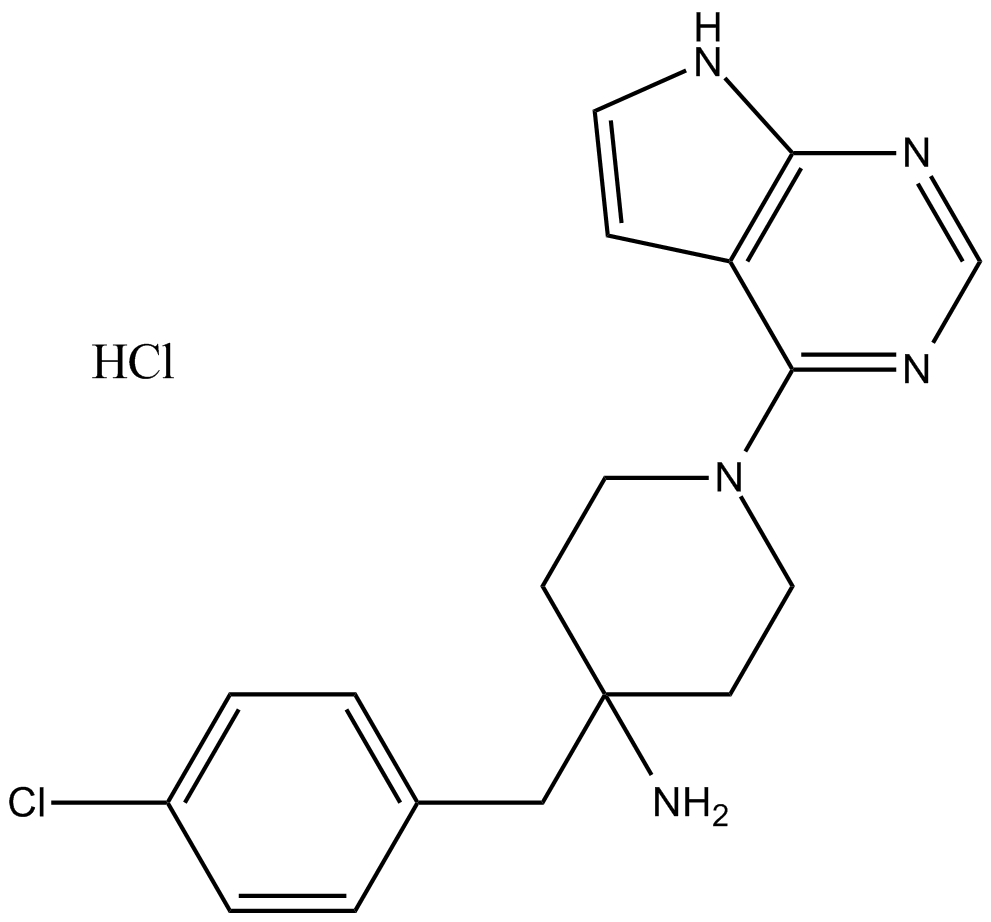 A8617 CCT128930 HClTarget: AktSummary: AKT inhibitor
A8617 CCT128930 HClTarget: AktSummary: AKT inhibitor -
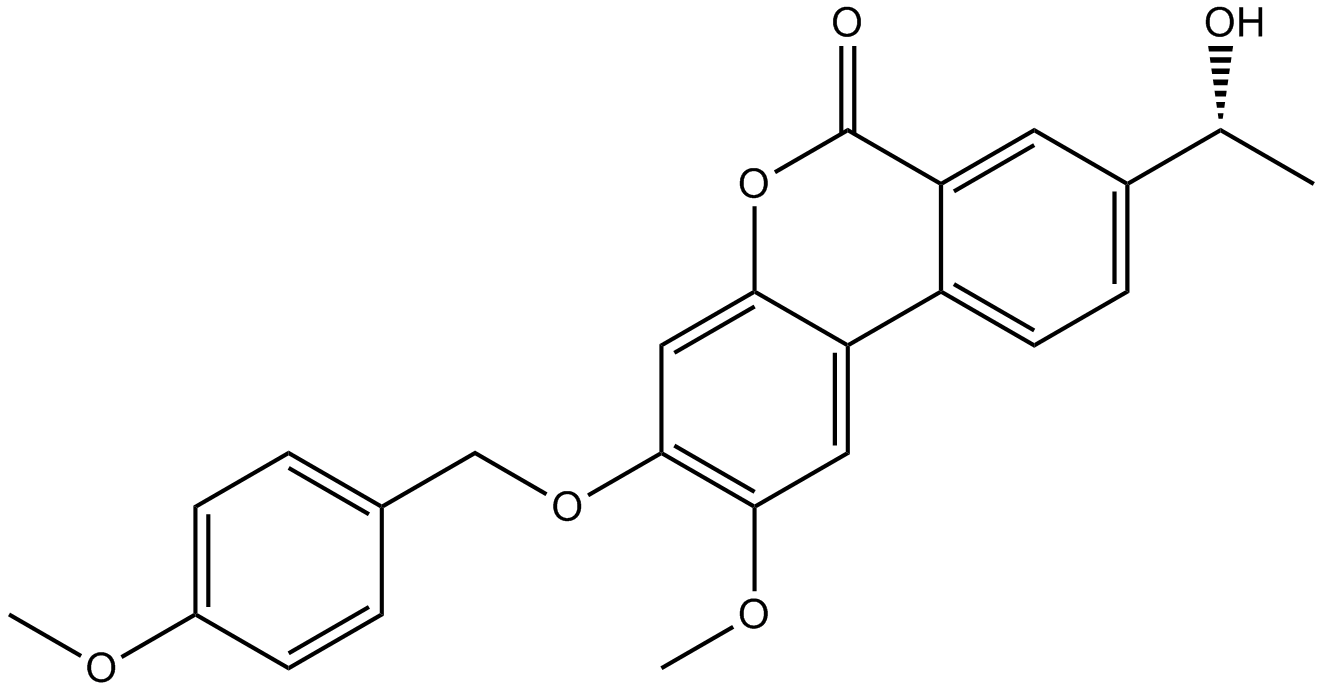 A8618 Palomid 529Summary: PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitor
A8618 Palomid 529Summary: PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitor -
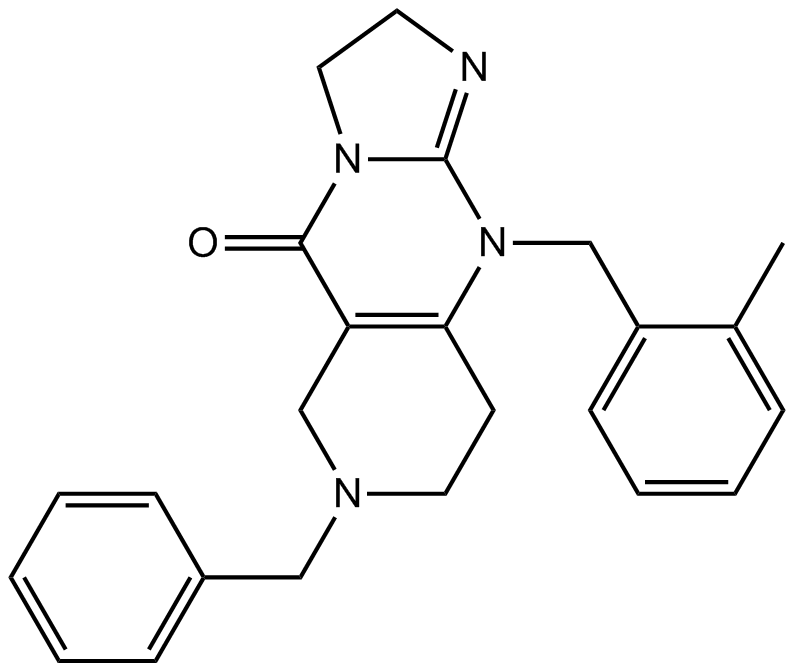 A8619 TIC10Summary: Potent Akt/ERK inhibitor
A8619 TIC10Summary: Potent Akt/ERK inhibitor

