Microbiology & Virology

Virology
A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates inside living cells. Viruses cause many human diseases from small illnesses, like influenza, to more deadly diseases, like hepatitis B and HIV. Our body’s immune system defends against viral infection by generating specific antibodies to bind to and neutralize viral particles and by cell mediated immunity that destroys infected host cells. read more
-
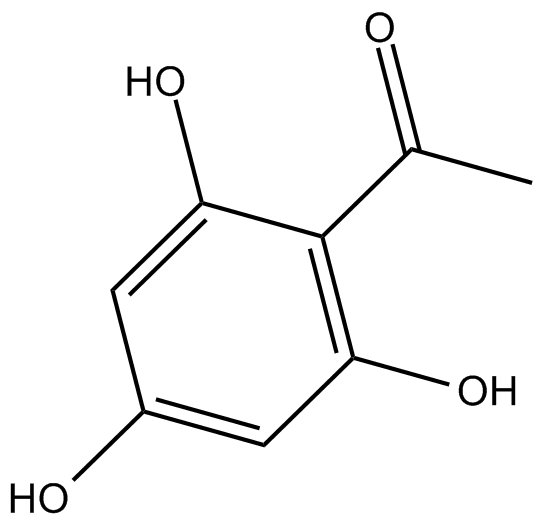 C3086 MonoacetylphloroglucinolSummary: broad range of antibiotic activity with fairly weak potency
C3086 MonoacetylphloroglucinolSummary: broad range of antibiotic activity with fairly weak potency -
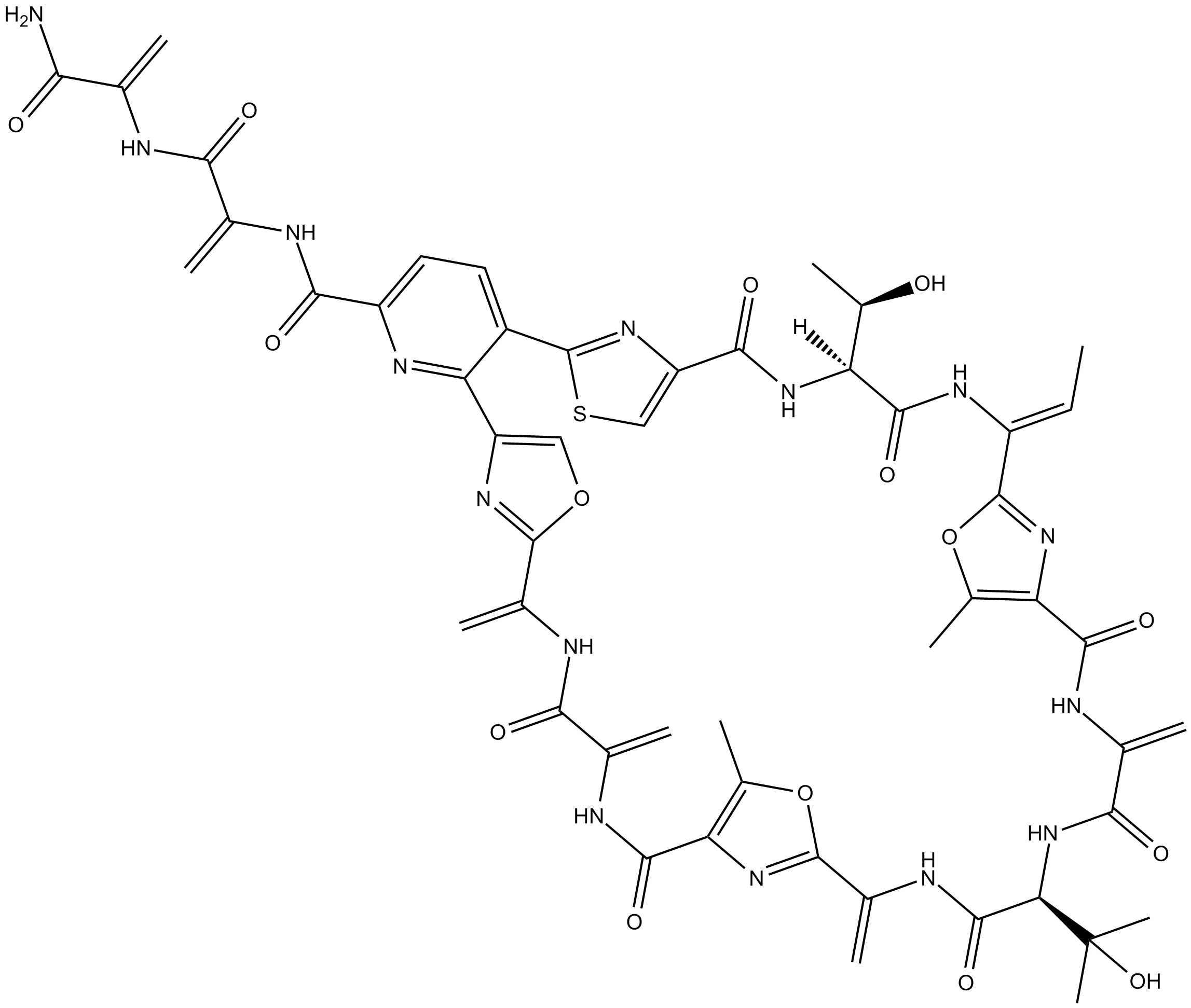 C3906 Berninamycin ASummary: cyclic thiopeptide antibiotic
C3906 Berninamycin ASummary: cyclic thiopeptide antibiotic -
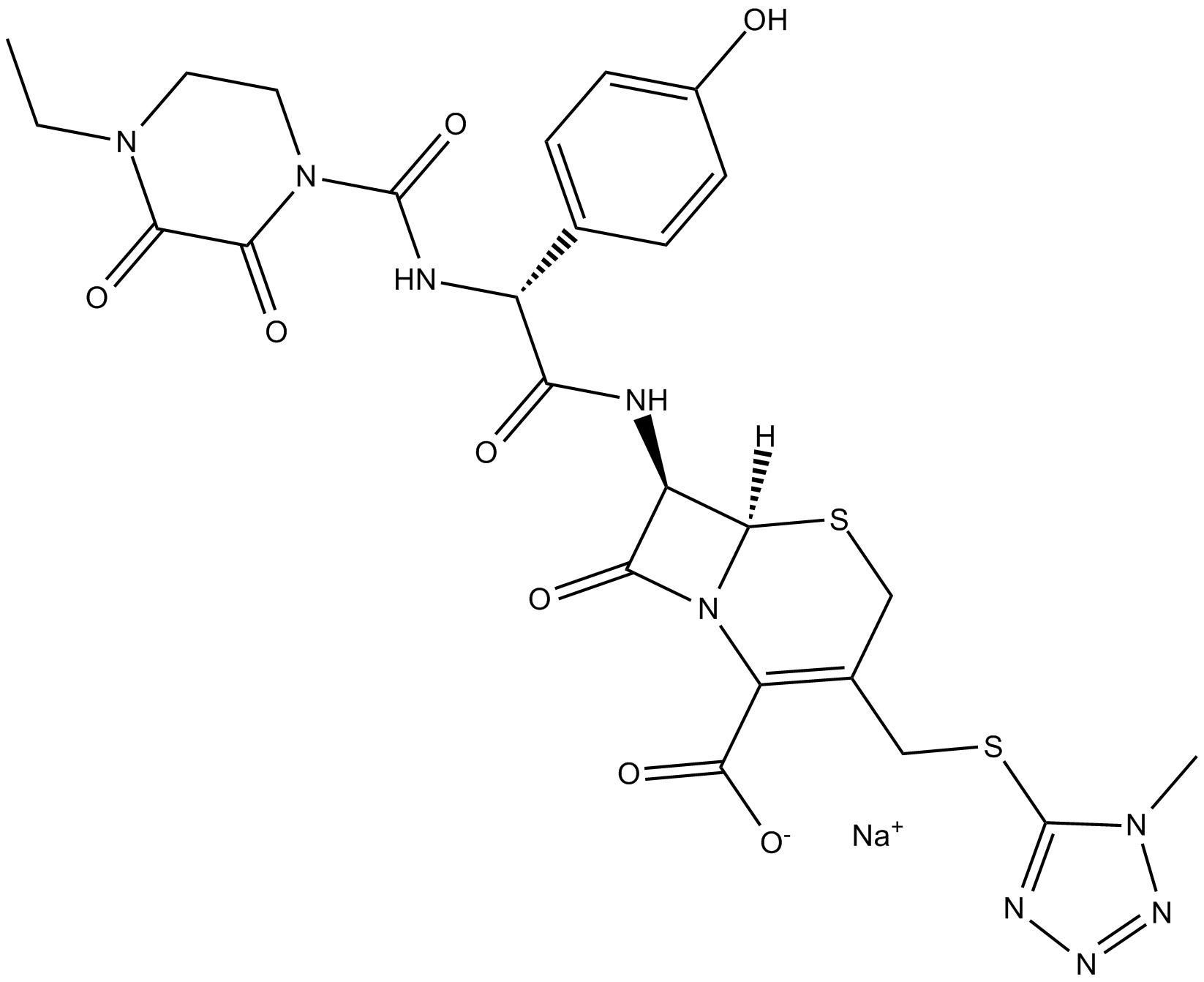 C3913 Cefoperazone (sodium salt)Summary: cephalosporin antibiotic
C3913 Cefoperazone (sodium salt)Summary: cephalosporin antibiotic -
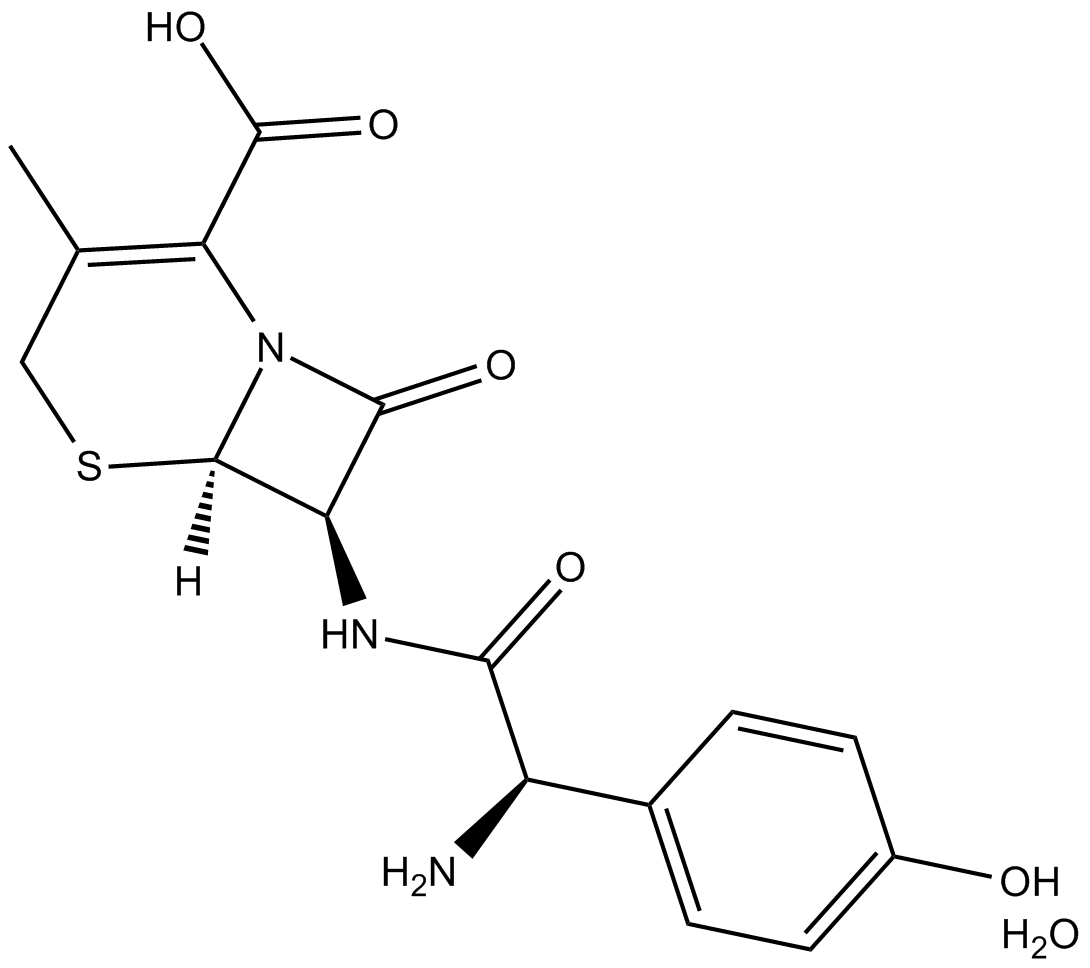 C3991 Cefadroxil (hydrate)Summary: broad-spectrum antibiotic
C3991 Cefadroxil (hydrate)Summary: broad-spectrum antibiotic -
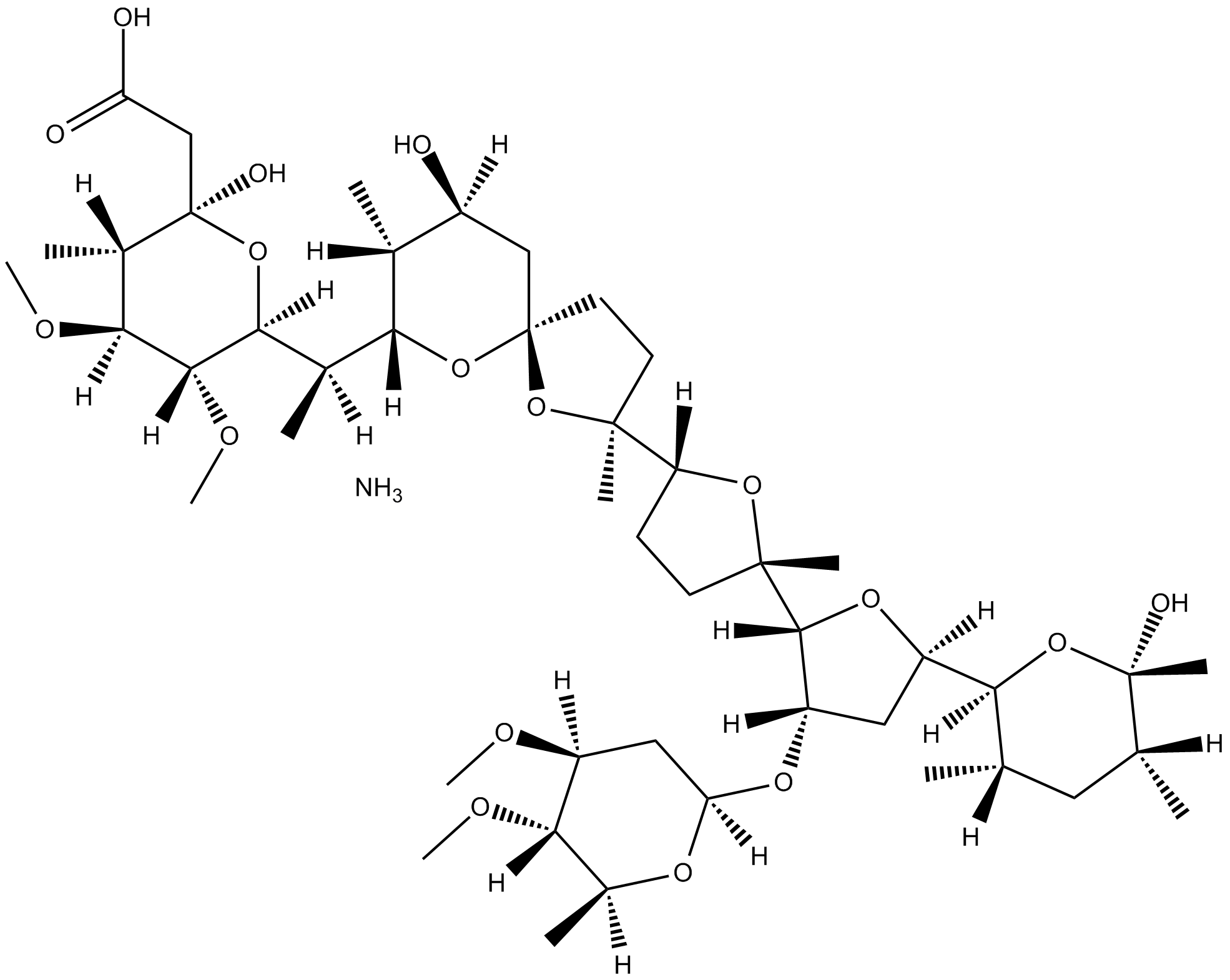 C4086 MaduramicinSummary: polyether ionophore antibiotic
C4086 MaduramicinSummary: polyether ionophore antibiotic -
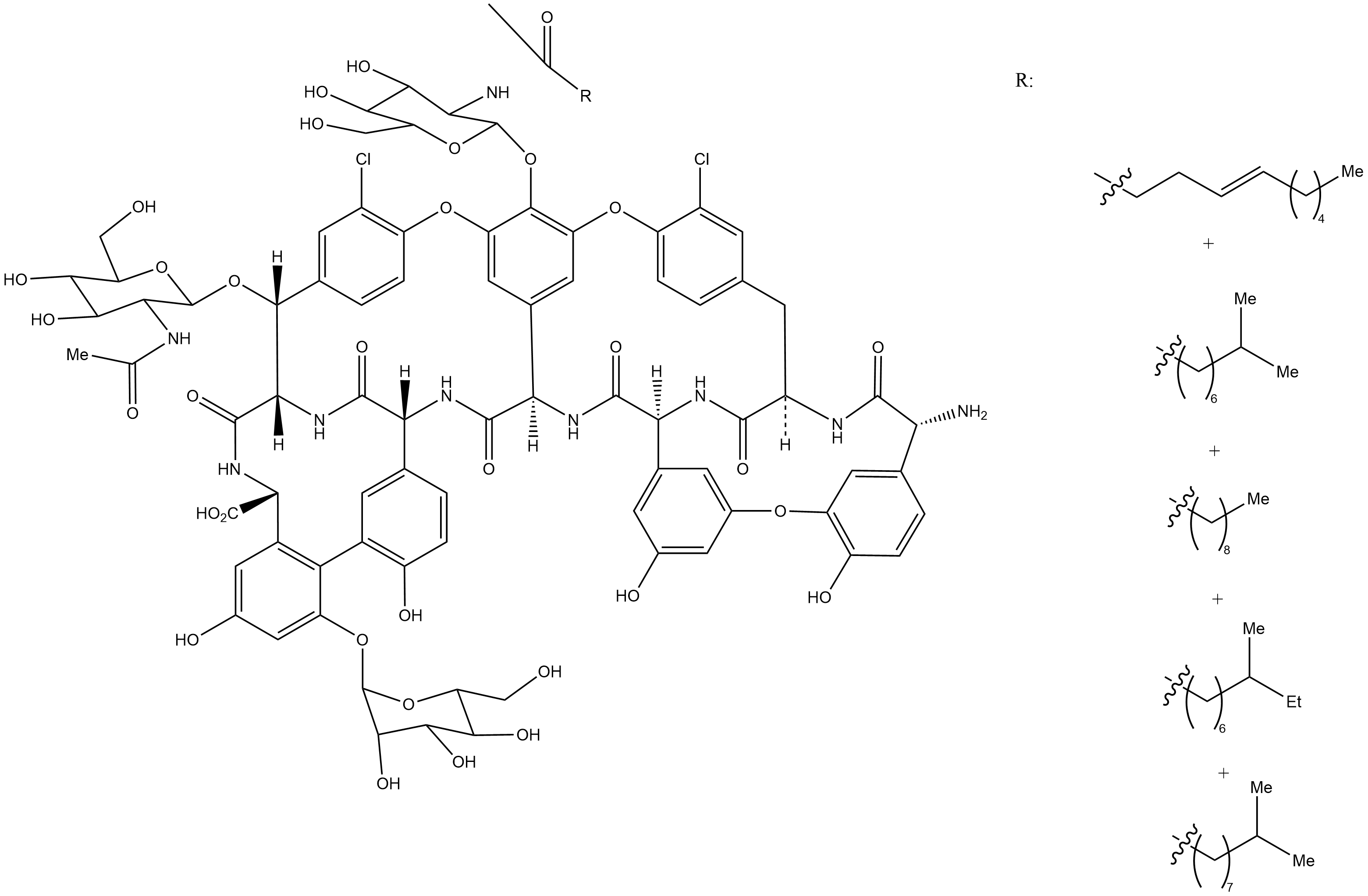 C3940 Teicoplanin A2Summary: glycopeptide antibiotic
C3940 Teicoplanin A2Summary: glycopeptide antibiotic -
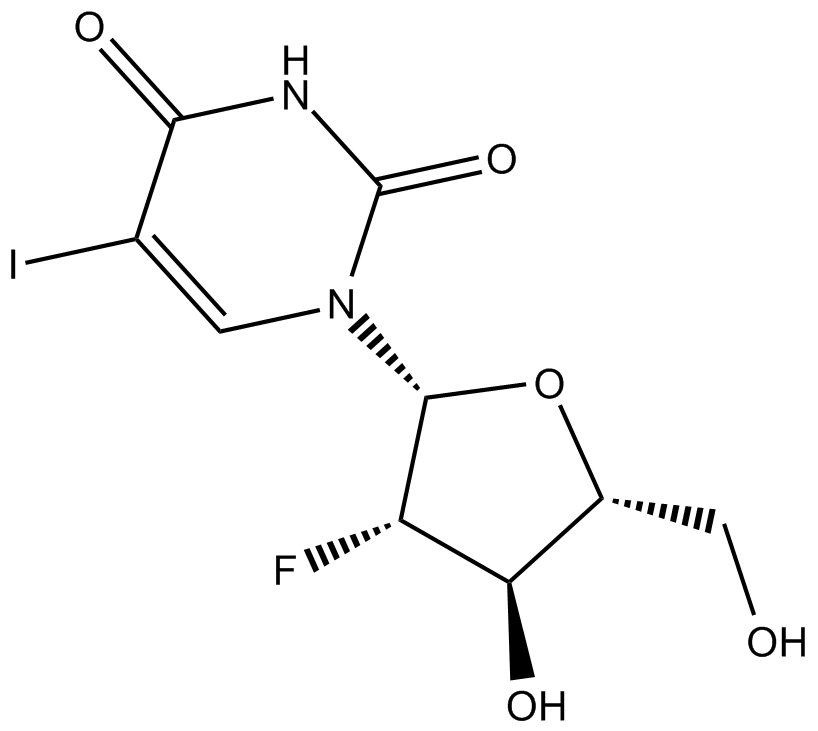 C3688 FialuridineSummary: nucleoside analog with antiviral activity
C3688 FialuridineSummary: nucleoside analog with antiviral activity -
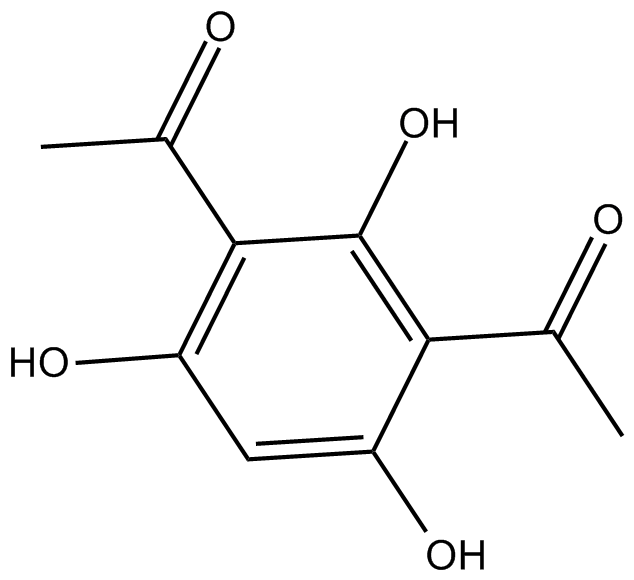 C3761 2,4-DiacetylphloroglucinolSummary: active against numerous plant pathogenic fungi, viruses, bacteria, and nematodes
C3761 2,4-DiacetylphloroglucinolSummary: active against numerous plant pathogenic fungi, viruses, bacteria, and nematodes -
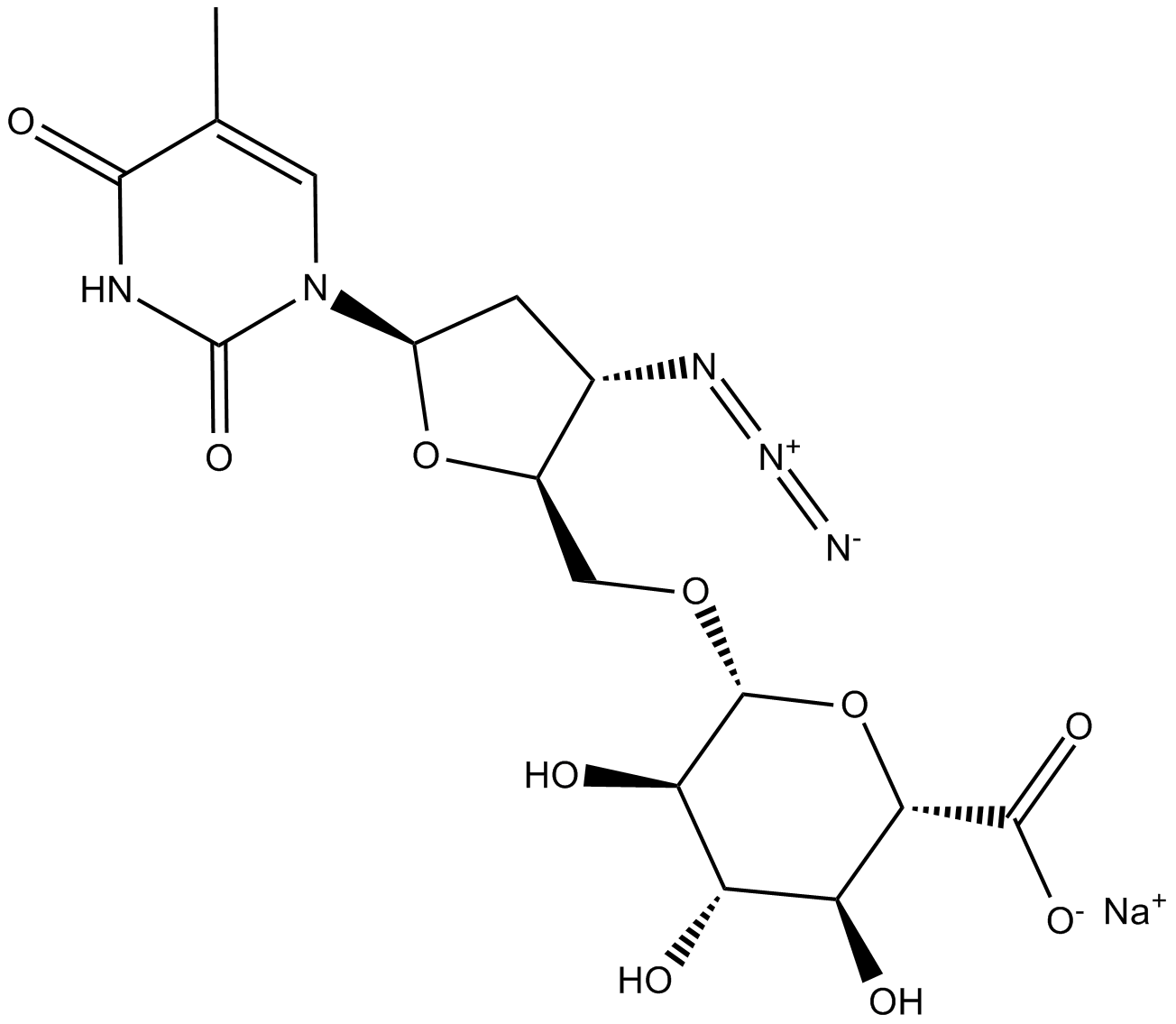 C3806 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine β-D-glucuronide (sodium salt)Summary: metabolite of the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, zidovudine
C3806 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine β-D-glucuronide (sodium salt)Summary: metabolite of the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, zidovudine -
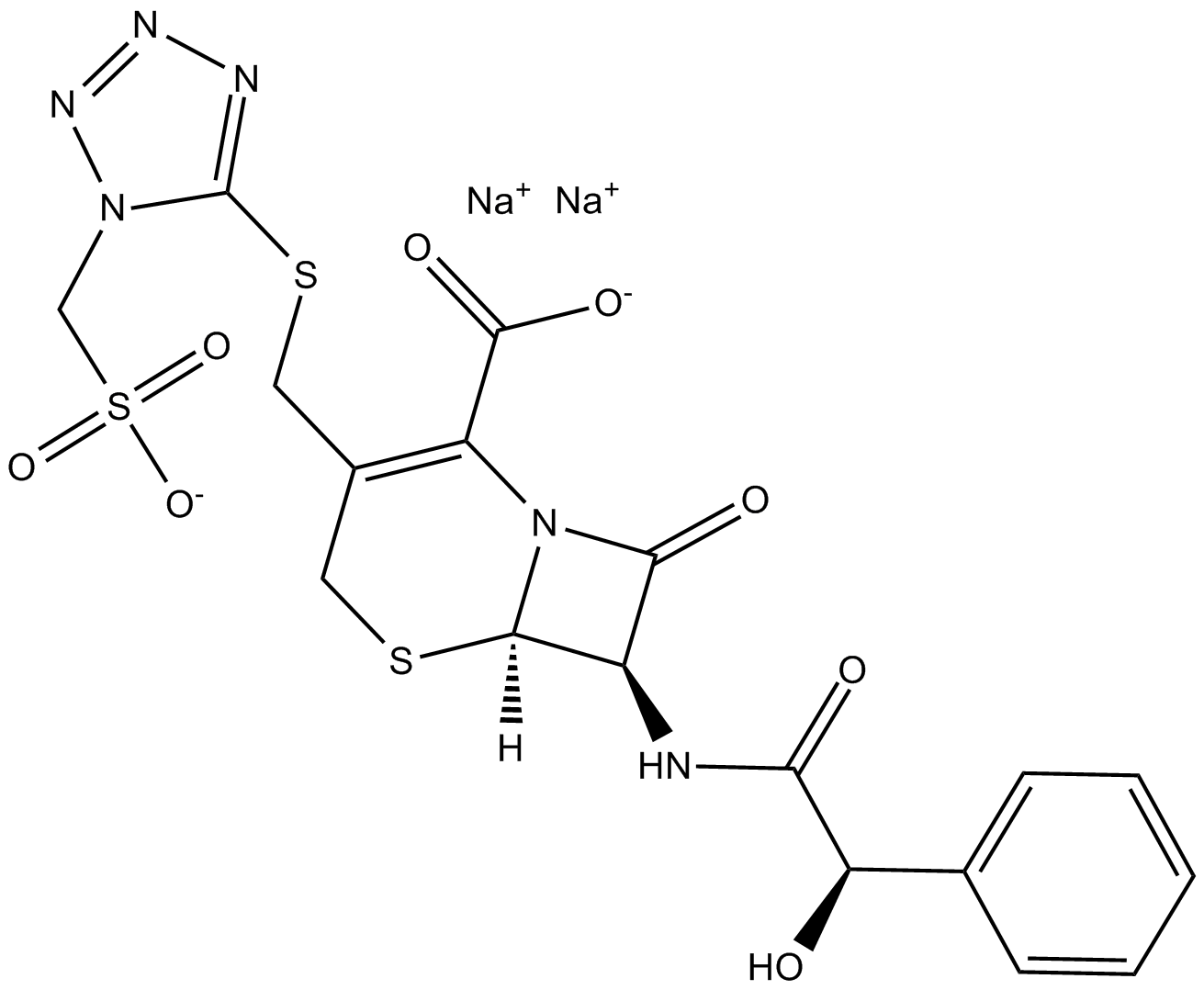 C3812 Cefonicid (sodium salt)Summary: second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic
C3812 Cefonicid (sodium salt)Summary: second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic

