Chromatin/Epigenetics
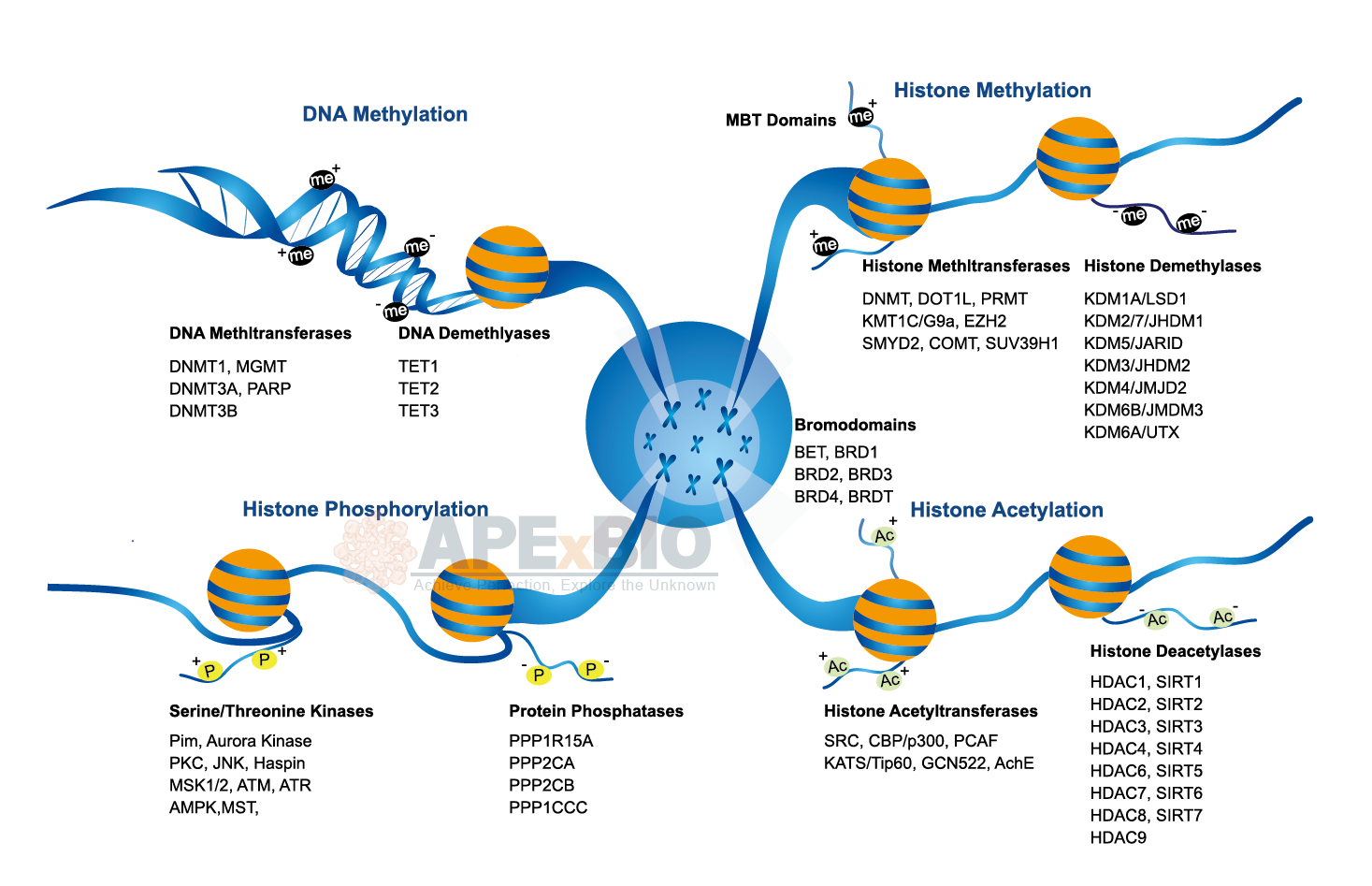
Epigenetics is the heritable modifications in gene expression that is not associated with changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetic modifications occur mostly on DNA or on the histone octamer. There are several types of epigenetics modifications, DNA methylation by DNA-methyl transferase (DNMT) and covalent modification of histones (e.g. acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitination). Histone acetylation by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) is involved in transcriptional activation, whereas histone deacetylation by histone deacetylases (HDACs) is connected with transcriptional repression. Histone demethylation is associated with lysine-specific demethylase (LSD) and JmjC domain containing histone demethylase (JHDM).
The nucleosome is consisted of four histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), they are primary building block of chromatin. The addition and removal of specific chemical groups refers to as epigenetic marks, it regulates chromatin structure and affects gene expression. Moreover, RNA is intimately involved in the formation of a repressive chromatin state.
Epigenetic mechanism responds to environmental changes at the cellular level and thus influences cellular plasticity. Chromatin and epigenetic regulation play a significant role in the programming of the genome during development and stress response, defects in epigenetics can lead to cancer, inflammation and metabolic disorders etc.
-
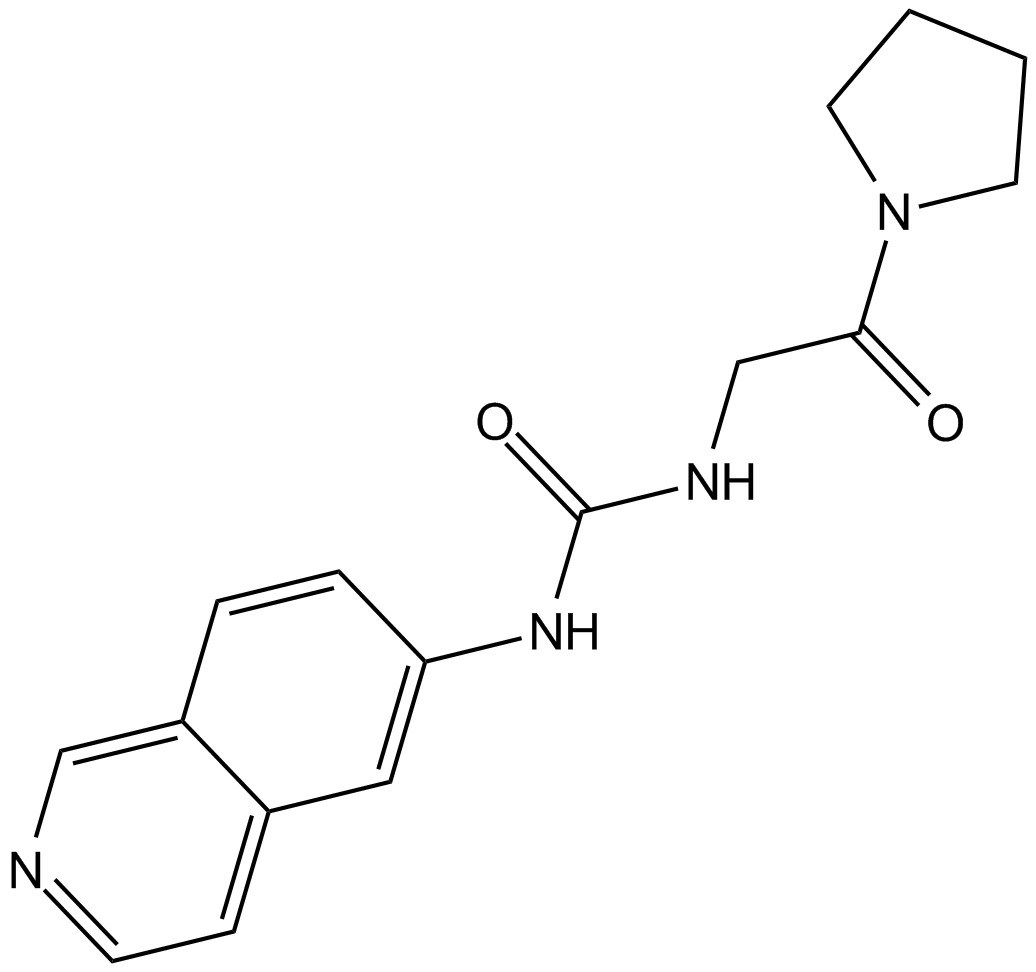 B6048 SGC707Summary: PRMT3 inhibitor
B6048 SGC707Summary: PRMT3 inhibitor -
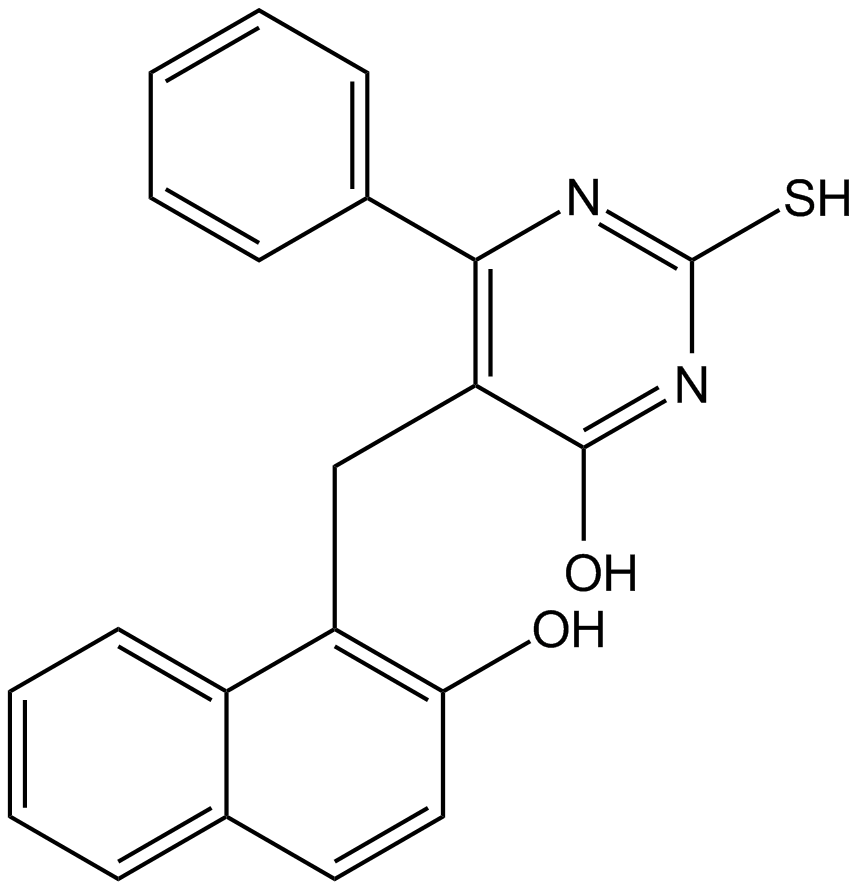 B6063 SIRT1/2 Inhibitor IVSummary: SIRT1 and SIRT2 inhibitor
B6063 SIRT1/2 Inhibitor IVSummary: SIRT1 and SIRT2 inhibitor -
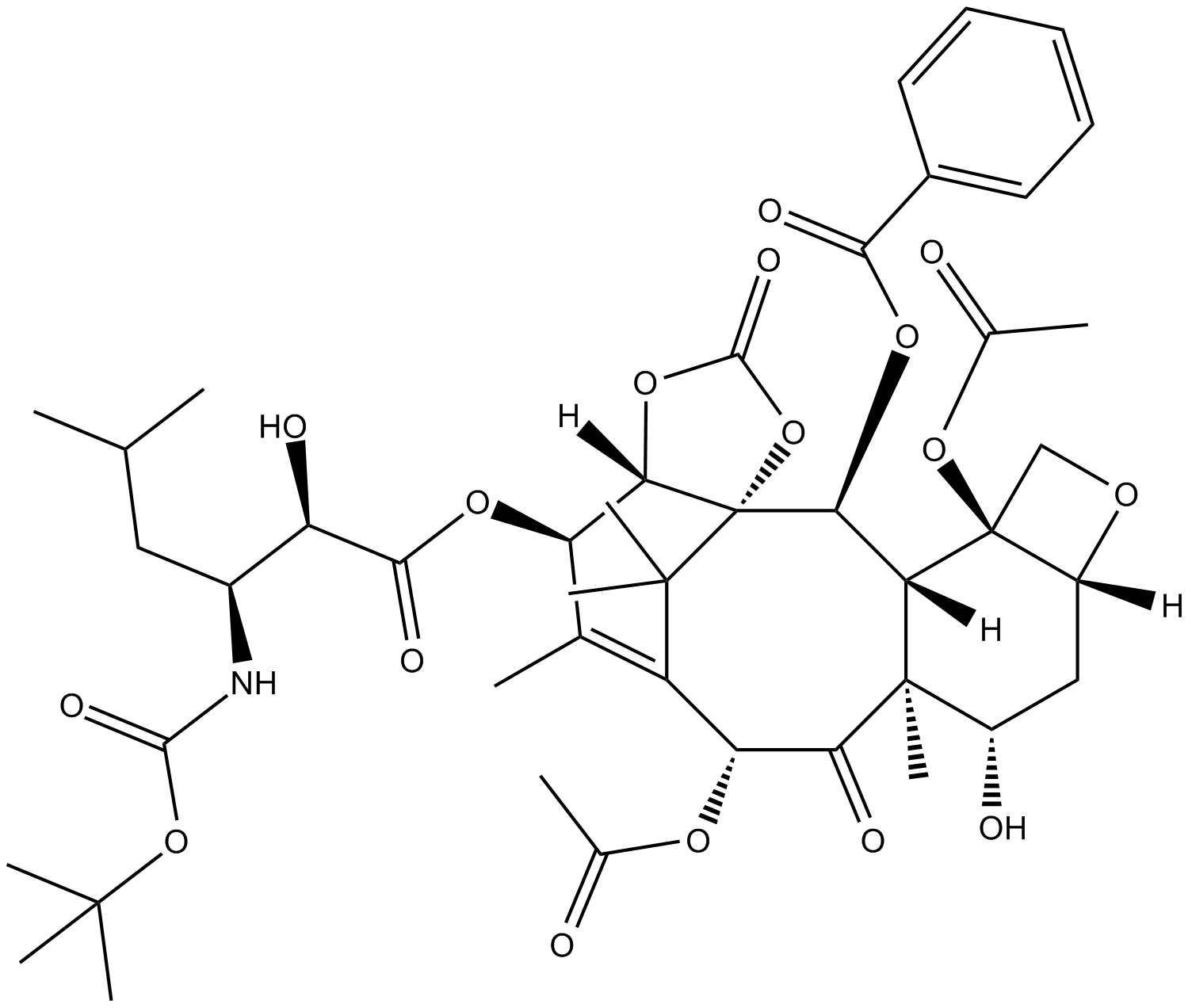 B6081 BAY-598Summary: SMYD2 inhibitor
B6081 BAY-598Summary: SMYD2 inhibitor -
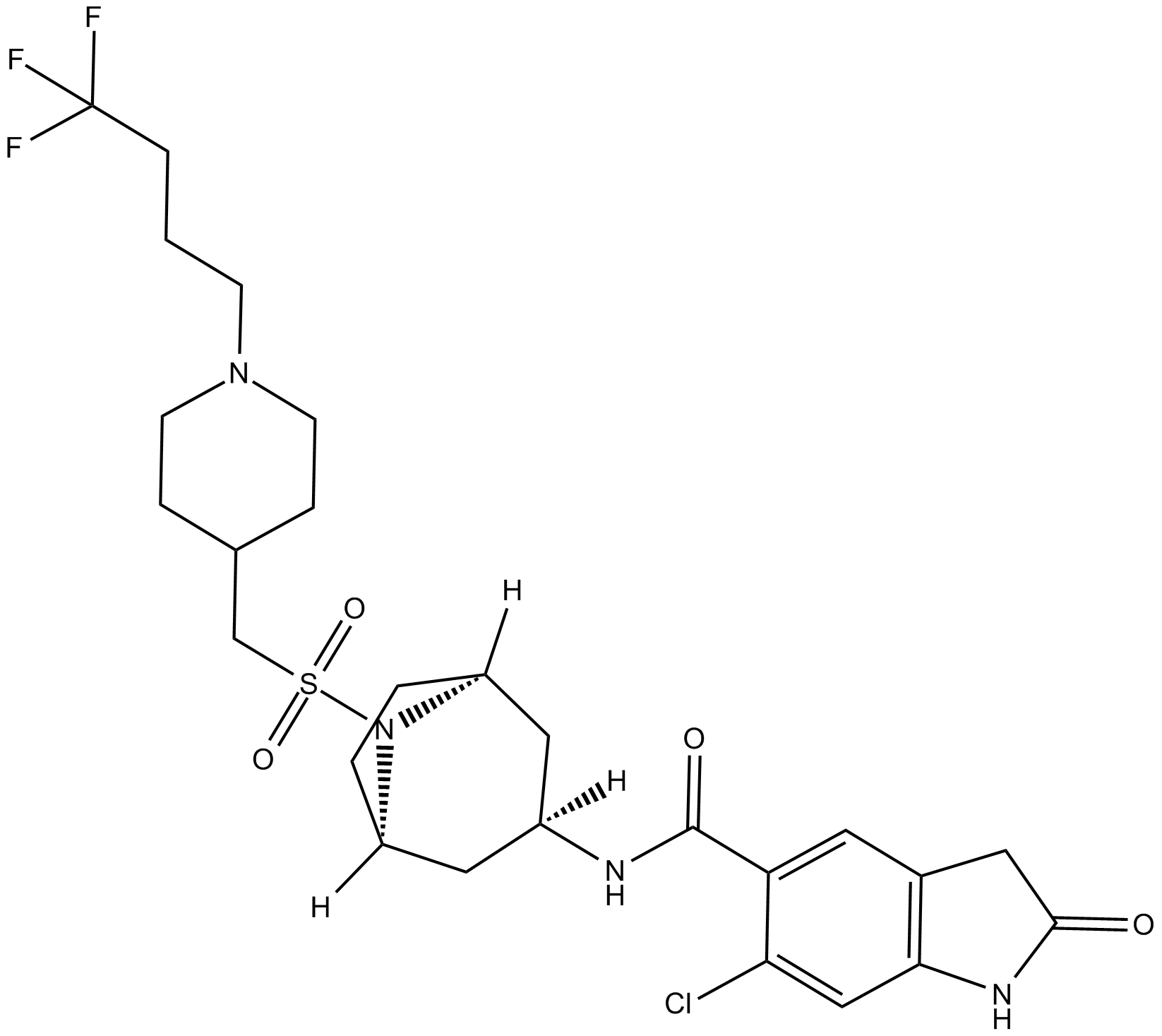 B6082 EPZ031686Summary: SMYD3 inhibitor
B6082 EPZ031686Summary: SMYD3 inhibitor -
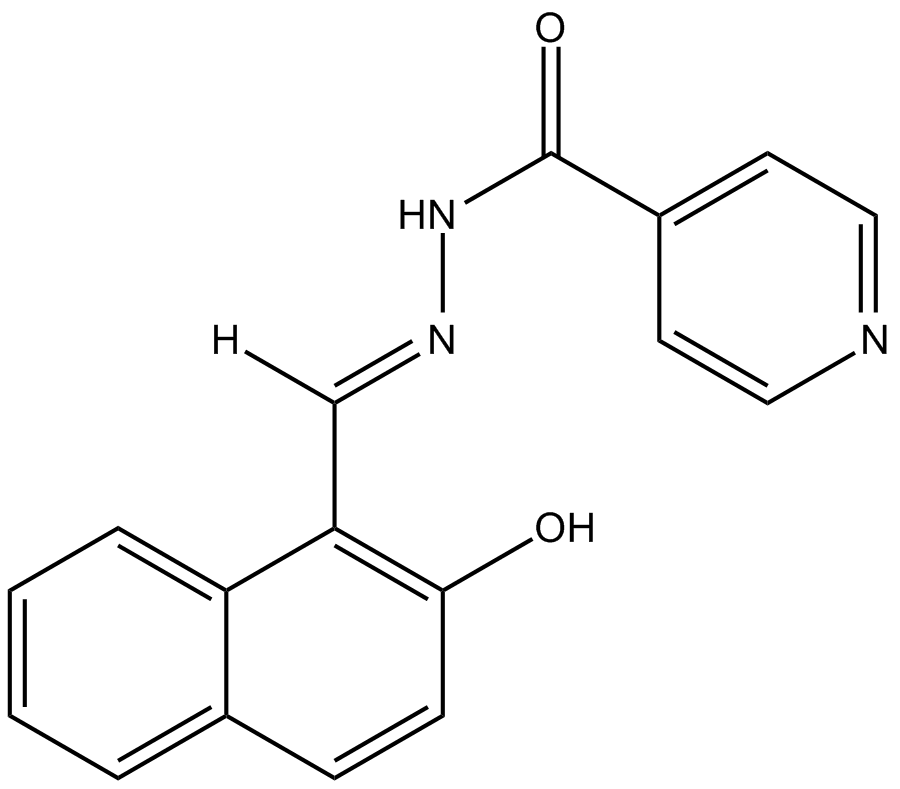 B6084 AS8351Summary: histone demethylase inhibitor
B6084 AS8351Summary: histone demethylase inhibitor -
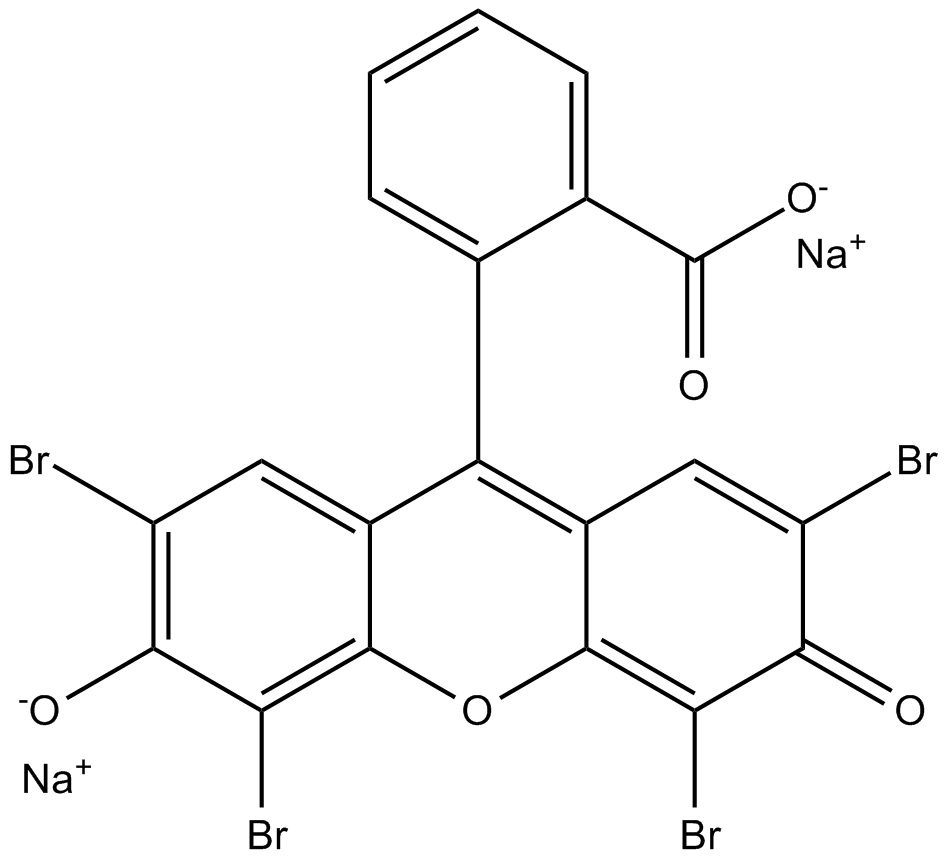 B6085 AMI5/Eosin Y disodium saltSummary: protein methyltransferase inhibitor/dye,used in HE staining
B6085 AMI5/Eosin Y disodium saltSummary: protein methyltransferase inhibitor/dye,used in HE staining -
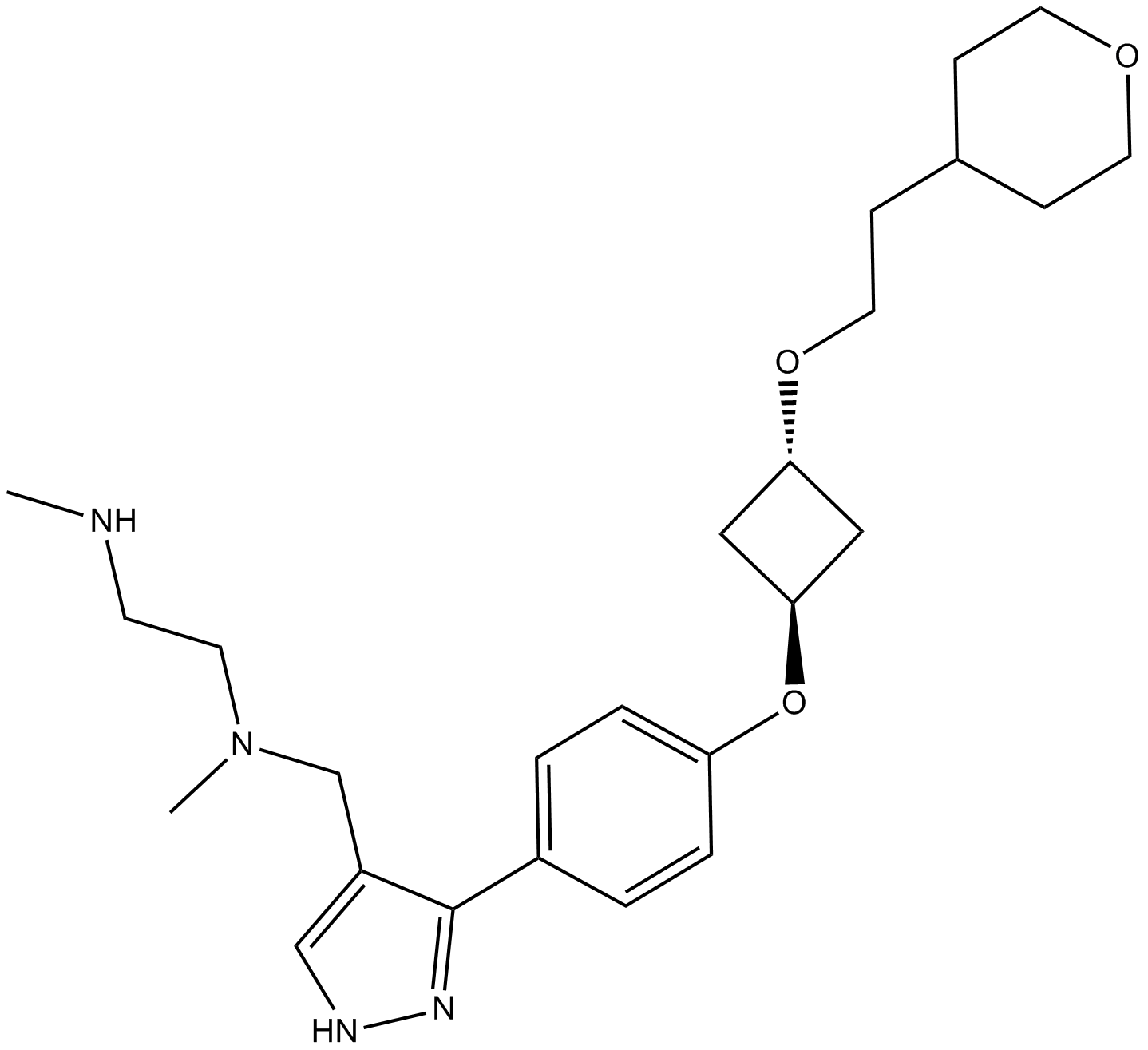 B6088 EPZ020411Summary: PRMT6 inhibitor
B6088 EPZ020411Summary: PRMT6 inhibitor -
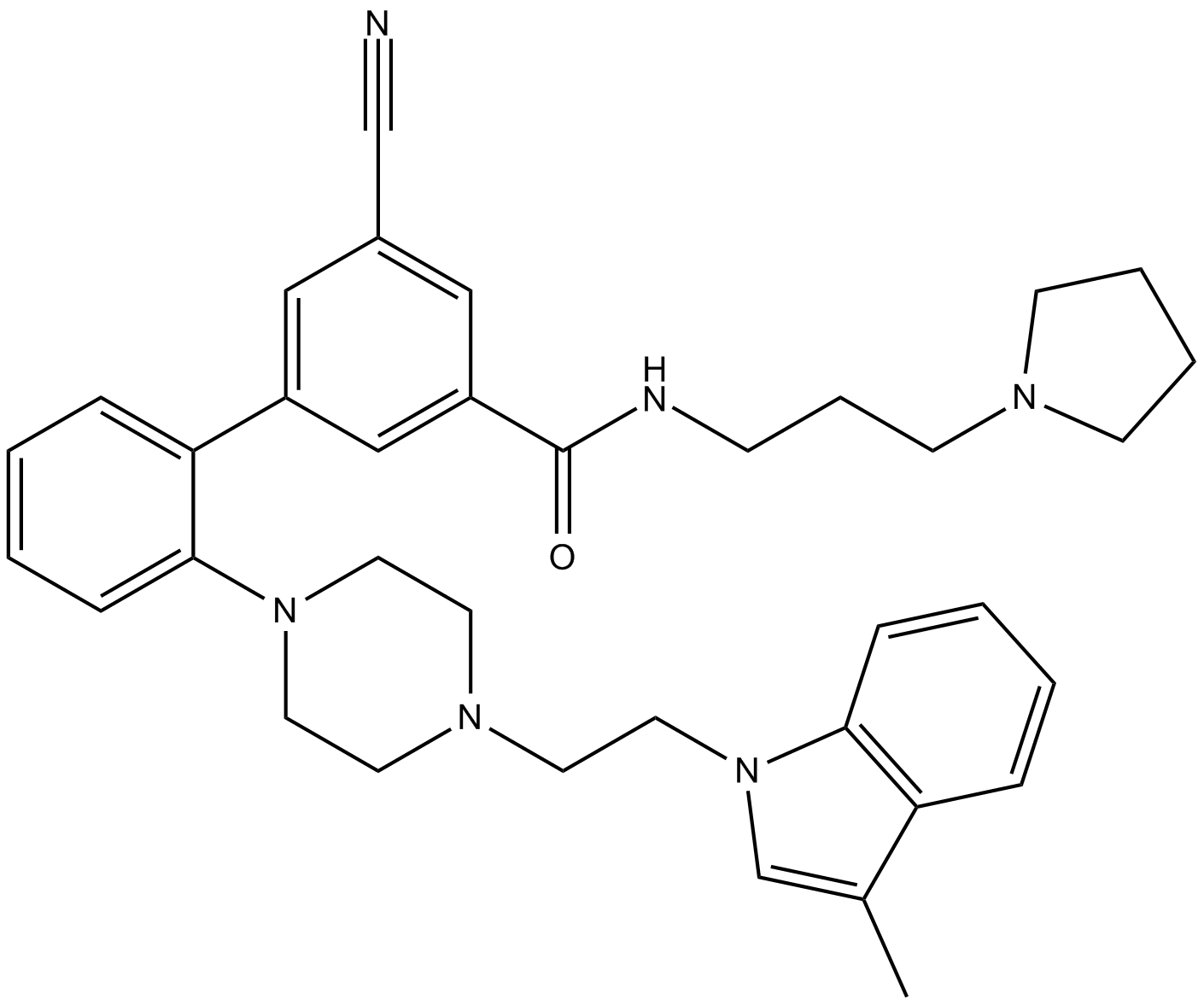 B6119 LLY507Summary: SMYD2 inhibitor
B6119 LLY507Summary: SMYD2 inhibitor -
 B6120 AdoxSummary: indirect methyltransferase inhibitor
B6120 AdoxSummary: indirect methyltransferase inhibitor -
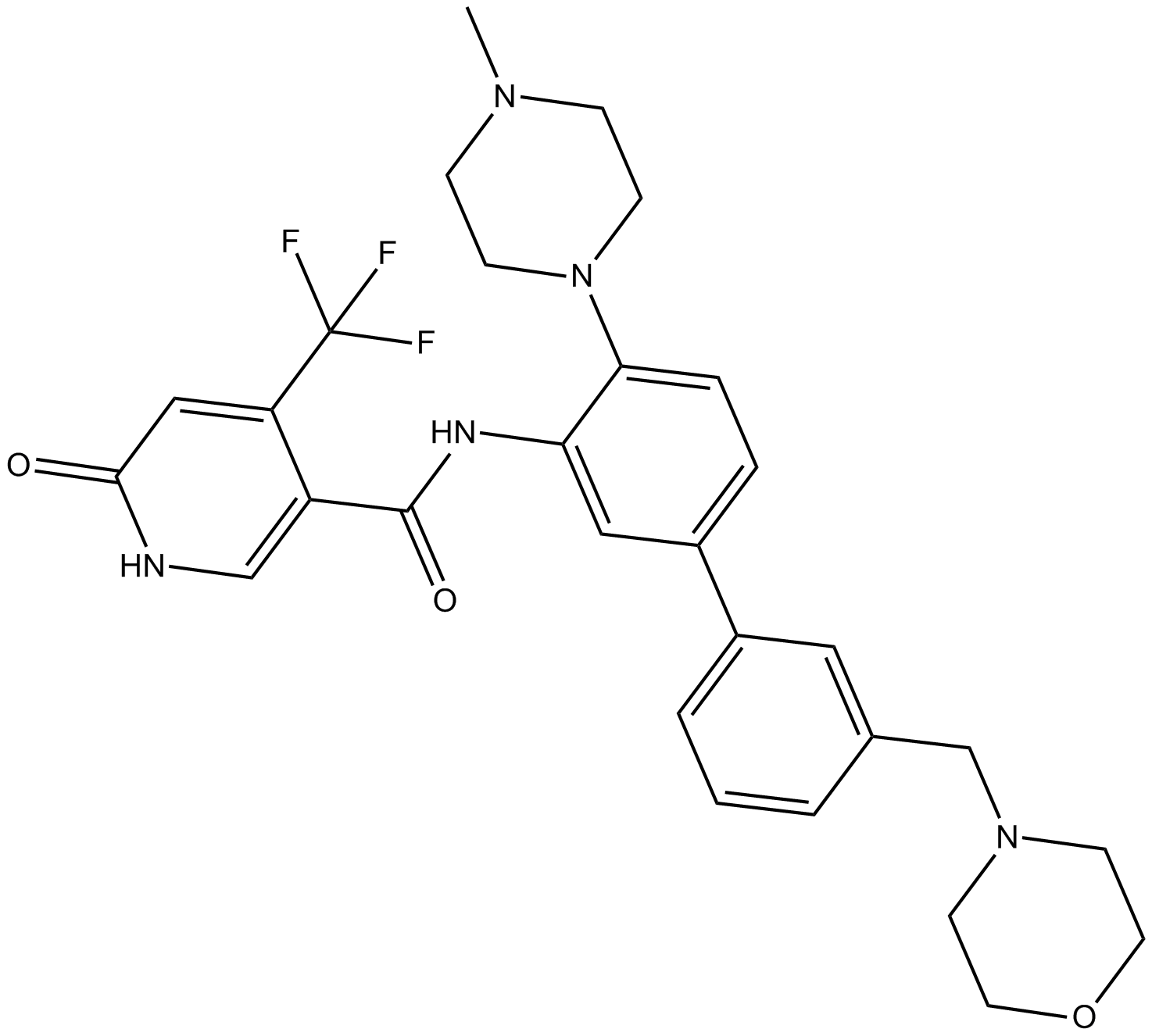 B6168 OICR-94293 CitationSummary: Wdr5-MLL interaction antagonist
B6168 OICR-94293 CitationSummary: Wdr5-MLL interaction antagonist

