EZ Cap™ Cy5 EGFP mRNA (5-moUTP)
EZ Cap™ Cy5 EGFP mRNA (5-moUTP) is a superior dual-fluorescence reporter tool engineered for advanced gene delivery research and real-time analysis. This product integrates the tracking capability of Cy5 with the functional reporting of EGFP protein expression, providing a ready-to-use tool for validating and optimizing delivery systems. EGFP absorbs blue light, with an excitation peak around 488 nm, and emits bright green light, with an emission peak near 509-513 nm. Cy5 (Cyanine-5) is a fluorescent compound with an excitation peak at 646 nm and an emission peak at 662 nm. EZ Cap™ Cy5 EGFP mRNA (5-moUTP) is widely used in macrophage-targeted therapy development, nanoparticle validation, and quantitative transfection studies.
Key features:
Fluorescent Labeling: The mRNA is covalently conjugated with Cy5 dye, enabling direct visualization of mRNA delivery, cellular uptake, and intracellular trafficking using fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry, without the need for secondary detection steps.
Cap1 Structure: The mRNA incorporates a Cap1 analog at the 5' end, ensuring high translation initiation efficiency, improved stability, and reduced innate immune recognition, leading to stronger and more sustained luciferase expression.
Modified Nucleotides: It contains 5-methoxyuridine (5-moU) modified nucleotides, which decreases immunogenicity, enhances mRNA stability, and increases translational efficiency, resulting in more reliable and reproducible protein yield.
| mRNA Length | 996 nucleotides | ||
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | ||
| Buffer | 1 mM Sodium Citrate, pH 6.4 | Storage | -40°C or below |
| General tips | Dissolve it on ice and take care to prevent RNase contamination degradation. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as much as possible. Do not vortex. For the first time, it is gently centrifuged and divided into several parts for stand-alone use. Use RNase-free reagents and consumables, using appropriate RNase-free technology. It can not be added to the serum-containing medium until it is mixed with the transfection reagent. | ||
| Shipping Condition | ship with dry ice. | ||
- 1. Shuling Ren, Xinyu Lin, et al. "Redox-Responsive Peptide Coacervates for Enhanced mRNA Delivery and Intracellular Release." ACS Nano. 2025 Dec 26. PMID: 41451635
- 2. Paul Joshua Hurst, Yuan Jia, Summer Ramsay-Burrough. "The Structure and Morphology of Single-Component Oligomeric RNA Delivery Vectors Derived from Amphiphilic Charge-Altering Releasable Transporters." ACS Nano. 2025 Nov 5. PMID: 41194596
- 3. Ruiteng Song, Yongqi Lin, et al. "Ocular delivery of lipid nanoparticles-formulated mRNA encoding lanosterol synthase ameliorates cataract in rats." Nat Commun. 2025 Sep 26;16(1):8522. PMID: 41006301
- 4. Christopher J LaSalle, David V Morrissey, et al. "Clickable and Degradable Polycarbonate Vehicles for mRNA Delivery." Bioconjug Chem. 2025 Jul 9. PMID: 40633113
- 5. Sidharth Panda, Ella J. Eaton, et al. "Machine LearningReveals Amine Type in Polymer MicellesDetermines mRNA Binding." JACS Au. 2025 Apr 14;5(4):1845-1861. PMID: 40313817
- 6. Caroline T. Holick, Tobias Klein, et al. "Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (POx) as Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)‐Lipid Substitute for Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations." Small. 2025 Apr;21(16):e2411354. PMID: 40103543
- 7. Nicholas W. Kreofsky, Punarbasu Roy, et al. "Blending Carbohydrate and Quinine-Based Polymers Imparts Colloidal Stability, Improved Performance, and Cell Specificity for mRNA Delivery." Biomacromolecules August 28, 2025
- 8. Harrison Douglas Lawson, Huy Hoang Nguyen, et al. "Synthetic Strategy for mRNA Encapsulation and Gene Delivery with Nanoscale Metal‐Organic Frameworks." ADVANCED FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS 19 May 2025
- 9. Marshall S. Padilla, Sarah J. Shepherd, Andrew R. Hanna. "Elucidating lipid nanoparticle properties and structure through biophysical analyses." Nat Biotechnol (2025).
- 10. Punarbasu Roy, Nicholas W. Kreofsky, Theresa M. Reineke. "Quinine-Based Polymers Are Versatile and Effective Vehicles for Intracellular pDNA, mRNA, and Cas9 Protein Delivery." Biomacromolecules. 2024 Oct 14;25(10):6693-6707. PMID: 39324490
- 11. Harrison Lawson, Huy Nguyen, et al. "Synthetic Strategy for mRNA Encapsulation and Gene Delivery with Metal-Organic Frameworks." ChemRxiv. 12 April 2024
- 12. Valentina Andretto, Mathieu Repellin, et al. "Hybrid core-shell particles for mRNA systemic delivery ." J Control Release. 2023 Jan:353:1037-1049. PMID: 36442614
- 13. Zhihui Dong, Zhuoshan Huang, et al. "Nanoparticles (NPs)-mediated systemic mRNA delivery to reverse trastuzumab resistance for effective breast cancer therapy." Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. Volume 13, Issue 3, March 2023, Pages 955-966
- 14. Xuan Liu, An-Yi Chang, et al. "Robust three-dimensional nanotube-in-micropillar array electrodes to facilitate size independent electroporation in blood cell therapy." Lab Chip. 2021 Oct 26;21(21):4196-4207. PMID: 34546271
- 15. Chen Q, Gao M, et al. "Biodegradable nanoparticles decorated with different carbohydrates for efficient macrophage-targeted gene therapy." J Control Release. 2020 Apr 22;323:179-190 PMID: 32334322
Quality Control & Datasheet
- View current batch:
Related Biological Data
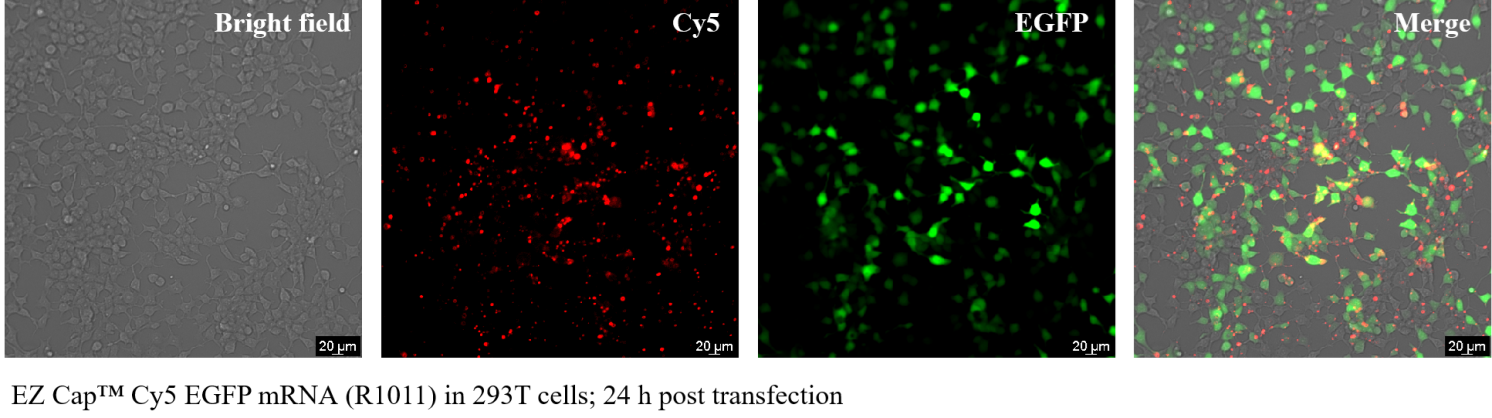
Related Biological Data
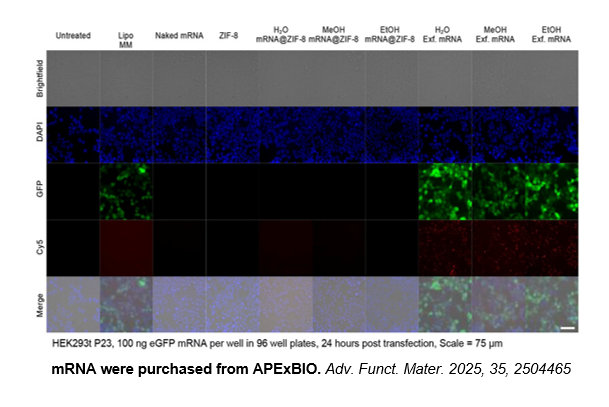
Related Biological Data
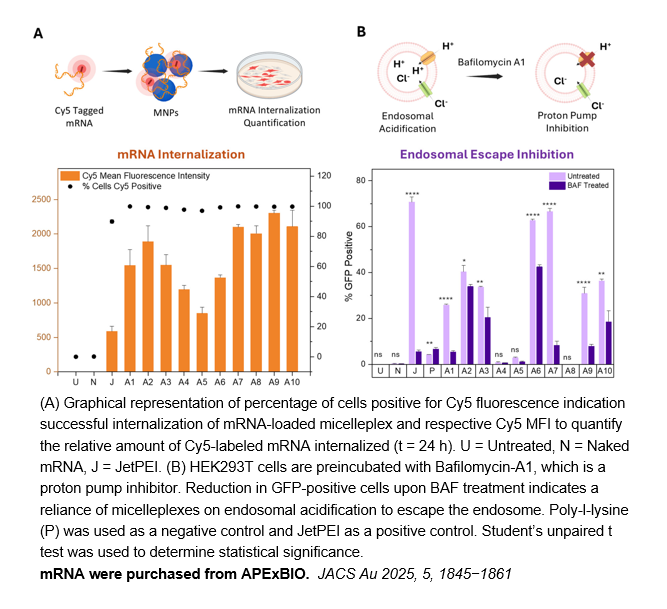
Related Biological Data
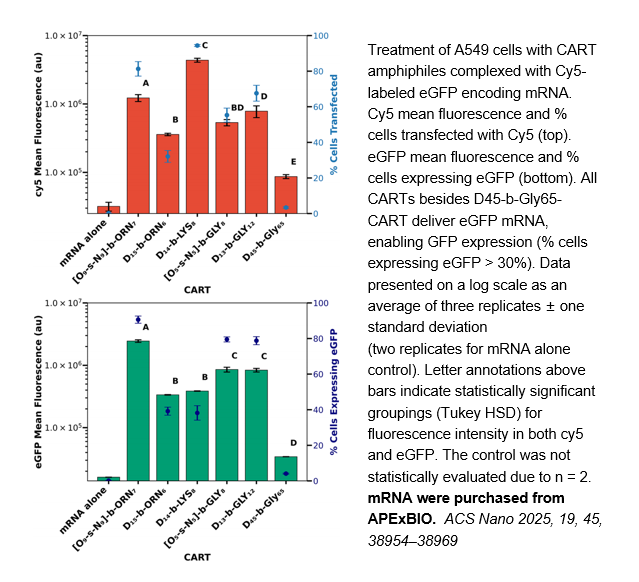
Related Biological Data
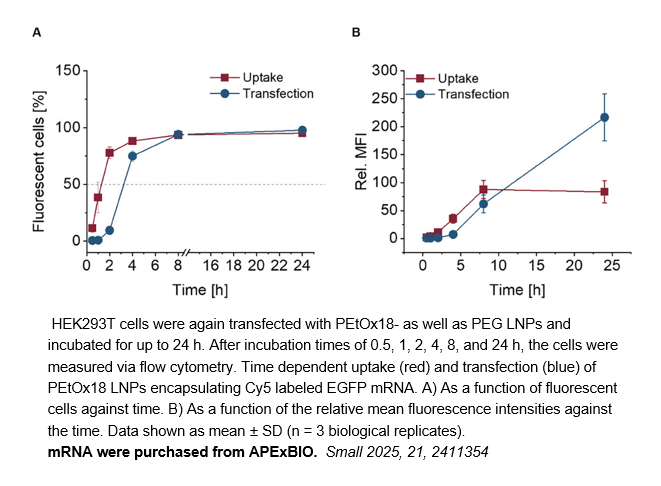
Related Biological Data
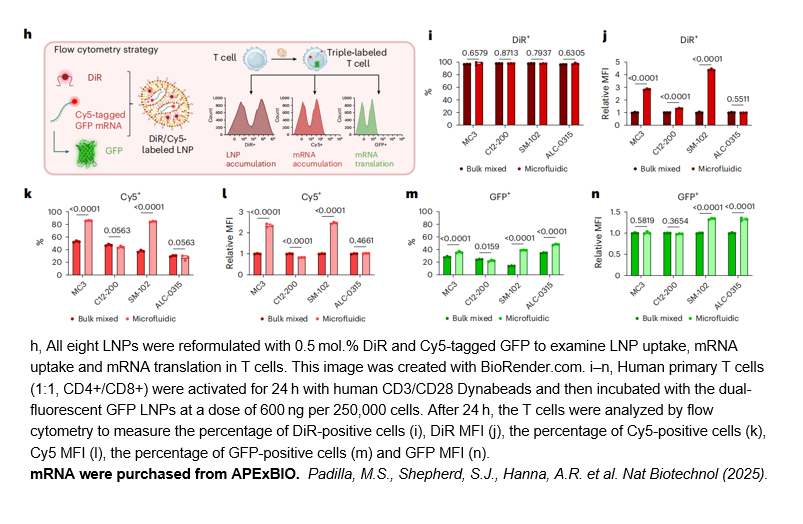
Related Biological Data
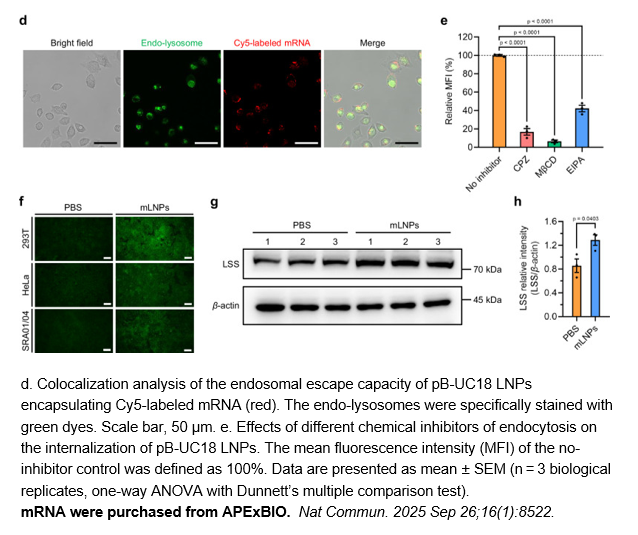
Related Biological Data
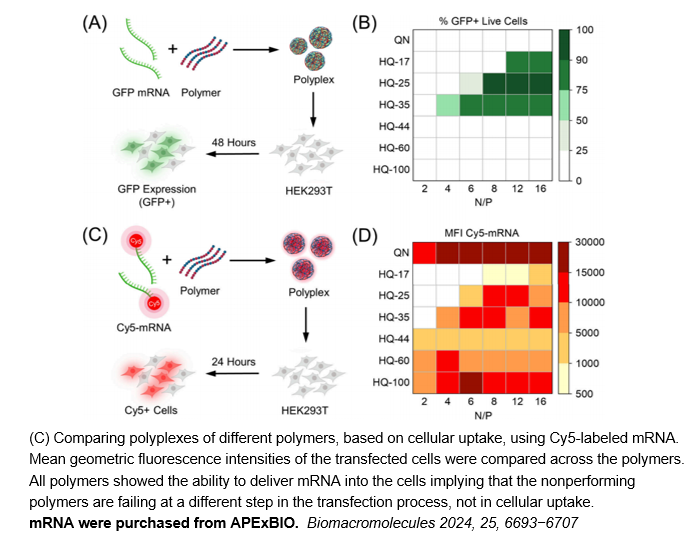
It can be based on your experimental goals:
- For Tracking Transfection and Translation Efficiency: APExBIO Reporter Gene mRNAs (e.g. EGFP, Firefly Luciferase mRNA) are commonly used to track transfection efficiency and protein expression duration; evaluate gene expression and cell viability; study mRNA localization and bio-distribution via in vivo imaging; optimize transfection conditions and validate LNP delivery system.
- For Gene Editing, Functional Studies and Gene Therapy Research: APExBIO offers various functional protein mRNAs, involving tumor suppressors (e.g. p53, PTEN), cytokines (e.g. IL-12, IL-10), gene-editing tools (e.g. spCas9, Cre Recombinase), gene replacement protein (e.g. EPO), and antigens (e.g. OVA, SARS-CoV-2 Spike).
- For Sustained Protein Expression: APExBIO Self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) and Circular RNA (circRNA) are recommended for applications requiring prolonged protein expression. saRNA enables lasting and strong protein expression at lower doses, while circRNA has enhanced structural stability and extended expression duration.
- Advanced Capping Technology: Utilizes Cap 1 structure (EZ Cap™ Cap) to achieve enhanced translation efficiency and minimizing activation of the host innate immune response. The capping efficiency can reach 90–99%.
- Diverse Modification Options: Provides a range of modified nucleotides, such as m1Ψ, 5-moUTP and Cy5-UTP, which reduce immunogenicity, improve mRNA stability, and maximize protein expression levels.
- Stringent Quality Control: Each batch undergoes rigorous quality assessment including capping efficiency, purity, integrity, and sterility to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.





















