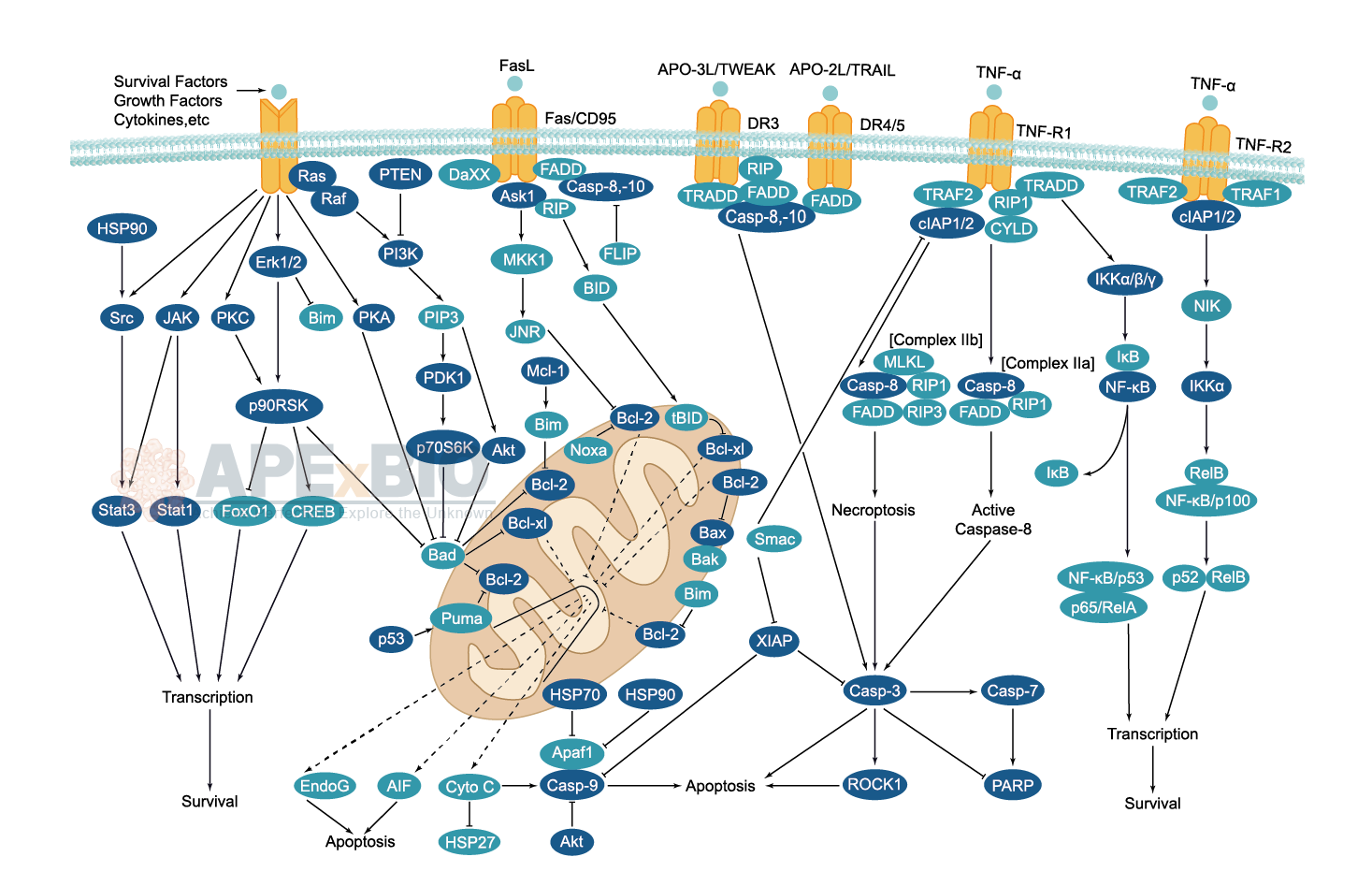
Apoptosis
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is rigorously controlled process of cell death that leads to phagocytosis of unwanted cell. It is triggered after sufficient cellular damage and activated through extrinsic or intrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway is mainly occurs via release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization by Bcl-2 family proteins. The extrinsic pathway is induced by ligand binding to death receptor, such as Fas, TNFαR, DR3, DR4, and DR5. Caspases then cleave target proteins and nuclear lamins to promote DNA degradation, resulting apoptotic cells undergo phagocytosis. In addition, p53 has the ability to activate intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis by inducing transcription of several proteins like Puma, Bid, Bax, TRAIL-R2, and CD95.
Some Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), such as XIAP/BIRC4 and Bruce/BIRC6, can block casapse activity through direct binding, while other IAPs, such as cIAP1/BIRC2, cIAP2/BIRC3, act as ubiquitin ligases that target caspases for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Apoptosis is essential for growth, development and aging in multicellular organisms. Any alterations or abnormalities occurring in apoptotic processes contribute to development of human diseases, including cancer.
-
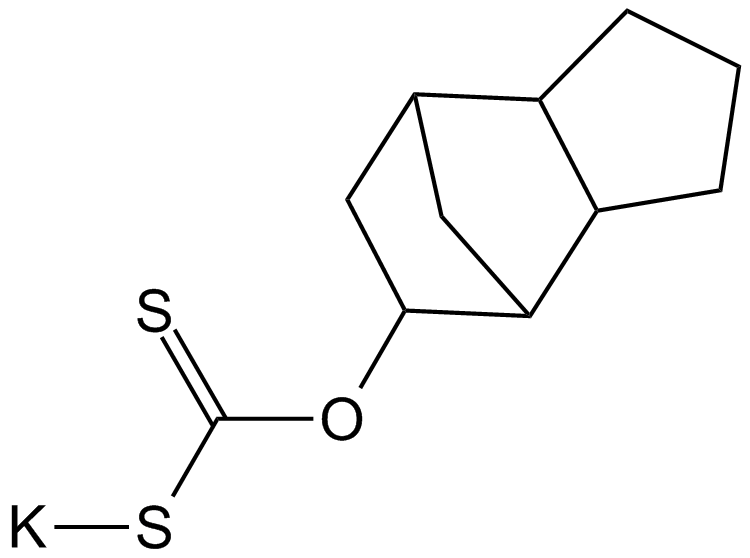 A3343 D609Target: PC-PLCSummary: PC-PLC inhibitor
A3343 D609Target: PC-PLCSummary: PC-PLC inhibitor -
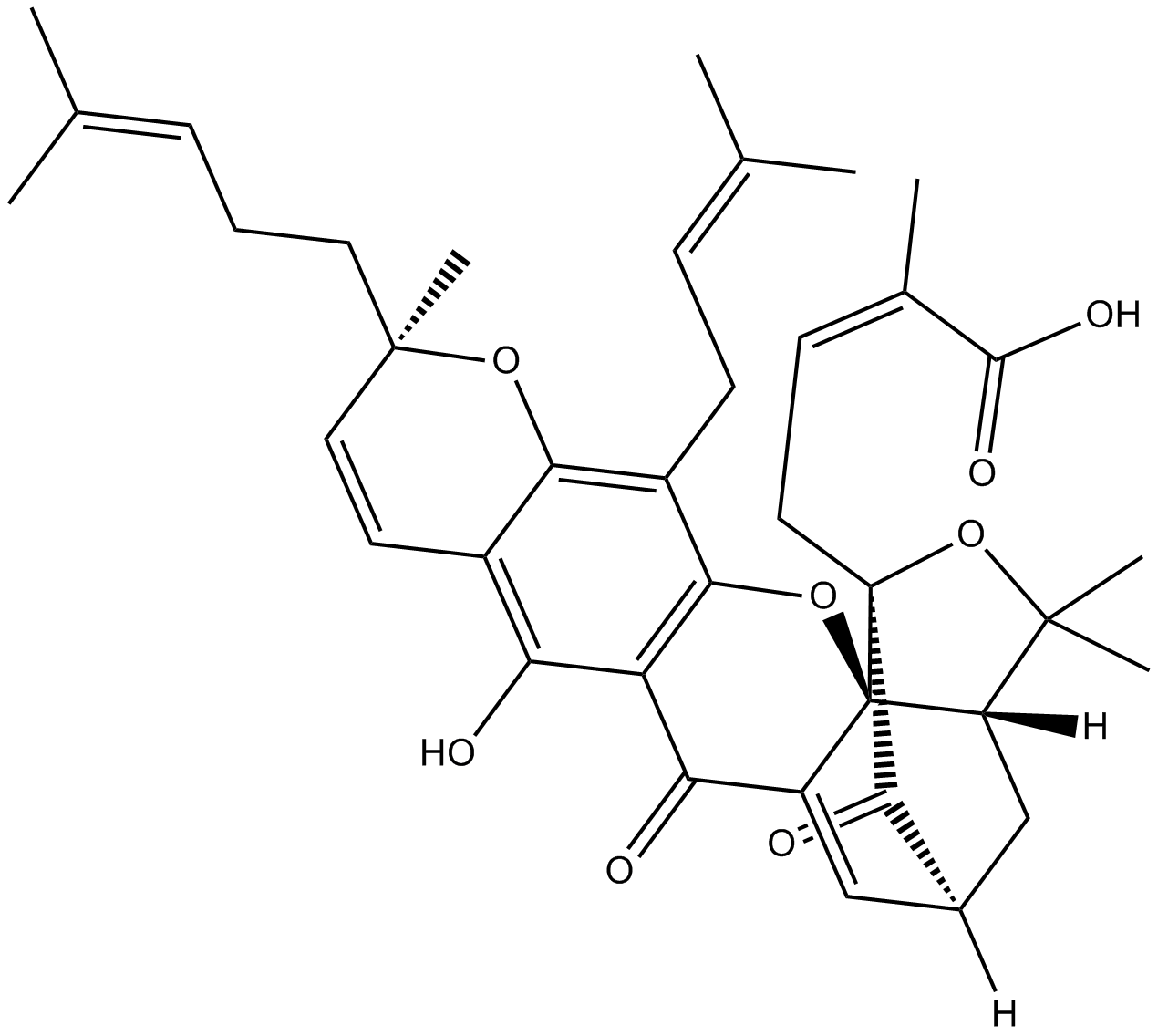 A3424 Gambogic AcidSummary: Caspase activator and apoptosis inducer
A3424 Gambogic AcidSummary: Caspase activator and apoptosis inducer -
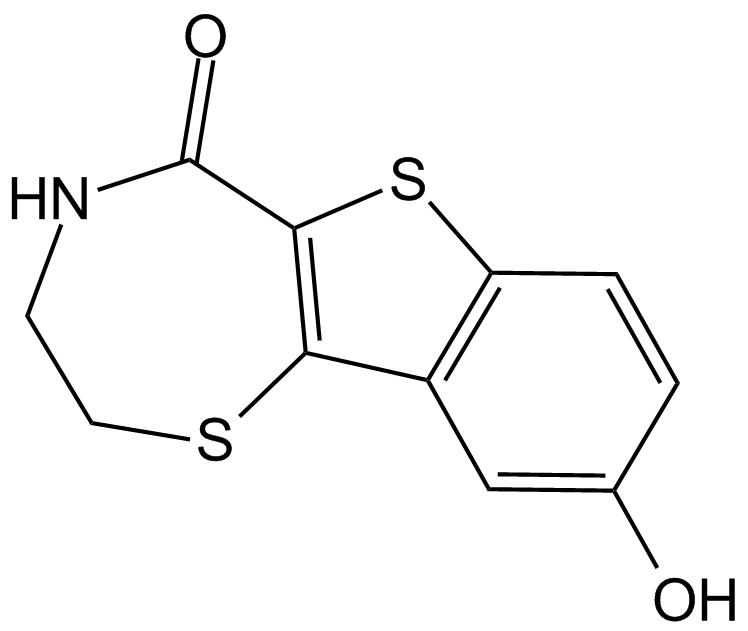 A3524 kb NB 142-70Summary: Inhibitor of protein kinase D,selective
A3524 kb NB 142-70Summary: Inhibitor of protein kinase D,selective -
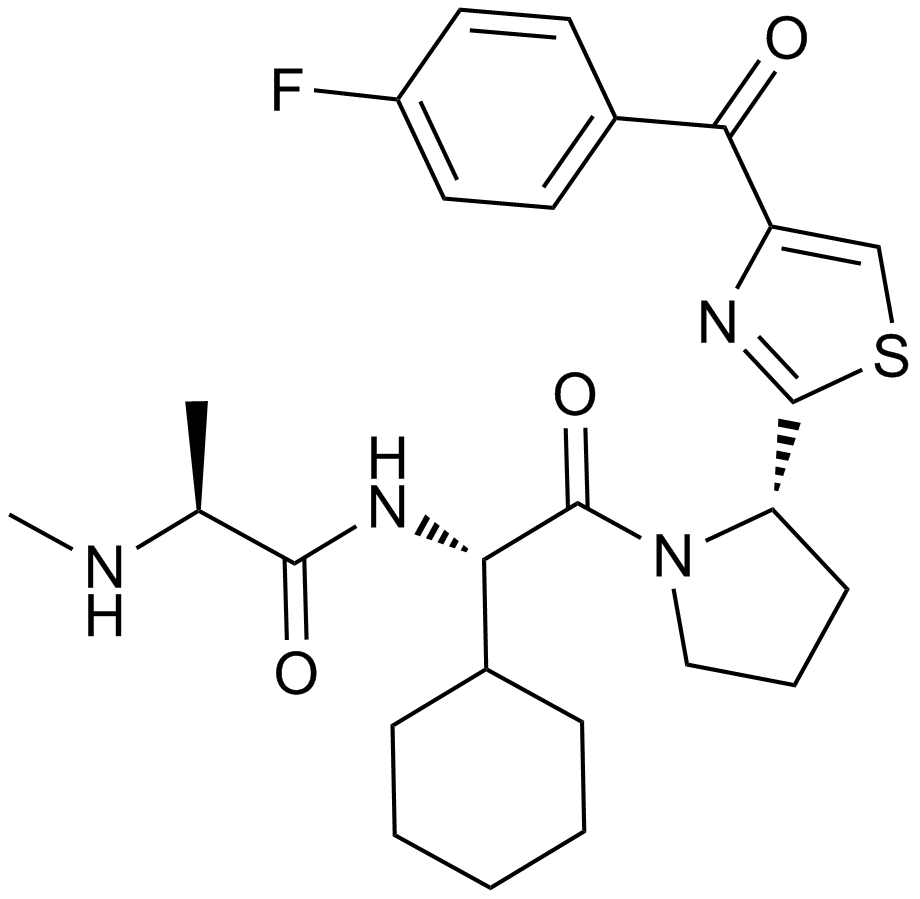 A3541 LCL1619 CitationTarget: Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP)Summary: Antagonist of IAPs inhibitor
A3541 LCL1619 CitationTarget: Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP)Summary: Antagonist of IAPs inhibitor -
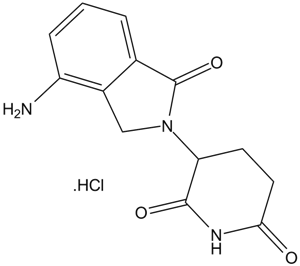 A3547 Lenalidomide hydrochlorideSummary: TNF-α secretion inhibitor
A3547 Lenalidomide hydrochlorideSummary: TNF-α secretion inhibitor -
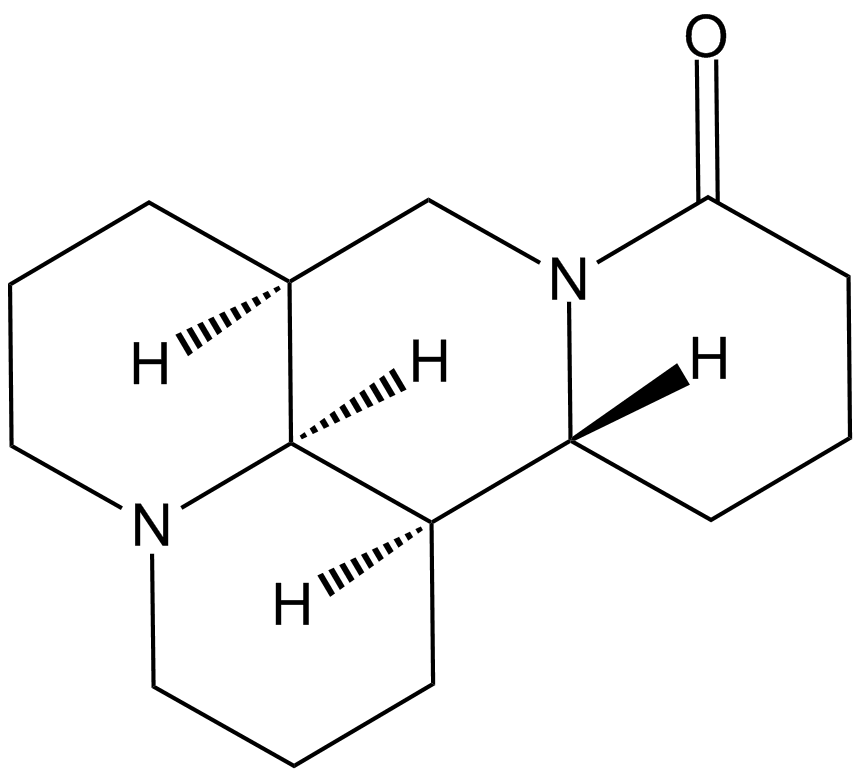 A3583 Matrine1 CitationSummary: Alkaloid found in Sophora plant
A3583 Matrine1 CitationSummary: Alkaloid found in Sophora plant -
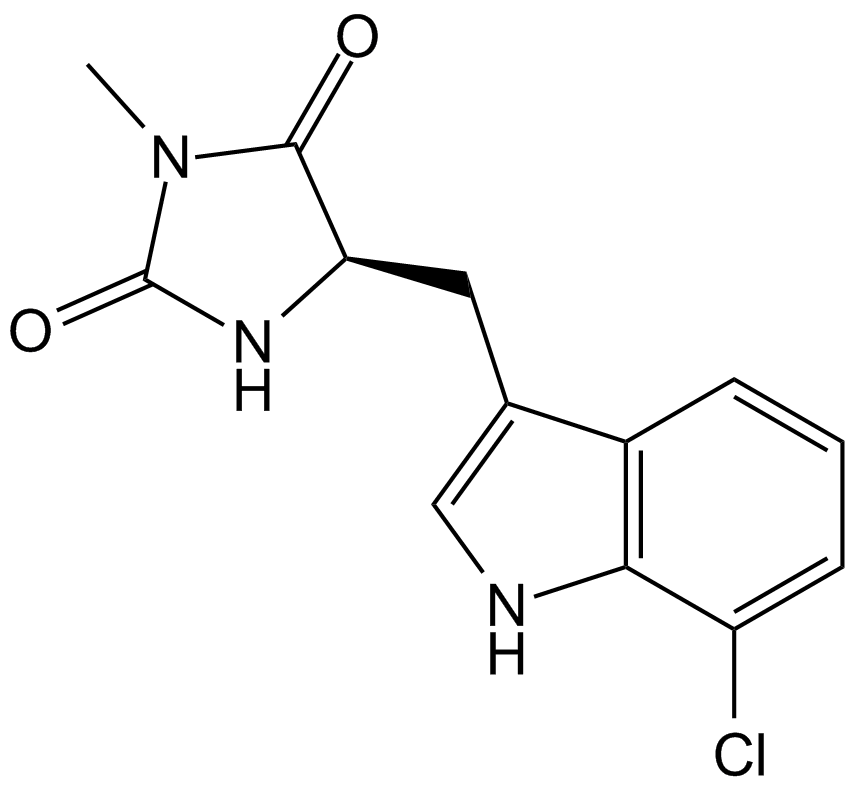 A3652 Necrostatin 23 CitationSummary: In vitro necroptosis inhibitor
A3652 Necrostatin 23 CitationSummary: In vitro necroptosis inhibitor -
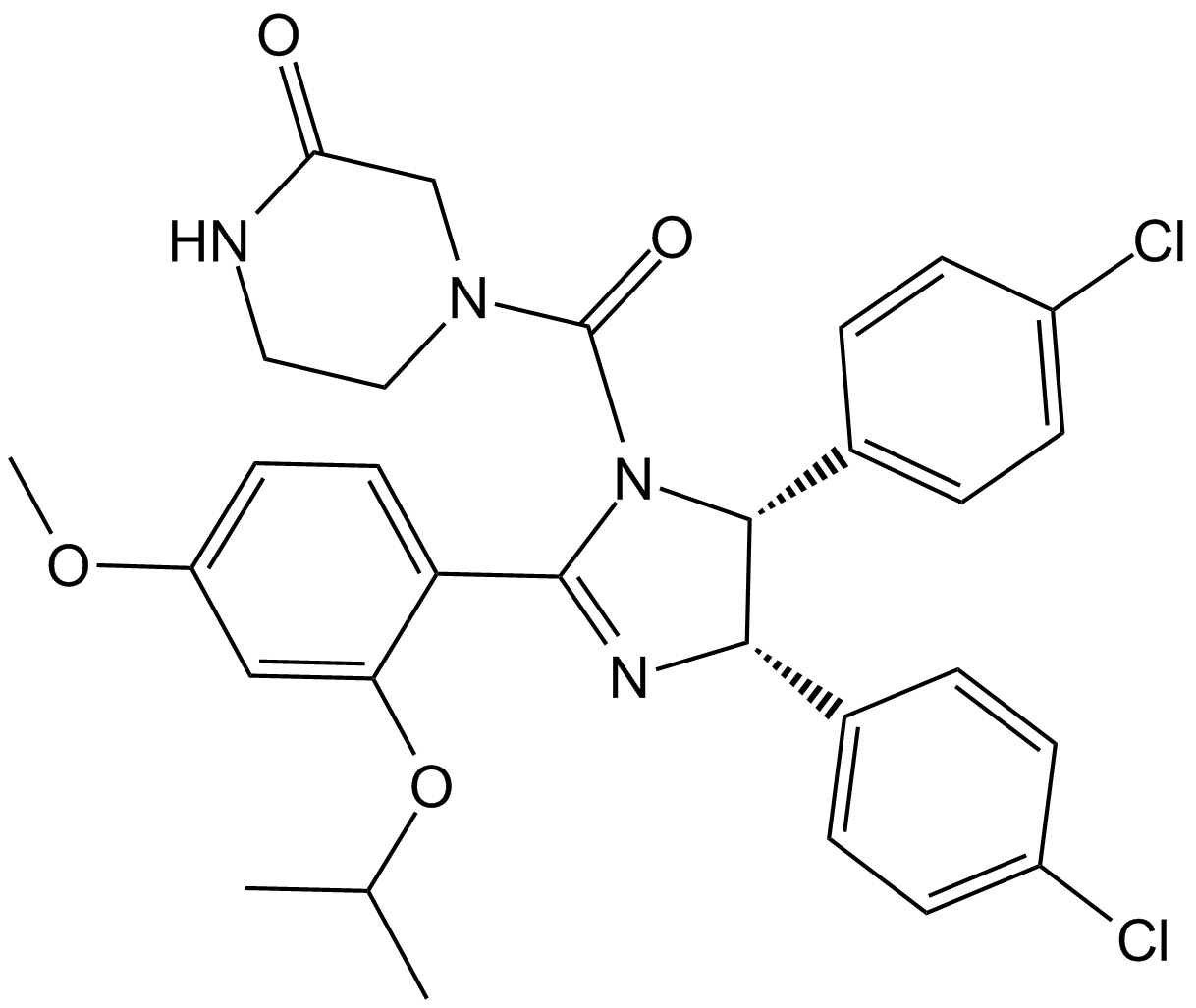 A3671 Nutlin-3a chiral2 CitationSummary: MDM2 inhibitor, antiproliferative and antiproapoptotic
A3671 Nutlin-3a chiral2 CitationSummary: MDM2 inhibitor, antiproliferative and antiproapoptotic -
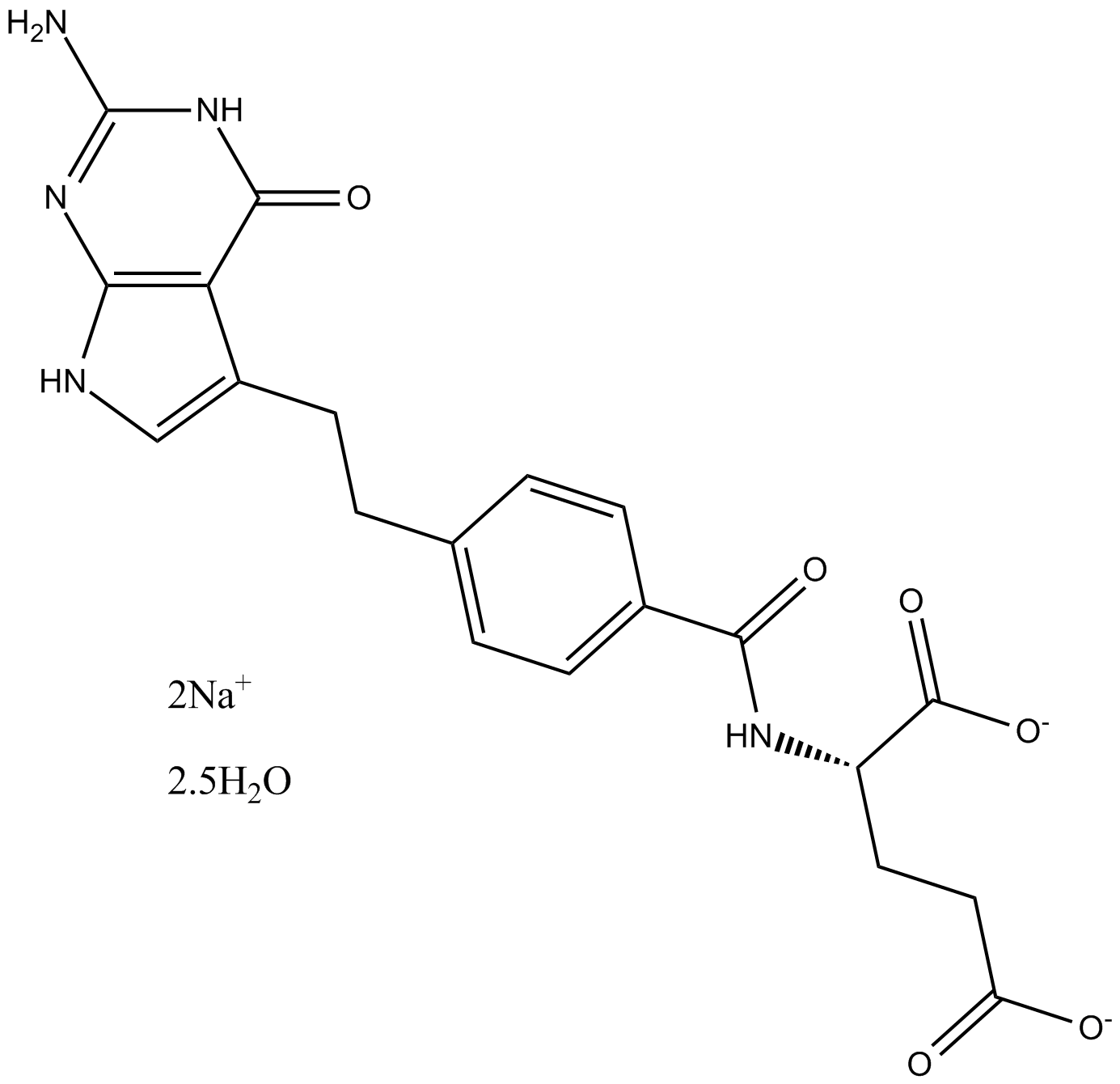 A3707 Pemetrexed disodium hemipenta hydrateSummary: Antifolate and antimetabolite agent
A3707 Pemetrexed disodium hemipenta hydrateSummary: Antifolate and antimetabolite agent -
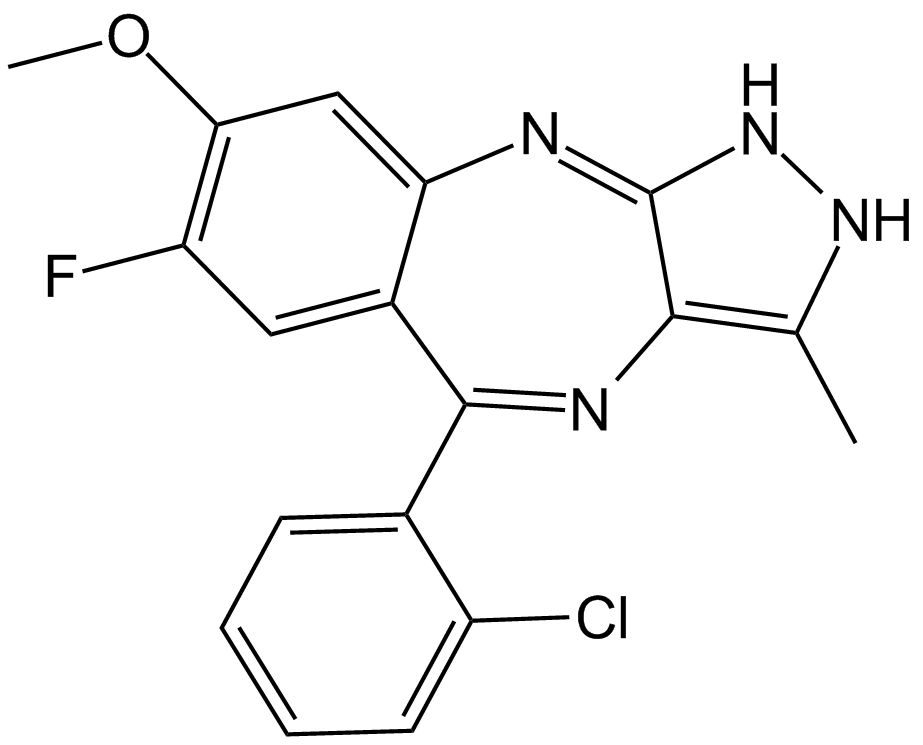 A3746 R1530Summary: Antiangiogenesis,mitosis-angiogenesis inhibitor (MAI)
A3746 R1530Summary: Antiangiogenesis,mitosis-angiogenesis inhibitor (MAI)