Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
 N2878 MalvidinSummary: A natural pigment
N2878 MalvidinSummary: A natural pigment -
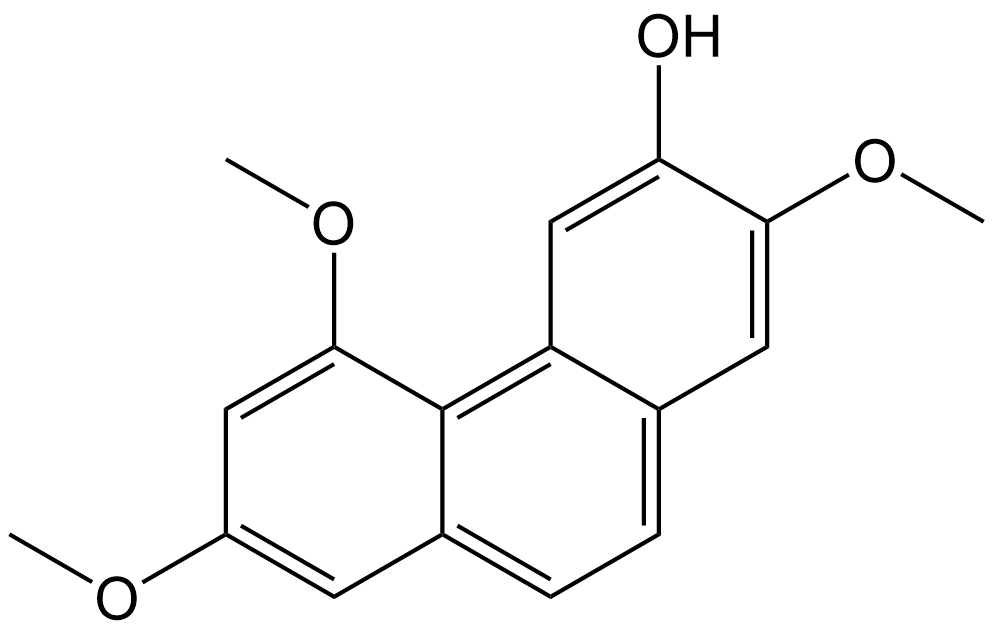 N2879 Batatasin ISummary: A natural phenanthrene derivative
N2879 Batatasin ISummary: A natural phenanthrene derivative -
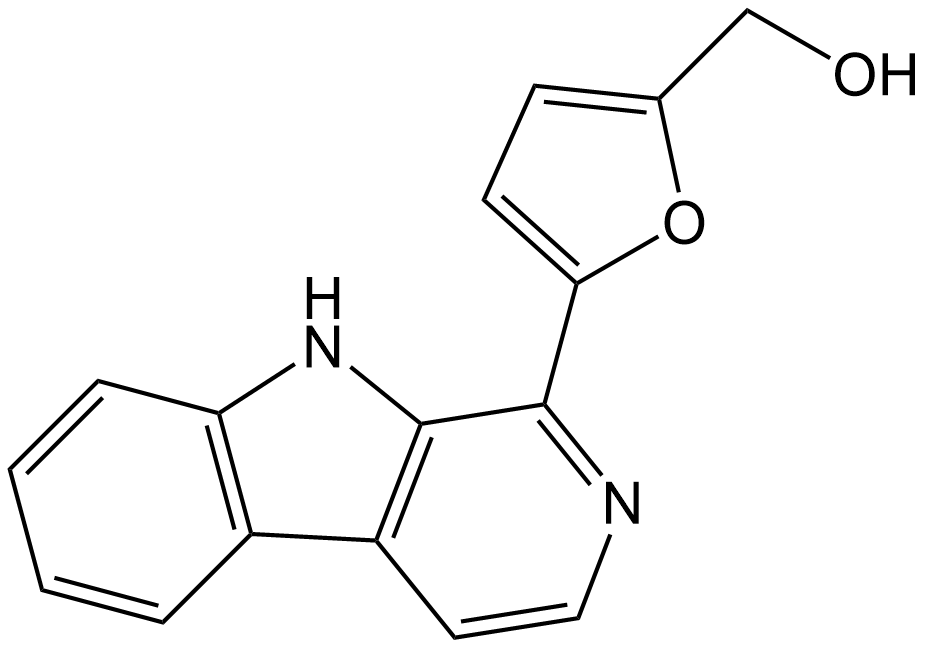 N2880 PerlolyrineSummary: A natural β-carboline compound
N2880 PerlolyrineSummary: A natural β-carboline compound -
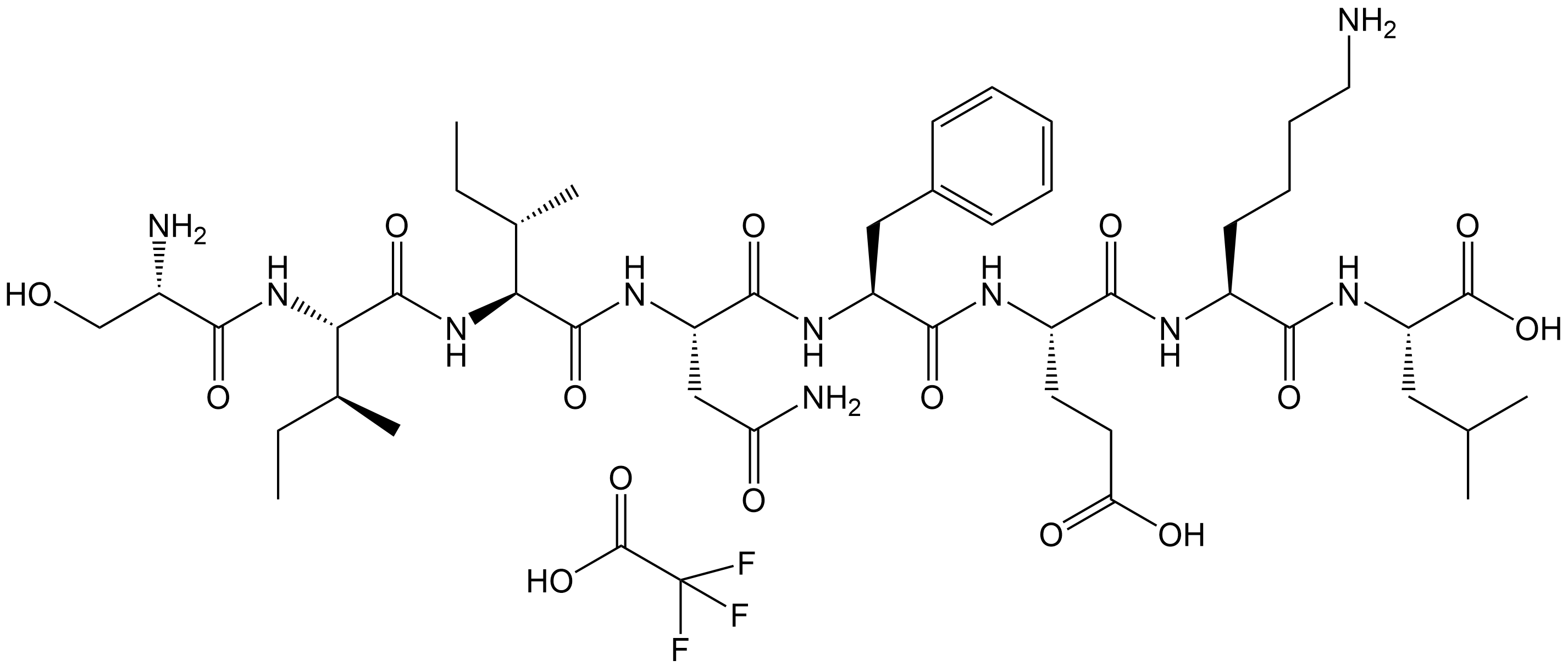 C8690 OVA Peptide(257-264) TFASummary: A core antigenic epitope of chicken ovalbumin (OVA)
C8690 OVA Peptide(257-264) TFASummary: A core antigenic epitope of chicken ovalbumin (OVA) -
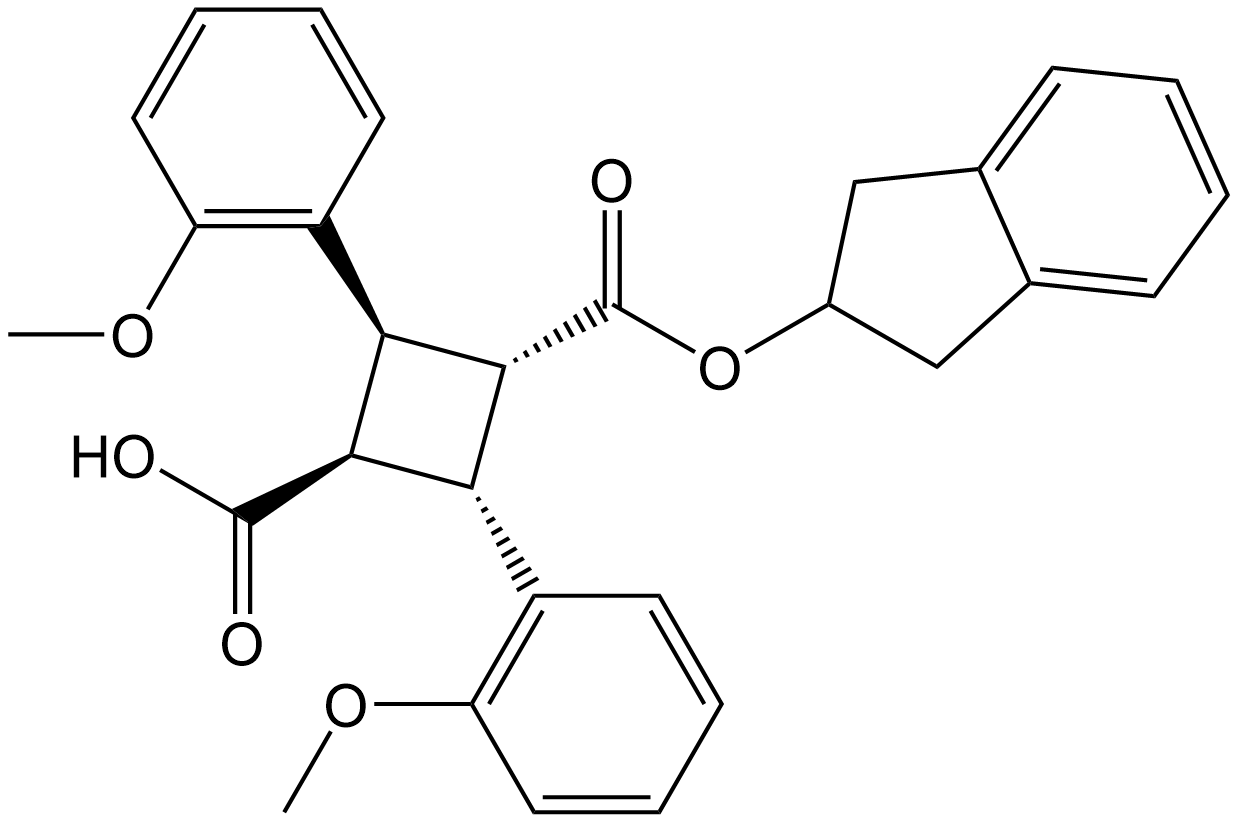 C8691 ART26.12Summary: A highly selective inhibitor of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5)
C8691 ART26.12Summary: A highly selective inhibitor of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) -
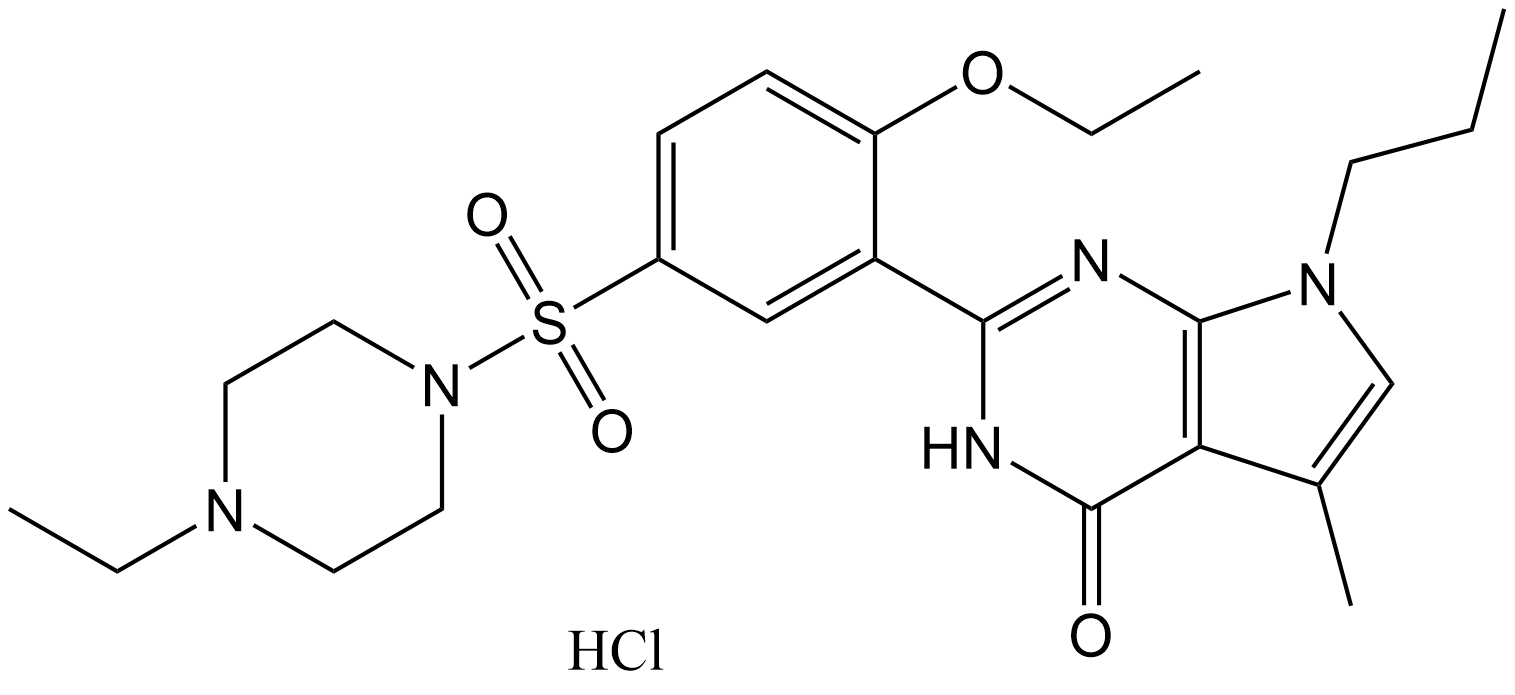 C8692 Yonkenafil hydrochlorideSummary: A highly selective phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor
C8692 Yonkenafil hydrochlorideSummary: A highly selective phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor -
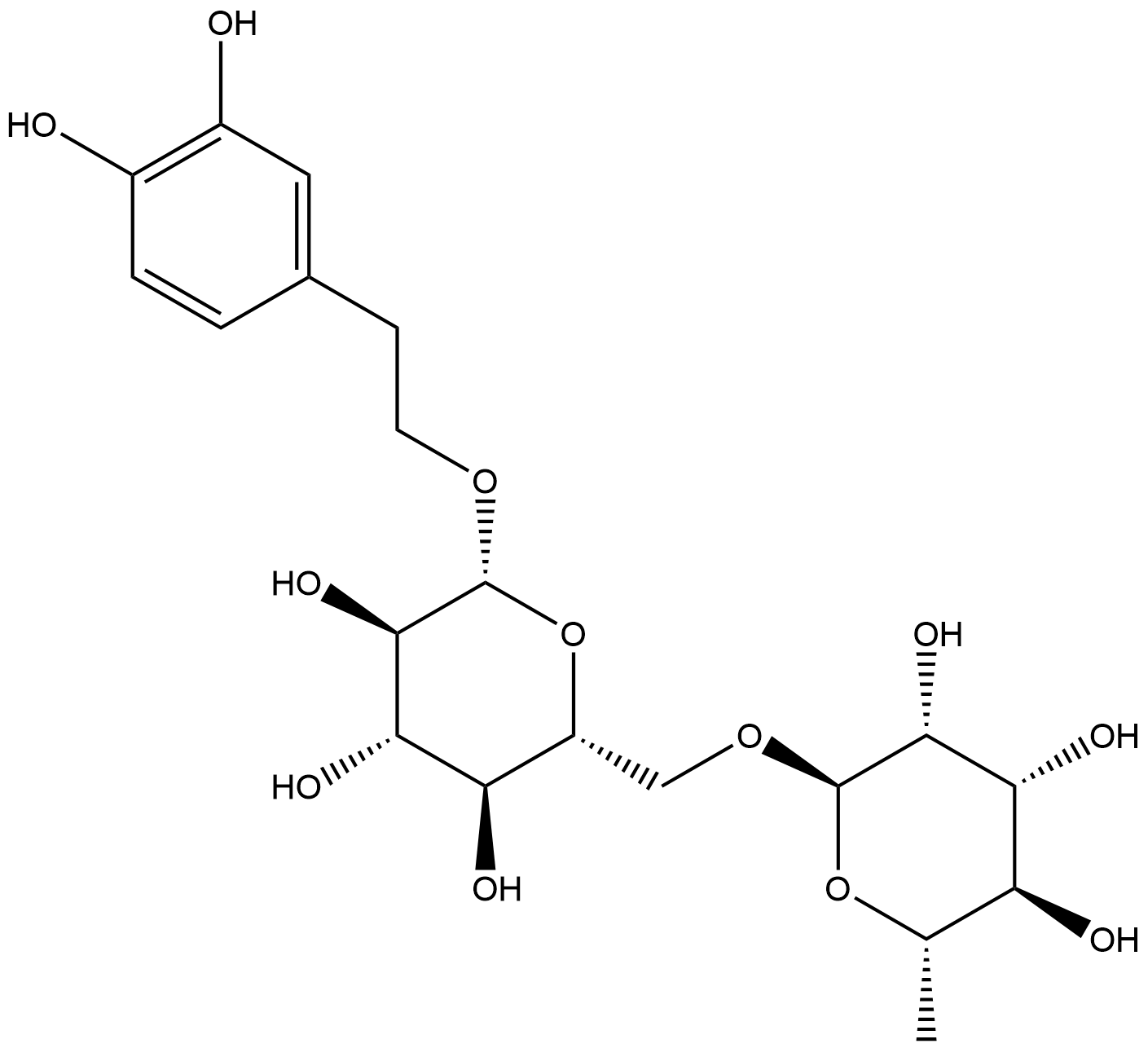 N2883 Forsythoside ESummary: A phenolic acid glycoside compound isolated from Forsythia suspensa.
N2883 Forsythoside ESummary: A phenolic acid glycoside compound isolated from Forsythia suspensa. -
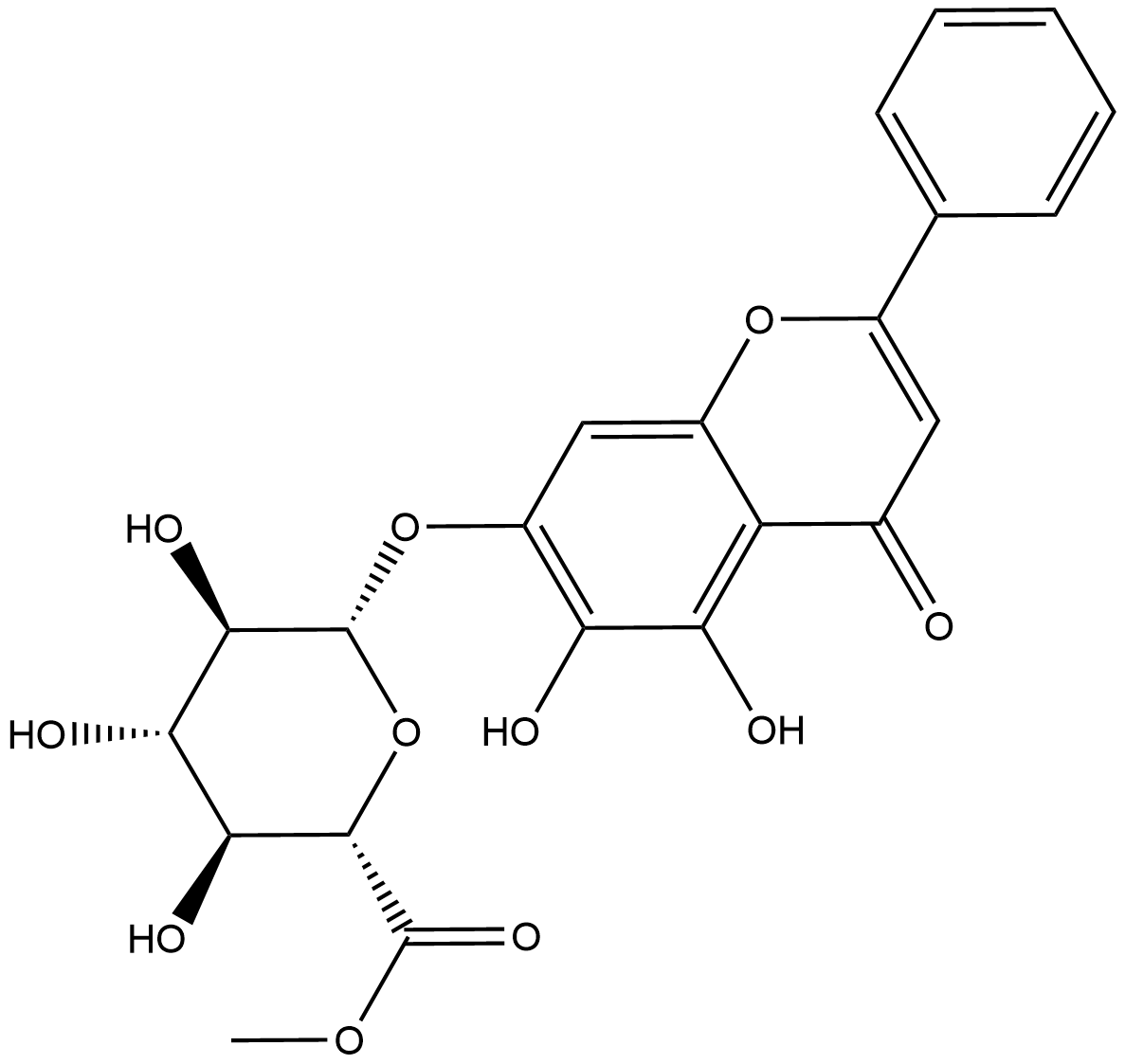 N2884 Baicalin methyl esterSummary: An esterified derivative of baicalin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi.
N2884 Baicalin methyl esterSummary: An esterified derivative of baicalin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. -
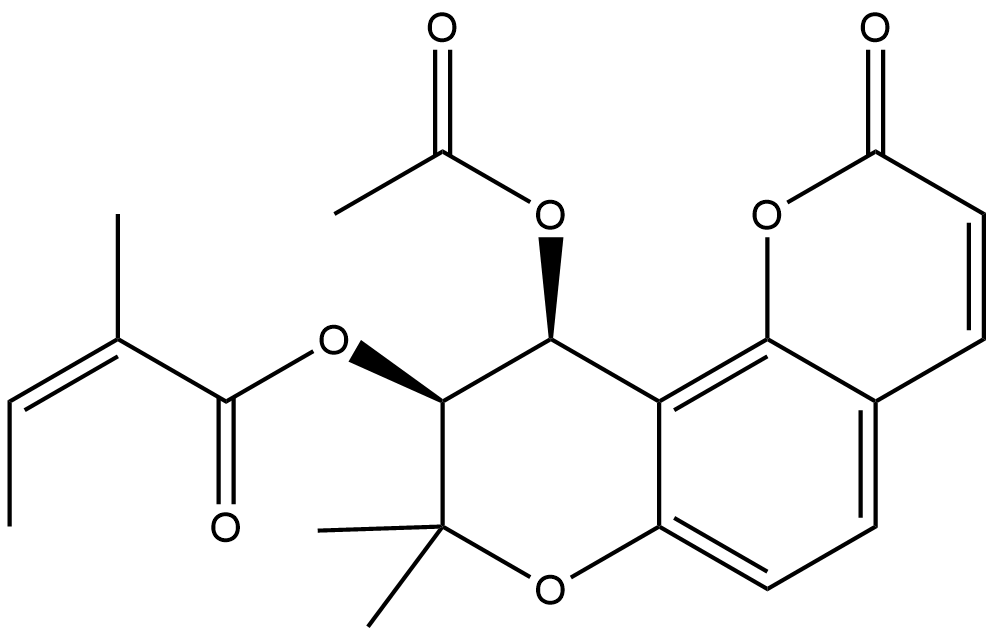 N2885 Pareruptorin ASummary: An angular pyranocoumarin compound derived from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn.
N2885 Pareruptorin ASummary: An angular pyranocoumarin compound derived from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn. -
 C8728 Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)Summary: An immune adjuvant, also commonly used to induce experimental autoimmune disease models.
C8728 Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)Summary: An immune adjuvant, also commonly used to induce experimental autoimmune disease models.


