Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
 C8557 L-NIL dihydrochloride
C8557 L-NIL dihydrochloride -
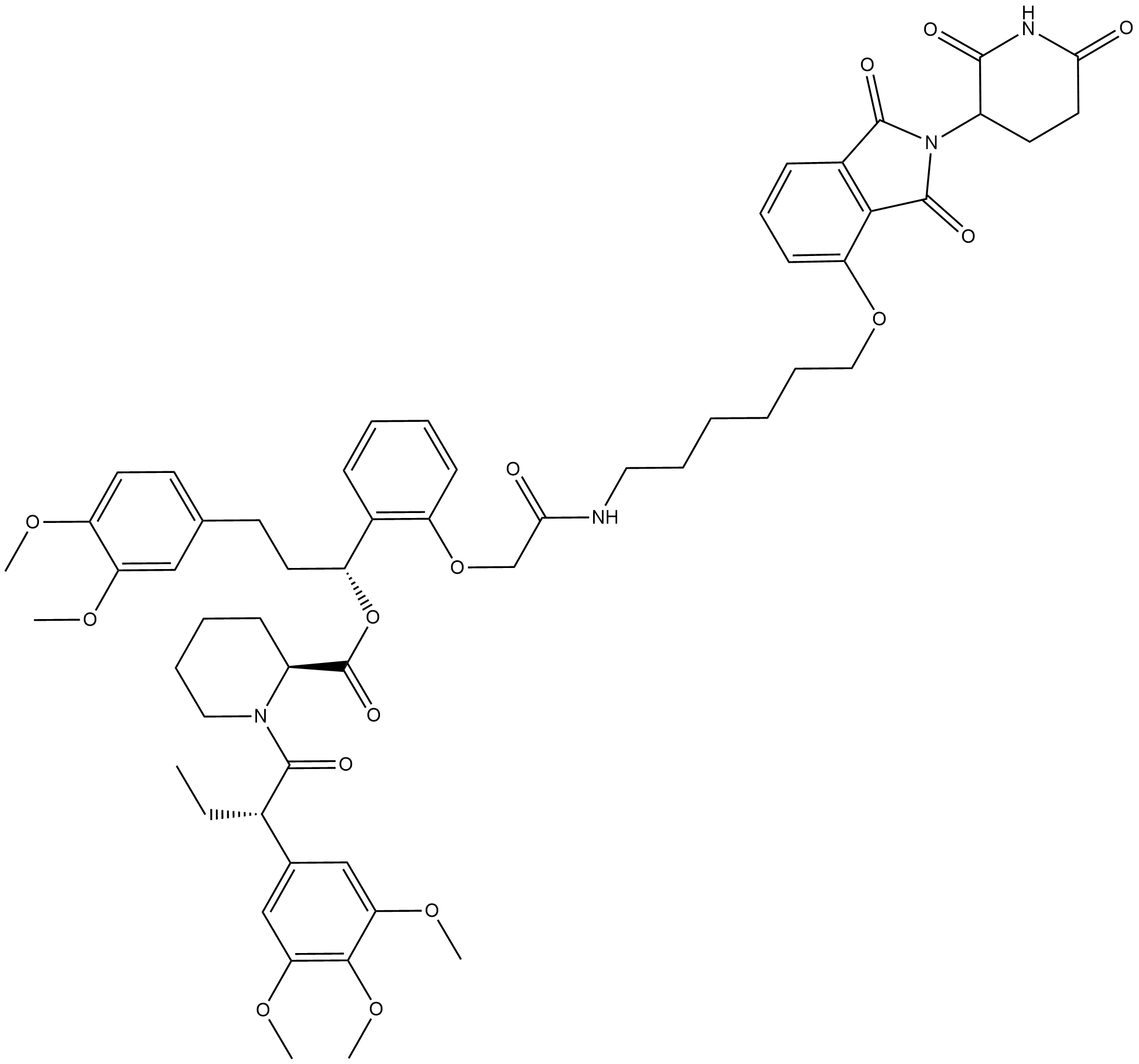 A9975 FKBP12 PROTAC dTAG-13Summary: A bifunctional depressant developed based on PROTAC technology
A9975 FKBP12 PROTAC dTAG-13Summary: A bifunctional depressant developed based on PROTAC technology -
 A9980 Cytochrome CSummary: A small, multifunctional enzyme protein located in the mitochondrial membrane space
A9980 Cytochrome CSummary: A small, multifunctional enzyme protein located in the mitochondrial membrane space -
 A9982 Vipivotide tetraxetanSummary: A potent prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) inhibitor
A9982 Vipivotide tetraxetanSummary: A potent prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) inhibitor -
 A9995 Agatolimod sodiumSummary: A synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) that acts as a TLR9 agonist
A9995 Agatolimod sodiumSummary: A synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) that acts as a TLR9 agonist -
 A9998 Uric acid sodiumSummary: An important antioxidant with the ability to scavenge oxygen radicals
A9998 Uric acid sodiumSummary: An important antioxidant with the ability to scavenge oxygen radicals -
 C8584 Cyclic-di-GMP disodiumSummary: An important STING agonist and also a bacterial second messenger
C8584 Cyclic-di-GMP disodiumSummary: An important STING agonist and also a bacterial second messenger -
 C8587 MUC1, mucin coreSummary: MUC1 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, which is overexpressed and glycosylated in cancer cells
C8587 MUC1, mucin coreSummary: MUC1 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, which is overexpressed and glycosylated in cancer cells -
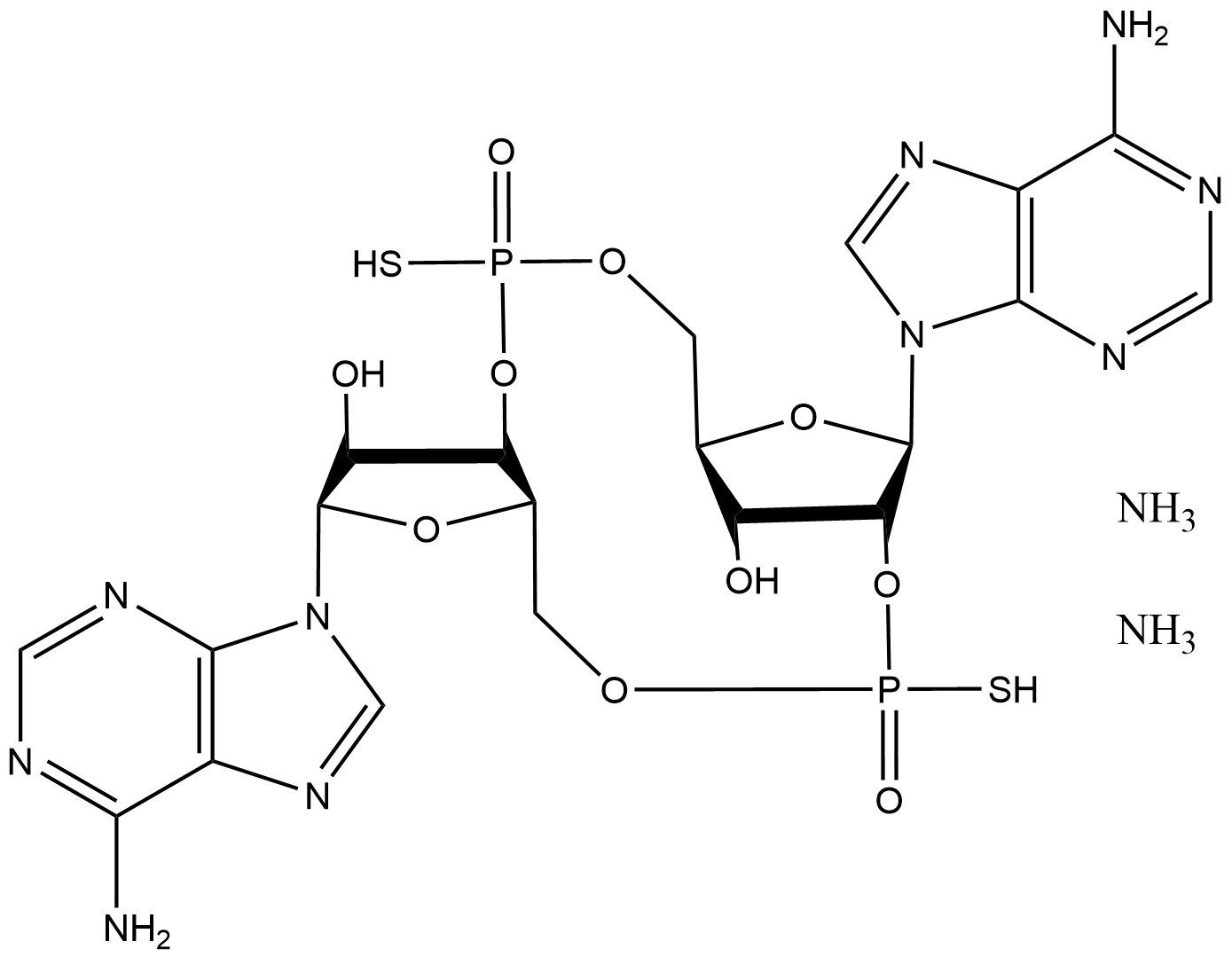 C8600 2’3’-c-di-AM(PS)2 (Rp,Rp) ammonium saltSummary: A potent agonist of interferon gene stimulant (STING)
C8600 2’3’-c-di-AM(PS)2 (Rp,Rp) ammonium saltSummary: A potent agonist of interferon gene stimulant (STING) -
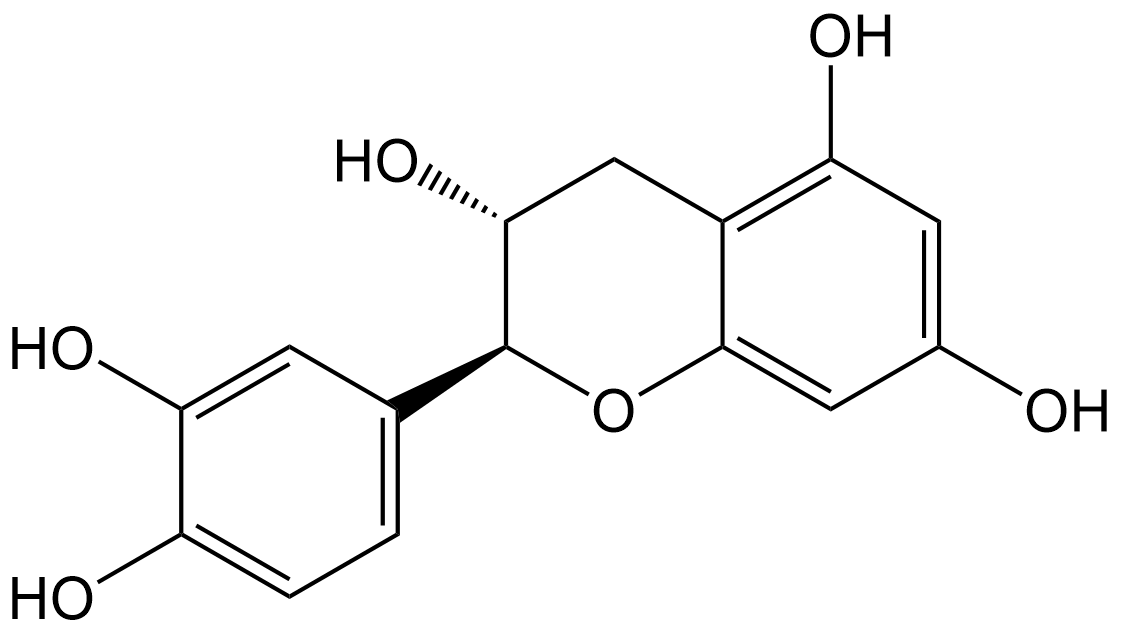 N2868 (-)-CatechinSummary: A diastereoisomer of catechin
N2868 (-)-CatechinSummary: A diastereoisomer of catechin


