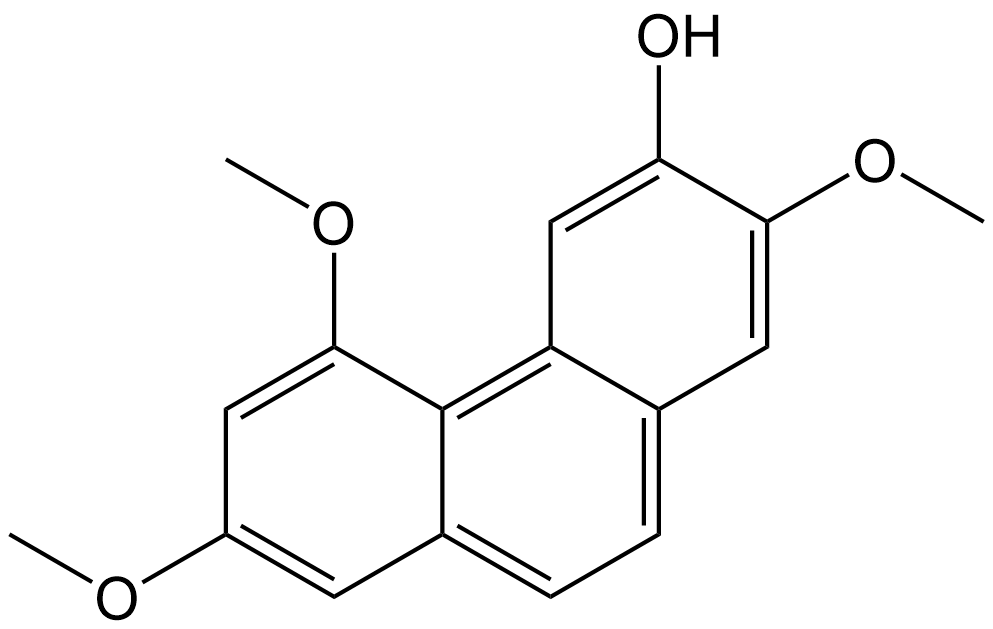
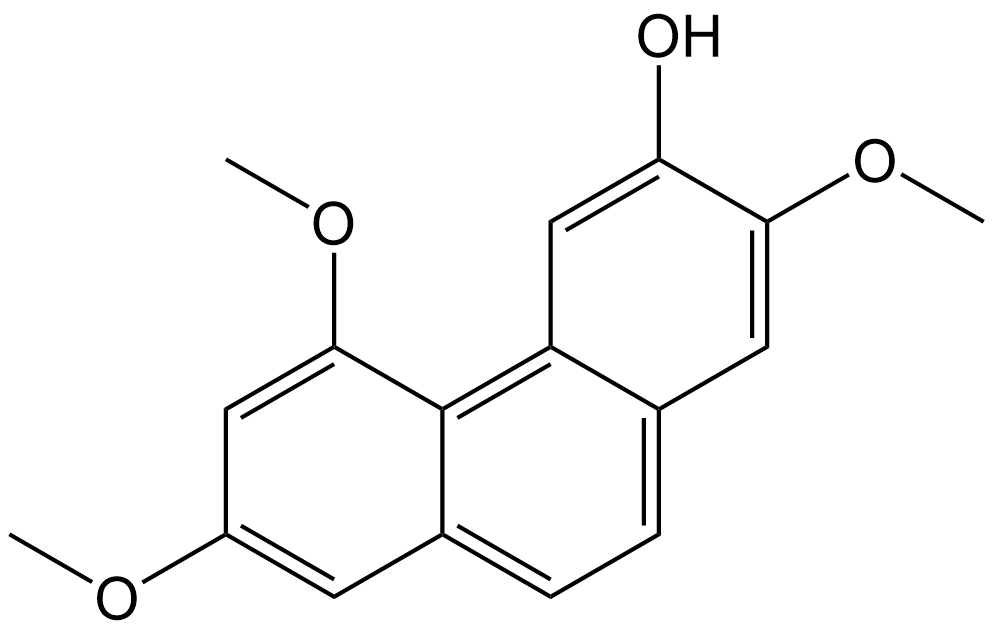
Batatasin I
Batatasin I (CAS 51415-00-0) is a natural phenanthrene derivative isolated from the tuberous roots of Dioscorea batatas, a Dioscorea species widely distributed in East Asia, by methanolic extraction, dichloromethane partition, and silica gel column chromatography. Its molecular targets include cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), cytosolic phospholipase A₂α (cPLA₂α), and phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1), which regulate eicosanoid production and mast cell degranulation-related pathways, respectively.
In mouse bone marrow–derived mast cells (BMMCs), Batatasin I is non-cytotoxic at concentrations up to 8 μM as verified by MTT assay. The IC₅₀ values for inhibition of COX-2–dependent prostaglandin D₂ (PGD₂) production, 5-LOX–dependent leukotriene C₄ (LTC₄) production, and mast cell degranulation (using β-hexosaminidase as a marker) are 1.78 μM, 1.56 μM, and 2.7 μM, respectively. In these experiments, the dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitor licofelone(Cat. No.: B1448), used as a positive control, was applied at 10 μM.
The experimental results demonstrate that Batatasin I inhibits COX-2–dependent PGD₂ production in a dose-dependent manner, accompanied by downregulation of COX-2 protein expression, and suppresses 5-LOX–dependent LTC₄ production by blocking cPLA₂α phosphorylation and preventing the nuclear membrane translocation of phosphorylated cPLA₂α and 5-LOX. In parallel, it interferes with calcium signaling by inhibiting PLCγ1 tyrosine phosphorylation, thereby dose-dependently suppressing mast cell degranulation. At higher concentrations, its inhibitory effects are comparable to those of licofelone. As a dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitor, Batatasin I can cooperatively suppress inflammatory responses and may avoid the gastrointestinal adverse effects associated with conventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), indicating its potential for the treatment of airway allergic inflammatory diseases such as asthma, as well as other inflammation-related disorders.
References:
[1] Lu Y, Jin M, Park SJ, Son KH, Son JK, Chang HW. Batatasin I, a naturally occurring phenanthrene derivative, isolated from tuberous roots of Dioscorea batatas suppresses eicosanoids generation and degranulation in bone marrow derived-mast cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(7):1021-5. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1021. PMID: 21720007.
| Storage | Store at 4°C, protect from light |
| M.Wt | 284.31 |
| Cas No. | 51415-00-0 |
| Formula | C17H16O4 |
| Synonyms | BTS-I; 6-hydroxy-2,4,7-trimethoxyphenanthrene |
| Chemical Name | 2,5,7-trimethoxyphenanthren-3-ol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC1=CC2=C(C(OC)=CC(OC)=C3)C3=CC=C2C=C1OC |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure