Immunology/Inflammation


The adaptive immune system consists of B and T lymphocytes which mediate humoral immunity (e.g. antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity, respectively. B cell receptor and T cell receptor signaling is responsible for activation of Src family tyrosine kinases, such as Blk, Fyn, and Lyn in B cells and Fyn and Lck in T cells, resulting phosphorylation of the receptor-associated ITAM motifs. Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as the docking sites for Syk family tyrosine kinases, e.g. Syk in B cells and Zap-70 in T cells. Activated Syk kinases then propagate the signals via phosphorylation of downstream proteins. Furthermore, lymphocyte receptor signaling facilitates B and T cell development, differentiation, proliferation and survival.
-
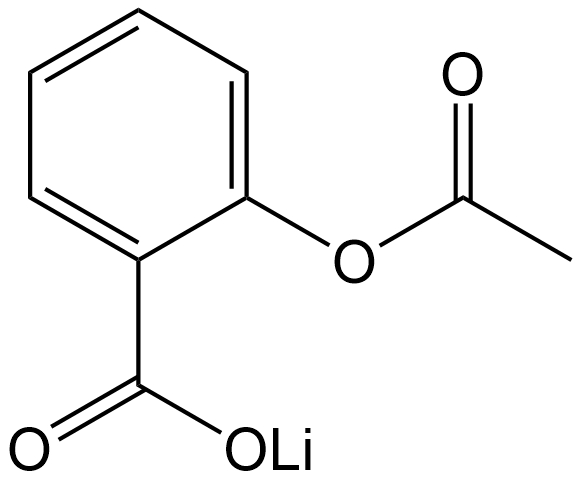 C8731 Acetylsalicylic acid lithiumSummary: An orally active, irreversible cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2) inhibitor, also commonly used to induce gastric ulcer models.
C8731 Acetylsalicylic acid lithiumSummary: An orally active, irreversible cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2) inhibitor, also commonly used to induce gastric ulcer models. -
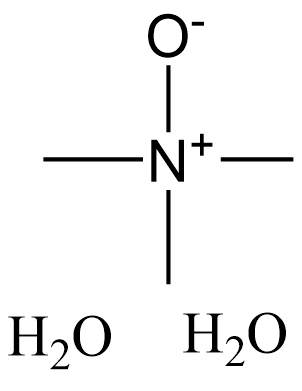 N2891 Trimethylamine oxide dihydrateSummary: ROS/NLRP3 activator; TGF-β/Smad2 signaling pathway activator
N2891 Trimethylamine oxide dihydrateSummary: ROS/NLRP3 activator; TGF-β/Smad2 signaling pathway activator -
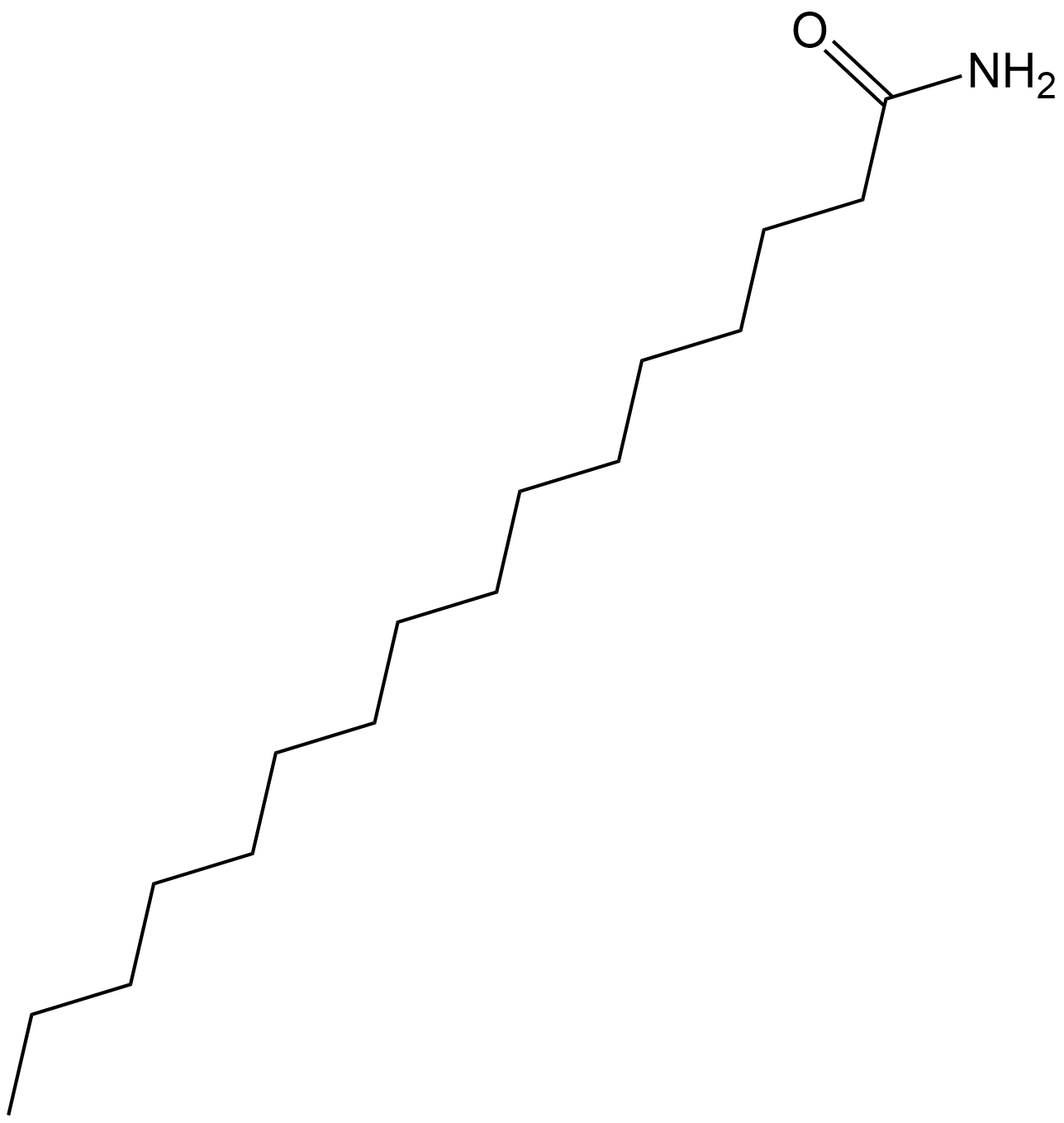 N2889 HexadecanamideSummary: A fatty acid amide derived from palmitic acid, commonly used to study its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects
N2889 HexadecanamideSummary: A fatty acid amide derived from palmitic acid, commonly used to study its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects


