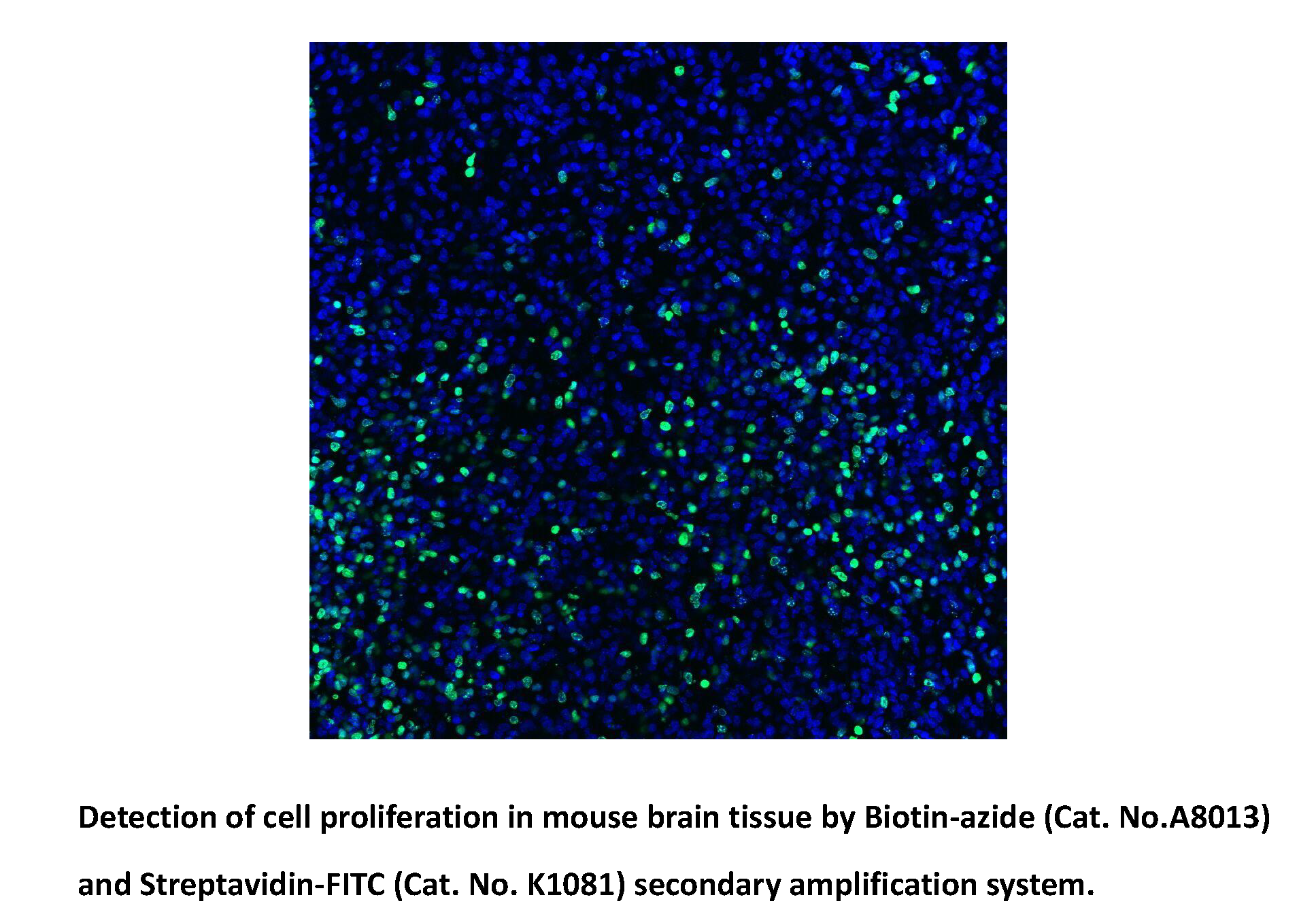
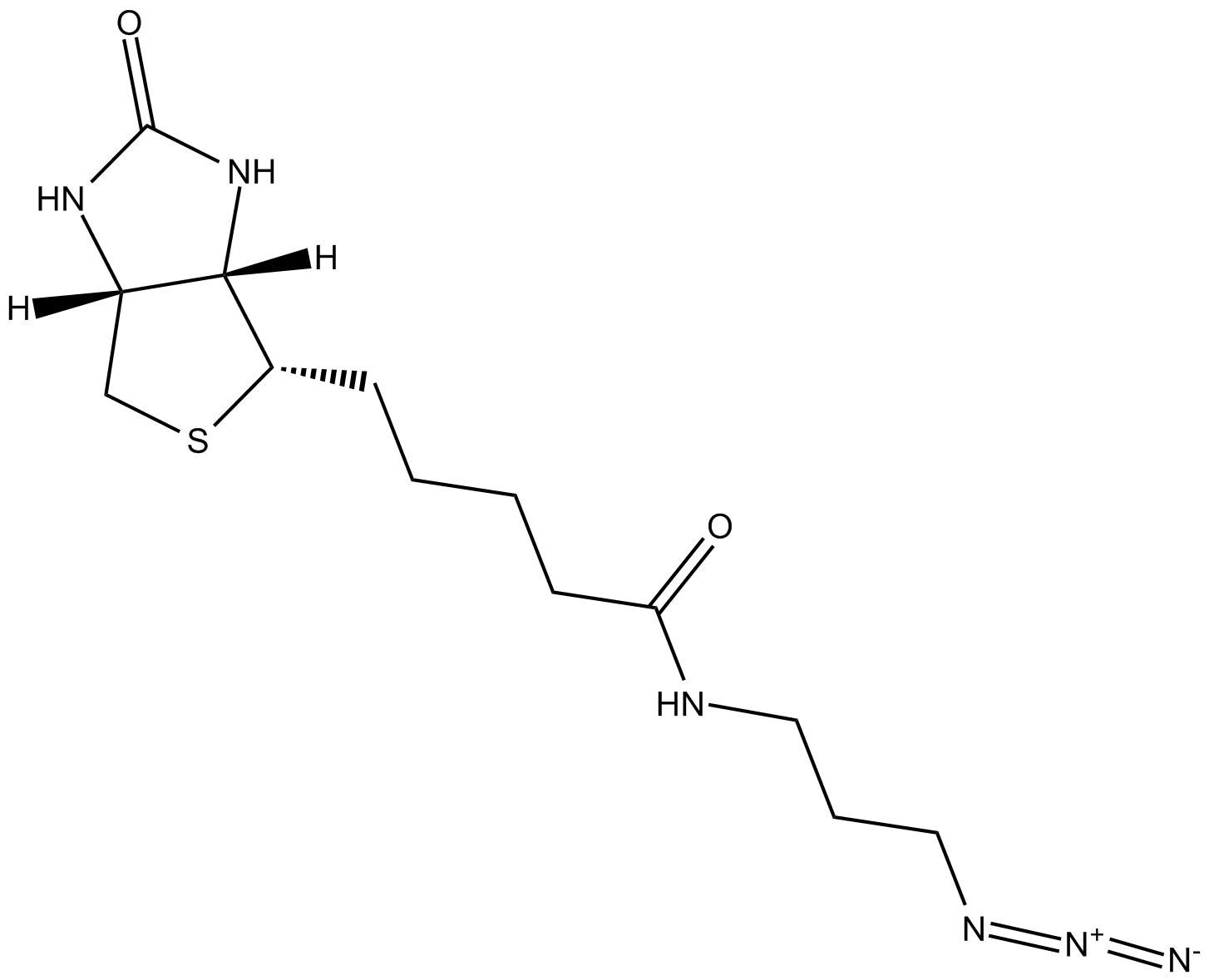
Biotin-azide
Biotin azide reacts with the terminal alkynes via a copper-catalyzed click reaction, including biomolecules containing alkyne groups through azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Biotin and biotin derivatives can be readily conjugated to various biomolecules through the well-known click chemistry and subsequently detected with streptavidin, avidin or NeutrAvidin biotin-binding protein. Biotin azide can be used to prepare various biotinylated conjugates via Click Chemistry. Click chemistry contains a class of chemical reactions that use bio-orthogonal or biologically unique moieties to label and detect the molecule in mild and aqueous conditions. This reagent allows labeling of various alkynylated molecules, such as DNA, oligonucleotides, and proteins with biotin. Biotin binding to avidin or streptavidin could be used in downstream affinity applications for the isolation of biotinylated molecules or their binding with streptavidin conjugates [1].
Reference:
[1] Bruckman M A, Czapar A E, VanMeter A, et al. Tobacco mosaic virus-based protein nanoparticles and nanorods for chemotherapy delivery targeting breast cancer[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 231: 103-113.
- 1. Viola Ellison, Alla Polotskaia, et al. "A cancer persistent DNA repair circuit driven by MDM2, MDM4 (MDMX), and mutant p53 for recruitment of MDC1 and 53BP1 on chromatin." Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf627 PMID: 40626562
- 2. Chunguo Wang, Jinli Shi, et al. "Obtain Substance of Anti-glioblastoma from Erigeron breviscapus through Fragment-based Target Research (FBTR): An Efficient Strategy for Pharmacology Investigation and Optimization of Natural Products." Available online 14 June 2025, 101366
- 3. Shaoqin Zheng, Jiahui Lin, et al. "Aberrant Cholesterol Metabolism and Wnt/β‐Catenin Signaling Coalesce via Frizzled5 in Supporting Cancer Growth." Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Oct;9(28):e2200750. PMID: 35975457
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 326.42 |
| Cas No. | 908007-17-0 |
| Formula | C13H22N6O2S |
| Solubility | ≥32.6 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥2.51 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
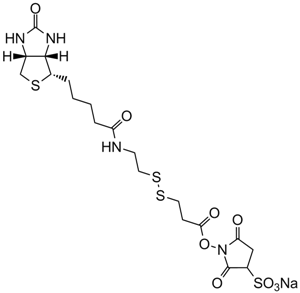
| Chemical Name | N-(3-azidopropyl)-5-((3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | [N-]=[N+]=NCCCNC(CCCC[C@@H]([C@H]1N2)SC[C@@H]1NC2=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data