Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
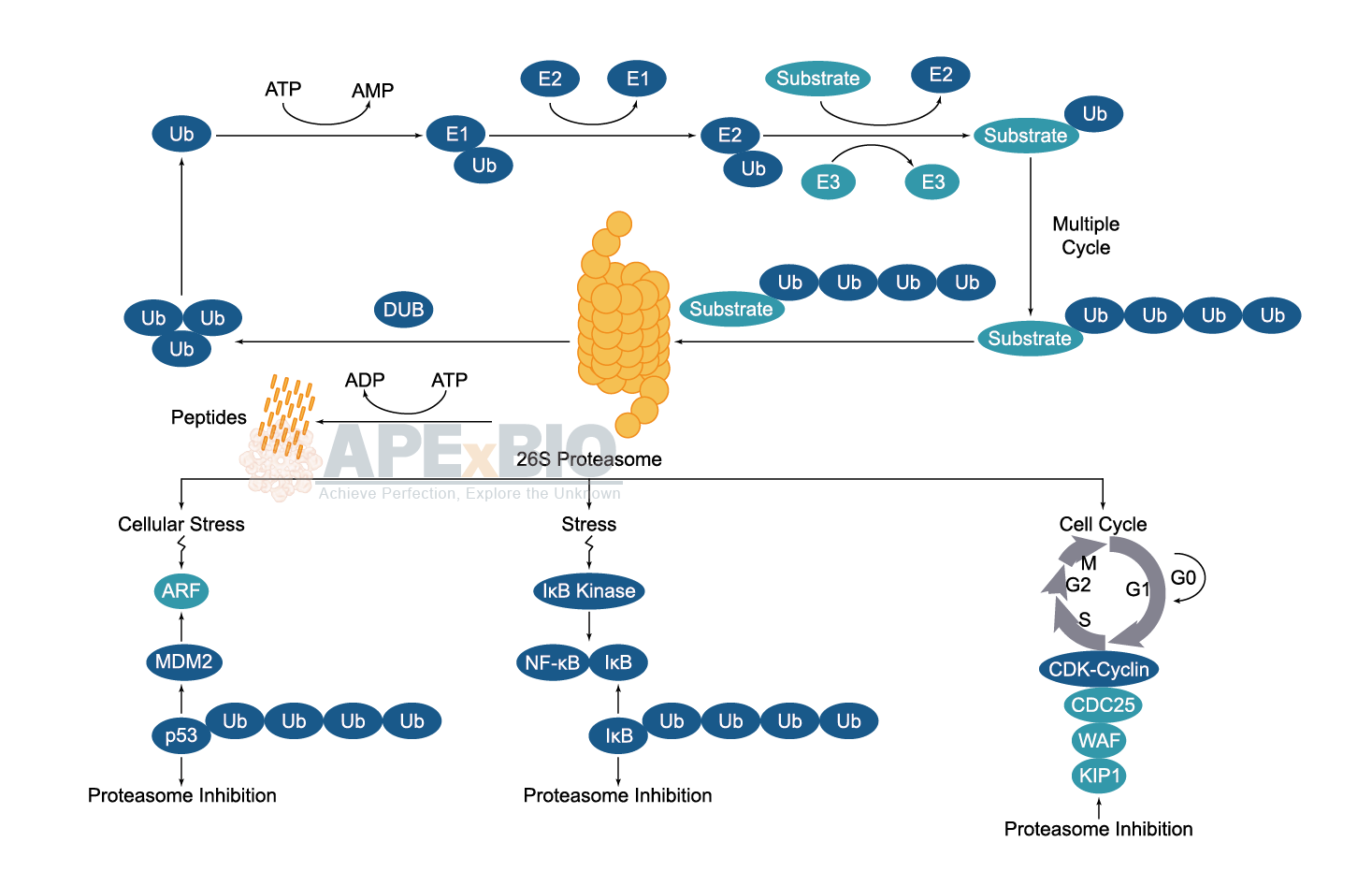

Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
 A8323 WP11301 CitationSummary: Deubiquitinase (DUB) inhibitor, Cell permeable
A8323 WP11301 CitationSummary: Deubiquitinase (DUB) inhibitor, Cell permeable -
 A8353 3-Methyladenine43 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor
A8353 3-Methyladenine43 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor -
 A8484 NimodipineSummary: Calcium Channel inhibitor & Autophagy activator
A8484 NimodipineSummary: Calcium Channel inhibitor & Autophagy activator -
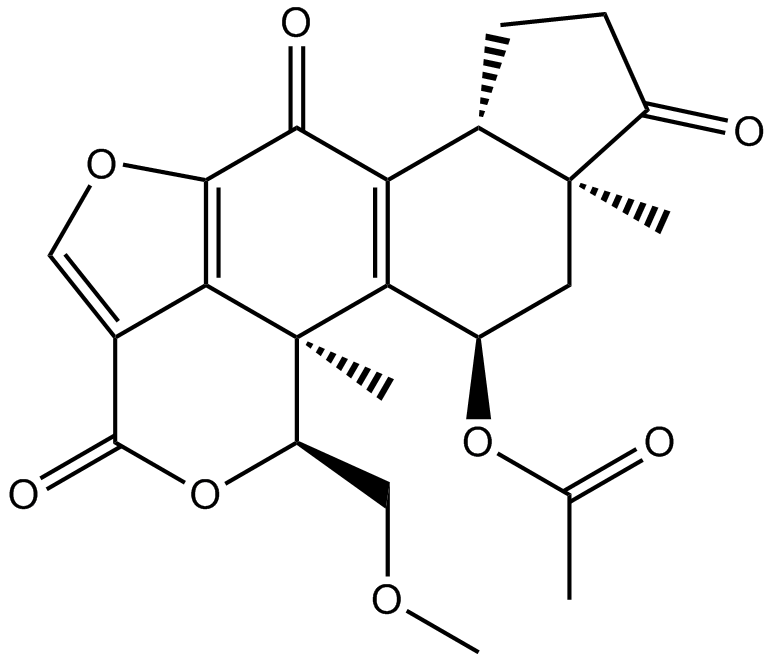 A8544 Wortmannin5 CitationSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and irreversible
A8544 Wortmannin5 CitationSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and irreversible -
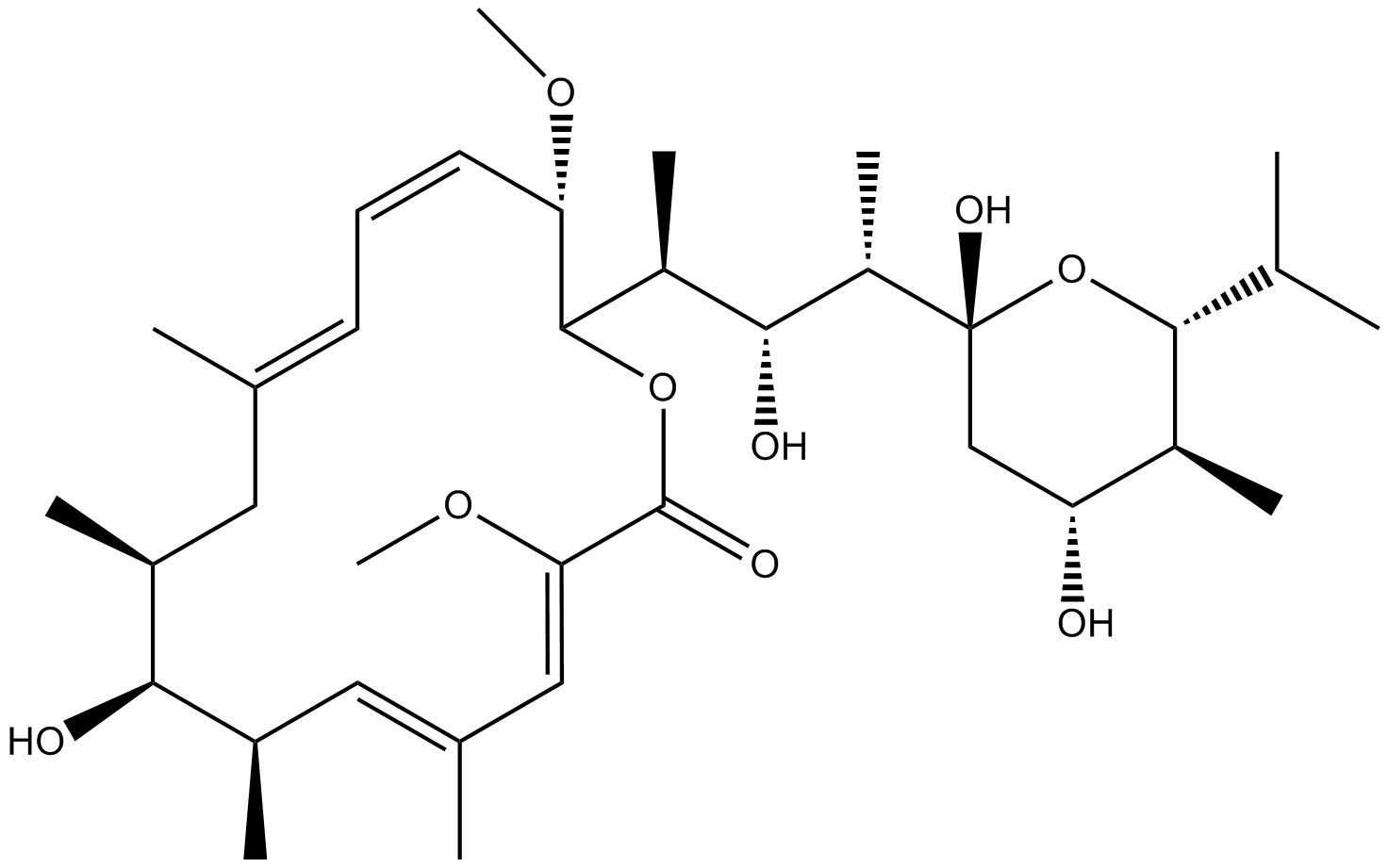 A8627 Bafilomycin A131 CitationSummary: V-ATPases inhibitor
A8627 Bafilomycin A131 CitationSummary: V-ATPases inhibitor -
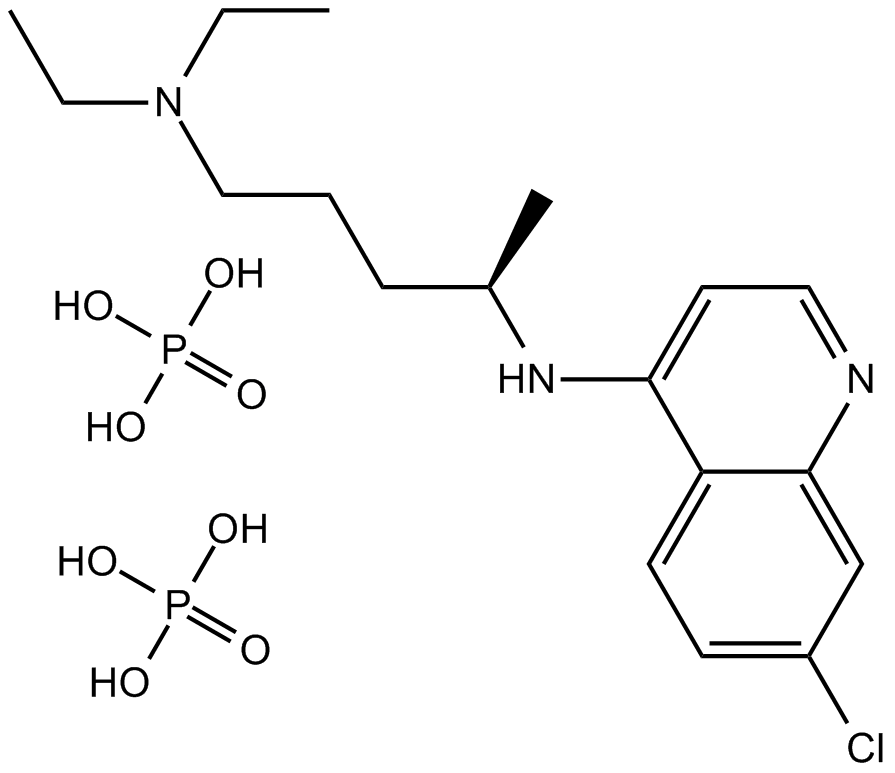 A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate16 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug, TLR7 and TLR9 inhibitor
A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate16 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug, TLR7 and TLR9 inhibitor -
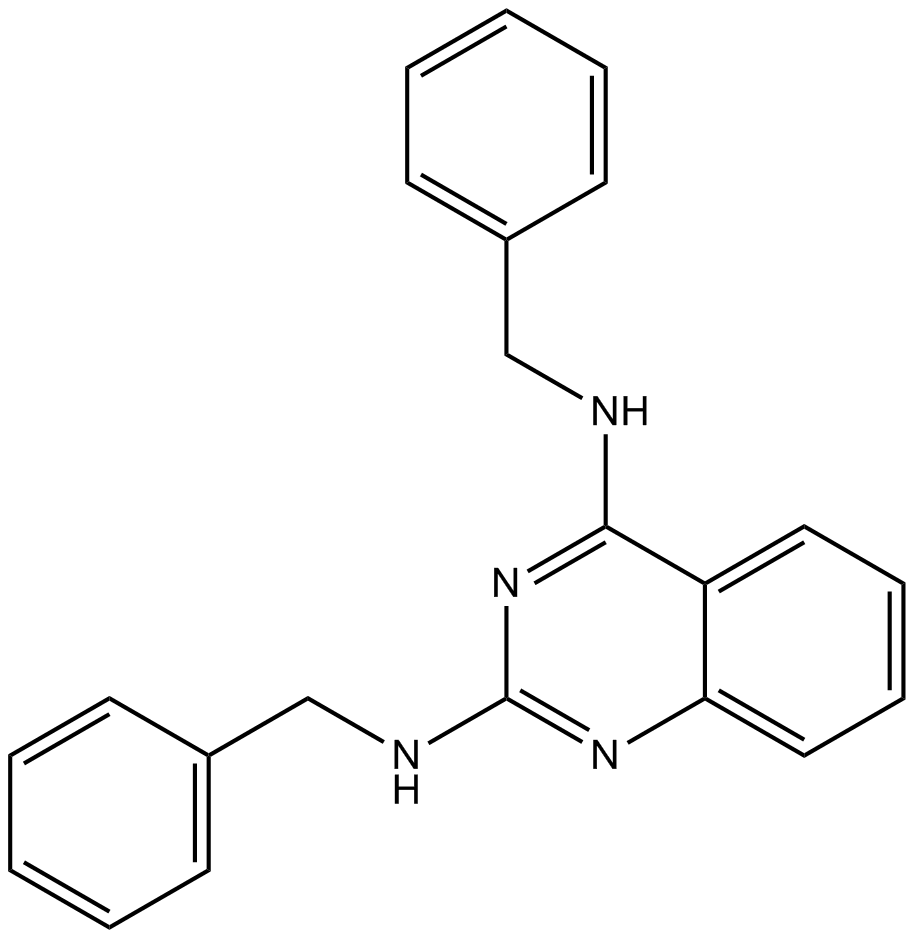 A8629 DBeQTarget: P97 ATPaseSummary: P97 ATPase inhibitor
A8629 DBeQTarget: P97 ATPaseSummary: P97 ATPase inhibitor -
 A8630 XanthohumolSummary: VCP inhibitor
A8630 XanthohumolSummary: VCP inhibitor -
 A8631 FK 866 hydrochlorideTarget: NMPRTaseSummary: NMPRTase inhibitor
A8631 FK 866 hydrochlorideTarget: NMPRTaseSummary: NMPRTase inhibitor -
 A8632 (±)-Bay K 8644Summary: L-type Ca2+-channel activator
A8632 (±)-Bay K 8644Summary: L-type Ca2+-channel activator


