Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
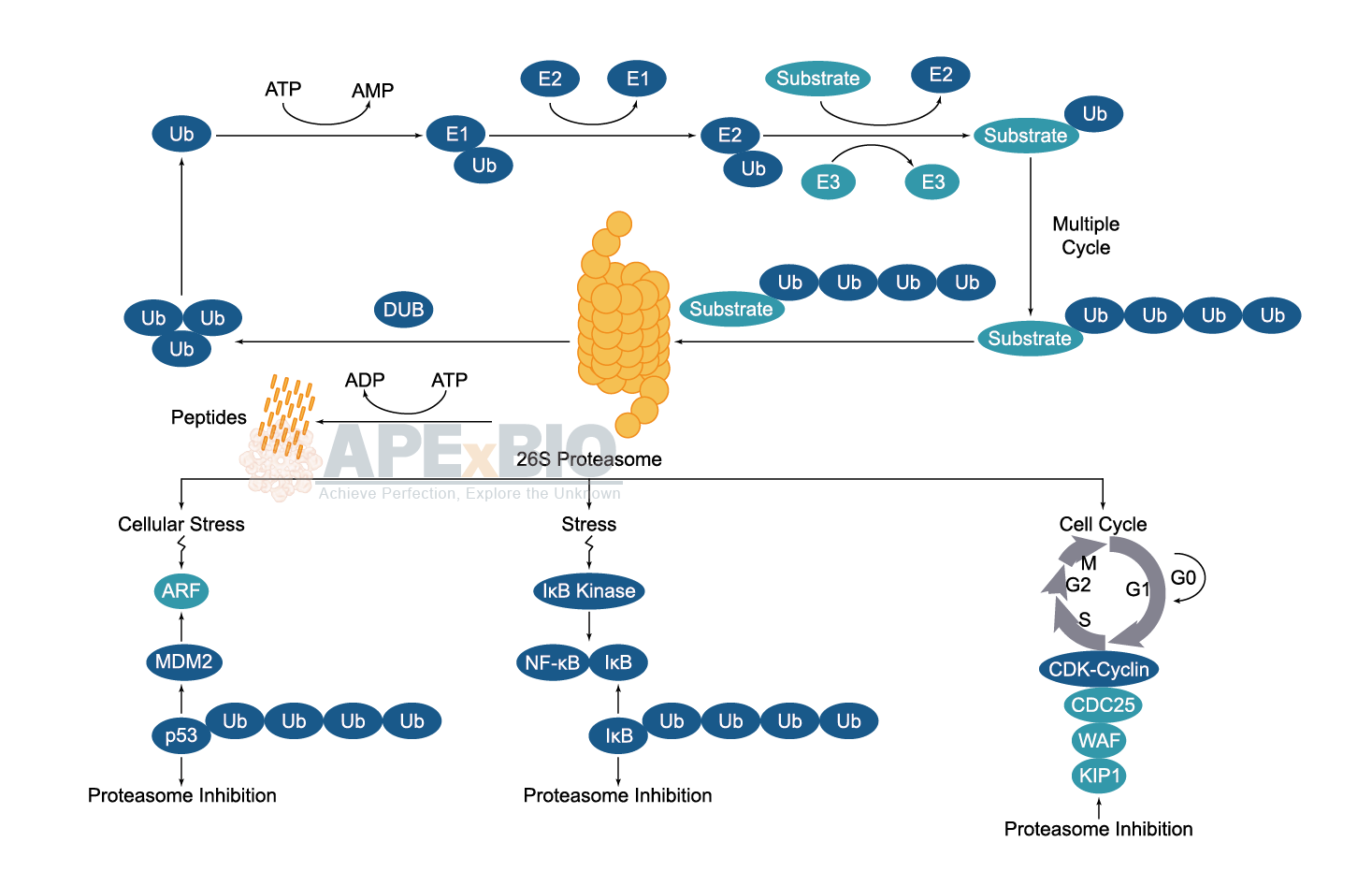

Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
 BA2869 VII-31Summary: VII-31 is a NEDDylation pathway activator that inhibits tumors in vitro and in vivo.
BA2869 VII-31Summary: VII-31 is a NEDDylation pathway activator that inhibits tumors in vitro and in vivo. -
 BA2904 RO8994Summary: A potent and selective MDM2 inhibitor with IC50 of nM (HTRF binding assay) and 20 nM (MTT proliferation assay).
BA2904 RO8994Summary: A potent and selective MDM2 inhibitor with IC50 of nM (HTRF binding assay) and 20 nM (MTT proliferation assay). -
 BA2912 PhenoxodiolSummary: Phenoxodiol (Idronoxil) is a synthetic analog of Genestein that activates the mitochondrial system, inhibits (an apoptosis inhibitor), and sensitizes cancer cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis.
BA2912 PhenoxodiolSummary: Phenoxodiol (Idronoxil) is a synthetic analog of Genestein that activates the mitochondrial system, inhibits (an apoptosis inhibitor), and sensitizes cancer cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis. -
 BA3695 MTX115325Summary: MTX115325 is an orally potent
BA3695 MTX115325Summary: MTX115325 is an orally potent -
 BA3877 TNG348Summary: TNG348 is an orally active deubiquitinating enzyme inhibitor.
BA3877 TNG348Summary: TNG348 is an orally active deubiquitinating enzyme inhibitor. -
 BA3878 CapziminSummary: Capzimin is effective.
BA3878 CapziminSummary: Capzimin is effective. -
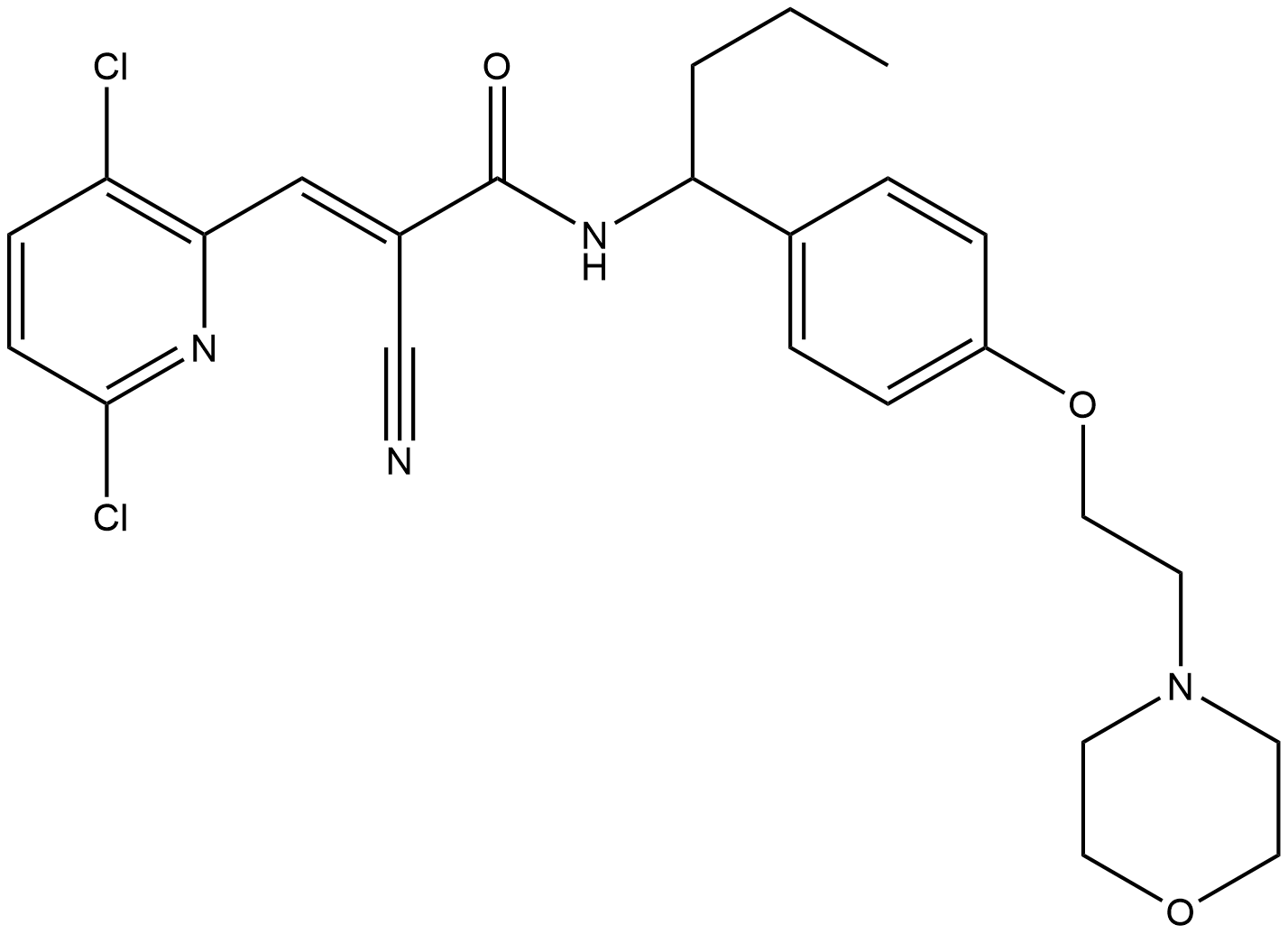 BA3881 EOAI3402143Summary: EOAI3402143 is a deubiquitinating enzyme inhibitor.
BA3881 EOAI3402143Summary: EOAI3402143 is a deubiquitinating enzyme inhibitor. -
 BA3886 FT206Summary: Carboxyamine ubiquitin-specific protease inhibitors.
BA3886 FT206Summary: Carboxyamine ubiquitin-specific protease inhibitors. -
 BA3887 FT709Summary: FT709 is a potent and selective inhibitor.
BA3887 FT709Summary: FT709 is a potent and selective inhibitor. -
 BA3888 6RK73Summary: 6RK73 is a covalent irreversible specific inhibitor.
BA3888 6RK73Summary: 6RK73 is a covalent irreversible specific inhibitor.


