Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
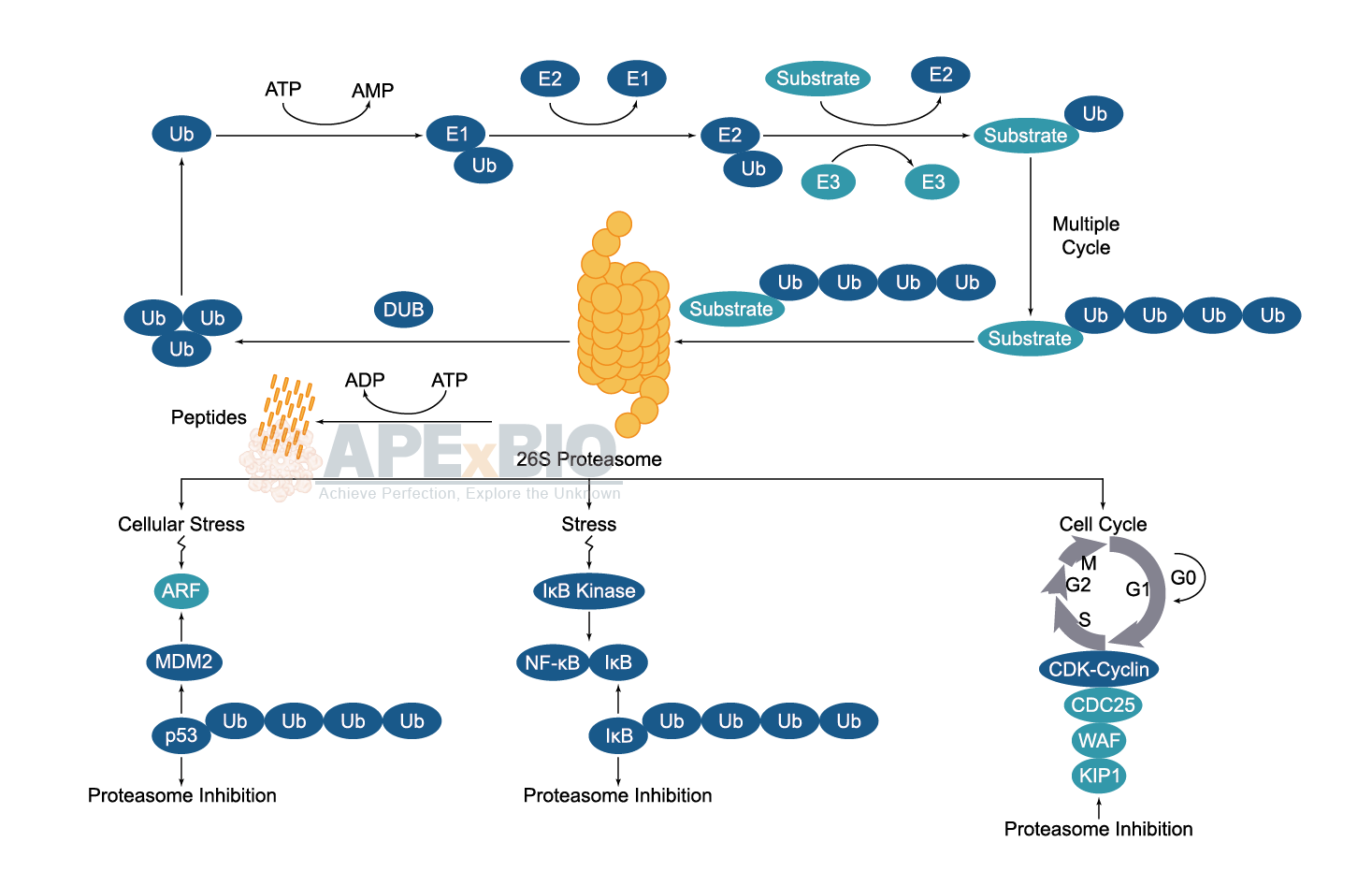

Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
 BA3898 8RK64Summary: 8RK64 is a covalent inhibitor.
BA3898 8RK64Summary: 8RK64 is a covalent inhibitor. -
 BA3907 LCAHASummary: LCAHA (LCAhydroxyamide), a deubiquitinase inhibitor, was found to be 9.7 μM and 3.7 μM in Ub-AMC analysis and Di-Ub analysis, respectively.
BA3907 LCAHASummary: LCAHA (LCAhydroxyamide), a deubiquitinase inhibitor, was found to be 9.7 μM and 3.7 μM in Ub-AMC analysis and Di-Ub analysis, respectively. -
 BA3908 STAMBP-IN-1Summary: STAMBP-IN-1 is a small molecule inhibitor of STAMBP deubiquitinase that interrupts the interaction.
BA3908 STAMBP-IN-1Summary: STAMBP-IN-1 is a small molecule inhibitor of STAMBP deubiquitinase that interrupts the interaction. -
 BA3913 USP7-IN-10Summary: USP7-IN-10 is a potent ubiquitin protein-specific protease 7 inhibitor.
BA3913 USP7-IN-10Summary: USP7-IN-10 is a potent ubiquitin protein-specific protease 7 inhibitor. -
 BA3914 USP7-IN-13Summary: USP7-IN-13 is an inhibitor value of 0.2 to 1 μM.
BA3914 USP7-IN-13Summary: USP7-IN-13 is an inhibitor value of 0.2 to 1 μM. -
 BA7375 BI8622Summary: BI8622 is a ubiquitin ligase-specific antagonist.
BA7375 BI8622Summary: BI8622 is a ubiquitin ligase-specific antagonist. -
 BA7394 SCFSkp2-IN-2Summary: SCFSkp2-IN-2 is an inhibitor.
BA7394 SCFSkp2-IN-2Summary: SCFSkp2-IN-2 is an inhibitor. -
 BA7460 IsovalerylcarnitineSummary: Isovalerylcarnitine is a product of L-leucine catabolism.
BA7460 IsovalerylcarnitineSummary: Isovalerylcarnitine is a product of L-leucine catabolism. -
 BA7581 DiacetoxyscirpenolSummary: Diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS) is a mono-terminal mycotoxin that is a secondary metabolite of fungi.
BA7581 DiacetoxyscirpenolSummary: Diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS) is a mono-terminal mycotoxin that is a secondary metabolite of fungi. -
 BA7641 MyricanoneSummary: A compound isolated from the bark of the tree.
BA7641 MyricanoneSummary: A compound isolated from the bark of the tree.


