Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
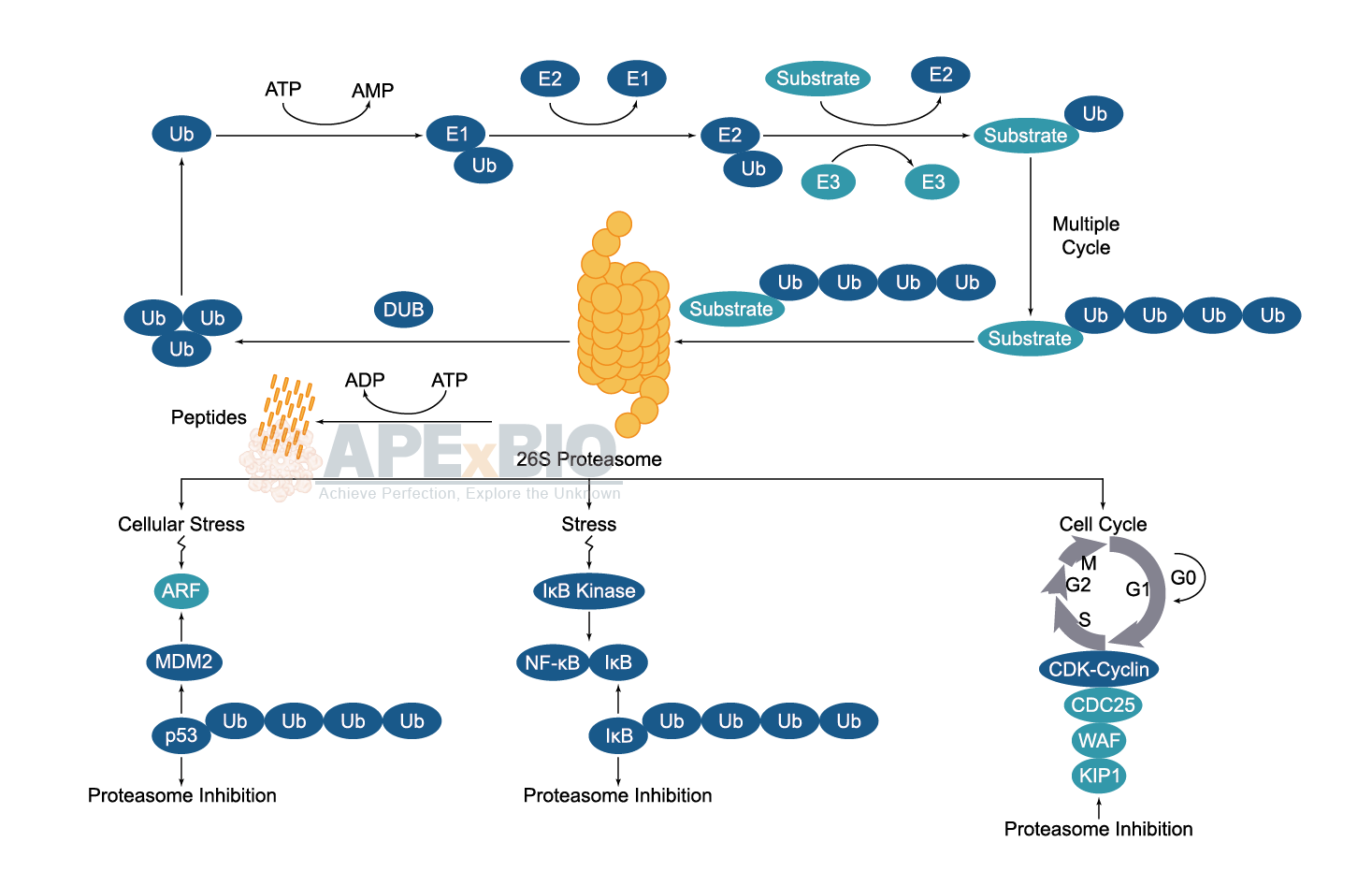

Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
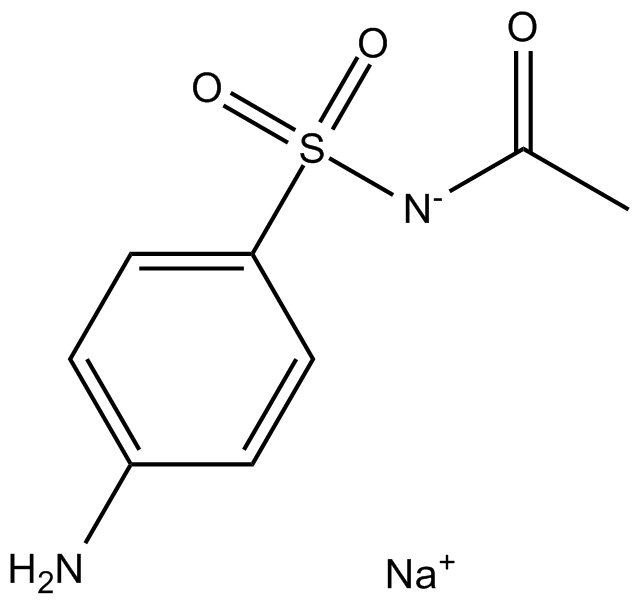 B1395 Sulfacetamide SodiumSummary: Sulfonamide antibiotic
B1395 Sulfacetamide SodiumSummary: Sulfonamide antibiotic -
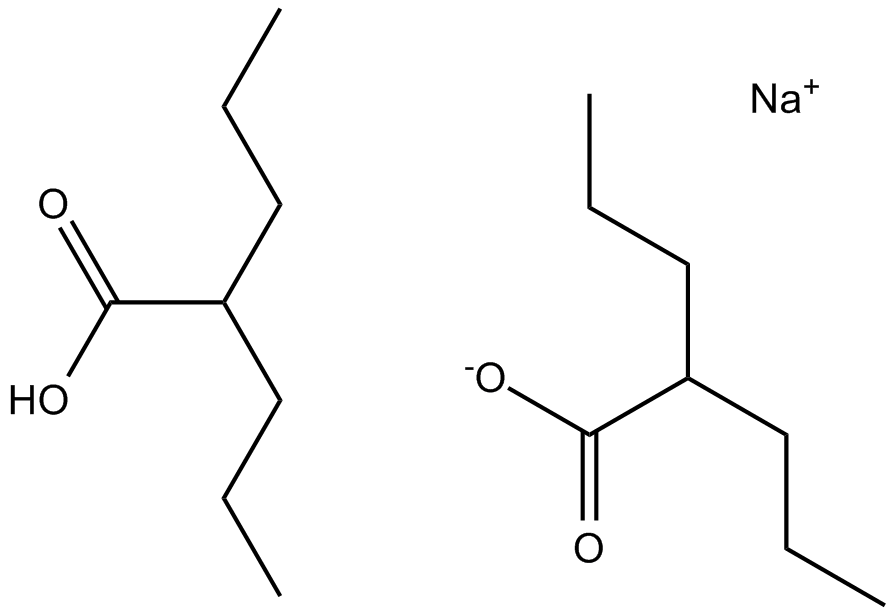 B1391 Divalproex SodiumSummary: Epilepsy/migraines/bipolar disorder medicine
B1391 Divalproex SodiumSummary: Epilepsy/migraines/bipolar disorder medicine -
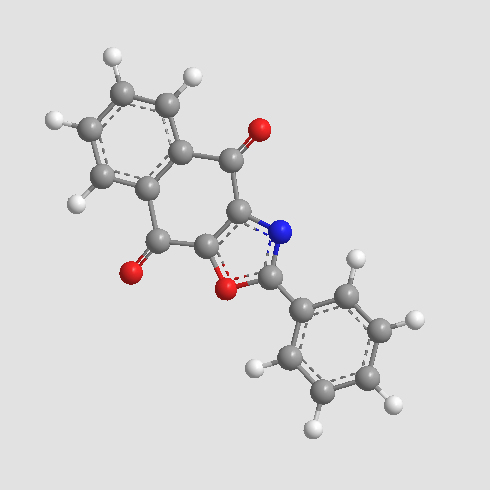 A3823 SJB2-043Target: USPSummary: USP1 inhibitor
A3823 SJB2-043Target: USPSummary: USP1 inhibitor -
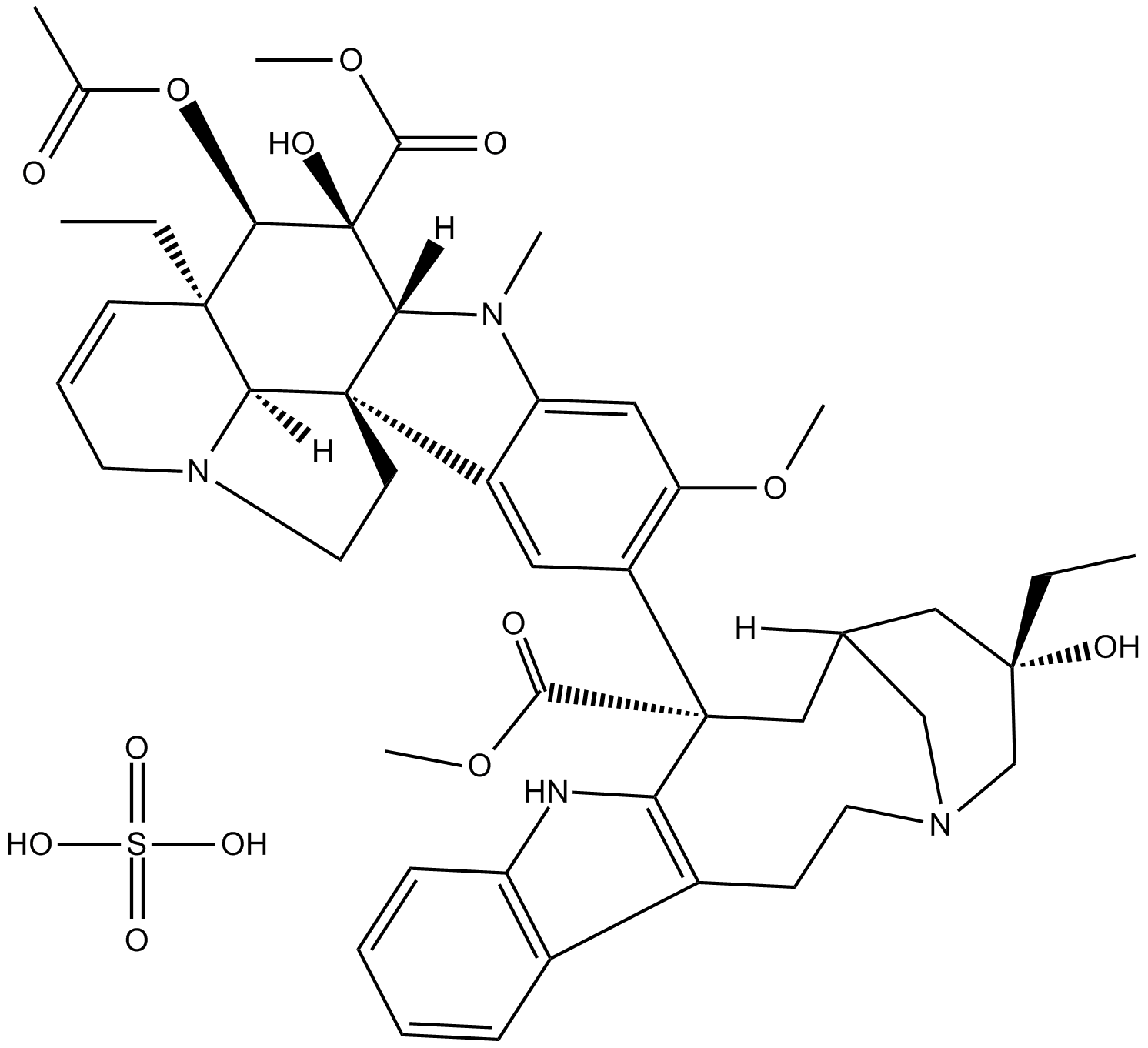 A3920 Vinblastine sulfate2 CitationSummary: Anti-mitotic agent
A3920 Vinblastine sulfate2 CitationSummary: Anti-mitotic agent -
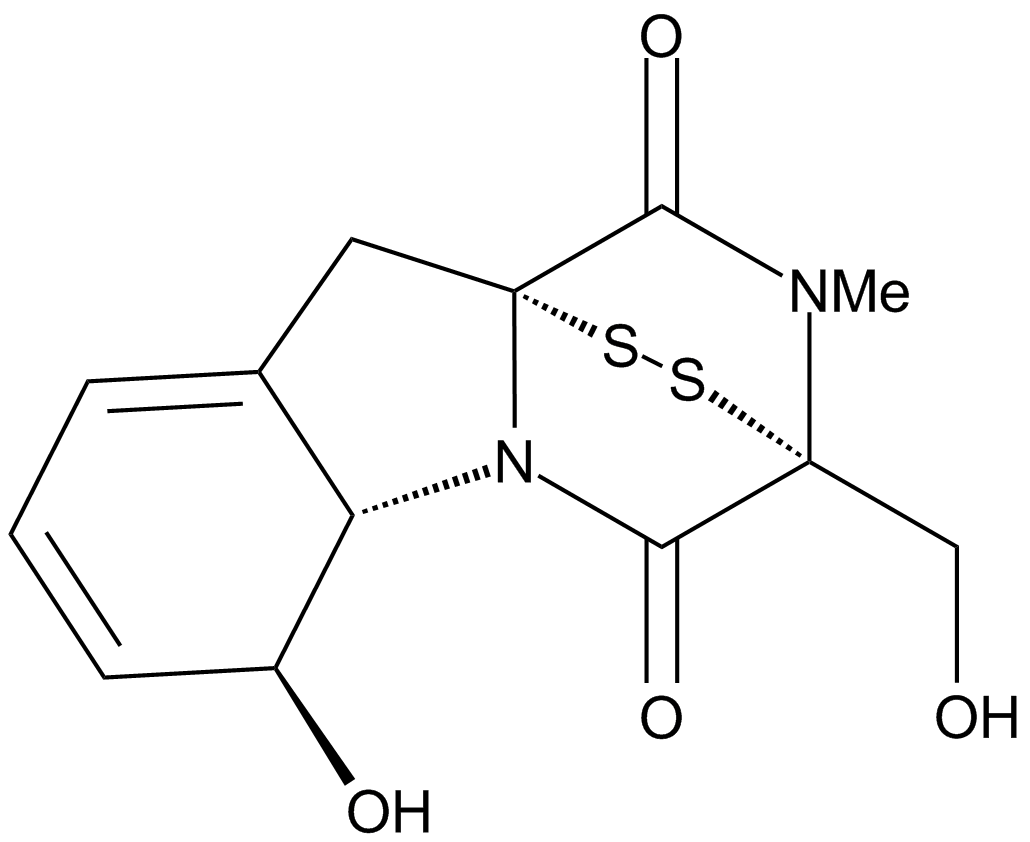 A4443 Gliotoxin1 CitationTarget: 20S proteasomal chymotrypsin|Geranylgeranyltransferase I|FarnesyltransferaseSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor
A4443 Gliotoxin1 CitationTarget: 20S proteasomal chymotrypsin|Geranylgeranyltransferase I|FarnesyltransferaseSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor -
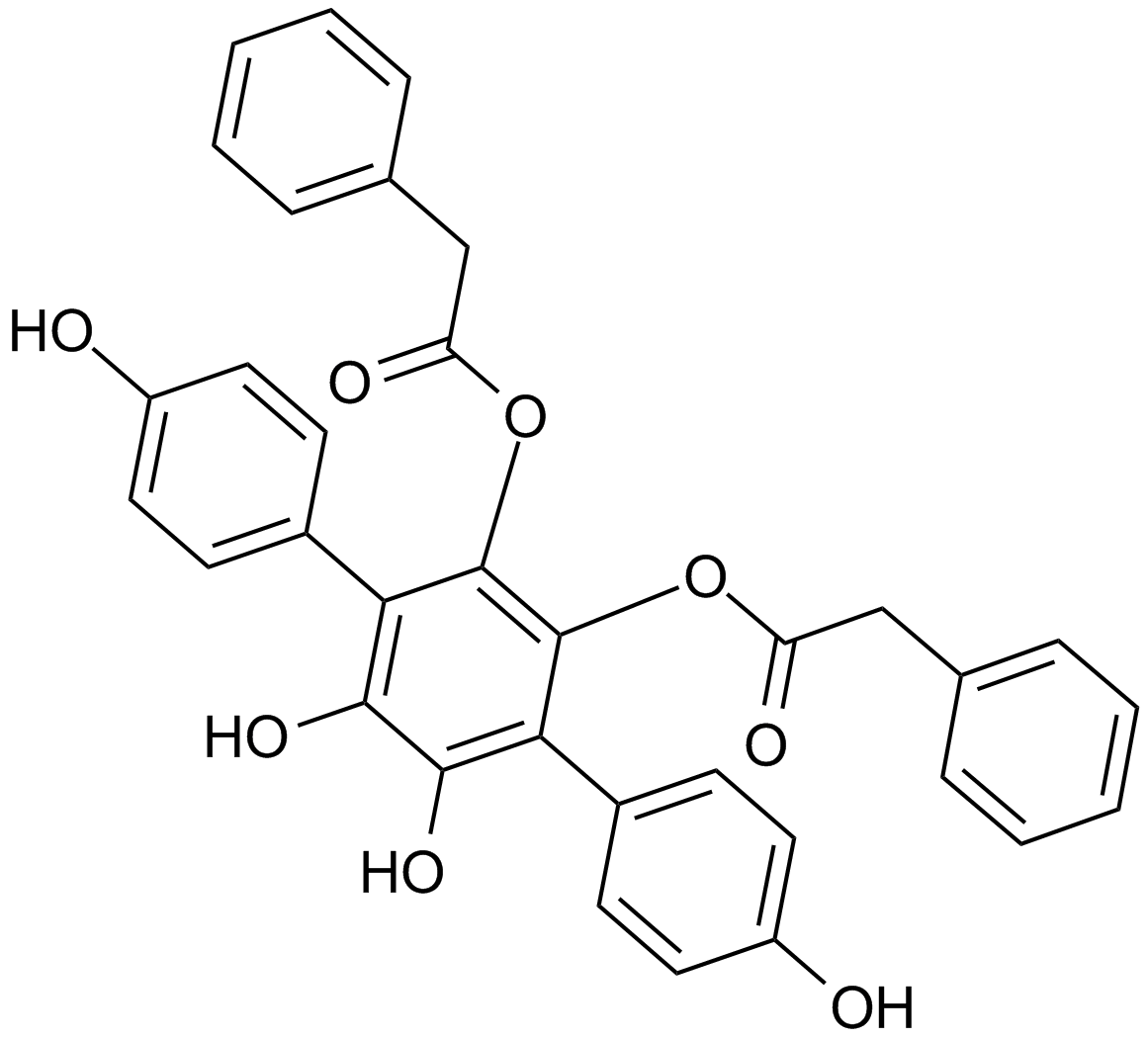 A4429 Vialinin ATarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|IL Receptors|CCL2Summary: USP/isopeptidase T (IsoT)/UCH-L1 DUB inhibitor
A4429 Vialinin ATarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|IL Receptors|CCL2Summary: USP/isopeptidase T (IsoT)/UCH-L1 DUB inhibitor -
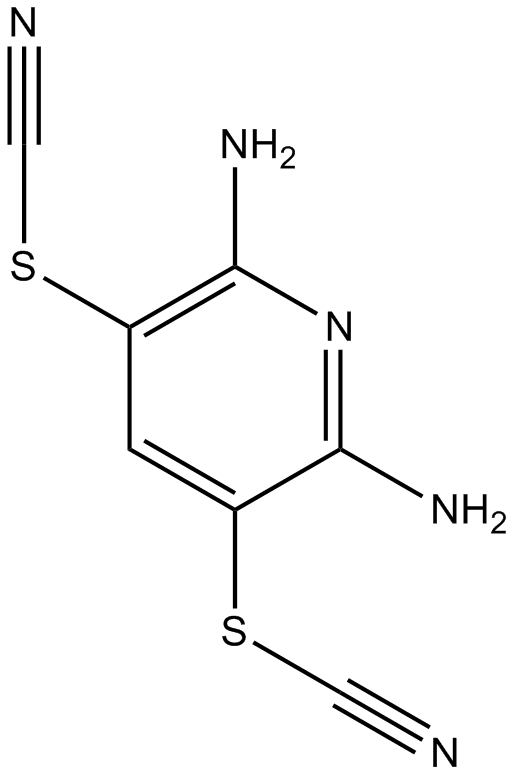 A8212 PR-6194 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: Deubiquitylating enzymes (DBUs) inhibitor
A8212 PR-6194 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: Deubiquitylating enzymes (DBUs) inhibitor -
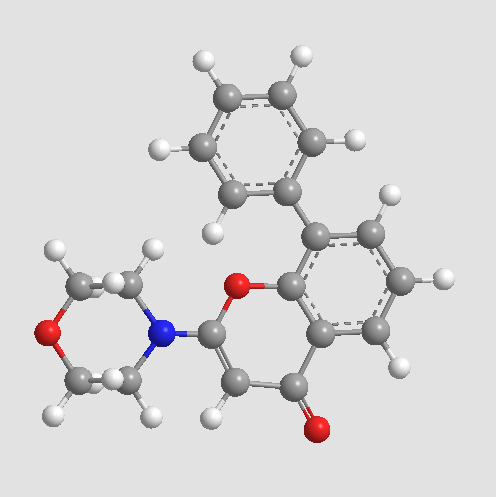 A8250 LY 29400264 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Potent PI3K inhibitor
A8250 LY 29400264 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Potent PI3K inhibitor -
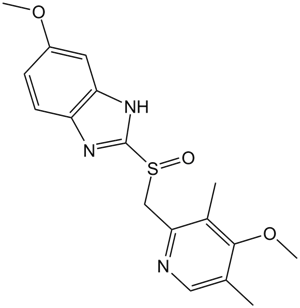 A2845 Omeprazole2 CitationSummary: H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor
A2845 Omeprazole2 CitationSummary: H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor -
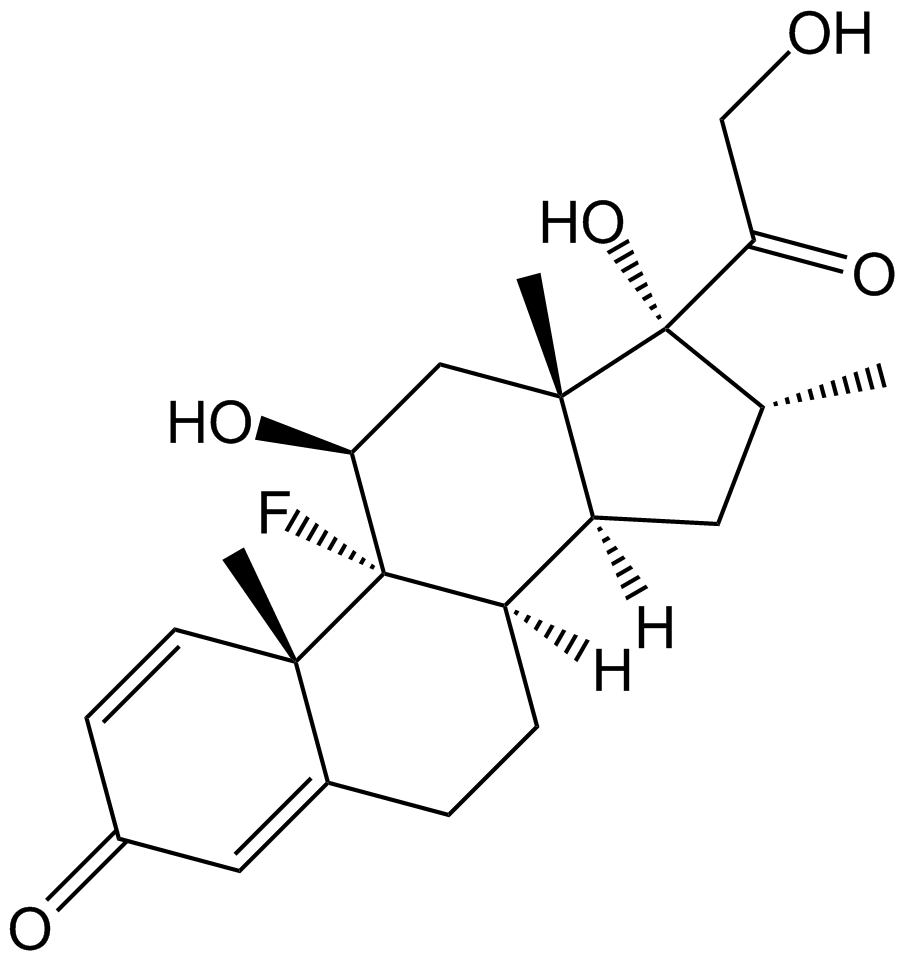 A2324 Dexamethasone (DHAP)10 CitationTarget: interleukin receptorSummary: Glucocorticoidan; anti-inflammatory
A2324 Dexamethasone (DHAP)10 CitationTarget: interleukin receptorSummary: Glucocorticoidan; anti-inflammatory


