Cancer Biology

Cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. A diverse array of chemical and biological compounds has been developed to target cancer cells through various mechanisms, ranging from direct cytotoxicity to modulation of specific molecular pathways.
Traditional chemotherapeutic agents, such as alkylating agents, antimetabolites, topoisomerase inhibitors, and mitotic inhibitors, exert their effects primarily by interfering with DNA replication or cell division, thereby preferentially targeting rapidly proliferating tumor cells. Targeted therapy agents, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors, selectively suppress oncogenic signaling pathways, thereby offering enhanced specificity and reduced systemic toxicity. Immunotherapeutic agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, harness the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. In addition, epigenetic modulators, DNA repair inhibitors, and angiogenesis-targeting compounds constitute novel therapeutic strategies.
-
![ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1069.png) A1069 ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]Summary: Ferritin heavy chain fragment
A1069 ferritin heavy chain fragment [Multiple species]Summary: Ferritin heavy chain fragment -
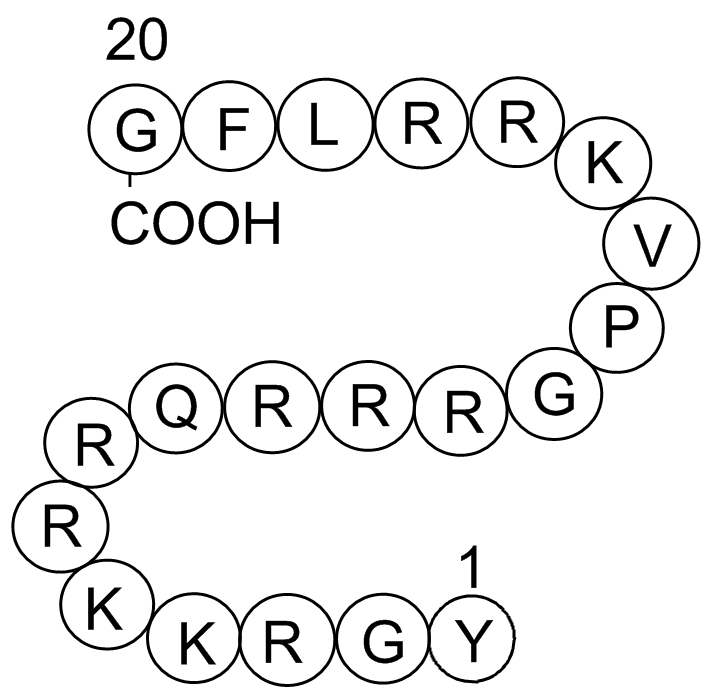 A1107 Cdk2/Cyclin Inhibitory Peptide ISummary: Cell division protein kinase 2
A1107 Cdk2/Cyclin Inhibitory Peptide ISummary: Cell division protein kinase 2 -
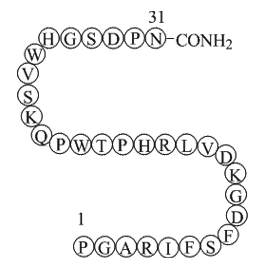 A1109 Endostatin (84-114)-NH2 (JKC367)Summary: Angiogenesis inhibitor
A1109 Endostatin (84-114)-NH2 (JKC367)Summary: Angiogenesis inhibitor -
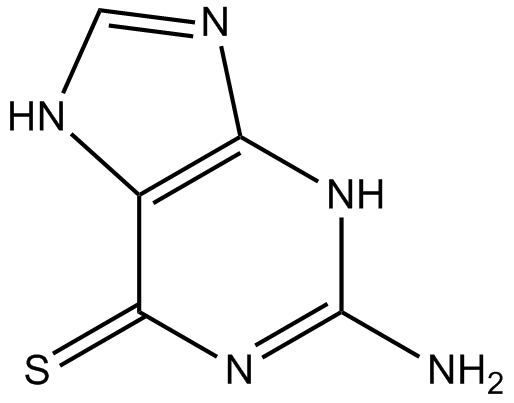 A4176 ThioguanineSummary: A thiopurine immunosuppressant with antitumor and antiviral activities
A4176 ThioguanineSummary: A thiopurine immunosuppressant with antitumor and antiviral activities -
 A1118 S6 Kinase Substrate Peptide 32Summary: Measures the activity of kinases that phosphorylate ribosomal protein S6.
A1118 S6 Kinase Substrate Peptide 32Summary: Measures the activity of kinases that phosphorylate ribosomal protein S6. -
 A1133 Epidermal growth factor receptor (994-1002) acetyl/amideSummary: EGF-family receptor
A1133 Epidermal growth factor receptor (994-1002) acetyl/amideSummary: EGF-family receptor -
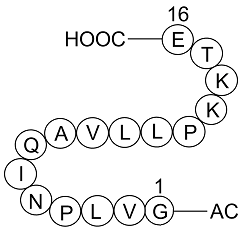 A1146 Histone-H2A-(107-122)-Ac-OHSummary: Histone-H2A peptide
A1146 Histone-H2A-(107-122)-Ac-OHSummary: Histone-H2A peptide -
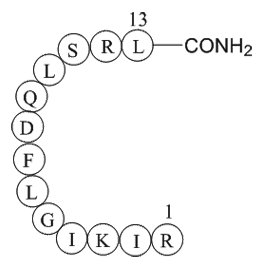 A1132 β-PompilidotoxinTarget: sodium channelsSummary: Slows Na+ channel inactivation
A1132 β-PompilidotoxinTarget: sodium channelsSummary: Slows Na+ channel inactivation -
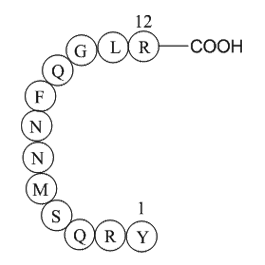 A1001 Adrenomedullin (1-12), humanSummary: Vasodilator
A1001 Adrenomedullin (1-12), humanSummary: Vasodilator -
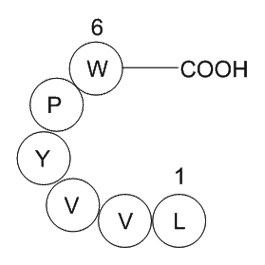 A1010 Myelopeptide-2 (MP-2)Summary: Peptide used for restoring human T lymphocytes
A1010 Myelopeptide-2 (MP-2)Summary: Peptide used for restoring human T lymphocytes


