Cancer Biology

Cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. A diverse array of chemical and biological compounds has been developed to target cancer cells through various mechanisms, ranging from direct cytotoxicity to modulation of specific molecular pathways.
Traditional chemotherapeutic agents, such as alkylating agents, antimetabolites, topoisomerase inhibitors, and mitotic inhibitors, exert their effects primarily by interfering with DNA replication or cell division, thereby preferentially targeting rapidly proliferating tumor cells. Targeted therapy agents, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors, selectively suppress oncogenic signaling pathways, thereby offering enhanced specificity and reduced systemic toxicity. Immunotherapeutic agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, harness the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. In addition, epigenetic modulators, DNA repair inhibitors, and angiogenesis-targeting compounds constitute novel therapeutic strategies.
-
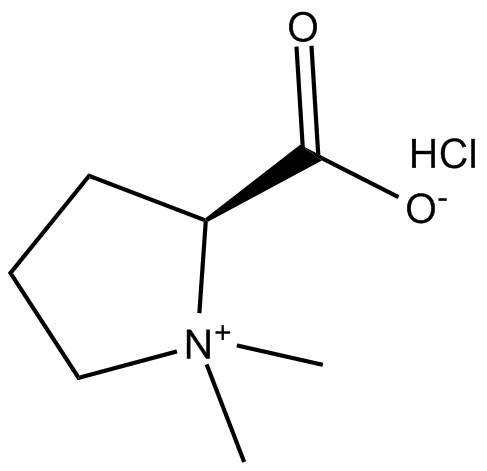 C3648 Stachydrine (hydrochloride)Summary: anti-metastatic agent
C3648 Stachydrine (hydrochloride)Summary: anti-metastatic agent -
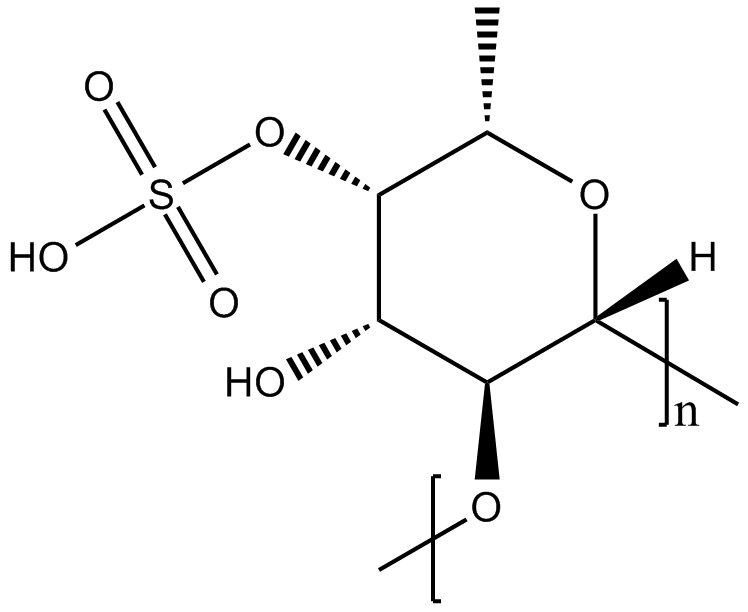 C4038 Fucoidan2 CitationSummary: anticancer, antiviral, neuroprotective, immune-modulating
C4038 Fucoidan2 CitationSummary: anticancer, antiviral, neuroprotective, immune-modulating -
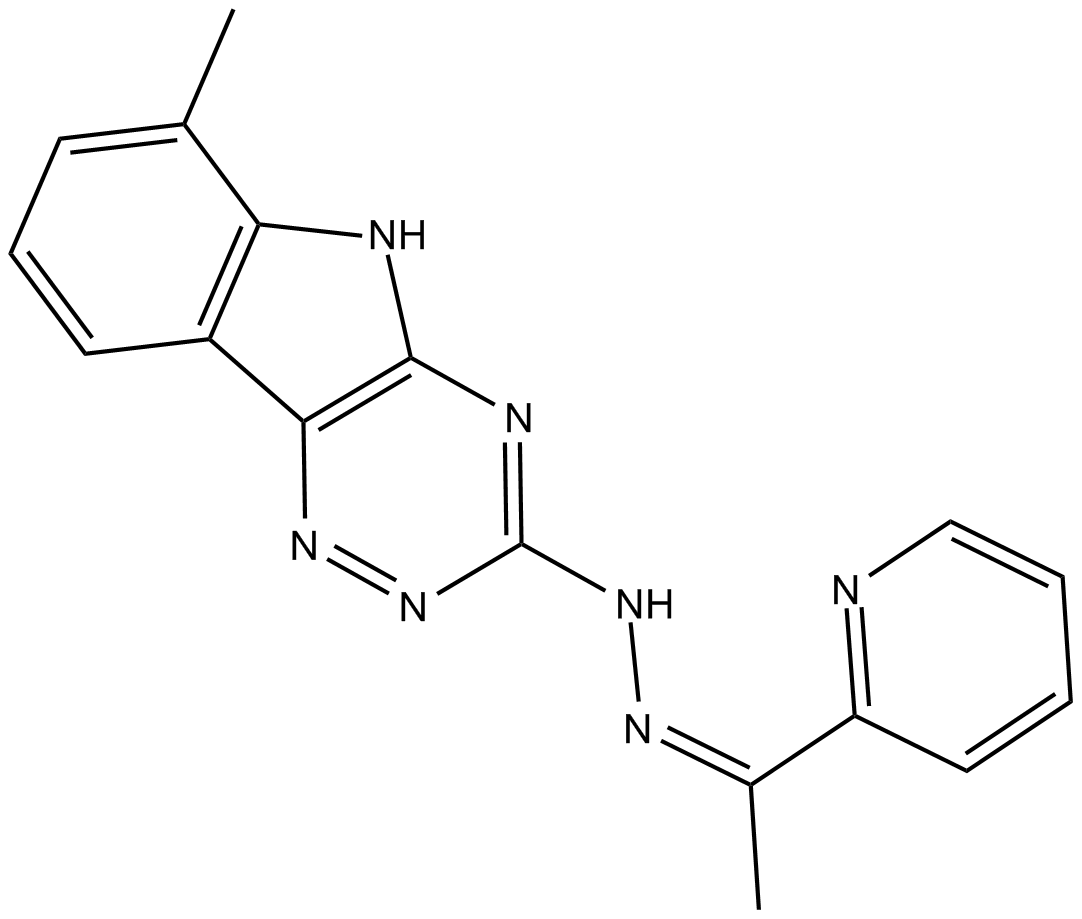 C4072 VLX600Summary: shows selective cytotoxicity against quiescent cancer cells
C4072 VLX600Summary: shows selective cytotoxicity against quiescent cancer cells -
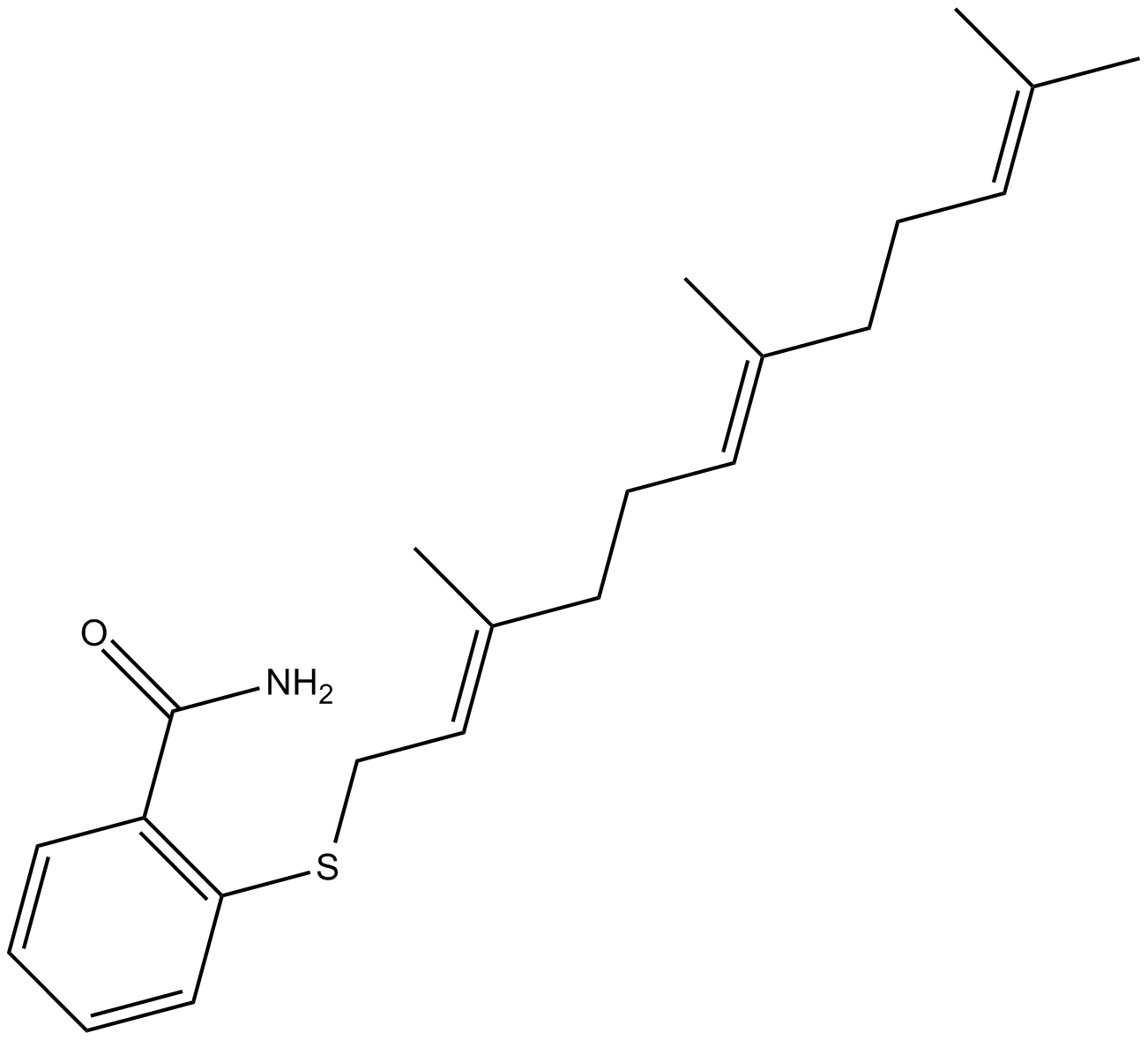 C4466 Farnesyl Thiosalicylic Acid AmideSummary: inhibits tumor growth
C4466 Farnesyl Thiosalicylic Acid AmideSummary: inhibits tumor growth -
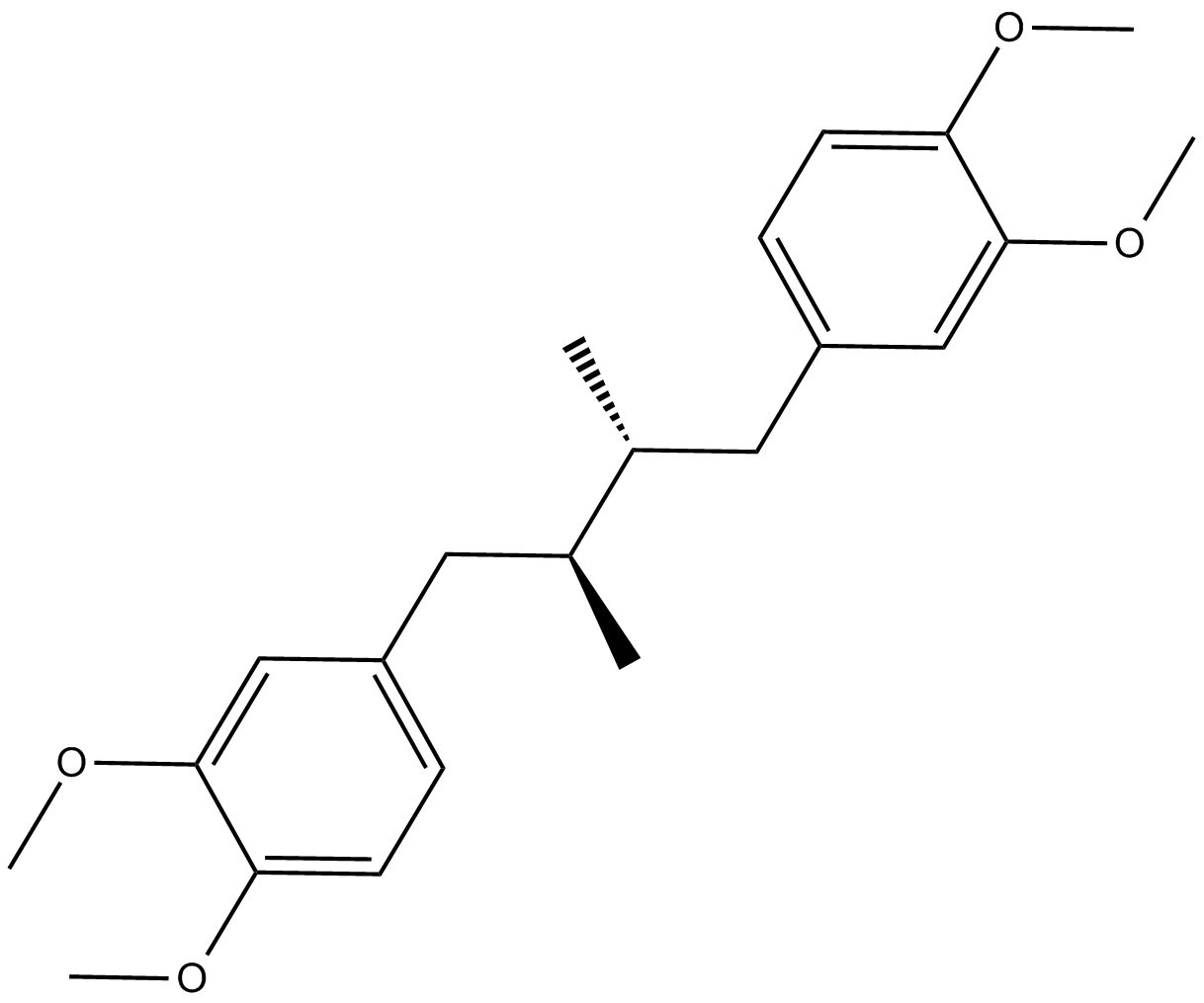 C4630 tetramethyl Nordihydroguaiaretic AcidSummary: antitumorigenic activity
C4630 tetramethyl Nordihydroguaiaretic AcidSummary: antitumorigenic activity -
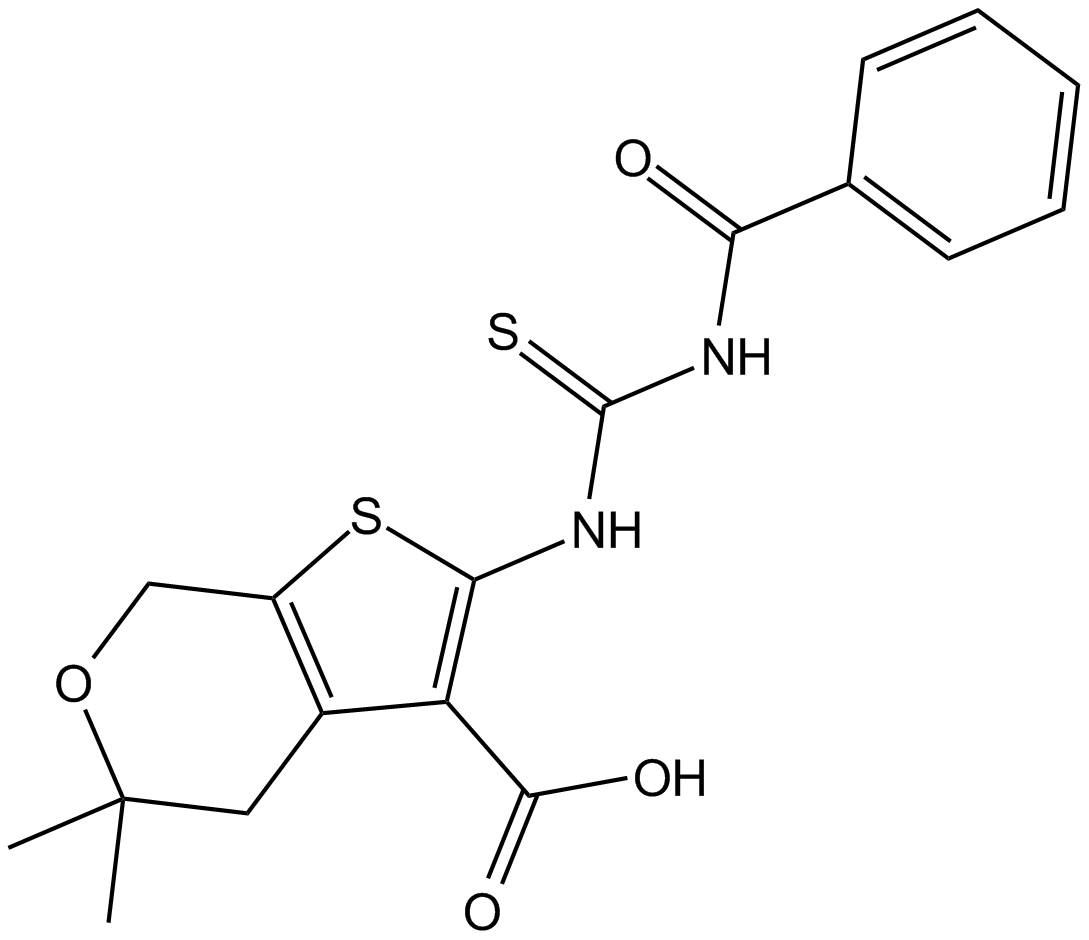 C4819 CID-1067700Summary: competitive inhibitor of nucleotide binding by Ras-related GTPases
C4819 CID-1067700Summary: competitive inhibitor of nucleotide binding by Ras-related GTPases -
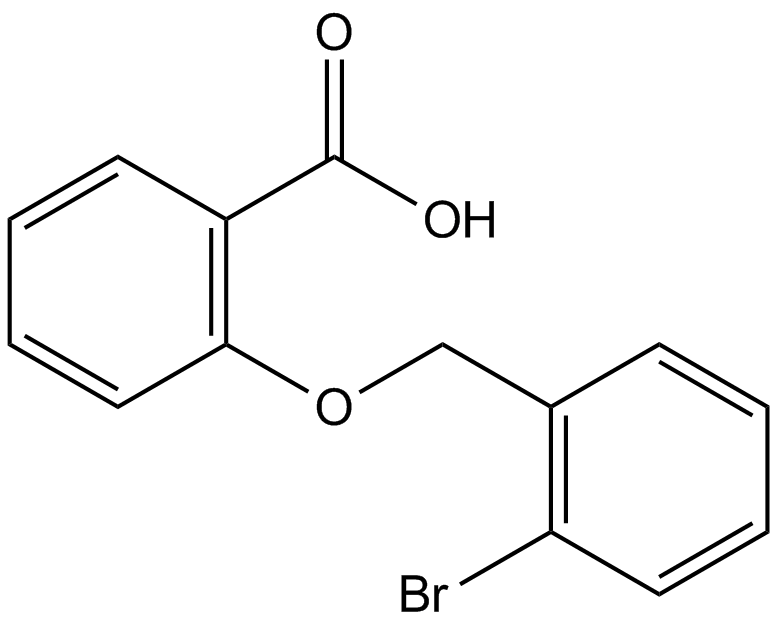 C4821 ML-097Summary: pan activator of Ras-related GTPases
C4821 ML-097Summary: pan activator of Ras-related GTPases -
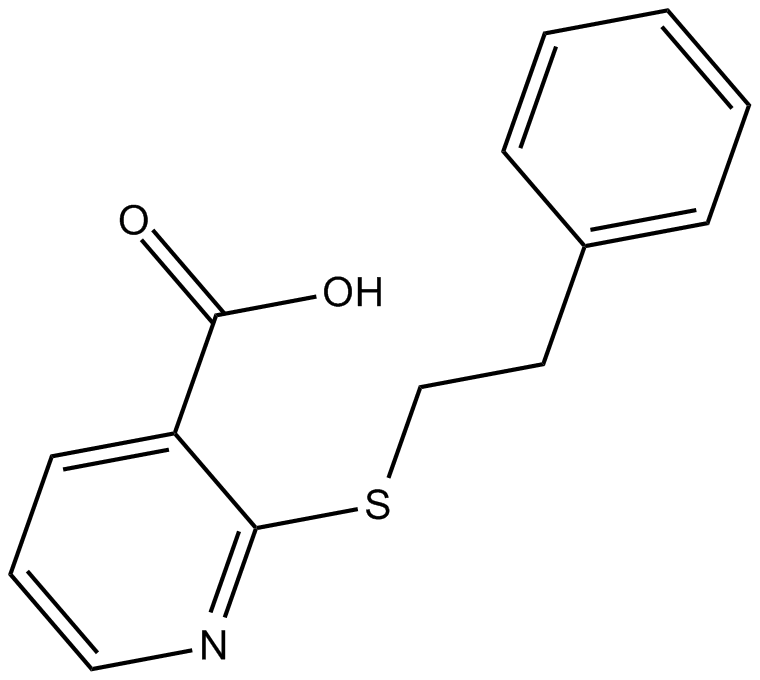 C4771 ML-099Summary: pan activator of Ras-related GTPases
C4771 ML-099Summary: pan activator of Ras-related GTPases -
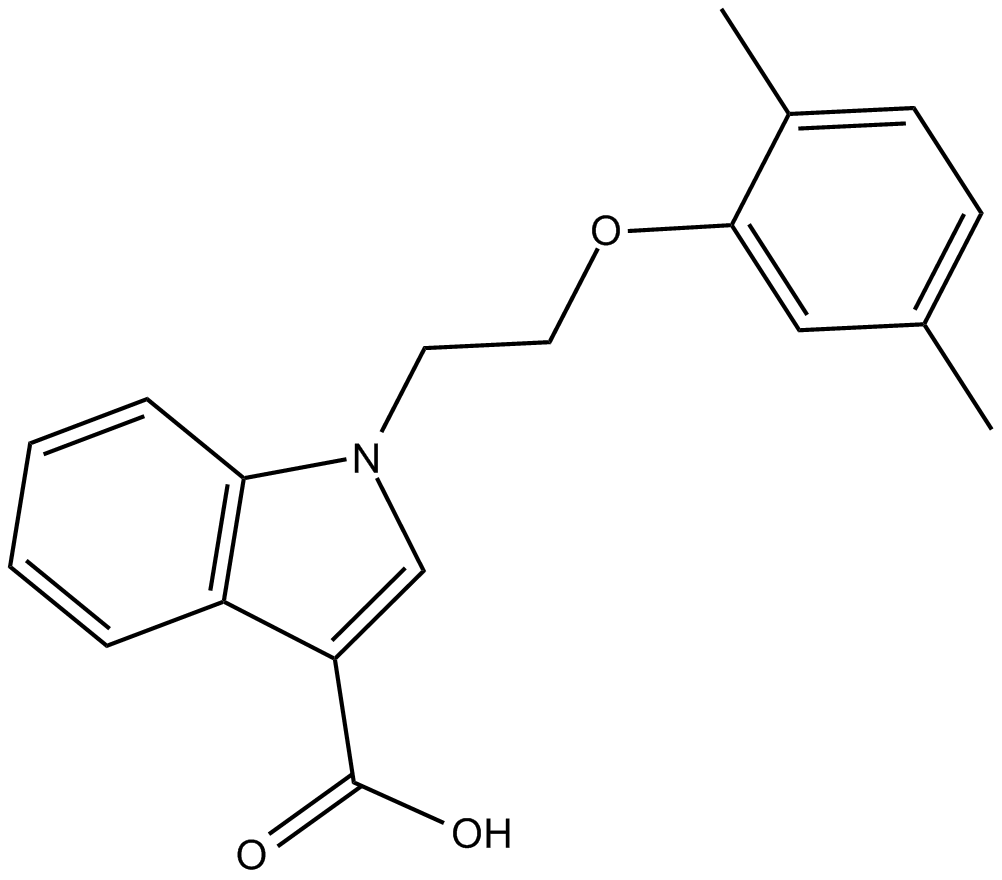 C4807 ML-098Summary: activator of the GTP-binding protein Rab7
C4807 ML-098Summary: activator of the GTP-binding protein Rab7 -
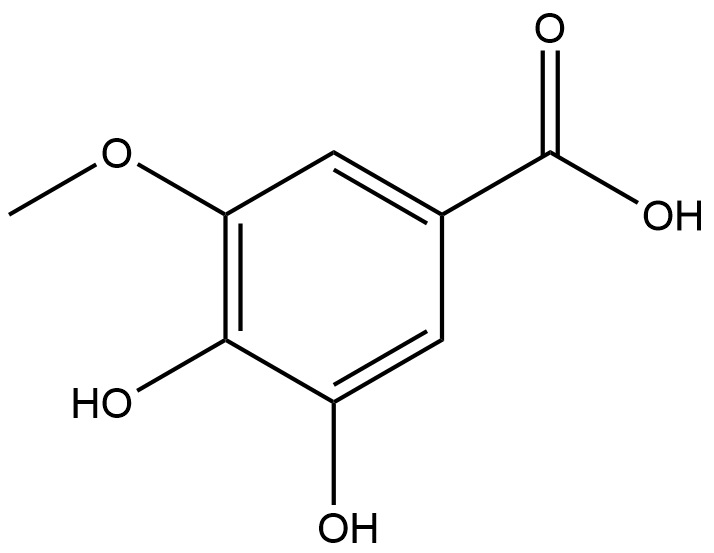 A4640 3-O-Methylgallic acid
A4640 3-O-Methylgallic acid


