Cancer Biology

Cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. A diverse array of chemical and biological compounds has been developed to target cancer cells through various mechanisms, ranging from direct cytotoxicity to modulation of specific molecular pathways.
Traditional chemotherapeutic agents, such as alkylating agents, antimetabolites, topoisomerase inhibitors, and mitotic inhibitors, exert their effects primarily by interfering with DNA replication or cell division, thereby preferentially targeting rapidly proliferating tumor cells. Targeted therapy agents, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors, selectively suppress oncogenic signaling pathways, thereby offering enhanced specificity and reduced systemic toxicity. Immunotherapeutic agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, harness the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. In addition, epigenetic modulators, DNA repair inhibitors, and angiogenesis-targeting compounds constitute novel therapeutic strategies.
-
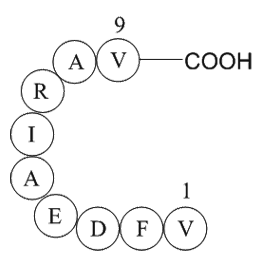 A1086 Rac GTPase fragmentSummary: Fragment of small signaling G proteins
A1086 Rac GTPase fragmentSummary: Fragment of small signaling G proteins -
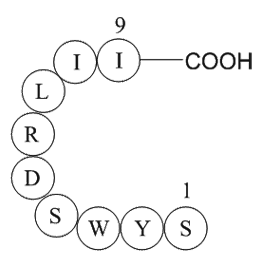 A1090 signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 fragmentSummary: STAT6 transcription factor
A1090 signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 fragmentSummary: STAT6 transcription factor -
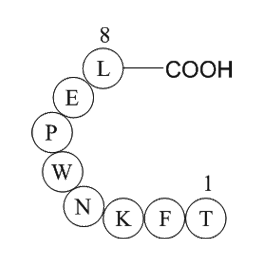 A1092 survivin (baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 5) (21-28)Summary: Cancer Biology Peptides
A1092 survivin (baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 5) (21-28)Summary: Cancer Biology Peptides -
![tumor protein p53 binding protein fragment [Homo sapiens]/[Mus musculus]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1094.png) A1094 tumor protein p53 binding protein fragment [Homo sapiens]/[Mus musculus]Summary: P53 binding protein fragment
A1094 tumor protein p53 binding protein fragment [Homo sapiens]/[Mus musculus]Summary: P53 binding protein fragment -
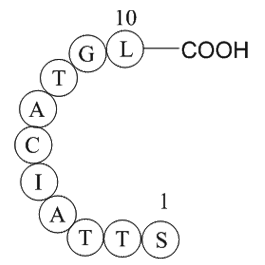 A1097 ubiquitin specific protease 3 fragmentSummary: Deubiquitinates uH2A/uH2B
A1097 ubiquitin specific protease 3 fragmentSummary: Deubiquitinates uH2A/uH2B -
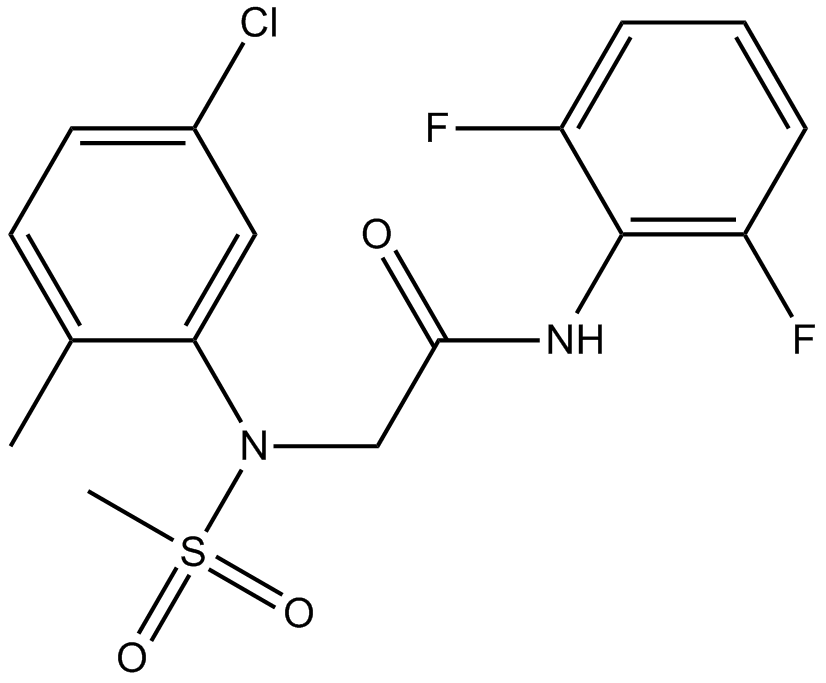 B3701 FPH1 (BRD-6125)1 CitationSummary: Hepatocyte functional proliferation enhancer
B3701 FPH1 (BRD-6125)1 CitationSummary: Hepatocyte functional proliferation enhancer -
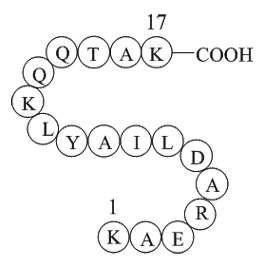 A1061 Cytochrome c - pigeon (88-104)Summary: Triggers T Cell response
A1061 Cytochrome c - pigeon (88-104)Summary: Triggers T Cell response -
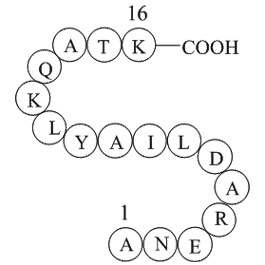 A1062 Cytochrome c fragment (93-108)Summary: Initiates apoptosis
A1062 Cytochrome c fragment (93-108)Summary: Initiates apoptosis -
![Cytochrome P450 CYP1B1 (190-198) [Homo sapiens]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1063.png) A1063 Cytochrome P450 CYP1B1 (190-198) [Homo sapiens]Summary: Sequence: H2N-FLDPRPLTV-OH
A1063 Cytochrome P450 CYP1B1 (190-198) [Homo sapiens]Summary: Sequence: H2N-FLDPRPLTV-OH -
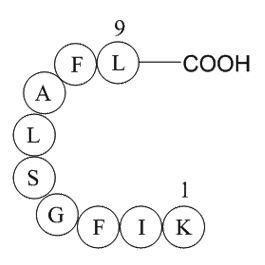 A1066 erbB-2Summary: Tyrosine kinase (TK) receptor
A1066 erbB-2Summary: Tyrosine kinase (TK) receptor


