JAK/STAT Signaling
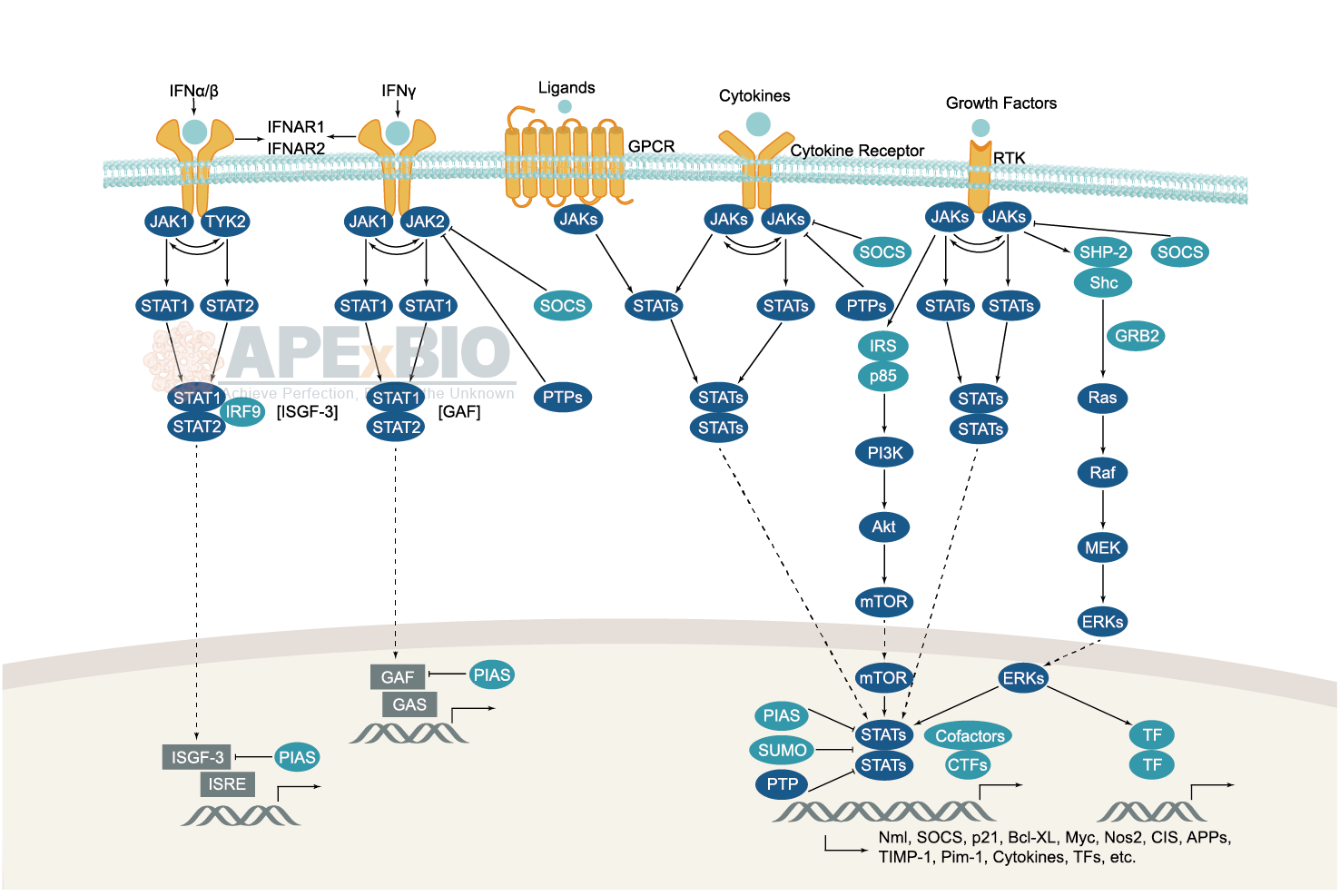

Various ligands including cytokines (e.g. interferons and interleukins), hormones (e.g. erythropoietin and growth hormone) and their cell surface receptors activate JAK proteins, which autophosphorylate, and then phosphorylate the receptor. Subsequently, JAKs phosphorylate a specific tyrosine residue on the STAT protein, promoting dimerization via SH2 domains. The activated STATs form homo-/heterodimers and translocate to the nucleus to trigger target gene transcription. In addition, suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family inhibit receptor signaling via homologous or heterologous feedback regulation. Dysregulation in JAK/STAT signaling is associated with diseases such as atherosclerosis, immunodeficiencies and cancer.
-
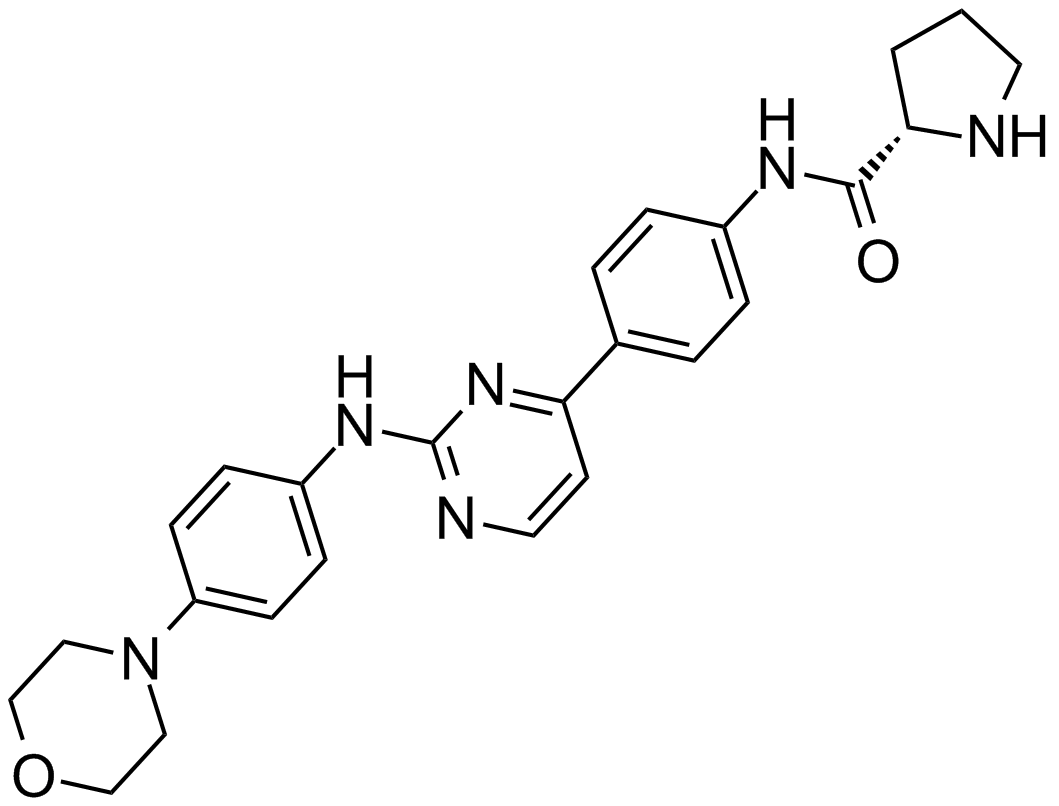 A3937 XL019Target: JAKSummary: JAK2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A3937 XL019Target: JAKSummary: JAK2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
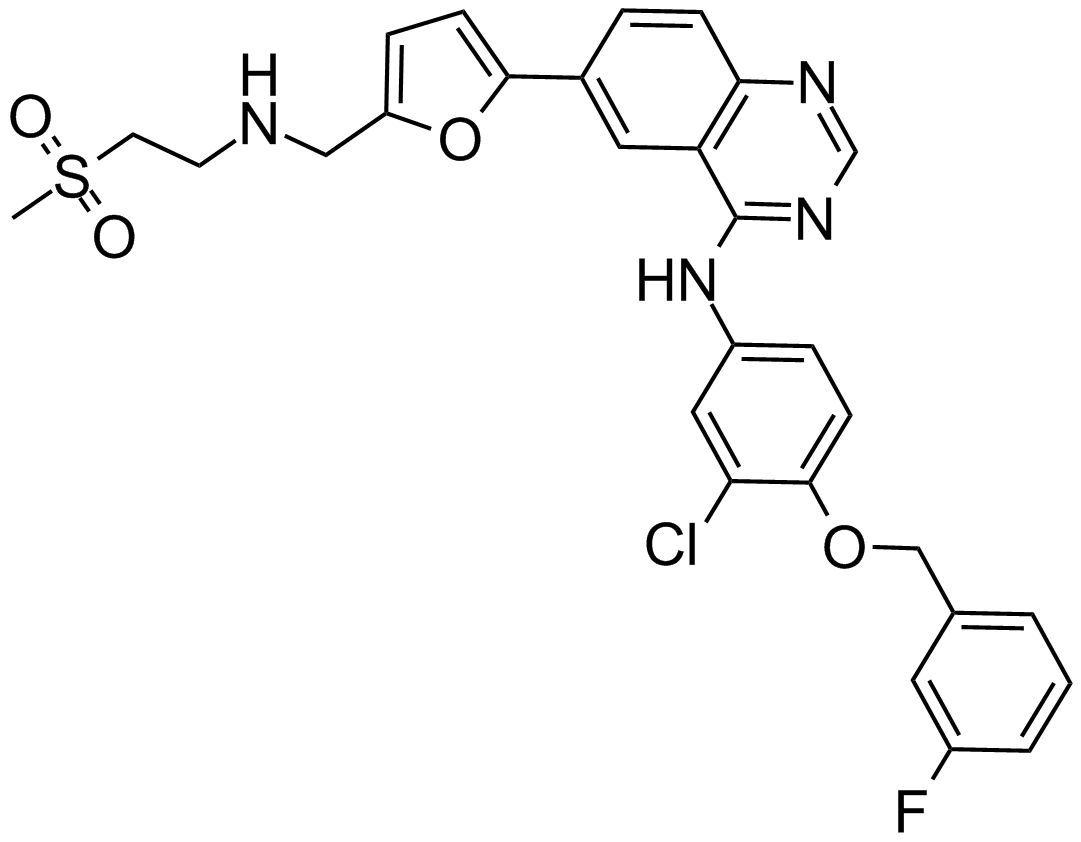 A8218 Lapatinib7 CitationTarget: ErbBSummary: EGFR/HER2 inhibitor,potent,selective and reversible
A8218 Lapatinib7 CitationTarget: ErbBSummary: EGFR/HER2 inhibitor,potent,selective and reversible -
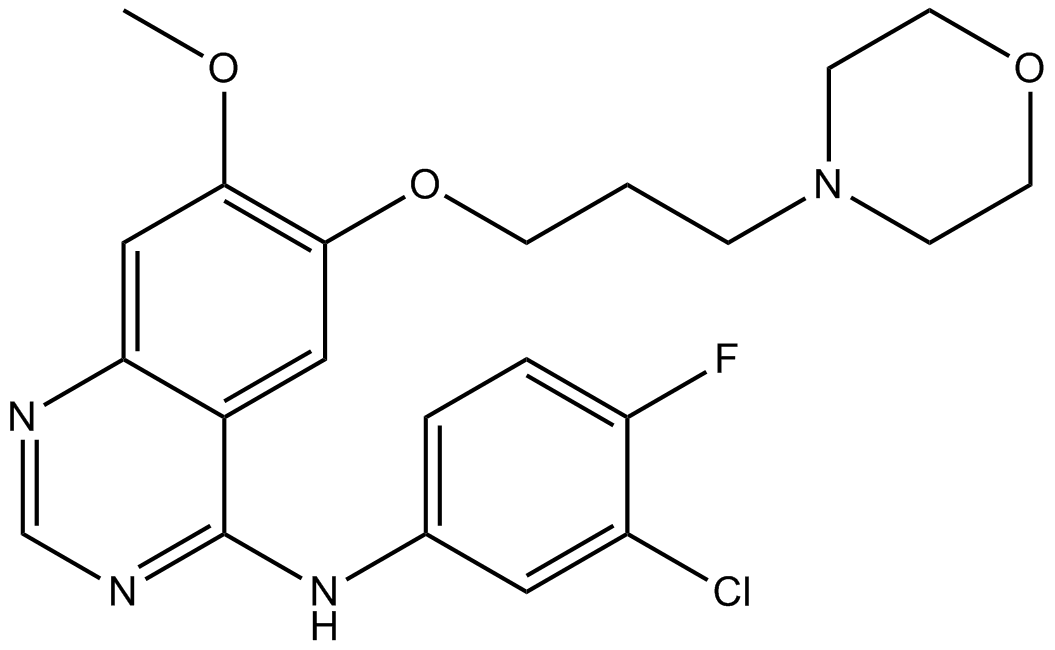 A8219 Gefitinib (ZD1839)15 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor
A8219 Gefitinib (ZD1839)15 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor -
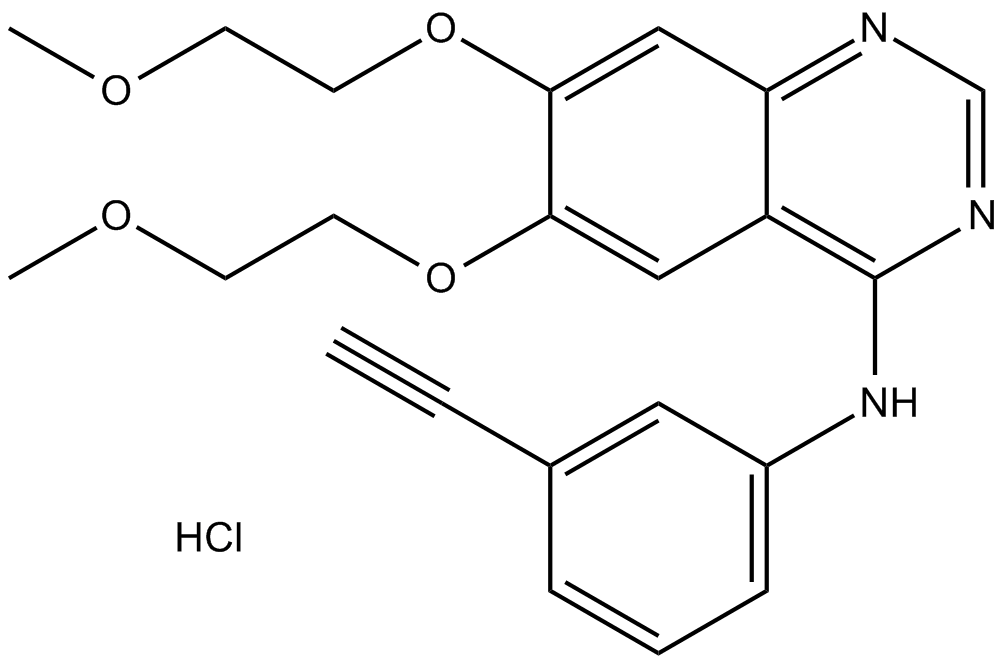 A8234 Erlotinib Hydrochloride2 CitationSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor
A8234 Erlotinib Hydrochloride2 CitationSummary: Selective EGFR inhibitor -
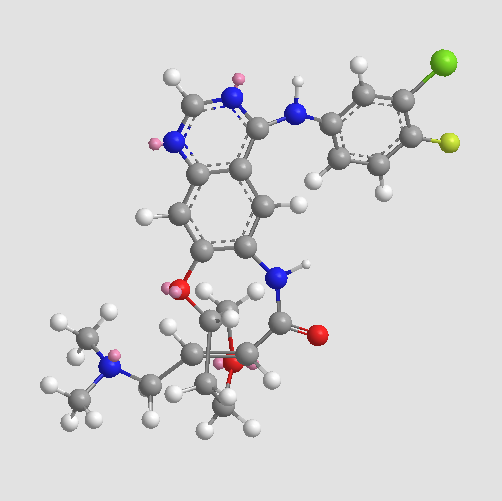 A8247 Afatinib (BIBW2992)2 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor
A8247 Afatinib (BIBW2992)2 CitationTarget: EGFRSummary: Irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor -
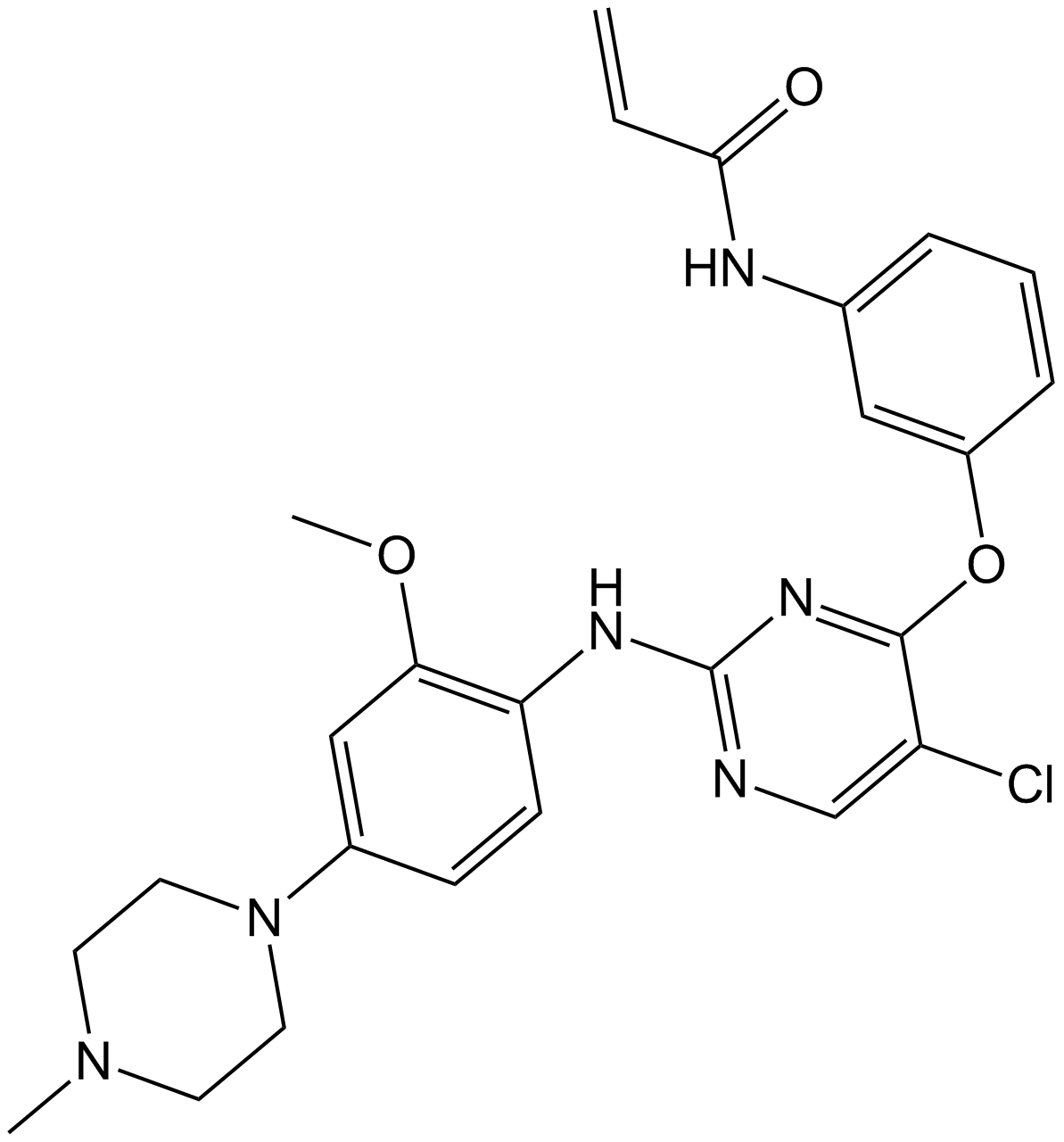 A1389 WZ4002Summary: Mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor(L858R,T790M), irreversible and potent
A1389 WZ4002Summary: Mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor(L858R,T790M), irreversible and potent -
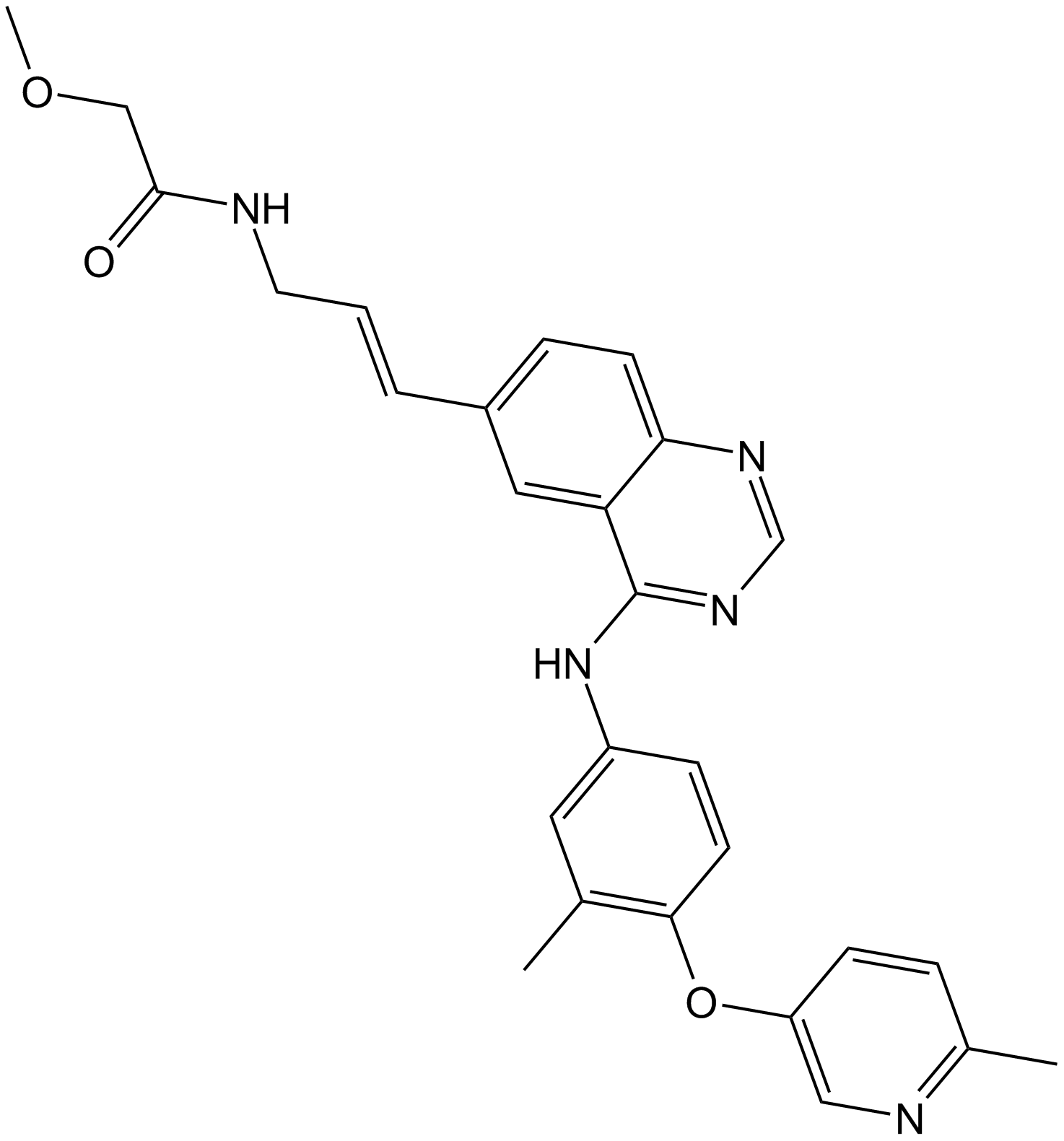 A2412 CP-724714Target: VEGFR|PDGFR|Bcr-Abl|Src|EGFR|c-MET|Insulin Receptors|IRG-1RSummary: HER2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A2412 CP-724714Target: VEGFR|PDGFR|Bcr-Abl|Src|EGFR|c-MET|Insulin Receptors|IRG-1RSummary: HER2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
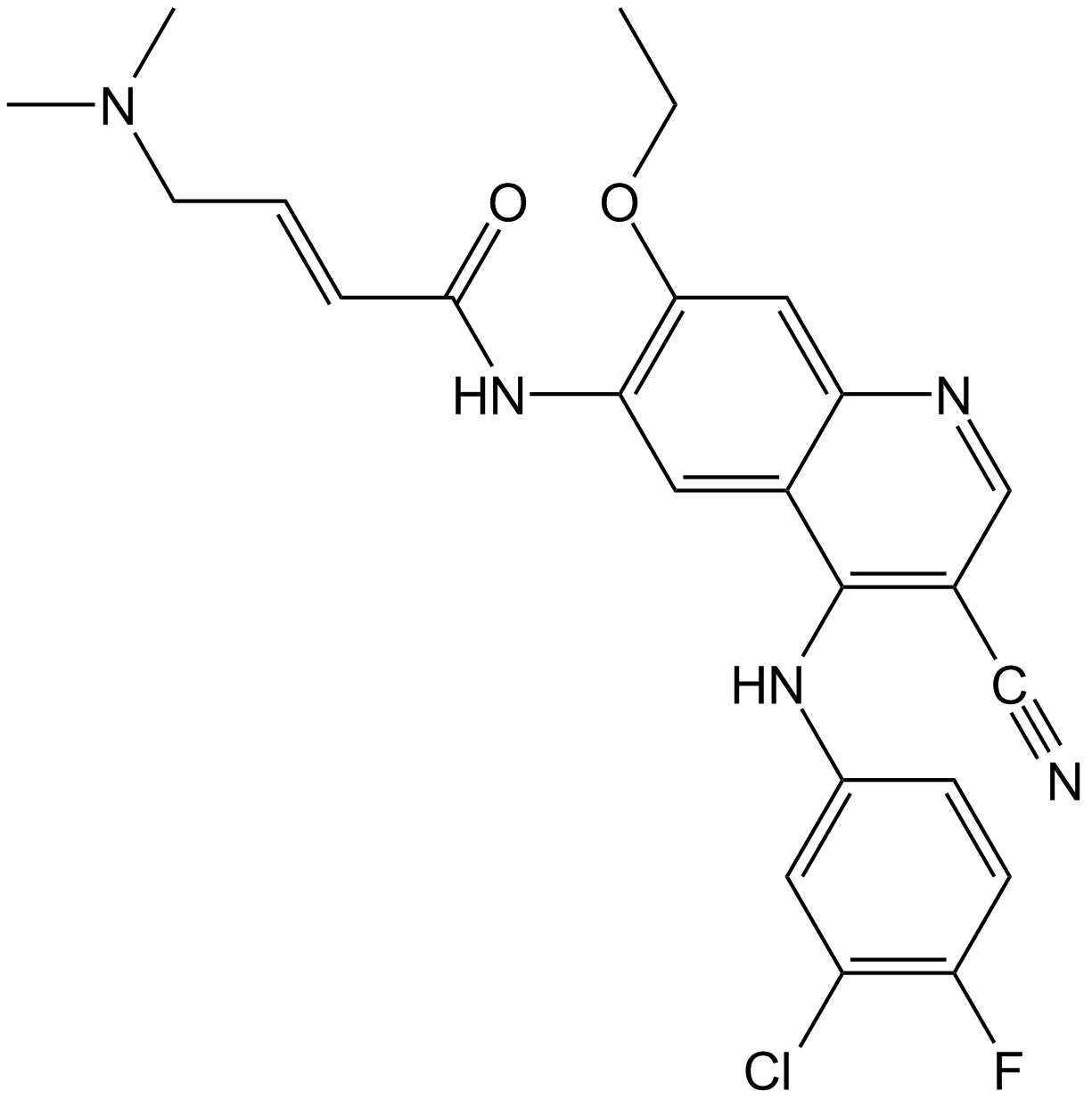 A1835 Pelitinib (EKB-569)Summary: EGFR inhibitor,potent and irreversible
A1835 Pelitinib (EKB-569)Summary: EGFR inhibitor,potent and irreversible -
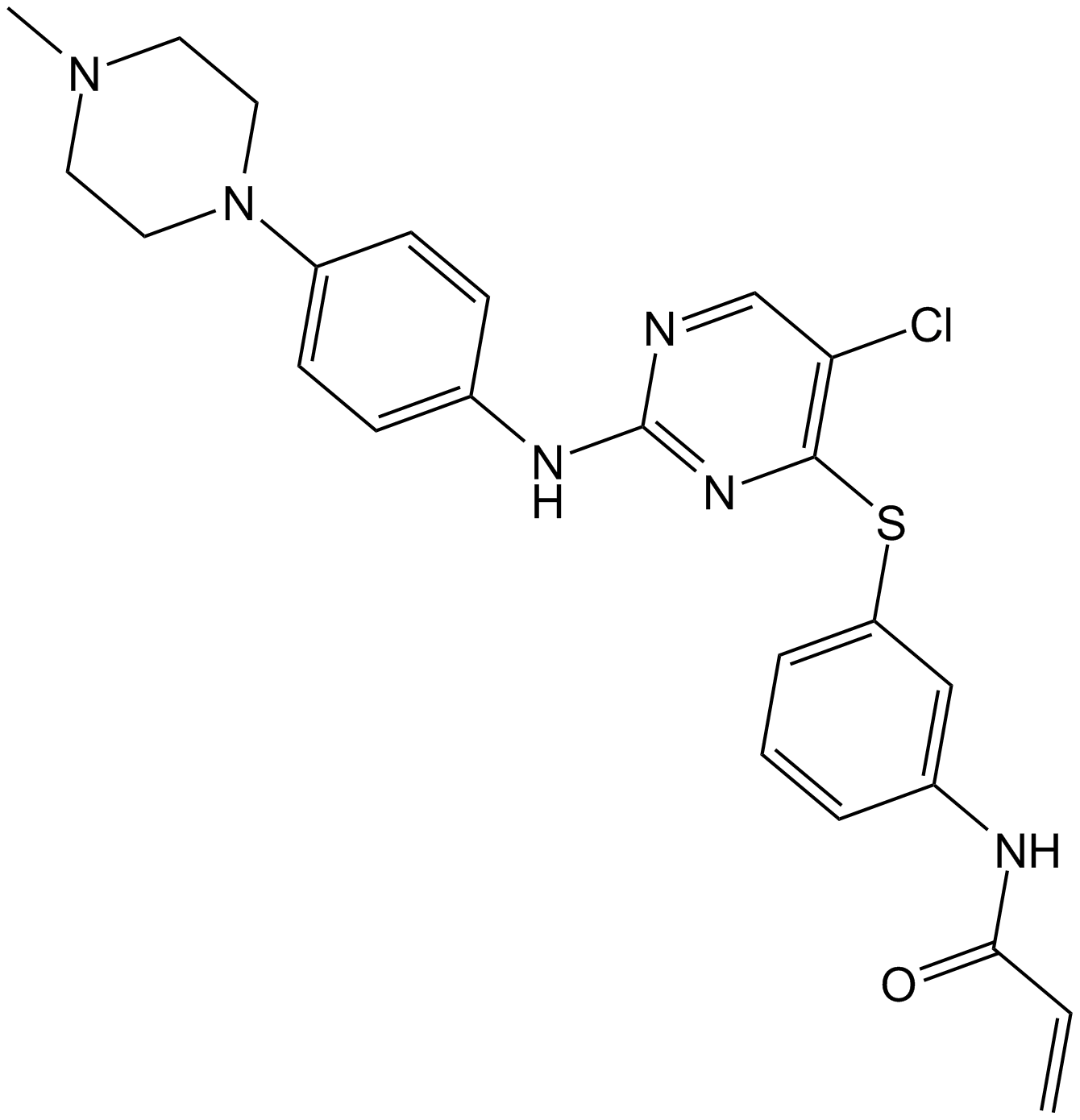 A1393 WZ8040Target: EGFRSummary: EGFR T790M inhibitor,irreversible amd potent
A1393 WZ8040Target: EGFRSummary: EGFR T790M inhibitor,irreversible amd potent -
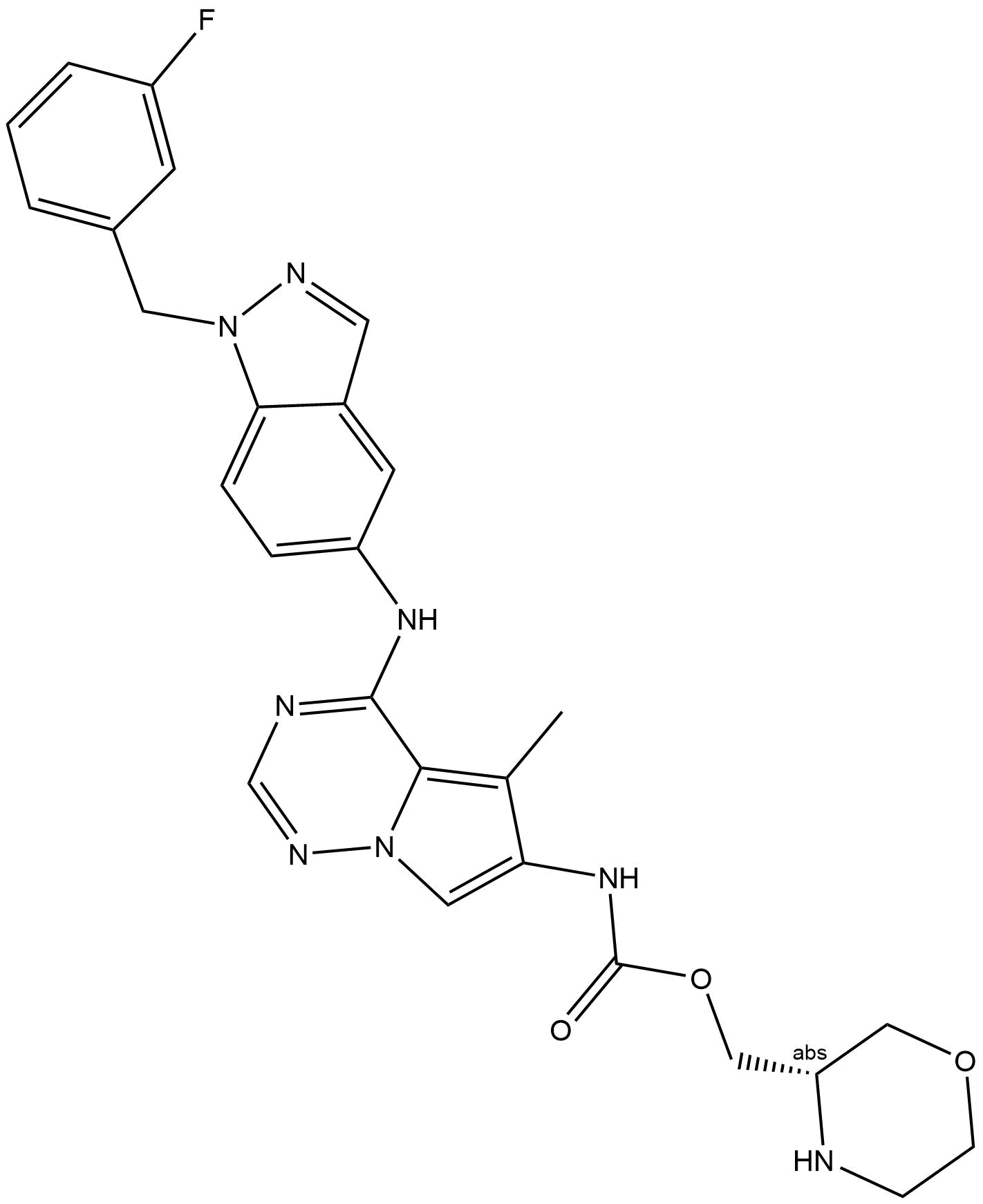 A2822 AC480 (BMS-599626)Target: EGFRSummary: HER1/2 inhibitor,selective and efficacious
A2822 AC480 (BMS-599626)Target: EGFRSummary: HER1/2 inhibitor,selective and efficacious


