Microbiology & Virology

Furthermore, small molecules enable selective modulation of the microbiome, balancing interactions between beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms. Coupled with advances in high-throughput screening technologies, they continue to overcome limitations related to target specificity and drug resistance, thereby serving as a crucial bridge between basic research and clinical anti-infective practice. Collectively, small-molecule compounds offer diversified solutions to global public health challenges.
-
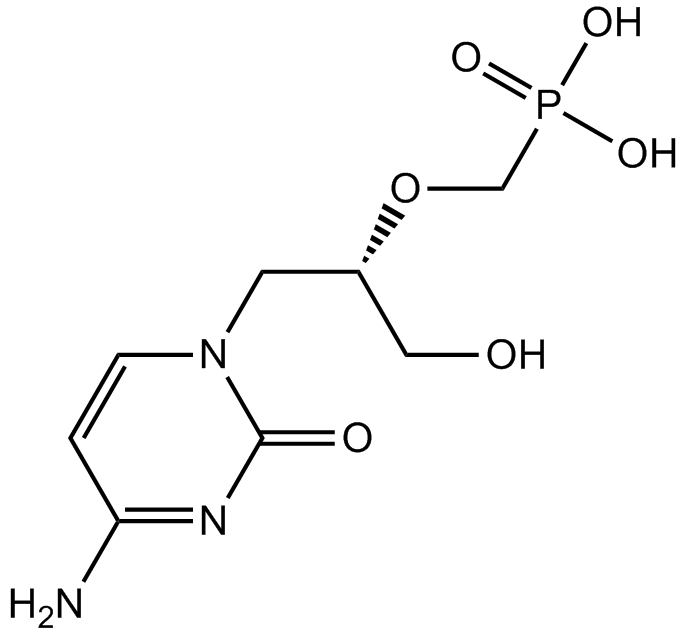 A5790 CidofovirTarget: CMVSummary: Anti-CMV drug;inhibitor of viral DNA syntheis
A5790 CidofovirTarget: CMVSummary: Anti-CMV drug;inhibitor of viral DNA syntheis -
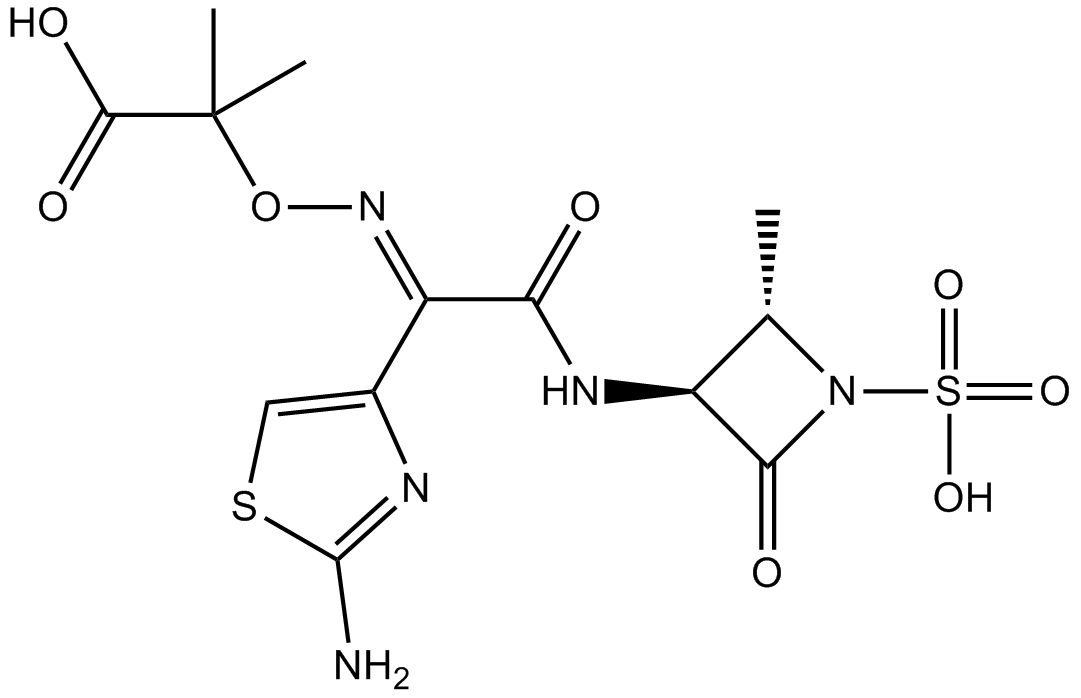 A5931 Aztreonam1 CitationSummary: Monobactam antibiotic,selectively active against Gram-negative aerobic bacteria
A5931 Aztreonam1 CitationSummary: Monobactam antibiotic,selectively active against Gram-negative aerobic bacteria -
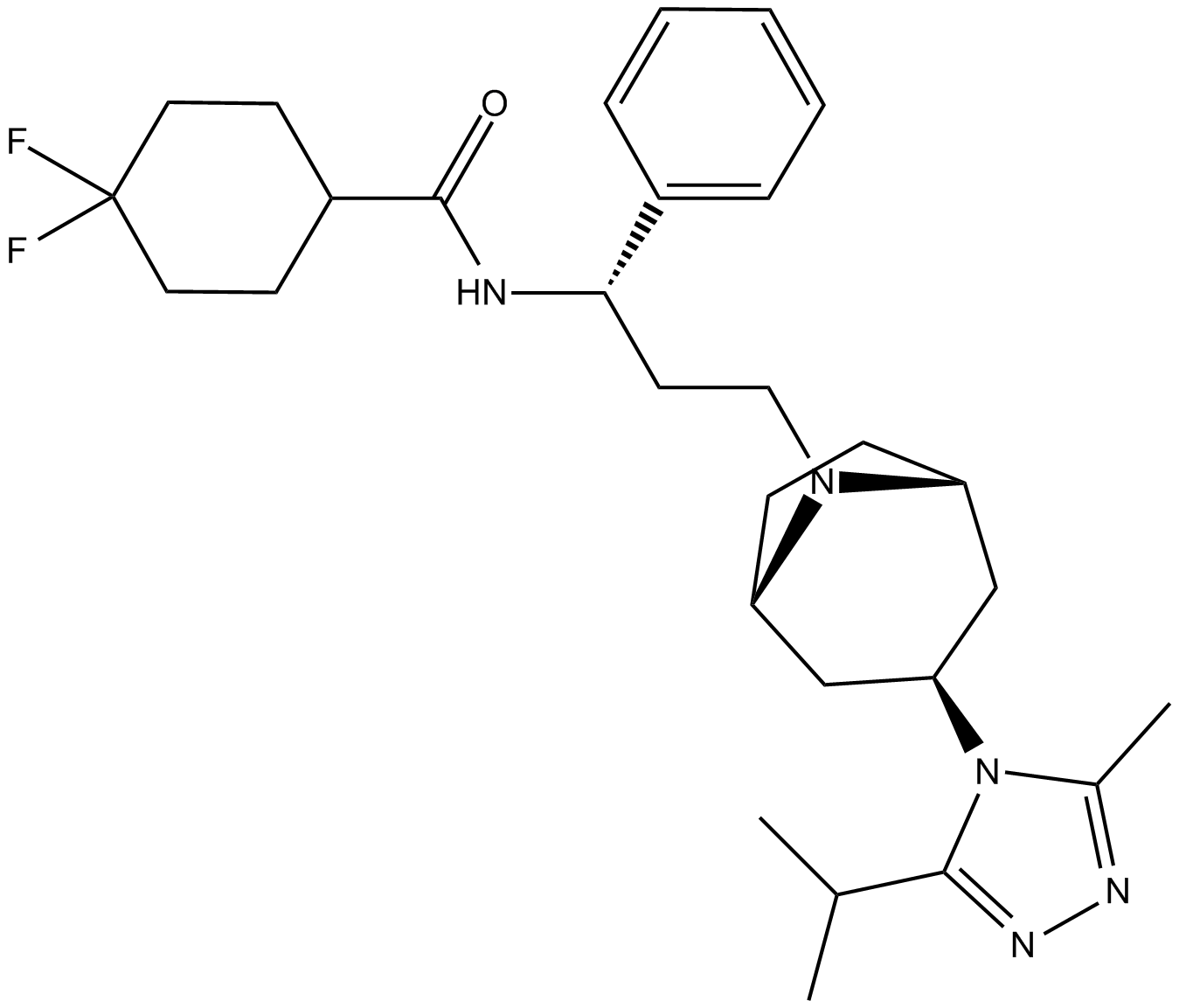 A8311 Maraviroc5 CitationTarget: CCRSummary: Selective CCR5 antagonist,antiretroviral agent
A8311 Maraviroc5 CitationTarget: CCRSummary: Selective CCR5 antagonist,antiretroviral agent -
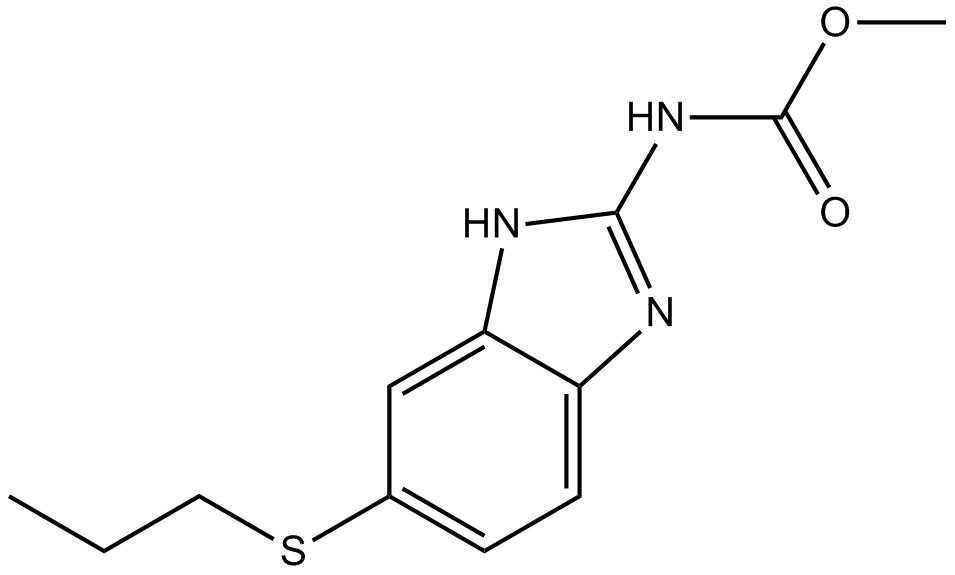 A8358 AlbendazoleSummary: treatment of a variety of parasitic worm infestations
A8358 AlbendazoleSummary: treatment of a variety of parasitic worm infestations -
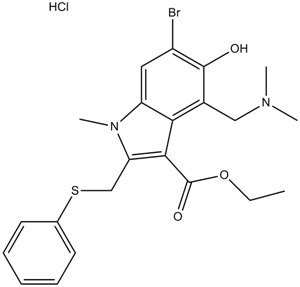 A8362 Arbidol HClSummary: Antiviral chemical agent
A8362 Arbidol HClSummary: Antiviral chemical agent -
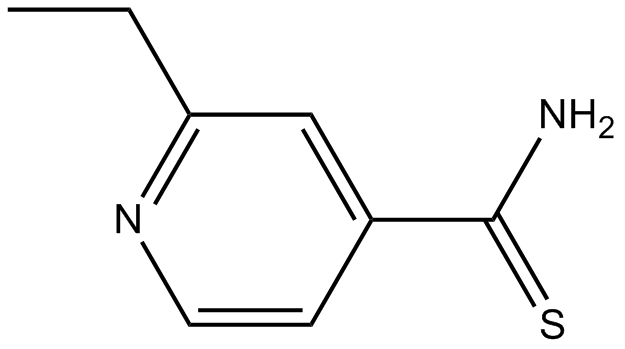 A8429 EthionamideSummary: Anti-tuberculosis antibiotic
A8429 EthionamideSummary: Anti-tuberculosis antibiotic -
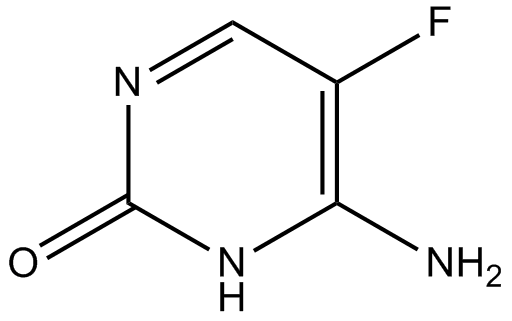 A8433 FlucytosineSummary: Antifungal drug
A8433 FlucytosineSummary: Antifungal drug -
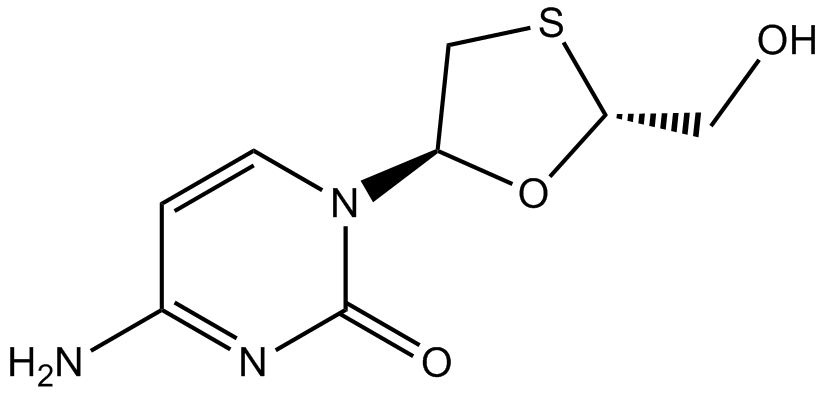 A8458 LamivudineTarget: HBV ProteasesSummary: Nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor
A8458 LamivudineTarget: HBV ProteasesSummary: Nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor -
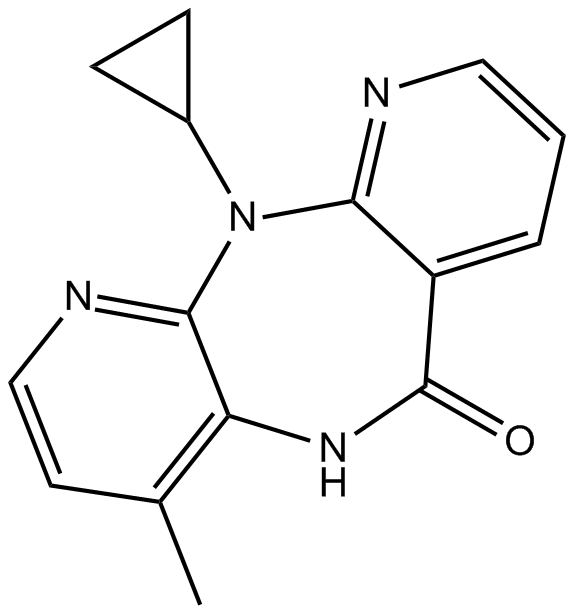 A8481 NevirapineSummary: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
A8481 NevirapineSummary: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor -
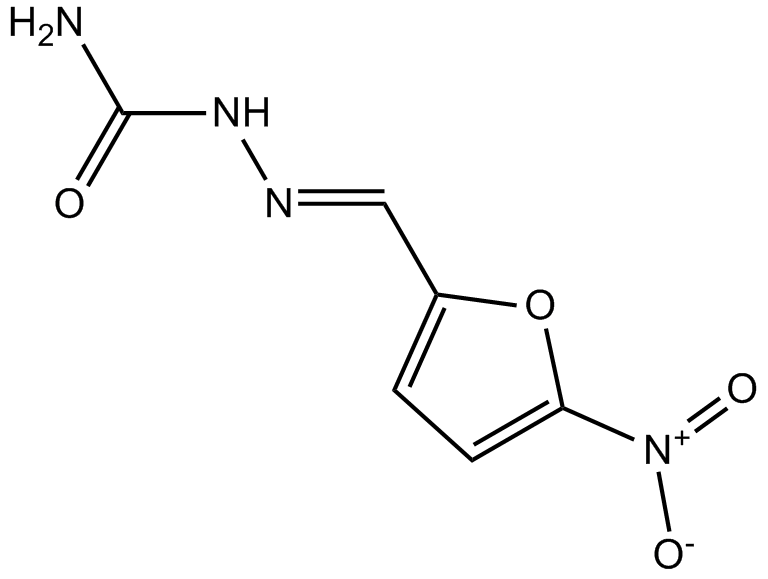 A8486 NitrofurazoneSummary: Antibiotic
A8486 NitrofurazoneSummary: Antibiotic


