Metabolism
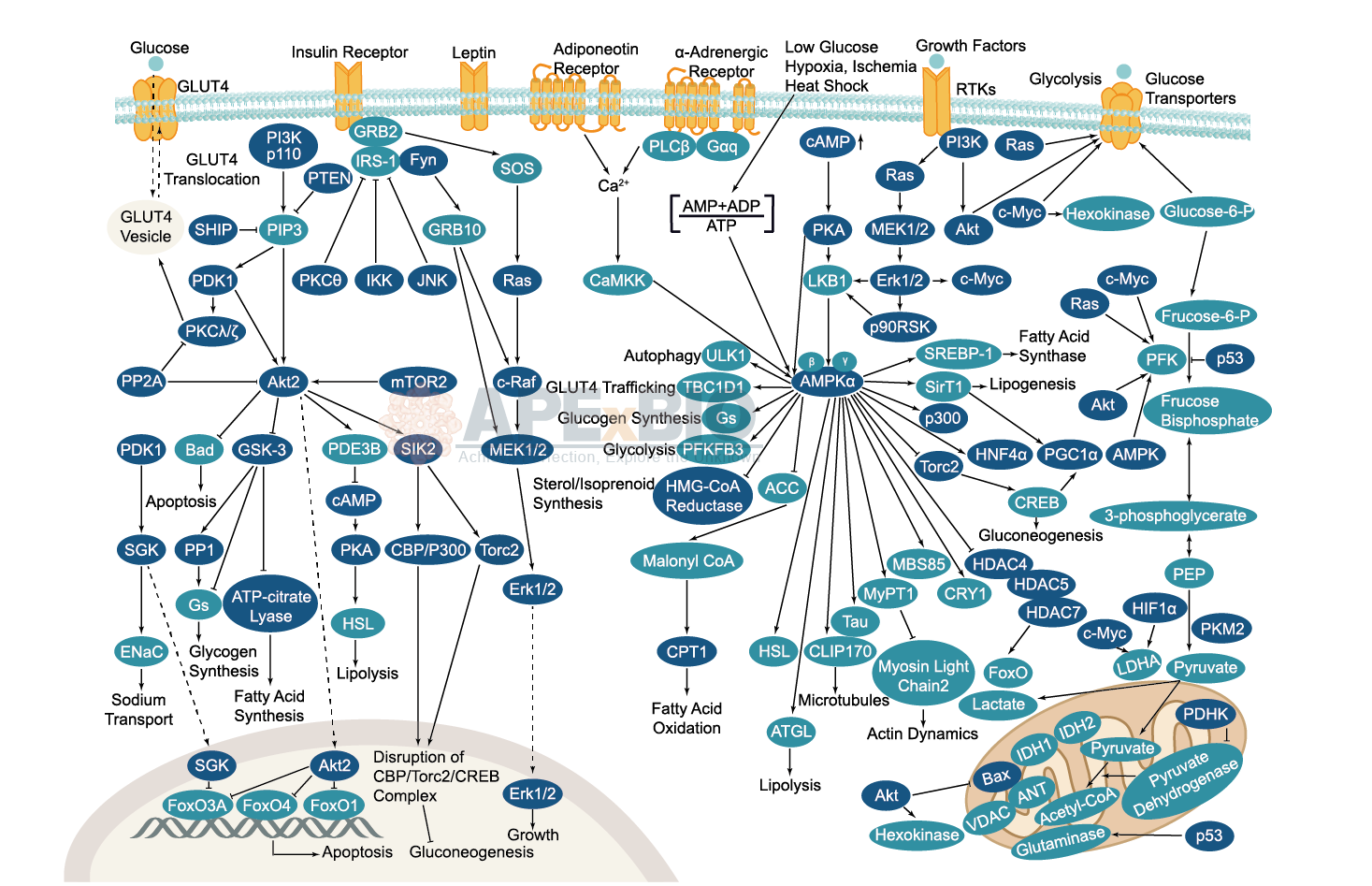

Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
 C5625 ONO-RS-082Summary: reversible inhibitor of Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2
C5625 ONO-RS-082Summary: reversible inhibitor of Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 -
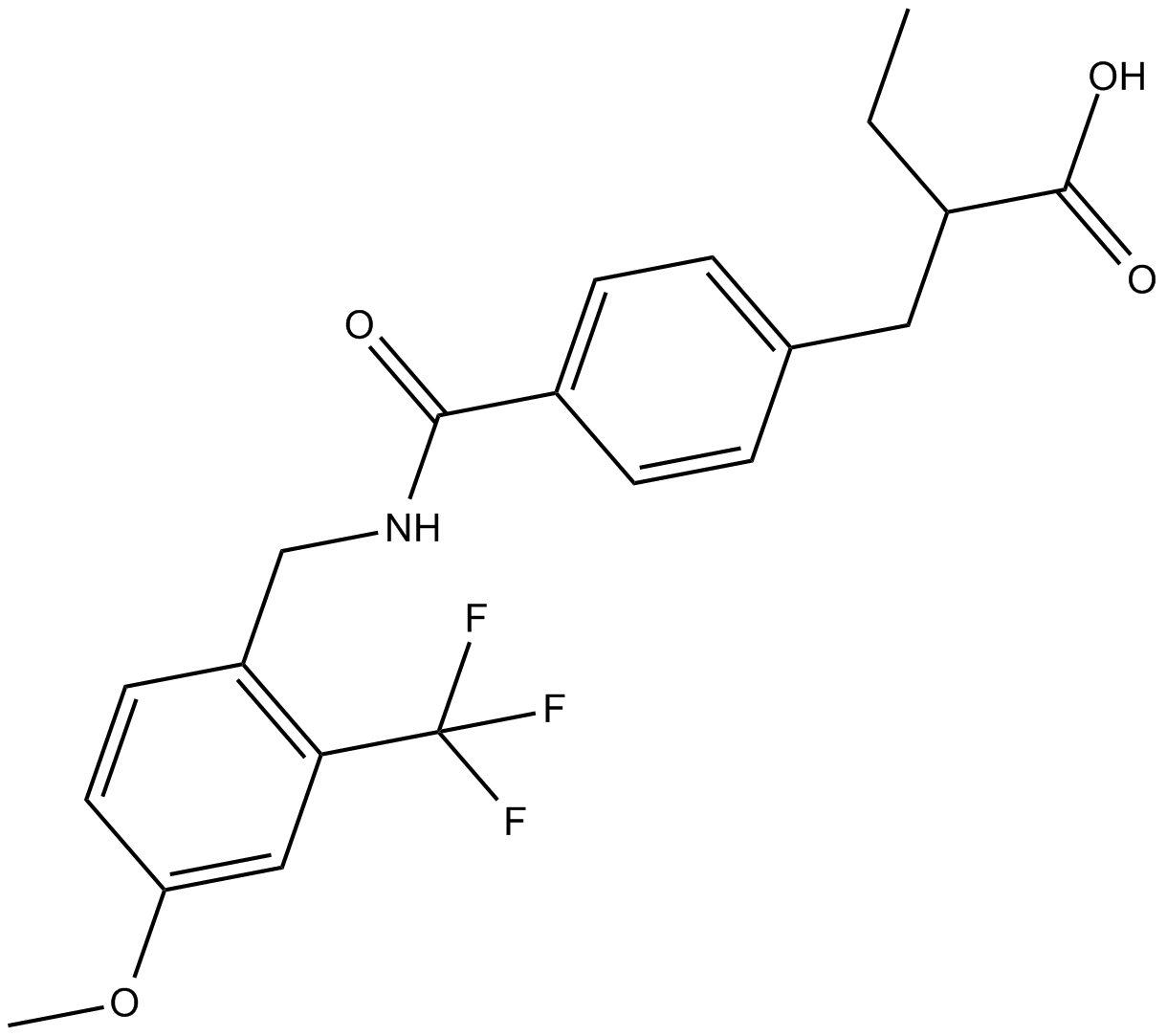 C5671 RB394Summary: dual modulator of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and PPARγ
C5671 RB394Summary: dual modulator of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and PPARγ -
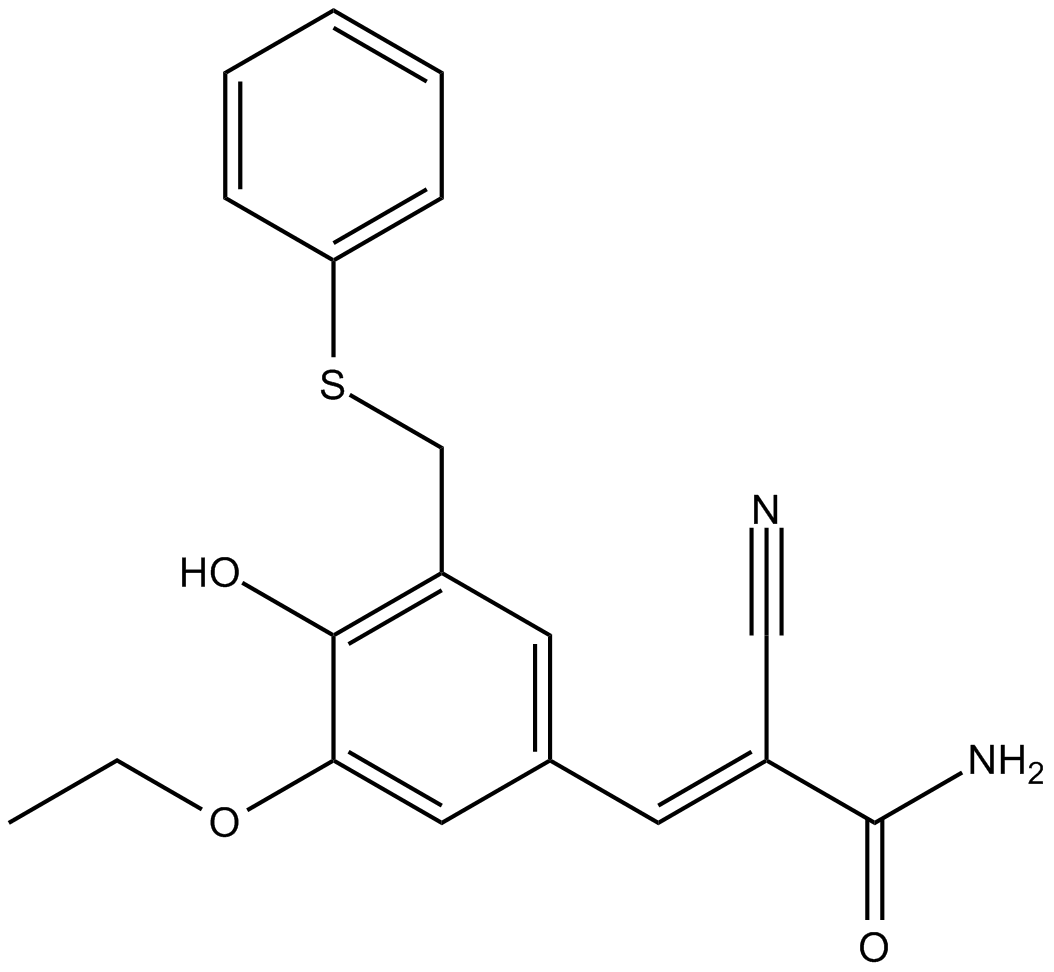 C5678 ST638Summary: tyrosine kinase inhibitor and PLD inhibitor
C5678 ST638Summary: tyrosine kinase inhibitor and PLD inhibitor -
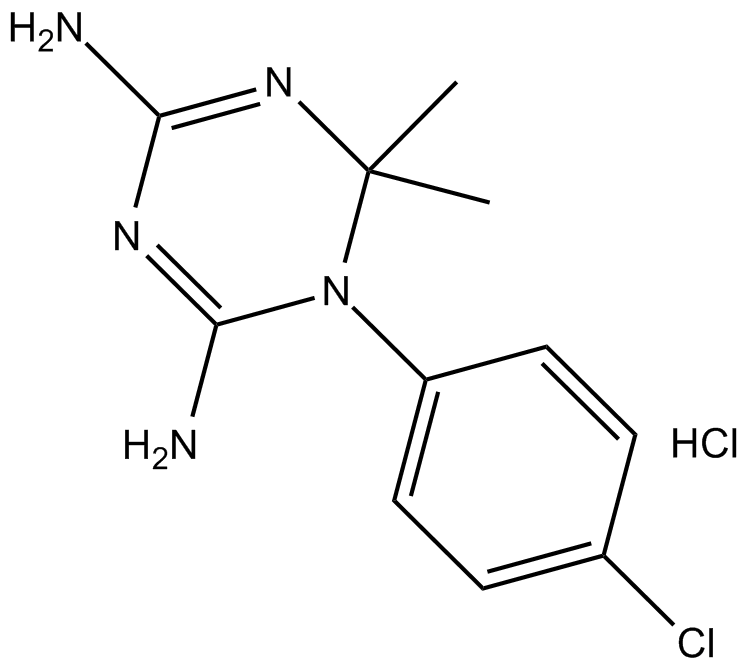 C5763 Cycloguanil (hydrochloride)Summary: inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
C5763 Cycloguanil (hydrochloride)Summary: inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) -
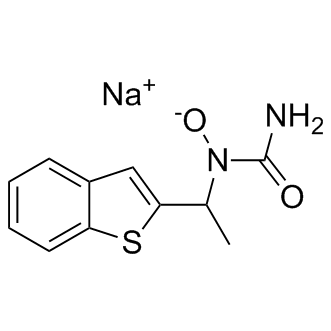 B1207 Zileuton sodiumSummary: 5-lipoxygenase and leukotrienes inhibitor
B1207 Zileuton sodiumSummary: 5-lipoxygenase and leukotrienes inhibitor -
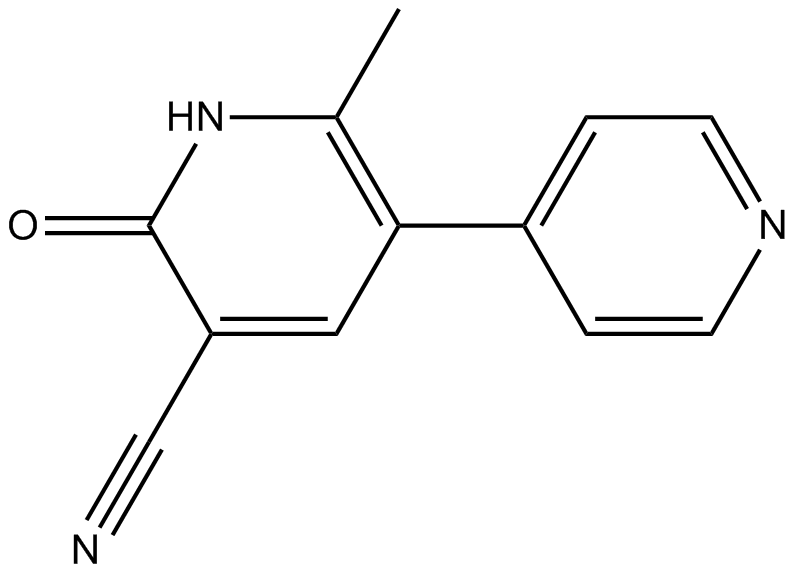 B1386 MilrinoneTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE-3 inhibitor
B1386 MilrinoneTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE-3 inhibitor -
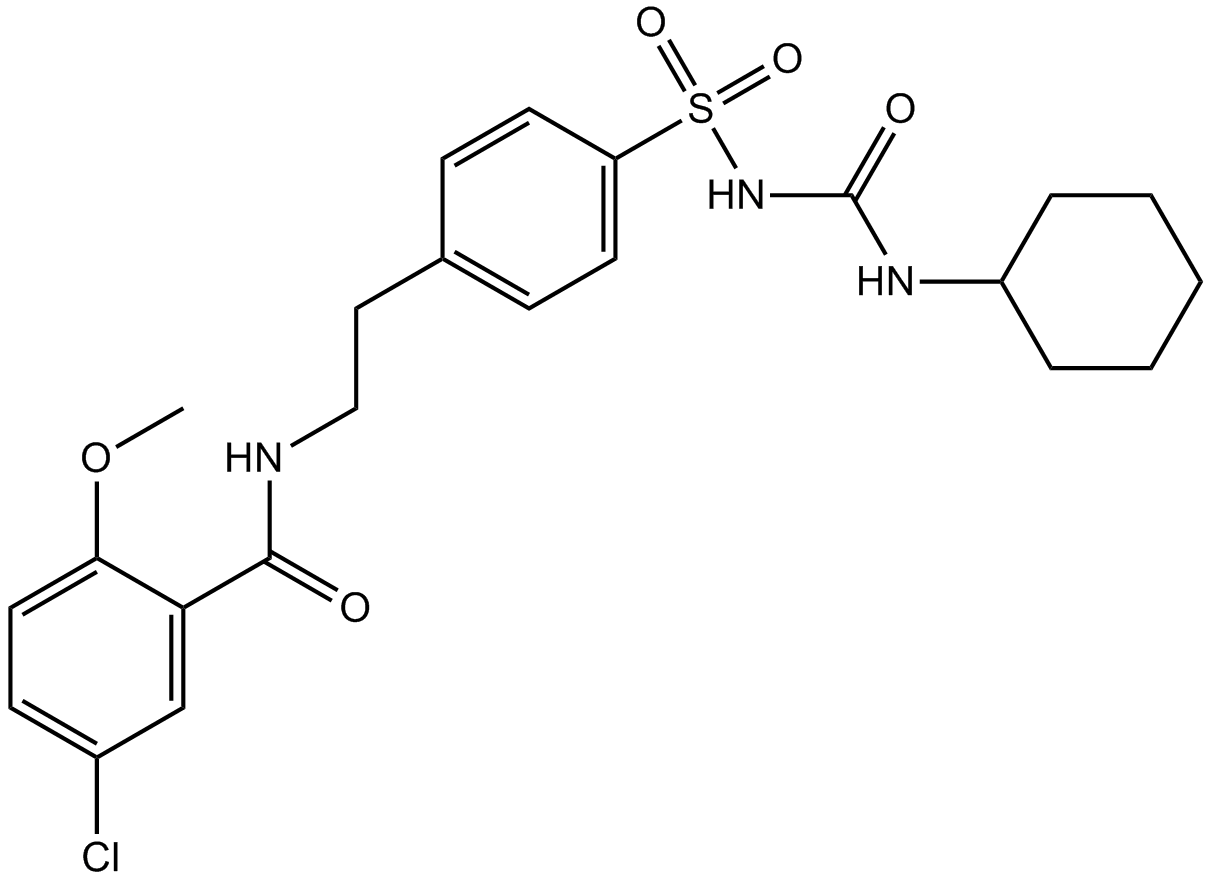 B1296 GlibenclamideTarget: Inward Rectifier Potassium (Kir) ChannelsSummary: Insulin production modulator
B1296 GlibenclamideTarget: Inward Rectifier Potassium (Kir) ChannelsSummary: Insulin production modulator -
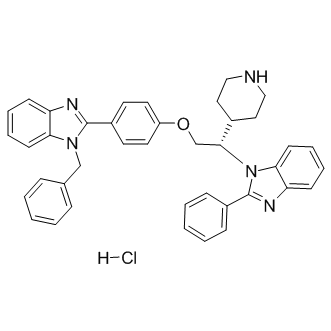 B1261 Deltarasin hydrochlorideSummary: inhibitor of KRAS-PDEδ interaction, potent and selective
B1261 Deltarasin hydrochlorideSummary: inhibitor of KRAS-PDEδ interaction, potent and selective -
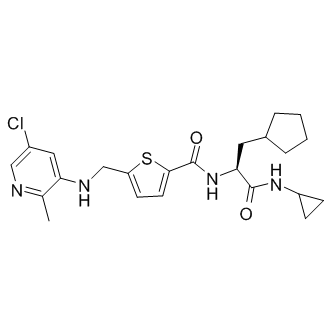 B1169 GSK 2830371Summary: Orally active, allosteric inhibitor of Wip1 phosphatase
B1169 GSK 2830371Summary: Orally active, allosteric inhibitor of Wip1 phosphatase -
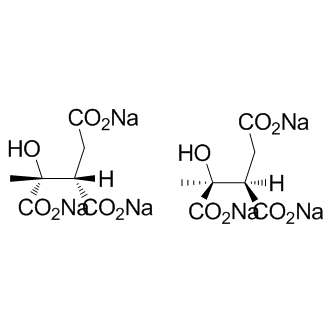 B1310 DL-threo-2-methylisocitrate sodiumSummary: Substrate of isocitrate lyase 1(ICL1)
B1310 DL-threo-2-methylisocitrate sodiumSummary: Substrate of isocitrate lyase 1(ICL1)


