Metabolism
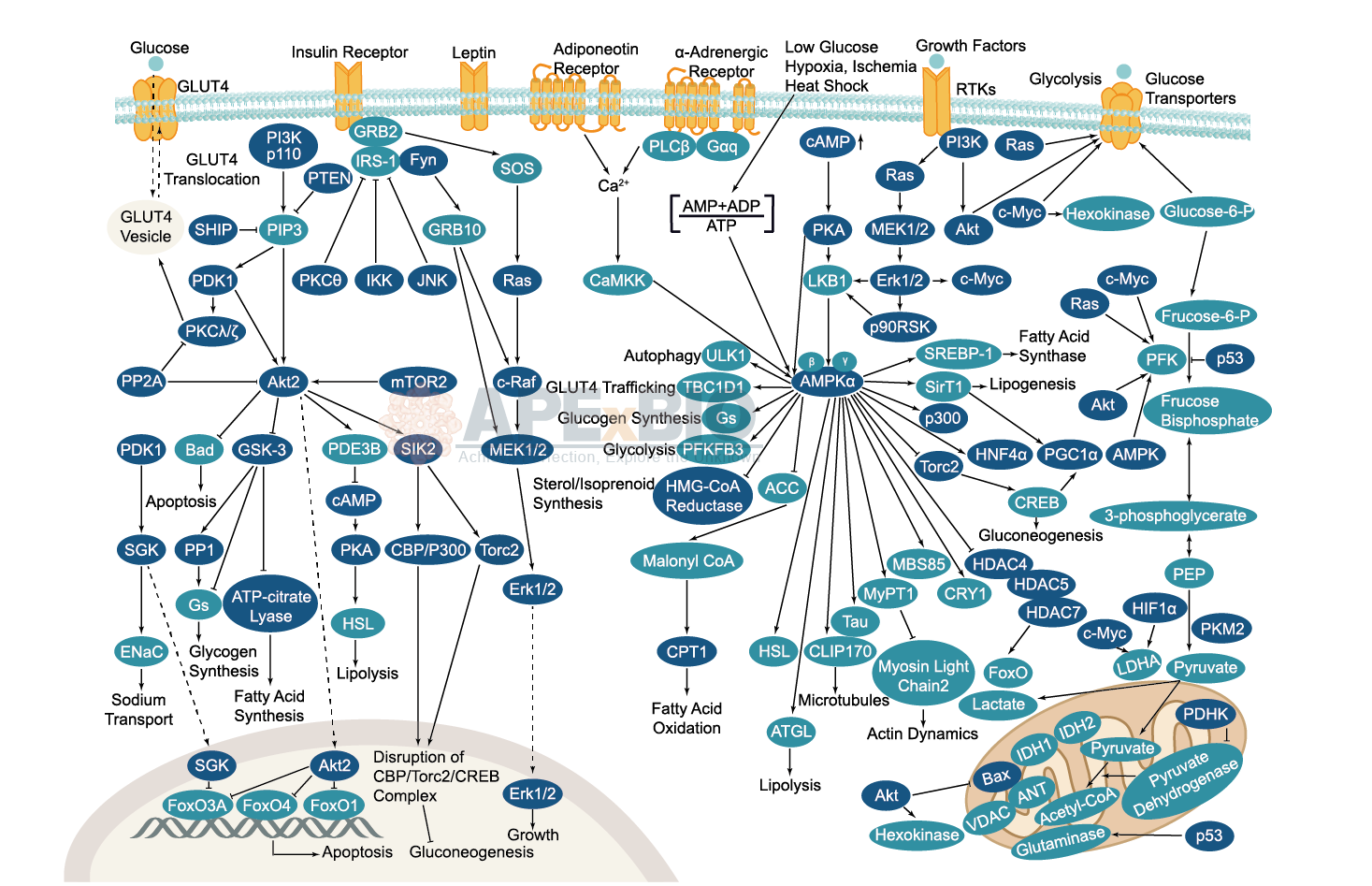

Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
 C5183 IbudilastSummary: inhibitor of PDE4
C5183 IbudilastSummary: inhibitor of PDE4 -
 C5221 galacto-DapagliflozinSummary: potent inhibitor of human SGLT2
C5221 galacto-DapagliflozinSummary: potent inhibitor of human SGLT2 -
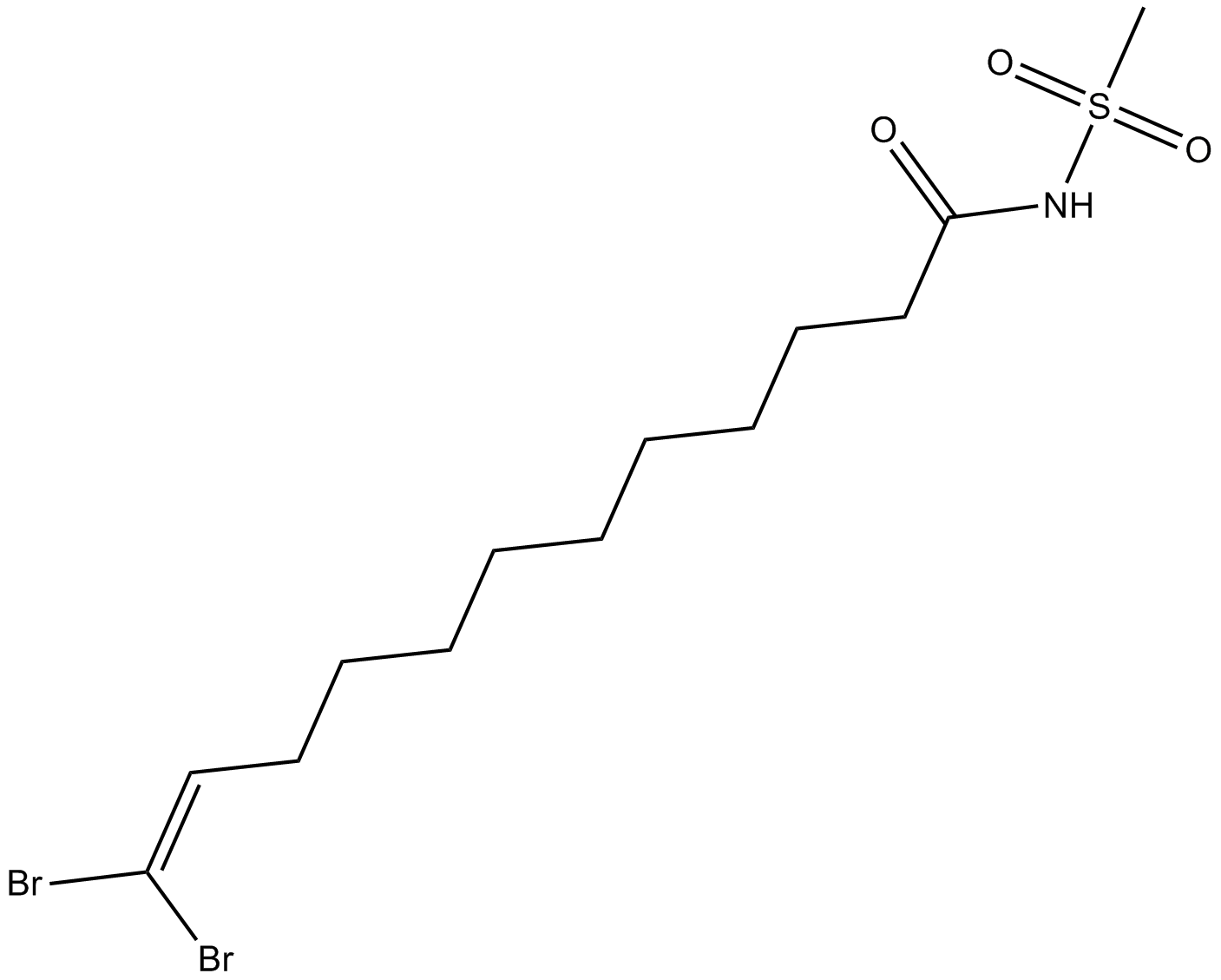 C5228 DDMSSummary: CYP4A2 enzyme inhibitor
C5228 DDMSSummary: CYP4A2 enzyme inhibitor -
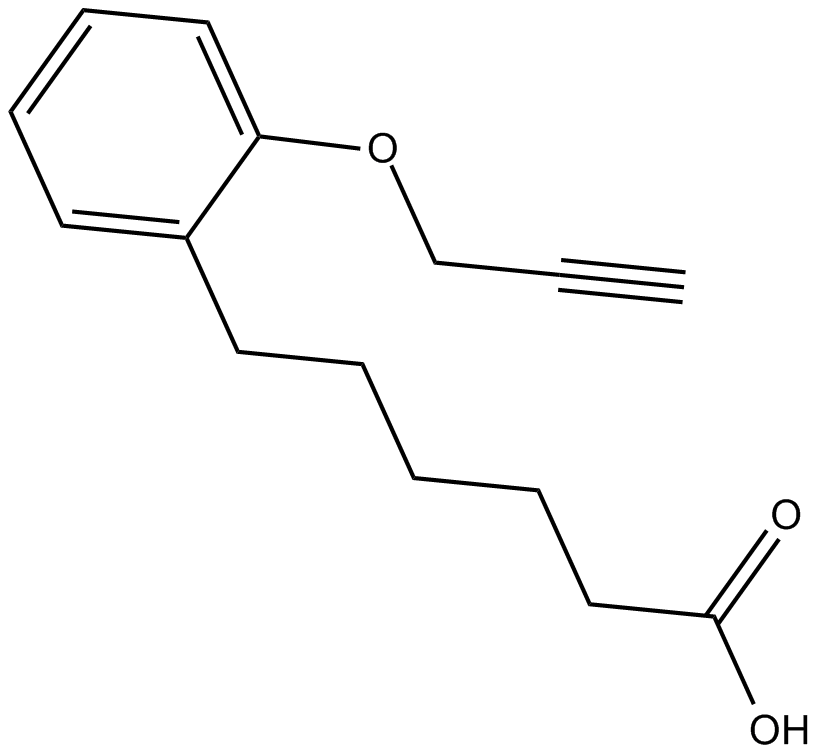 C5234 PPOHSummary: inhibitor of CYP epoxidase activity on arachadonic acid
C5234 PPOHSummary: inhibitor of CYP epoxidase activity on arachadonic acid -
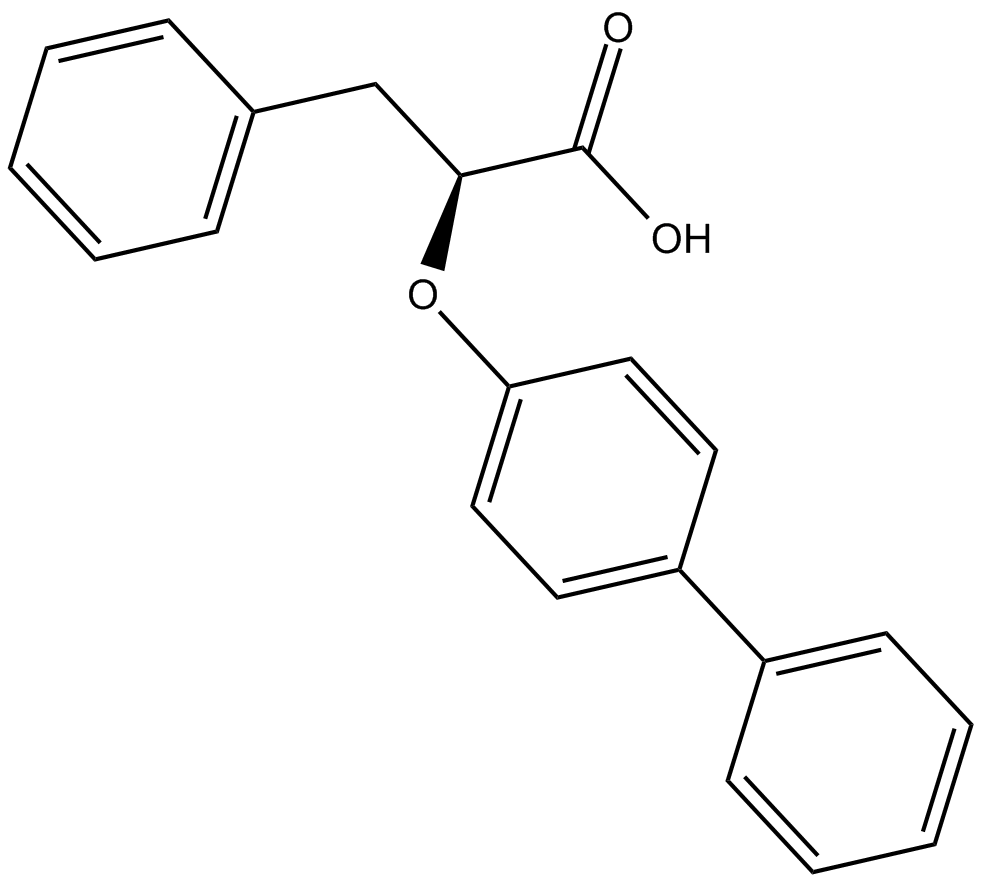 C5263 LT175Summary: dual PPARα/γ ligand
C5263 LT175Summary: dual PPARα/γ ligand -
 C5280 3-Thiatetradecanoic AcidSummary: activator of PPAR
C5280 3-Thiatetradecanoic AcidSummary: activator of PPAR -
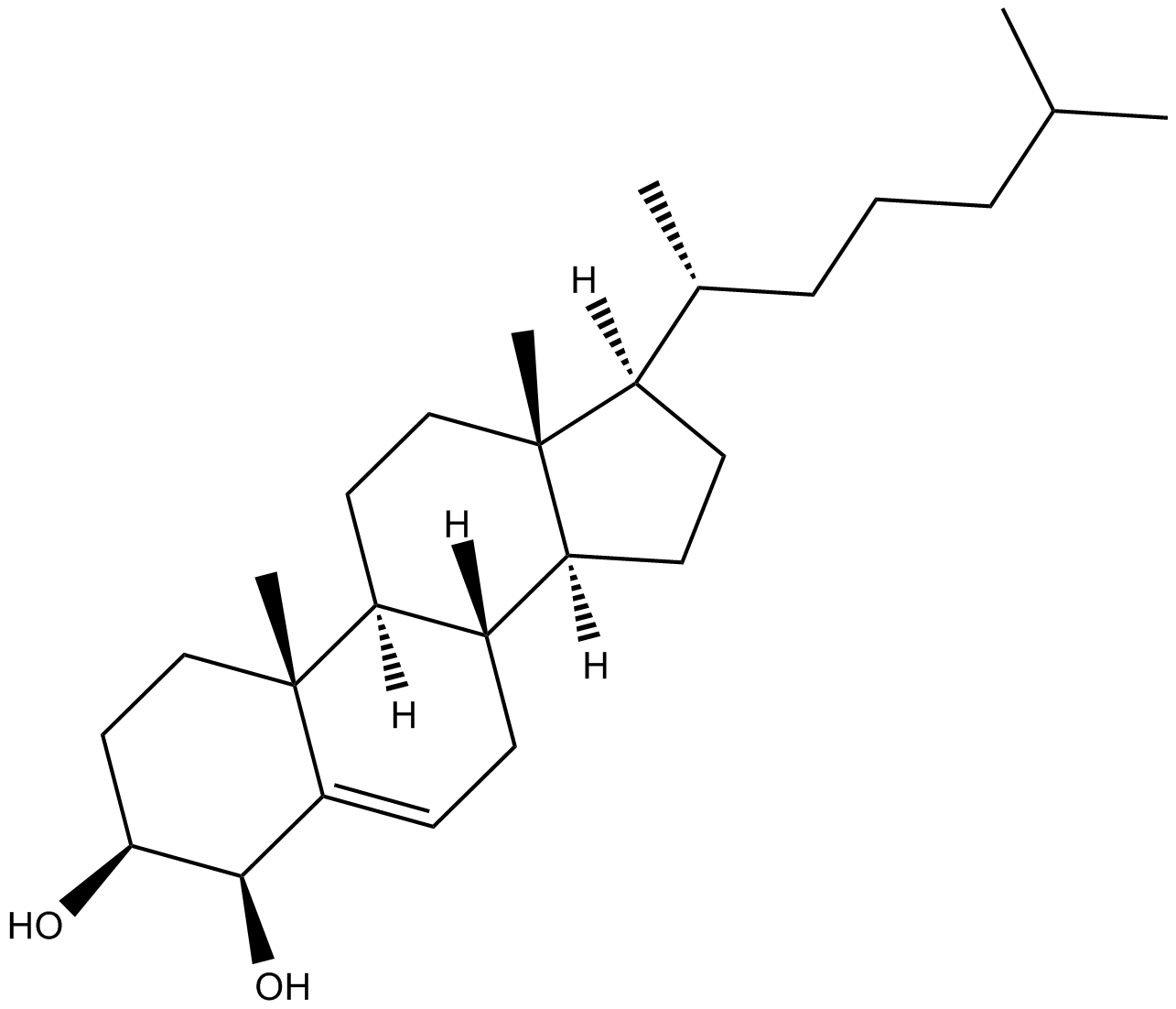 C5540 4β-hydroxy CholesterolSummary: marker for CYP3A4/5 activity
C5540 4β-hydroxy CholesterolSummary: marker for CYP3A4/5 activity -
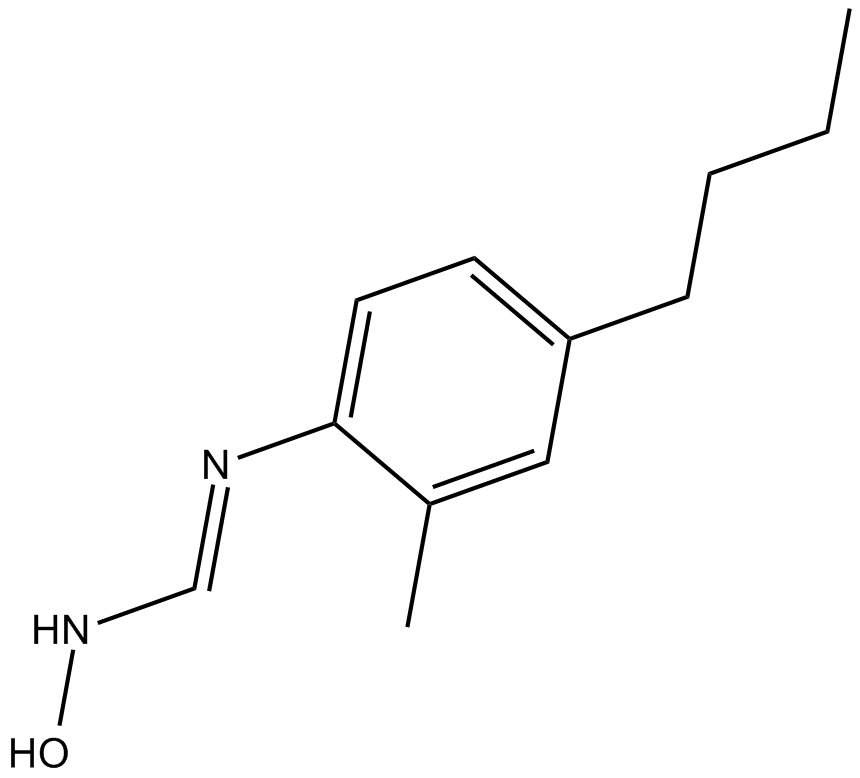 C5344 HET0016Summary: inhibitor of 20-HETE formation
C5344 HET0016Summary: inhibitor of 20-HETE formation -
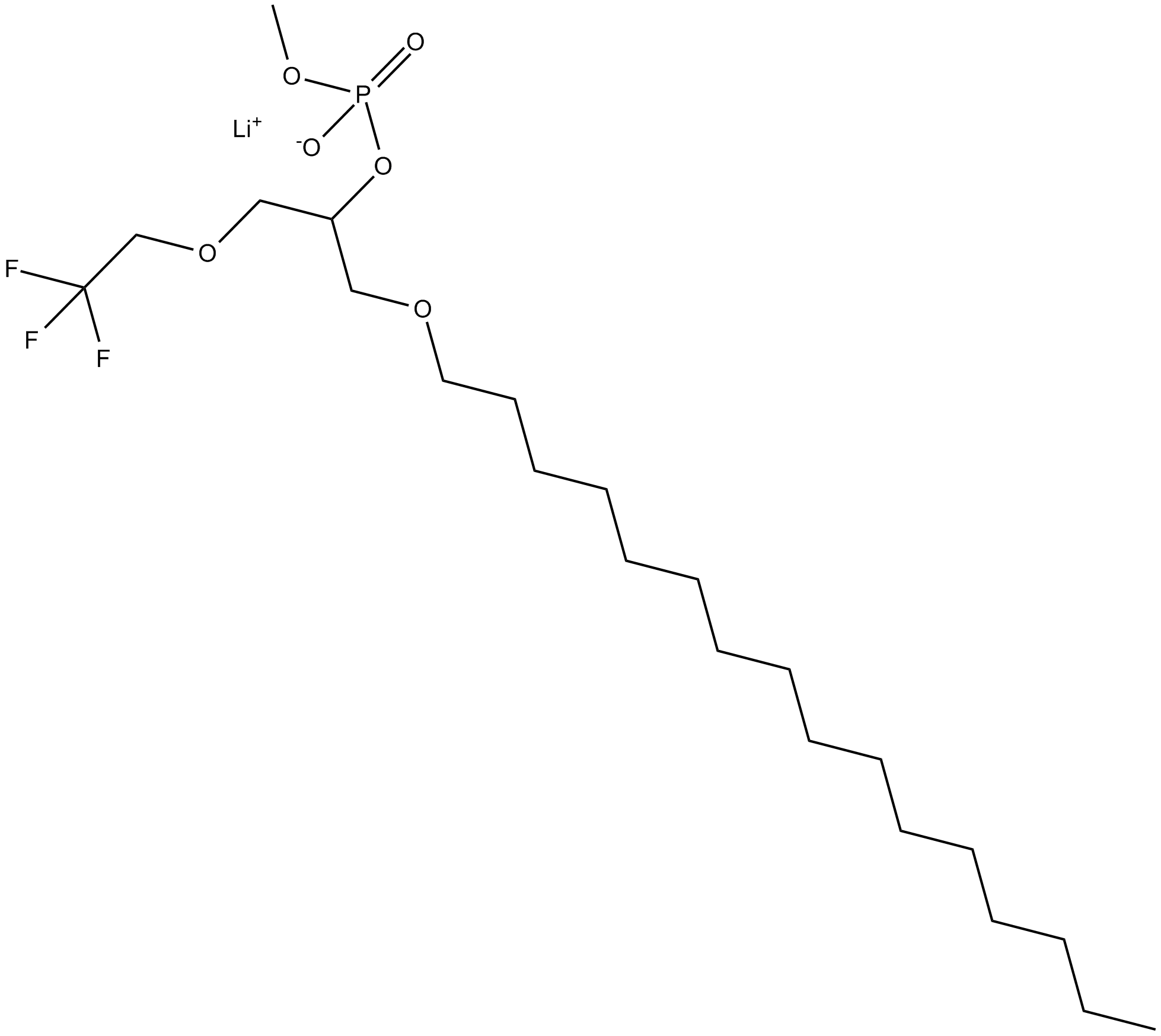 C5346 MJ33 (lithium salt)Summary: inhibitor of the acidic, calcium-independent (ai)PLA2 activity of Prdx6
C5346 MJ33 (lithium salt)Summary: inhibitor of the acidic, calcium-independent (ai)PLA2 activity of Prdx6 -
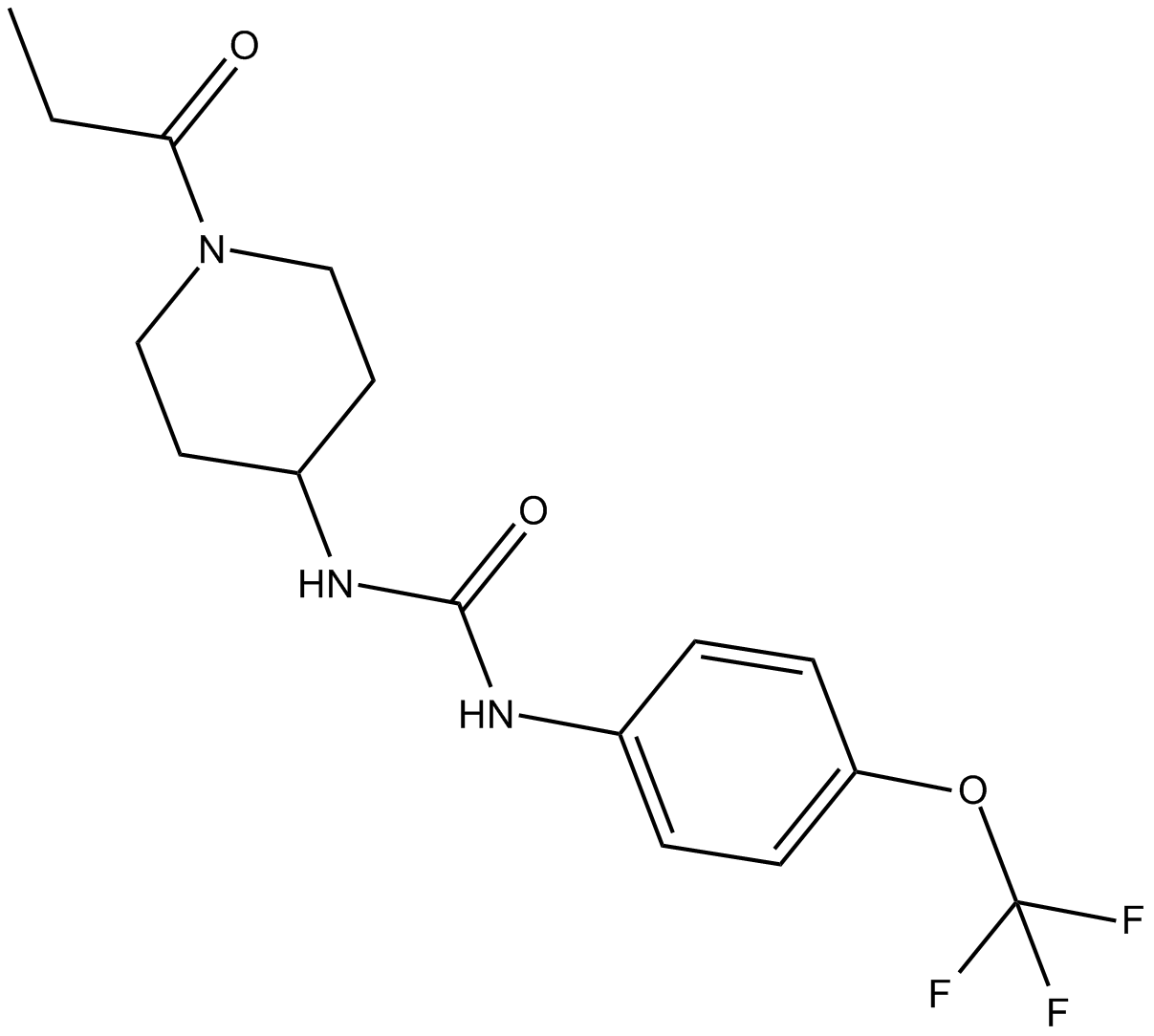 C5414 TPPU1 CitationTarget: epoxide hydrolaseSummary: potent inhibitor of both human and mouse sEH
C5414 TPPU1 CitationTarget: epoxide hydrolaseSummary: potent inhibitor of both human and mouse sEH


