JAK/STAT Signaling
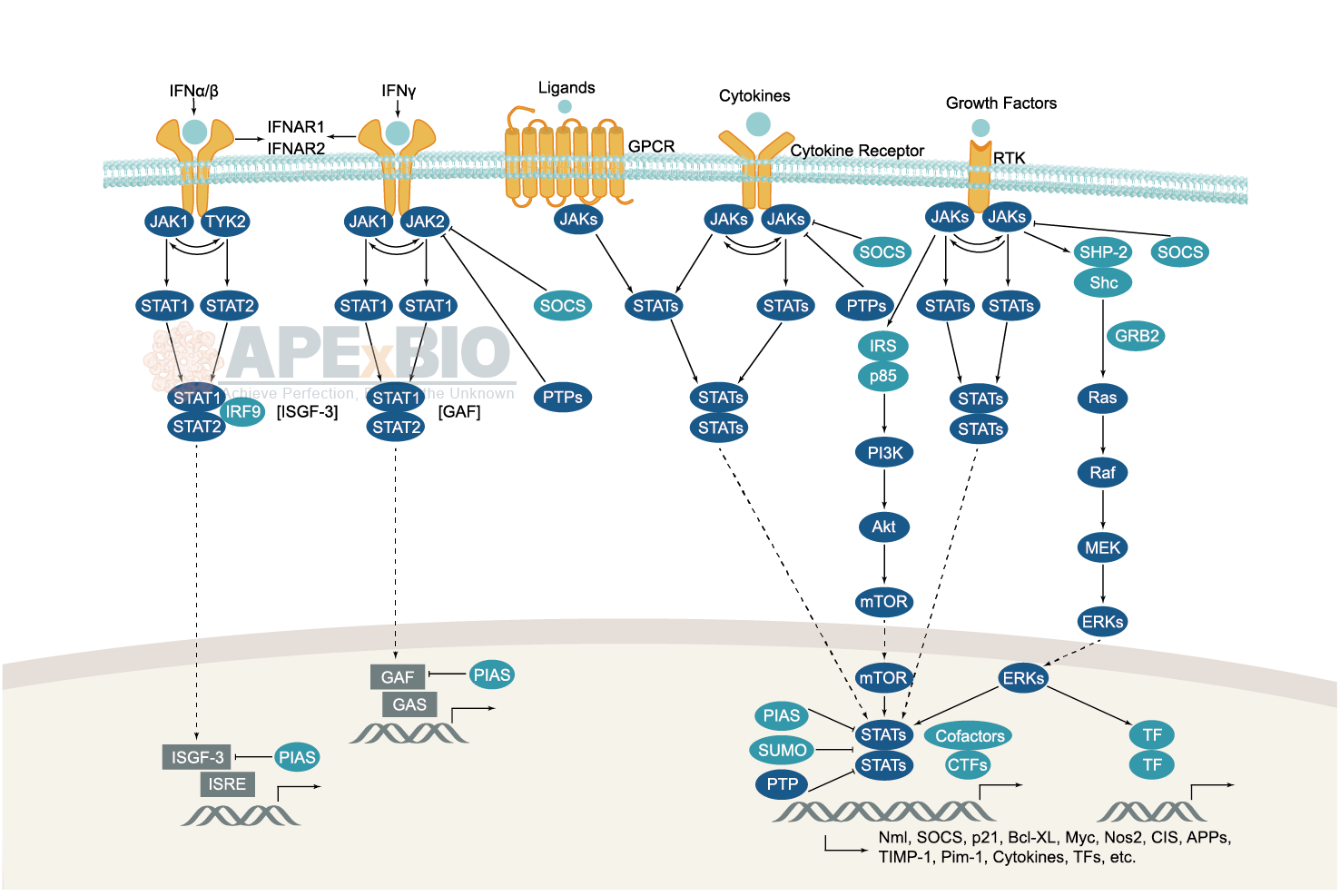

Various ligands including cytokines (e.g. interferons and interleukins), hormones (e.g. erythropoietin and growth hormone) and their cell surface receptors activate JAK proteins, which autophosphorylate, and then phosphorylate the receptor. Subsequently, JAKs phosphorylate a specific tyrosine residue on the STAT protein, promoting dimerization via SH2 domains. The activated STATs form homo-/heterodimers and translocate to the nucleus to trigger target gene transcription. In addition, suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family inhibit receptor signaling via homologous or heterologous feedback regulation. Dysregulation in JAK/STAT signaling is associated with diseases such as atherosclerosis, immunodeficiencies and cancer.
-
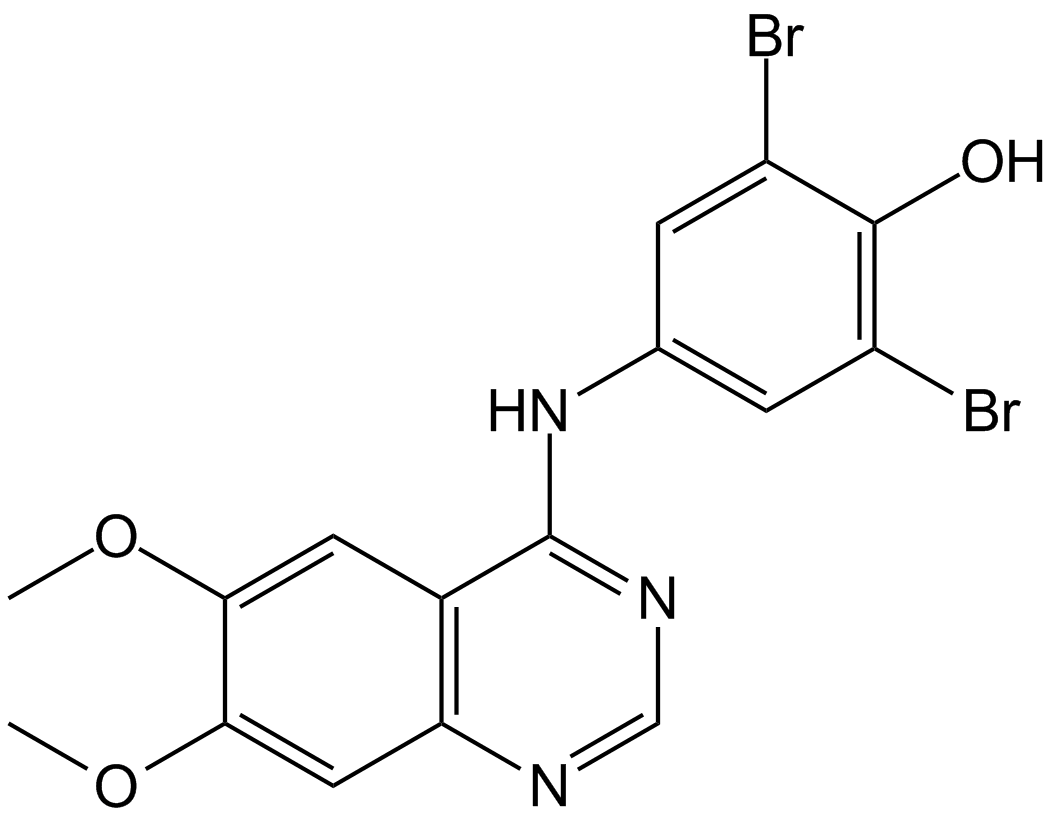 A3936 WHI-P97Summary: Janus kinase (JAK)-3 inhibitor
A3936 WHI-P97Summary: Janus kinase (JAK)-3 inhibitor -
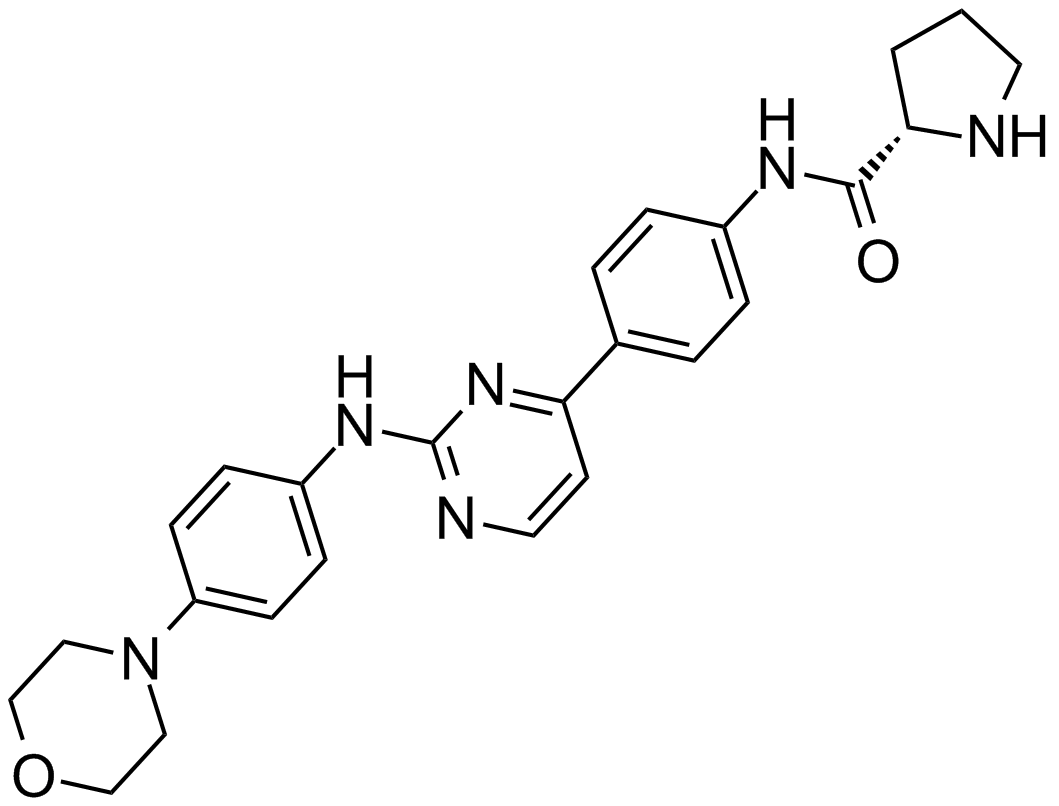 A3937 XL019Target: JAKSummary: JAK2 inhibitor,potent and selective
A3937 XL019Target: JAKSummary: JAK2 inhibitor,potent and selective -
 BA2725 C188-9Summary: C188-9 (TTI-101) is an inhibitor.
BA2725 C188-9Summary: C188-9 (TTI-101) is an inhibitor. -
 BA2752 AC-4-130Summary: AC-4-130 is a potent structural domain inhibitor.
BA2752 AC-4-130Summary: AC-4-130 is a potent structural domain inhibitor. -
 BA2753 SD-36Summary: SD-36 is an effective degradant (=~50nM) with high selectivity compared to other members.
BA2753 SD-36Summary: SD-36 is an effective degradant (=~50nM) with high selectivity compared to other members. -
 BA2797 STAT3-IN-1Summary: STAT3-IN-1 is a potent, selective, and orally effective inhibitor with values of 1.82 μM and 2.14 μM in HT29 and MDA-MB231 cells, respectively.
BA2797 STAT3-IN-1Summary: STAT3-IN-1 is a potent, selective, and orally effective inhibitor with values of 1.82 μM and 2.14 μM in HT29 and MDA-MB231 cells, respectively. -
 BA2806 SC-43Summary: SC-43, a derivative of Sorafenib, is a potent agonist with oral activity.
BA2806 SC-43Summary: SC-43, a derivative of Sorafenib, is a potent agonist with oral activity. -
 BA2881 AG-825Summary: AG-825 is a selective, ATP-competitive, inhibitor of tyrosine phosphorylation.
BA2881 AG-825Summary: AG-825 is a selective, ATP-competitive, inhibitor of tyrosine phosphorylation. -
 BA2996 UC-514321Summary: A selective TET1 inhibitor
BA2996 UC-514321Summary: A selective TET1 inhibitor -
 BA4122 GivinostatSummary: Inhibitors.
BA4122 GivinostatSummary: Inhibitors.


