JAK/STAT Signaling
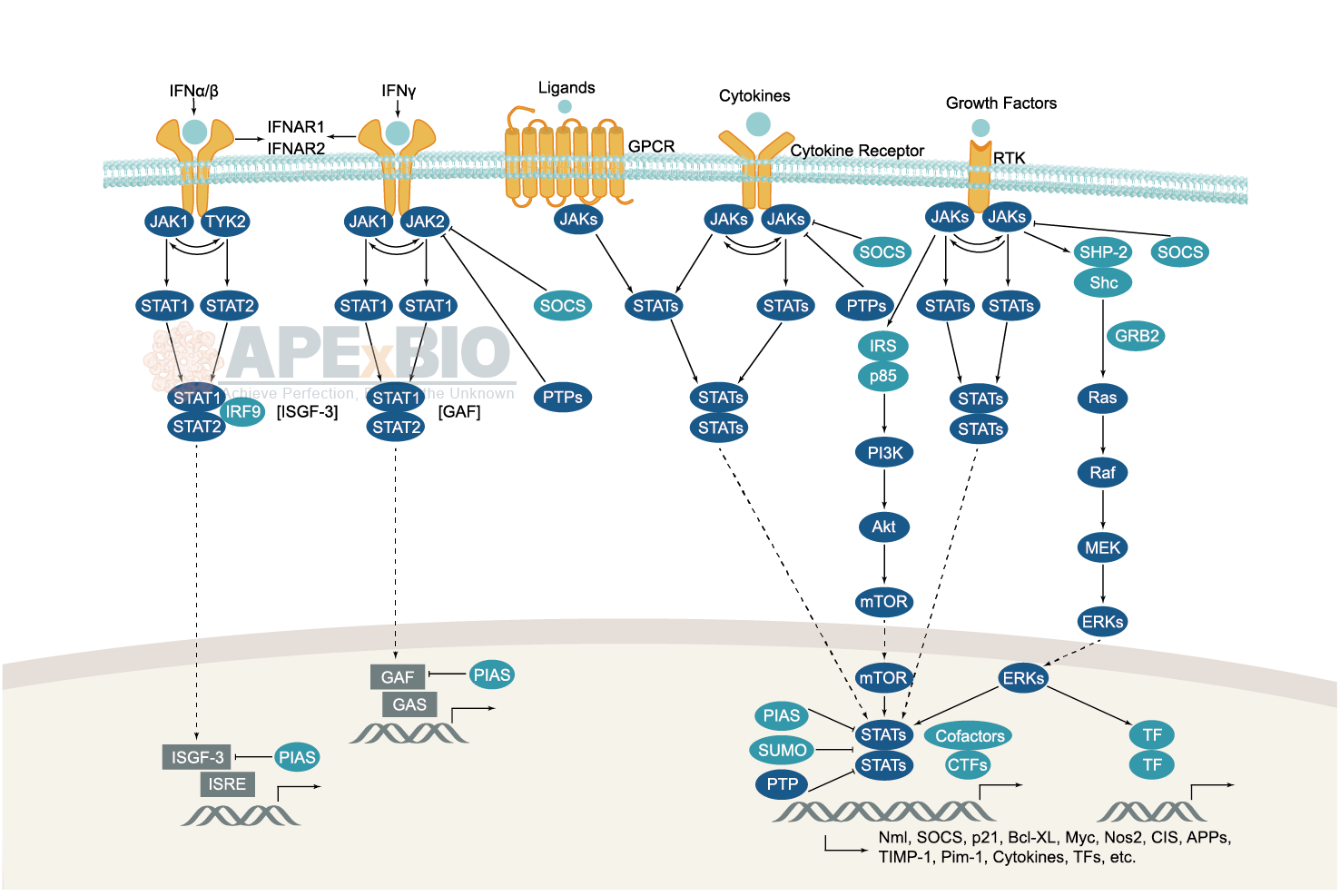

Various ligands including cytokines (e.g. interferons and interleukins), hormones (e.g. erythropoietin and growth hormone) and their cell surface receptors activate JAK proteins, which autophosphorylate, and then phosphorylate the receptor. Subsequently, JAKs phosphorylate a specific tyrosine residue on the STAT protein, promoting dimerization via SH2 domains. The activated STATs form homo-/heterodimers and translocate to the nucleus to trigger target gene transcription. In addition, suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family inhibit receptor signaling via homologous or heterologous feedback regulation. Dysregulation in JAK/STAT signaling is associated with diseases such as atherosclerosis, immunodeficiencies and cancer.
-
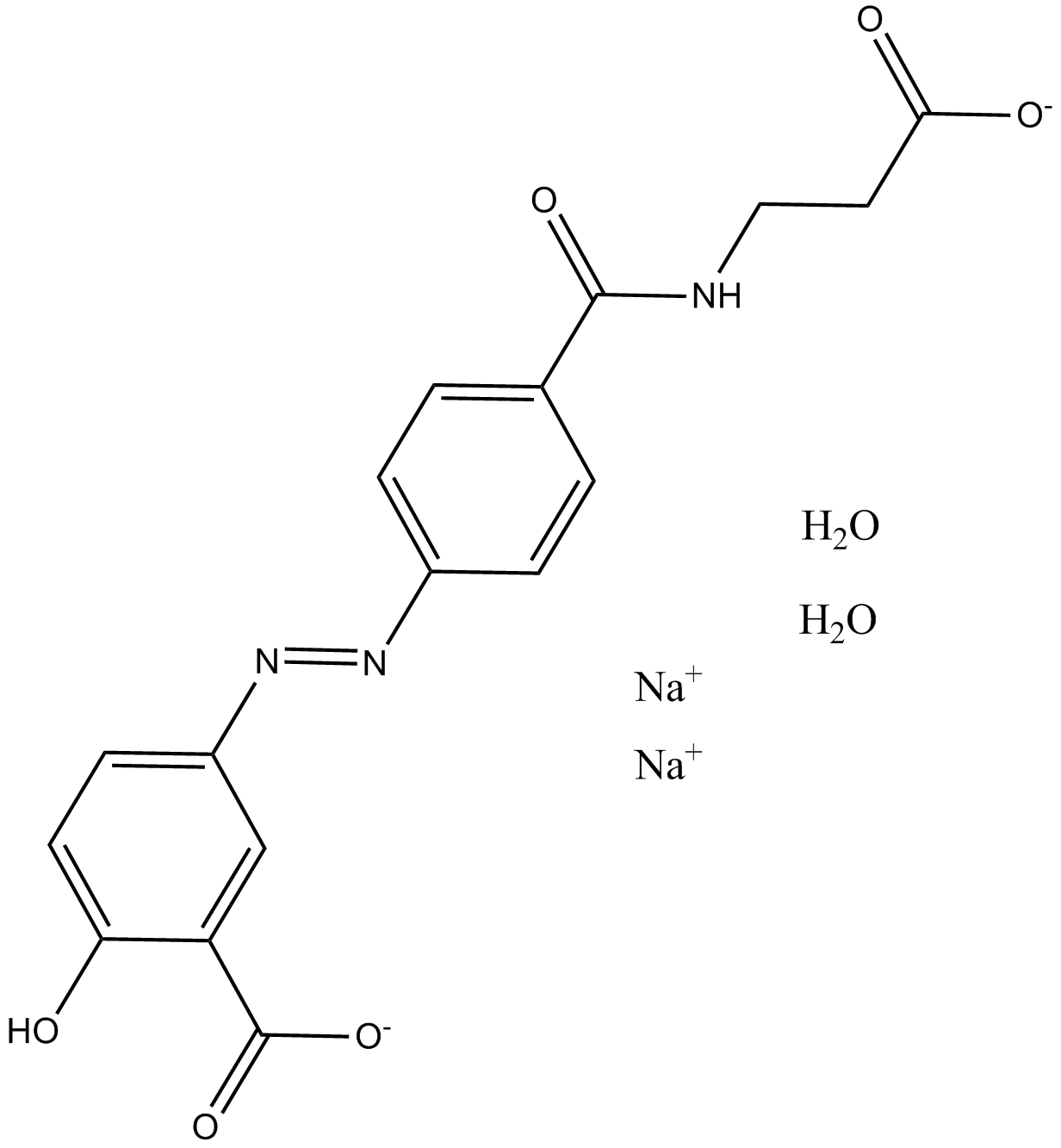 C6459 Balsalazide disodium dihydrateSummary: A prodrug of aminosalicylic acid that exerts local anti-inflammatory effects in the colon
C6459 Balsalazide disodium dihydrateSummary: A prodrug of aminosalicylic acid that exerts local anti-inflammatory effects in the colon -
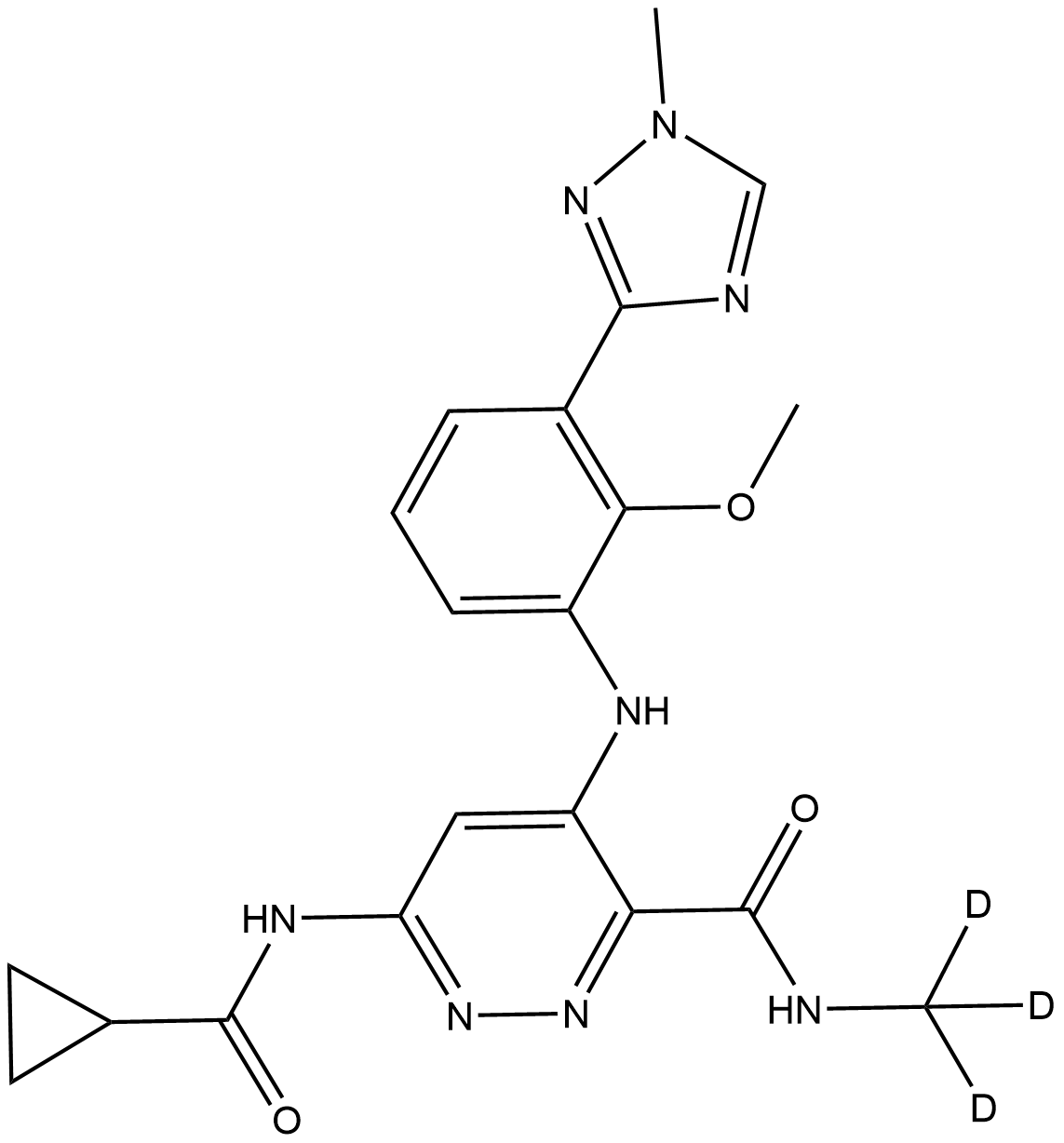 B8781 Deucravacitinib
B8781 Deucravacitinib -
 B8790 Trastuzumab
B8790 Trastuzumab -
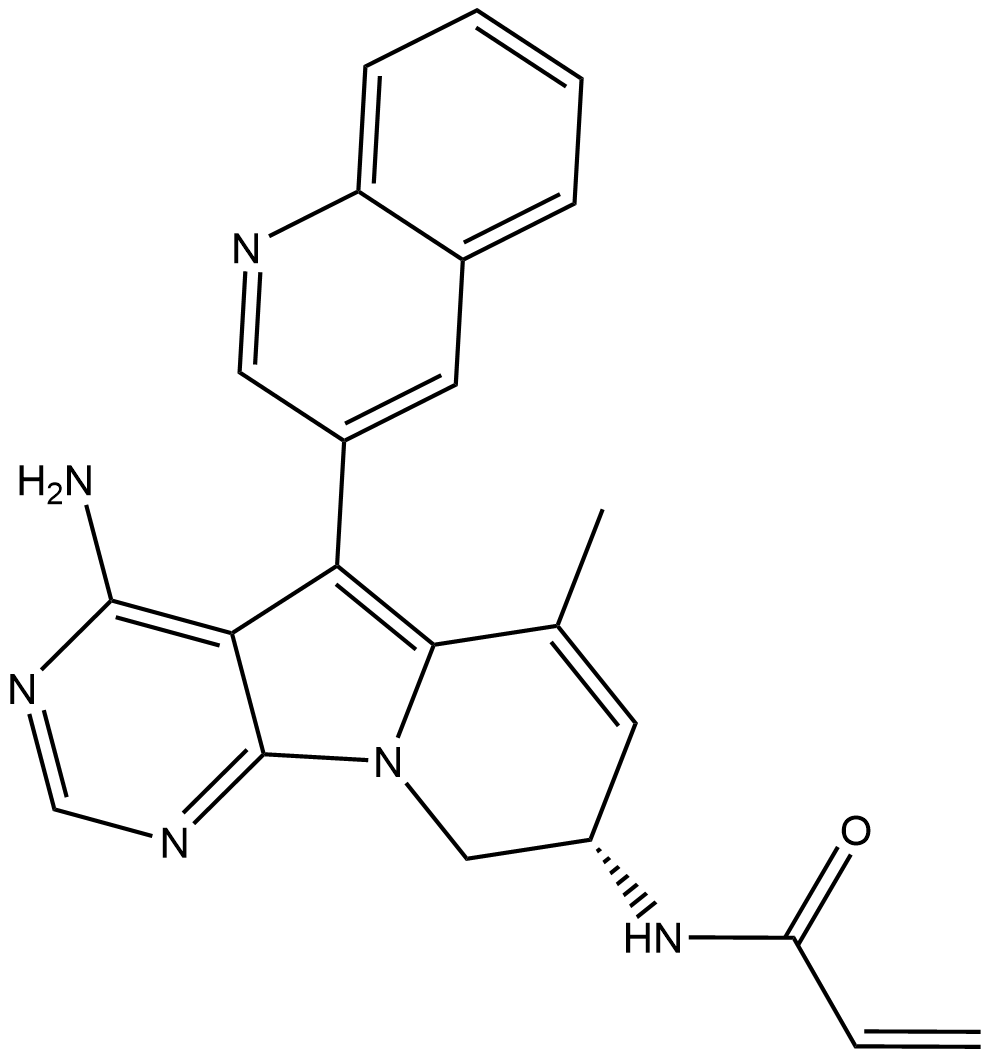 A4683 Zipalertinib
A4683 Zipalertinib -
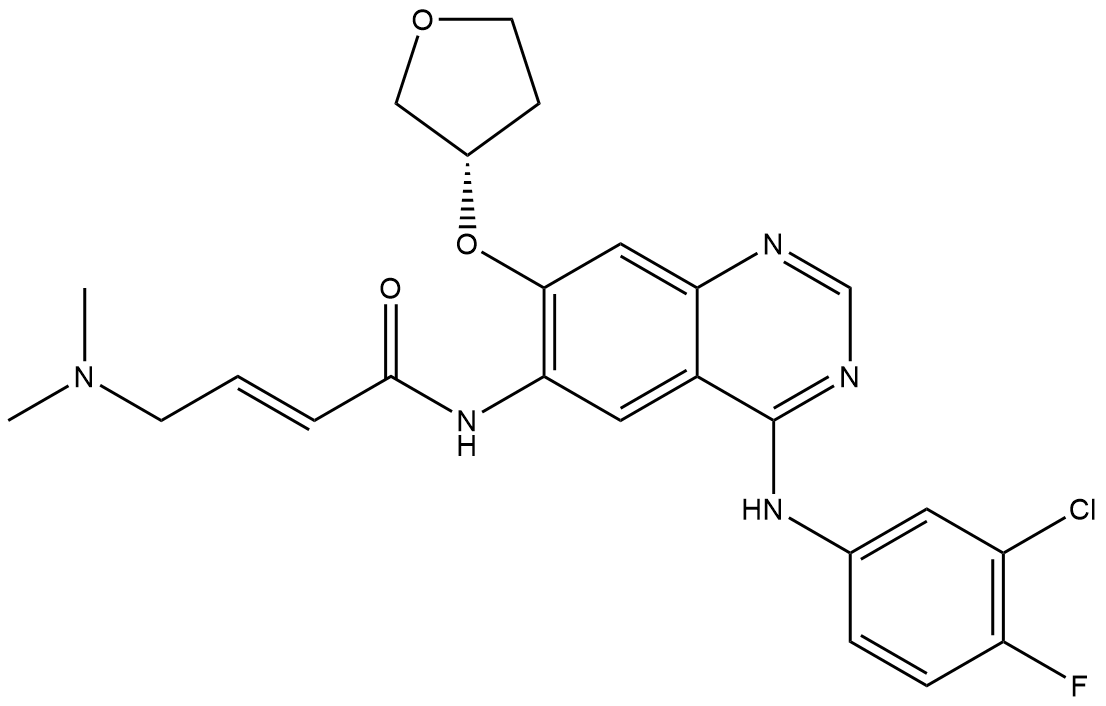 A4746 Afatinib2 CitationSummary: A covalent inhibitor targeting members of the ErbB family
A4746 Afatinib2 CitationSummary: A covalent inhibitor targeting members of the ErbB family -
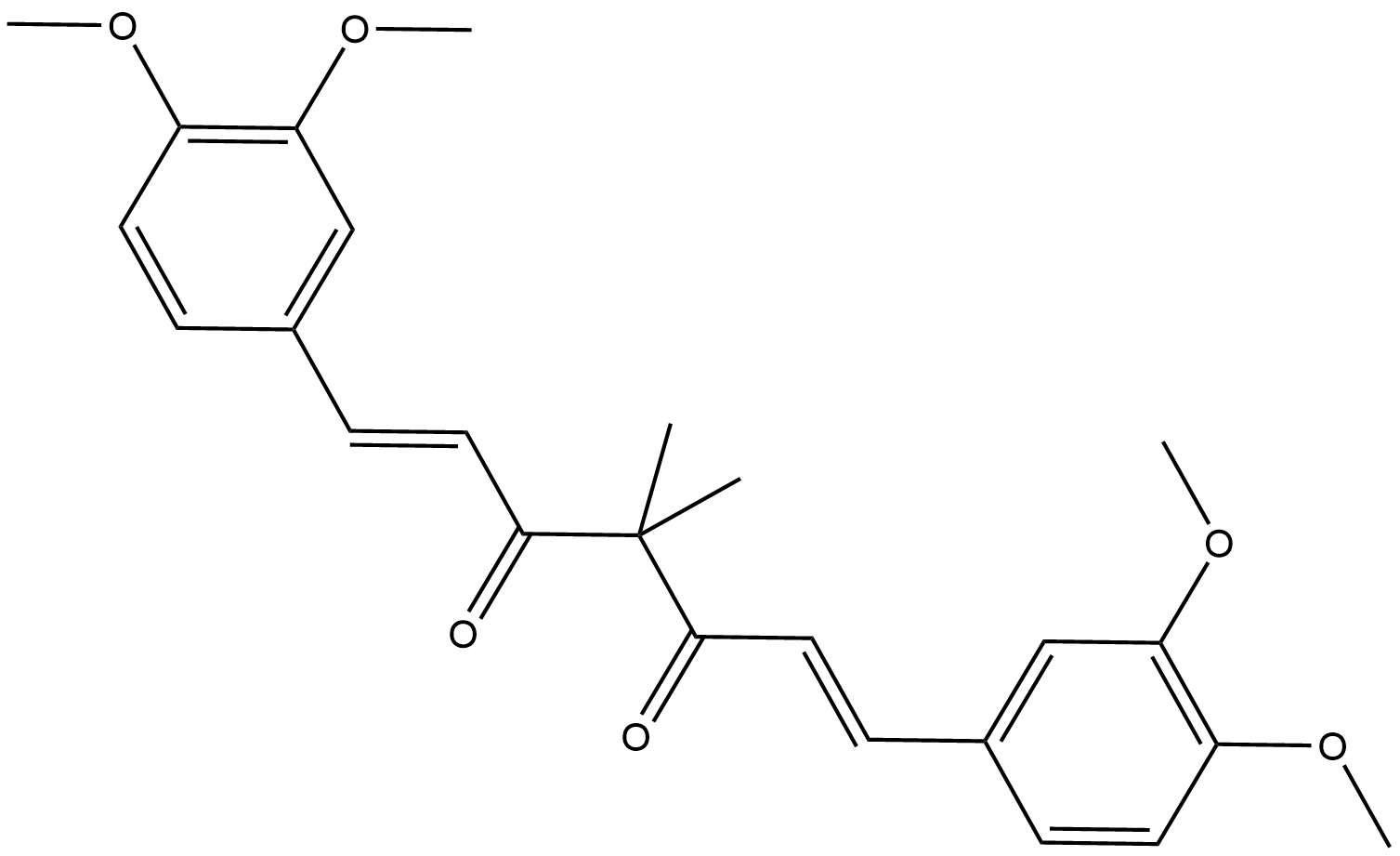 A4768 Tetramethylcurcumin
A4768 Tetramethylcurcumin -
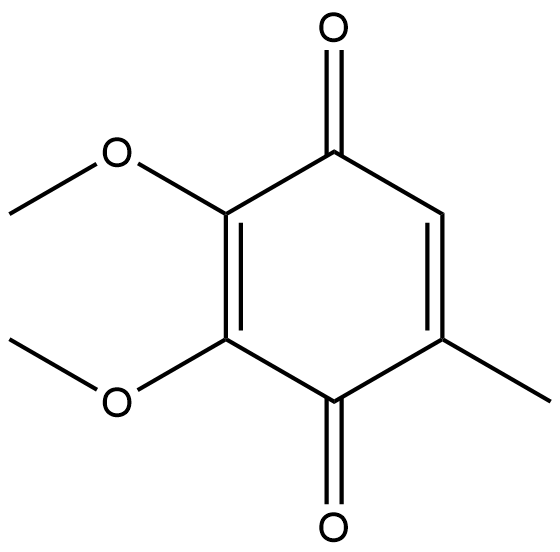 A4783 Coenzyme Q0
A4783 Coenzyme Q0 -
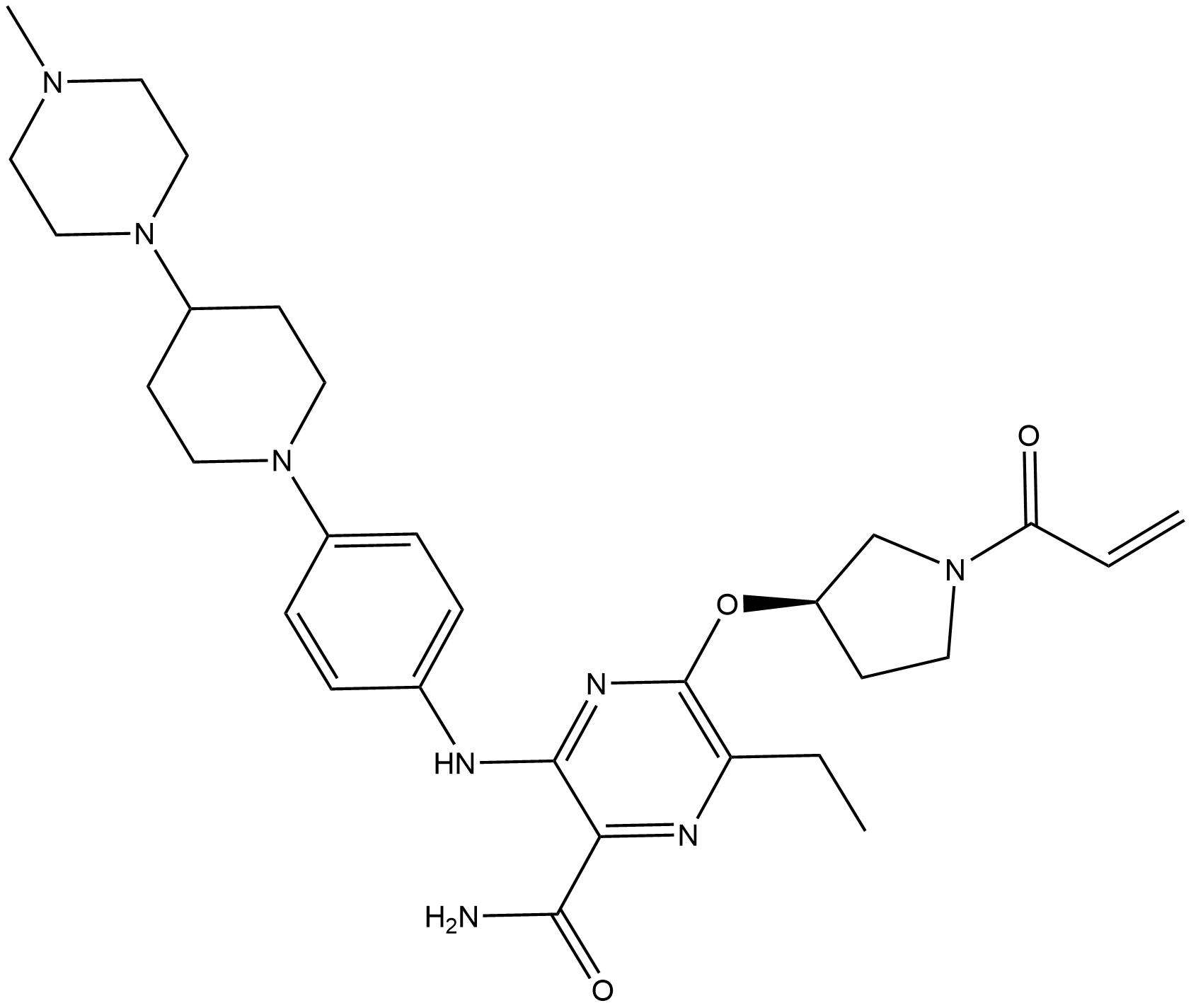 A8969 Naquotinib
A8969 Naquotinib -
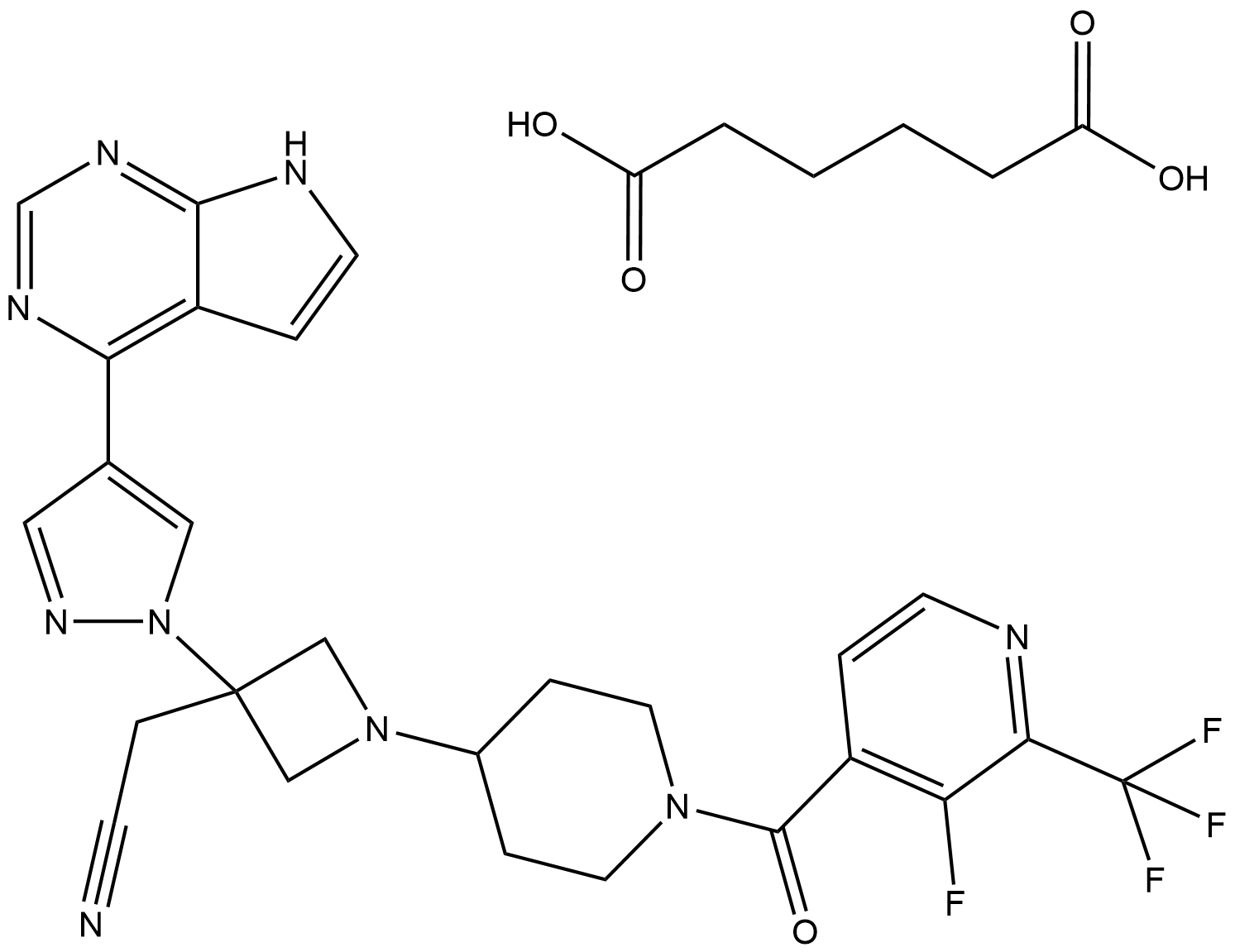 A8970 Itacitinib adipate
A8970 Itacitinib adipate -
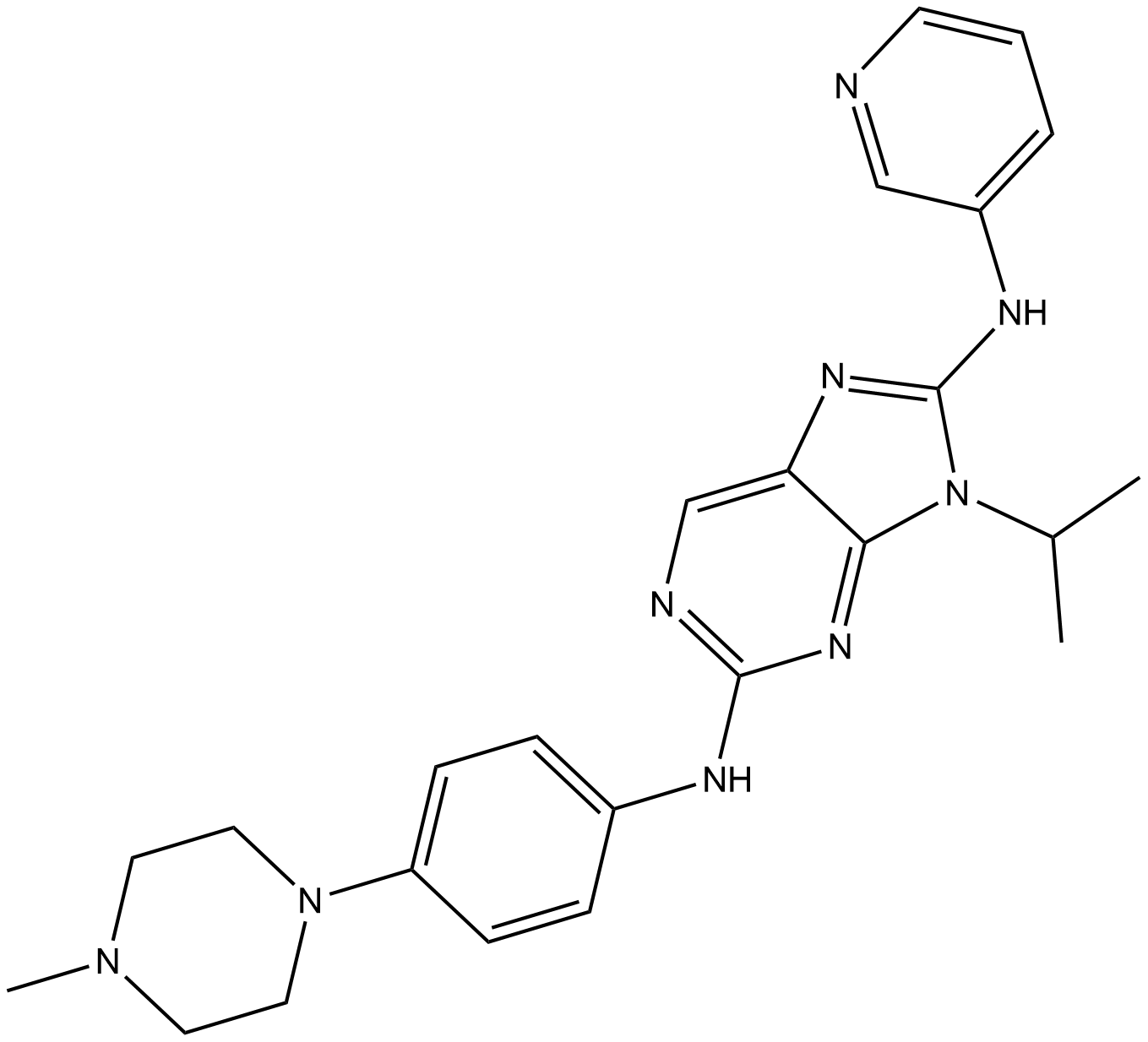 A8971 Ruserontinib
A8971 Ruserontinib


