Disease induced

Disease-induced compounds are chemical agents used to simulate specific pathological conditions in experimental systems, such as cell cultures, organoids, or animal models.
Disease-induced compounds play a pivotal role in translational biomedical research, allowing researchers to reproduce key features of human diseases under controlled conditions, enabling the study of disease mechanisms and the testing of therapeutic interventions. For example, neurotoxins such as MPTP are widely used to model Parkinson’s disease by selectively damaging dopaminergic neurons, while streptozotocin and alloxan are used to induce diabetes through pancreatic β-cell destruction. Similarly, agents like carbon tetrachloride, bleomycin, and lipopolysaccharide are utilized to reproduce hepatic injury, pulmonary fibrosis, and systemic inflammation, respectively.
Through the application of disease-induced compounds, researchers can bridge the gap between basic molecular research and translational medicine. Their use facilitates the elucidation of disease mechanisms and supports the rational design and preclinical testing of novel therapeutic agents.
-
 BA3529 OxazoloneSummary: Oxazolone is a semi-antagonist that induces acute or chronic colorectal inflammation and is used to construct models of colitis.
BA3529 OxazoloneSummary: Oxazolone is a semi-antagonist that induces acute or chronic colorectal inflammation and is used to construct models of colitis. -
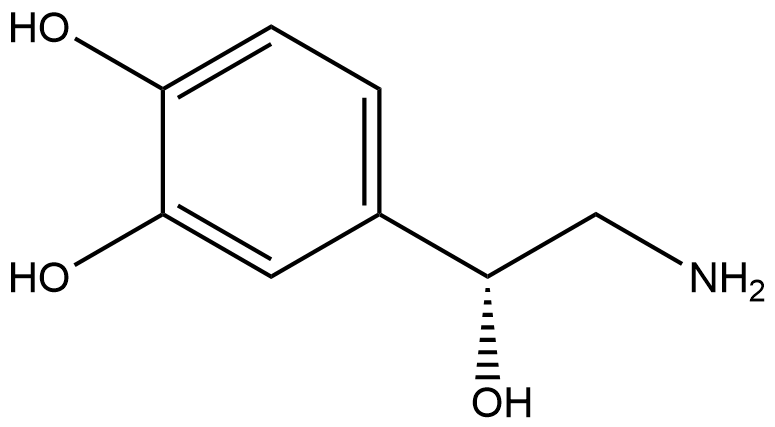 BA3580 NorepinephrineSummary: A potent adrenergic receptor agonist.
BA3580 NorepinephrineSummary: A potent adrenergic receptor agonist. -
 BA3917 N-Nitroso-N-methylureaSummary: N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU; MNU; NMH) is a potent carcinogen, mutagen and teratogen.
BA3917 N-Nitroso-N-methylureaSummary: N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU; MNU; NMH) is a potent carcinogen, mutagen and teratogen. -
 BA5891 BR103Summary: BR103 is a C3aR-specific small molecule ligand.
BA5891 BR103Summary: BR103 is a C3aR-specific small molecule ligand. -
 BA5985 CortodoxoneSummary: Cortodoxone (11-Deoxycortisol; cortexolone) is a glucocorticoid steroid hormone and a glucocorticoid antagonist.
BA5985 CortodoxoneSummary: Cortodoxone (11-Deoxycortisol; cortexolone) is a glucocorticoid steroid hormone and a glucocorticoid antagonist. -
 BA5766 ARS-1620Summary: ARS-1620 is a blocking allosteric and selective inhibitor.
BA5766 ARS-1620Summary: ARS-1620 is a blocking allosteric and selective inhibitor. -
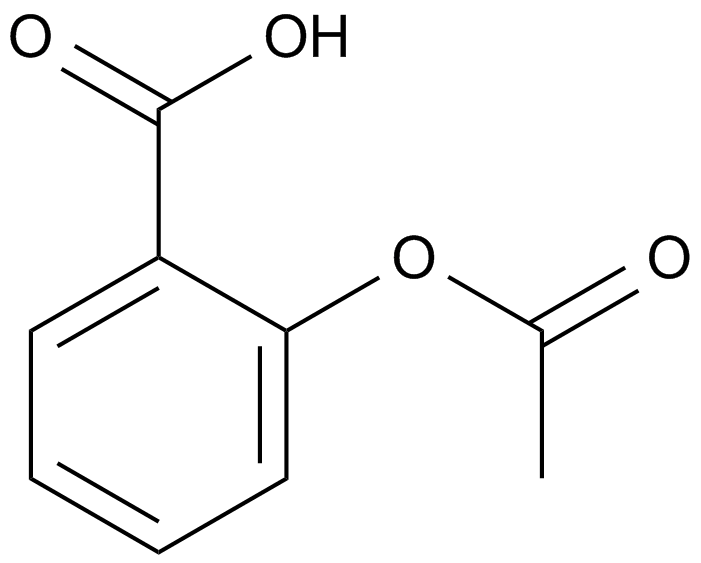 A4013 Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)Summary: Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor
A4013 Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)Summary: Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor -
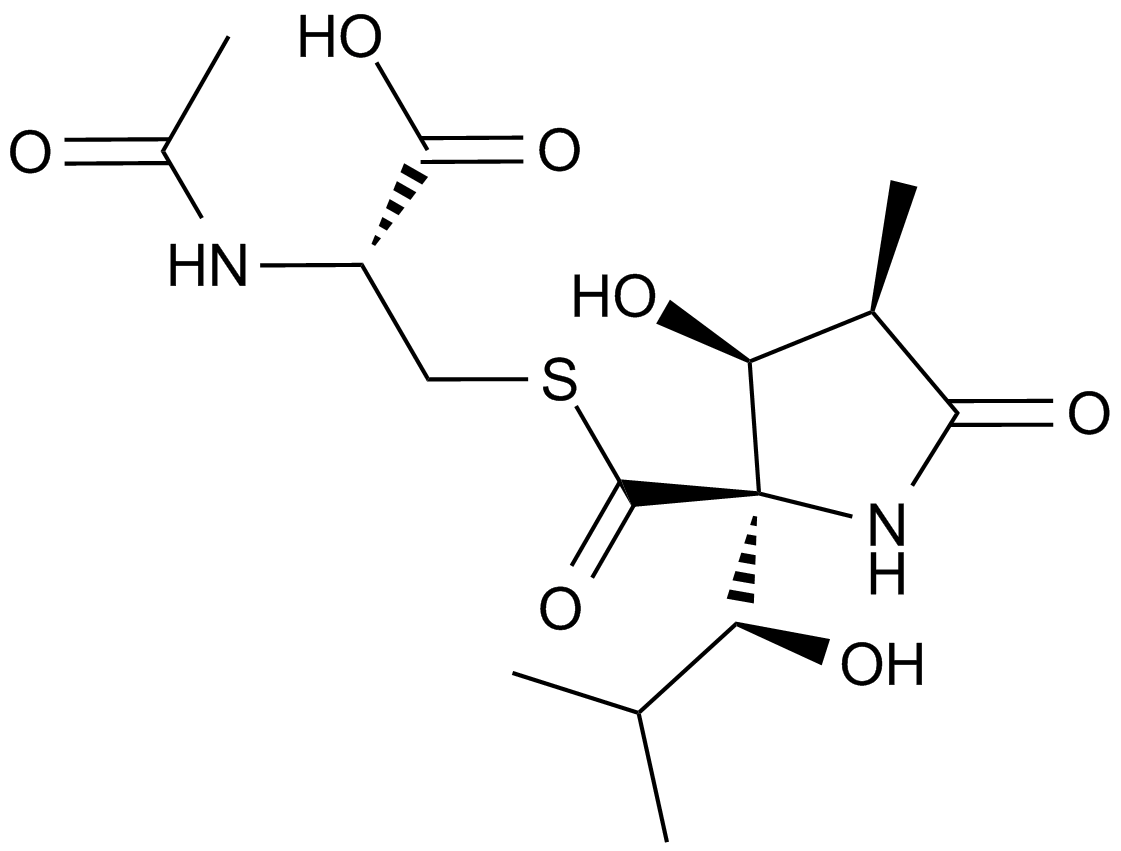 A2583 Lactacystin (Synthetic)1 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor
A2583 Lactacystin (Synthetic)1 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor -
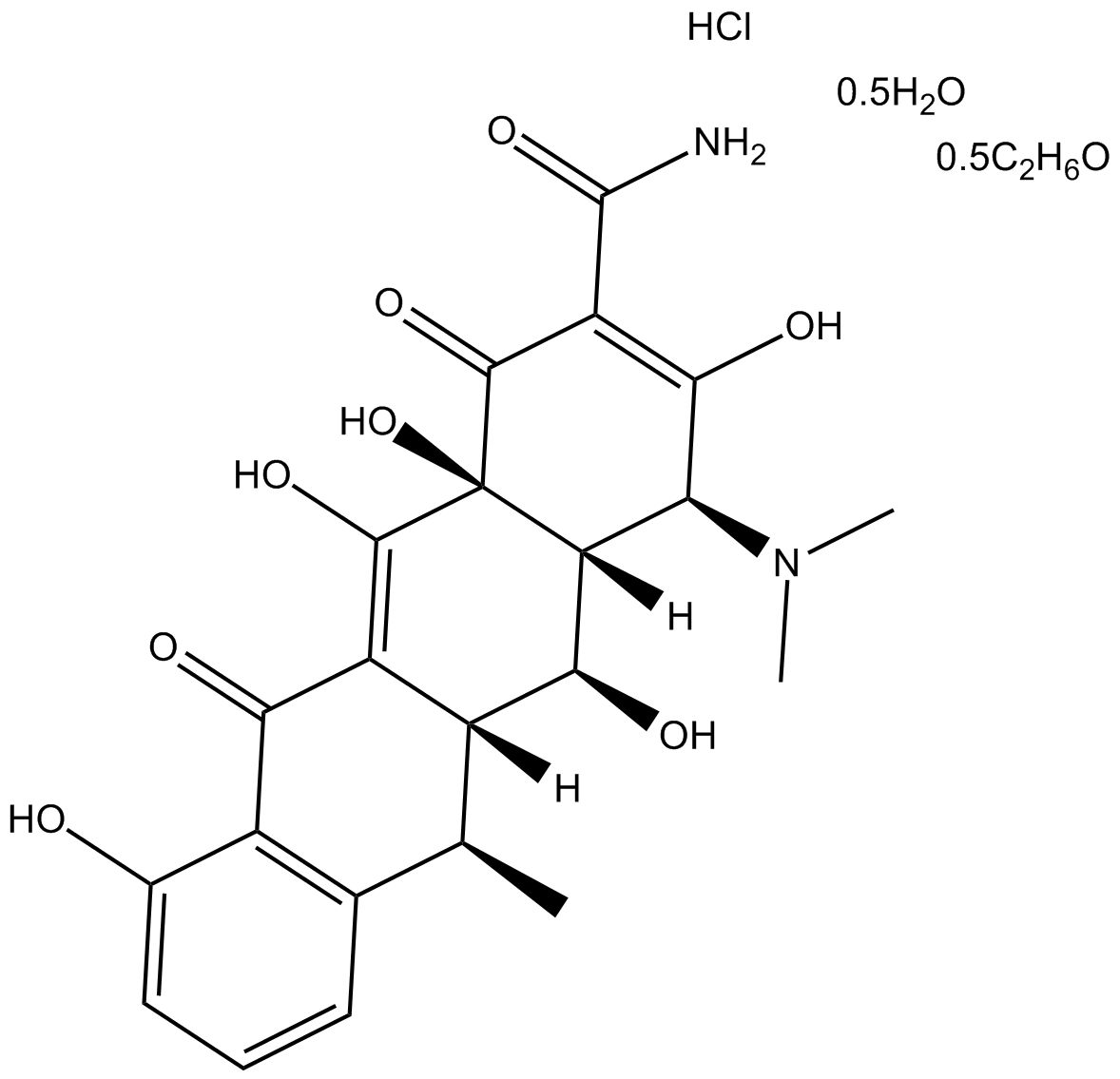 A4052 Doxycycline hyclateTarget: MMPSummary: matrix metalloproteinases inhibitor
A4052 Doxycycline hyclateTarget: MMPSummary: matrix metalloproteinases inhibitor -
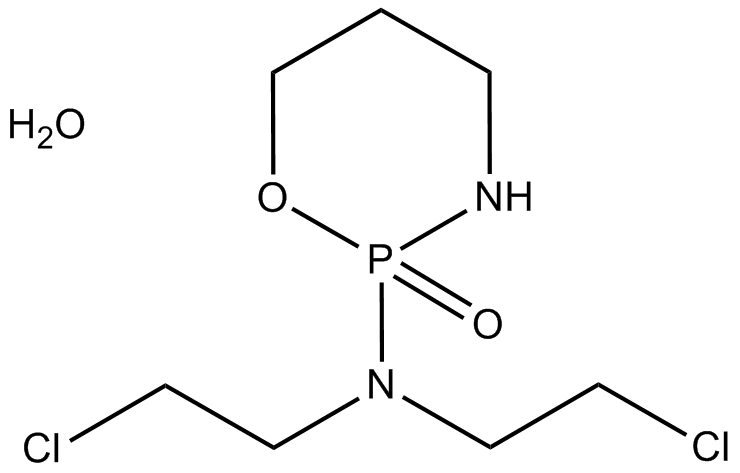 A4232 Cyclophosphamide monohydrateSummary: alkylating, cytotoxic agent,antitumor activity
A4232 Cyclophosphamide monohydrateSummary: alkylating, cytotoxic agent,antitumor activity


