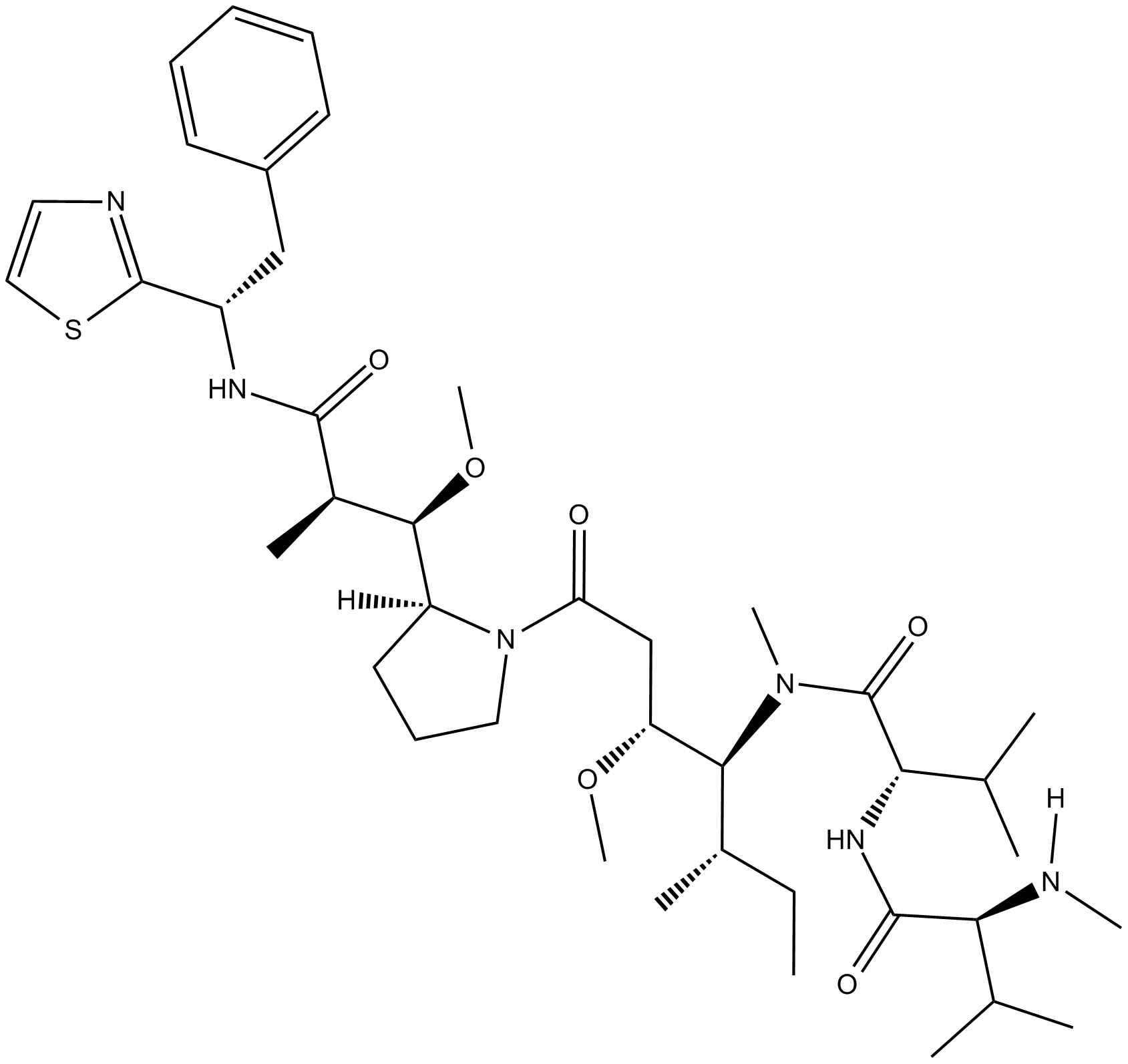
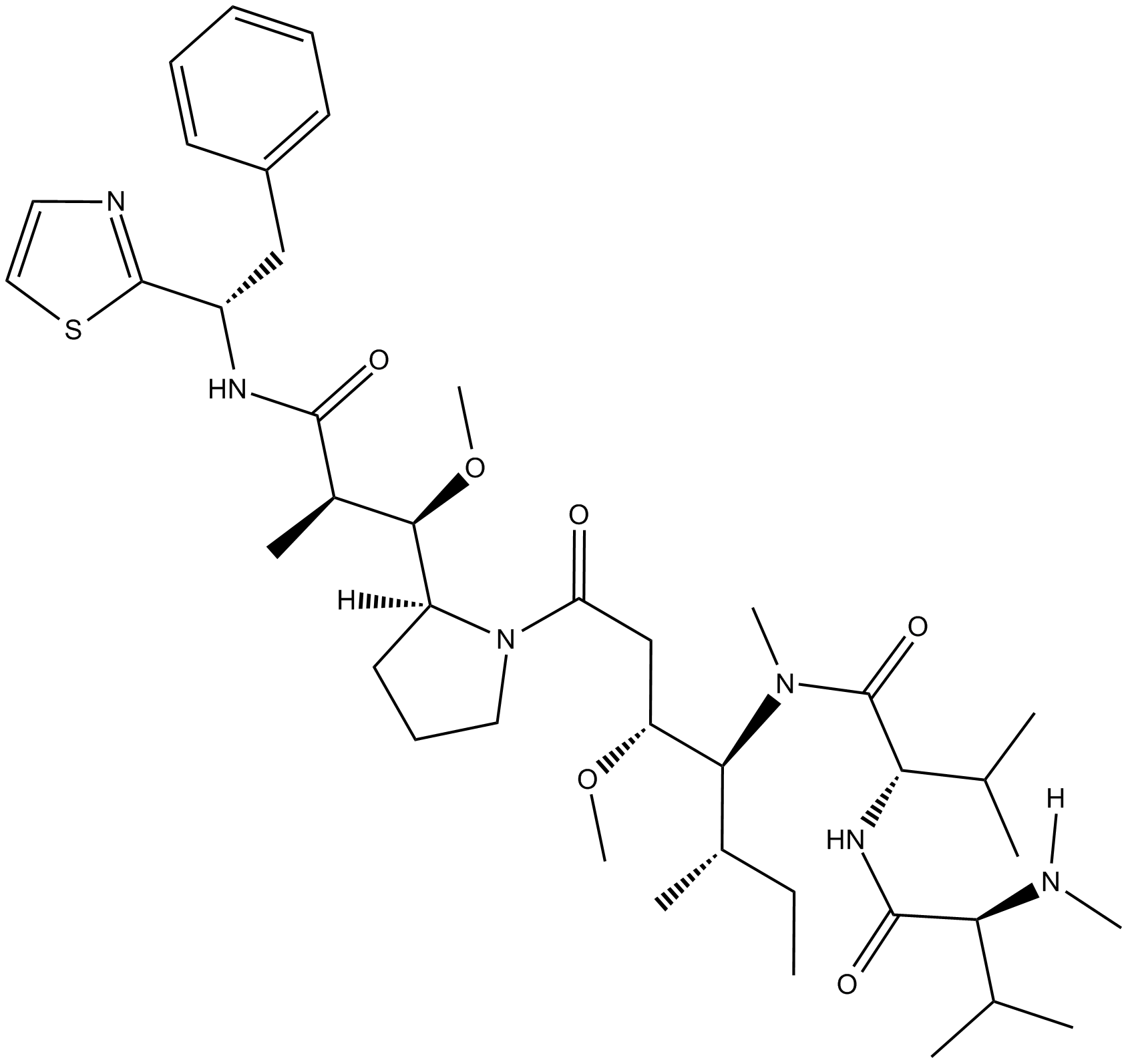
MMAD
MMAD is a highly potent inhibitor of tubulin [1].
MMAD is one of the auristatins, which are used as the drugs of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs). In ADCs, the therapeutic compounds and the high selectivity of antibodies are combined by the linkers. By taking advantage of antigen-selectivity of MAbs, it can deliver these cytotoxic drugs to antigen-expressing tumor cells, thus increasing both the efficacy and safety of therapy. As a payload of ADCs, MMAD is used to target the tubulin of the tumor cells. It can interfere with tubulin polymerization and induce rapid cell death at low picomolar concentrations [1].
Additionally, MMAD is reported to be used in the production of site-specific antibody drug conjugates (NDCs). In the NDCs, MMAD is combined with anti-5T4 antibody or anti-Her2 antibody. It is shown that the NDCs demonstrate better efficacy and pharmacokinetics [2].
References:
[1] Puja Sapra, Andrea T Hooper, Christopher J, O’Donnell & Hans-Peter Gerber. Investigational antibody drug conjugates for solid tumors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2011, 20(8):1131-1149.
[2] Feng Tiana, Yingchun Lu, Anthony Manibusan, Aaron Sellers et al. A general approach to site-specific antibody drug conjugates. PNAS. 2014, February, 111(5): 1766-1771.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 771.06 |
| Cas No. | 203849-91-6 |
| Formula | C41H66N6O6S |
| Synonyms | Demethyldolastatin 10;Monomethylauristatin D;Monomethyl Dolastatin 10 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C([C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@]1([H])CCCN1C(C[C@@H](OC)[C@@H](N(C)C([C@@H](NC([C@H](C(C)C)N([H])C)=O)C(C)C)=O)[C@@H](C)CC)=O)C)N[C@H](C2=NC=CS2)CC3=CC=CC=C3 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Applications |
MMAD is a highly potent inhibitor of tubulin [1]. MMAD is one of the auristatins, which are used as the drugs of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs). In ADCs, the therapeutic compounds and the high selectivity of antibodies are combined by the linkers. By taking advantage of antigen-selectivity of MAbs, it can deliver these cytotoxic drugs to antigen-expressing tumor cells, thus increasing both the efficacy and safety of therapy. As a payload of ADCs, MMAD is used to target the tubulin of the tumor cells. It can interfere with tubulin polymerization and induce rapid cell death at low picomolar concentrations [1]. Additionally, MMAD is reported to be used in the production of site-specific antibody drug conjugates (NDCs). In the NDCs, MMAD is combined with anti-5T4 antibody or anti-Her2 antibody. It is shown that the NDCs demonstrate better efficacy and pharmacokinetics [2]. |
|
References: [1] Puja Sapra, Andrea T Hooper, Christopher J, O’Donnell & Hans-Peter Gerber. Investigational antibody drug conjugates for solid tumors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2011, 20(8):1131-1149. [2] Feng Tiana, Yingchun Lu, Anthony Manibusan, Aaron Sellers et al. A general approach to site-specific antibody drug conjugates. PNAS. 2014, February, 111(5): 1766-1771. | |
| Description | Monomethyl auristatin D (MMAD) is a potent inhibitor of tubulin. | |||||
| Targets | tubulin | ADCs toxin | ||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure