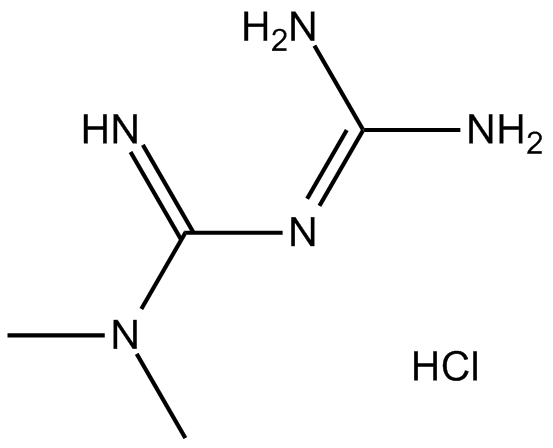
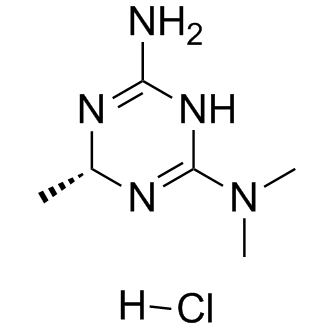
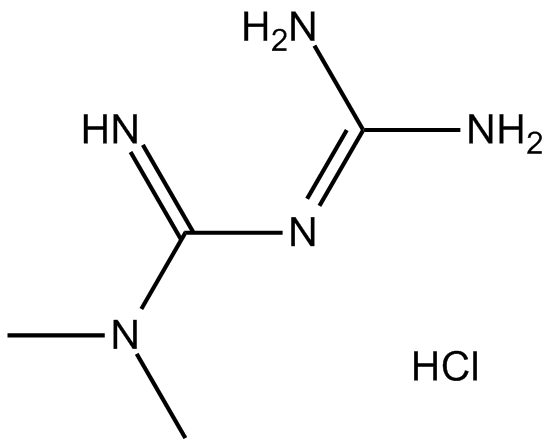
Metformin HCl
Metformin hydrochloride (Metformin HCl; CAS 1115-70-4) is a widely studied small molecule employed in biomedical research primarily for investigating glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes mechanisms. It acts through selective inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis without directly increasing insulin secretion. The molecular targets include activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), subsequently suppressing acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity, attenuating lipid biosynthesis, and promoting fatty acid oxidation. Additionally, metformin inhibits mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase (mGPD), changing cellular redox status and reducing lactate-driven gluconeogenesis pathways. Key research applications of Metformin HCl include studies on glucose homeostasis, metabolic disorders, and AMPK signaling cascades.
References:
1. Madiraju AK, Erion DM, Rahimi Y et al. Metformin suppresses gluconeogenesis by inhibiting mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase. Nature. 2014 Jun 26;510(7506):542-6.
2. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2001 Oct;108(8):1167-74.
3. Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D et al. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science. 2005 Dec 9;310(5754):1642-6.
- 1. Lucas Schoenfeldt, Patrick T Paine, et al. "Chemical reprogramming ameliorates cellular hallmarks of aging and extends lifespan." EMBO Mol Med. 2025 Aug;17(8):2071-2094. PMID: 40588563
- 2. Qinling Pan, Tengteng Xin, et al. "Metabolic immune regulation of macrophages by melanized fungus Fonsecaea monophora." Available online 28 July 2025, 101571
- 3. Xiangyun Li, Zixuan Xiang, et al. "Metformin attenuates colitis via blocking STAT3 acetylation by reducing acetyl-CoA production." J Adv Res. 2025 Mar 31:S2090-1232(25)00218-8.
- 4. Xin Wang, Xu Liang, et al. "Metformin inhibits pathological retinal neovascularization but promotes retinal fibrosis in experimental neovascular age-related macular degeneration." Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 20:16:1547492 PMID: 40183100
- 5. Ming-Li Sun, Jun-Min Dong, et al. "Metformin-mediated protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity." Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct 14:180:117535. PMID: 39405911
- 6. Yasmine Kamen, et al. "Clemastine and metformin extend the window of NMDA receptor surface expression in ageing oligodendrocyte precursor cells." Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 19;14(1):4091. PMID: 38374232
- 7. Rachel Aruldas, Laura Buczek Orenstein, et al. "Metformin Prevents Cocaine Sensitization: Involvement of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Trafficking between Subcellular Compartments in the Corticostriatal Reward Circuit." Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 28;24(23):16859. PMID: 38069180
- 8. Weizhi He, Xicheng Wang, et al. "Metformin reduces hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing downregulation of Cyp26a1 and CD8+ T cells." Clin Transl Med. 2023 Nov;13(11):e1465. PMID: 37997519
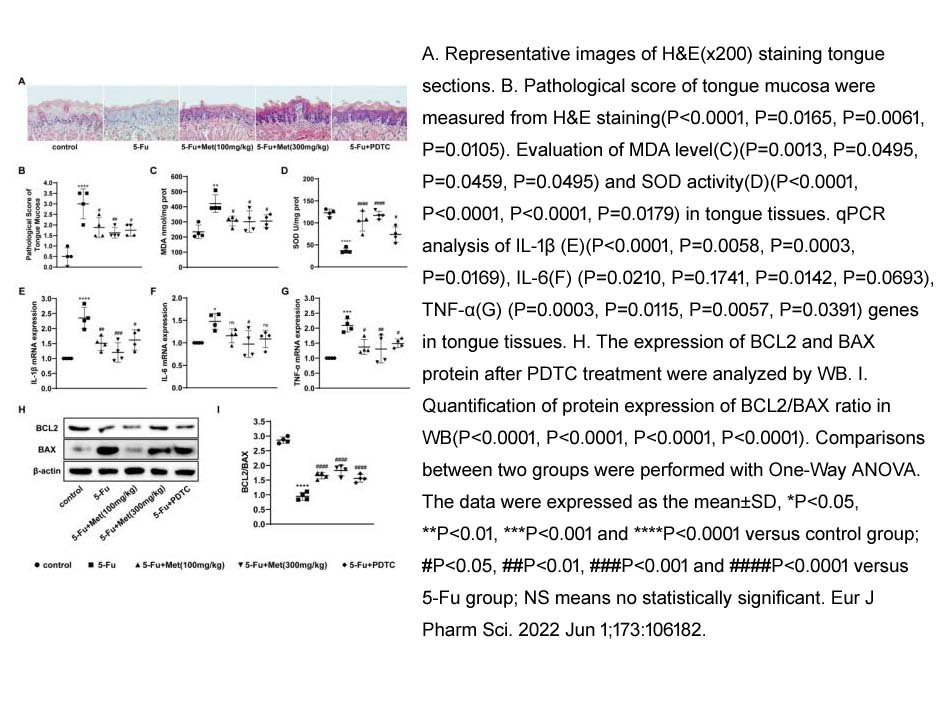
- 9. HangSun, YufengZhou, et al. "Metformin protects 5-Fu-induced chemotherapy oral mucositis by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice." Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jun 1;173:106182. PMID: 35405270
- 10. Alain Aguilar-Valdes, Lilia G. Noriega, et al. "SWATH-MS proteomics of PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells allows identification of drug targets alternative to MEK and PI3K inhibition." Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Mar 16;552:23-29. PMID: 33740661
- 11. Ma W, Liang F, et al. "Activated FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 ameliorates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodelling." Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020;e13519. PMID: 32480429
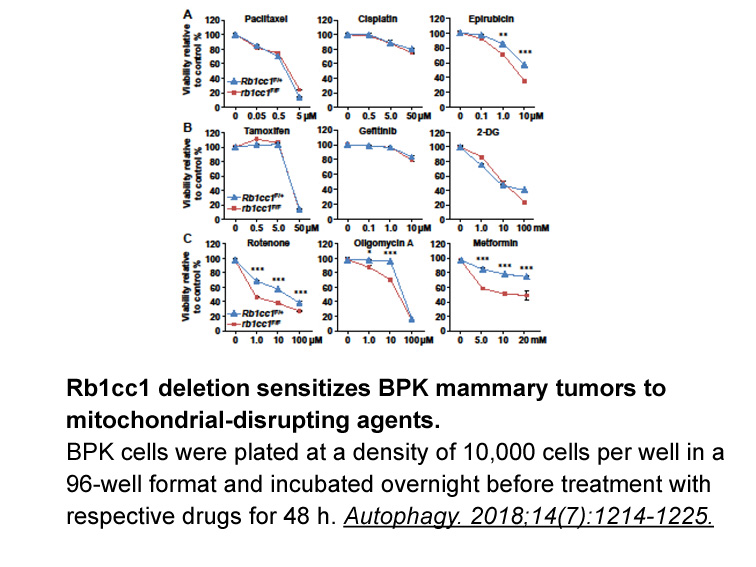
- 12. Yeo SK, Paul R, et al. "Improved efficacy of mitochondrial disrupting agents upon inhibition of autophagy in a mouse model of BRCA1-deficient breast cancer." Autophagy. 2018;14(7):1214-1225. PMID: 29938573
- 13. Dong L, Li Y, et al. "Dietary Apostichopus japonicus Alleviates Diabetes Symptoms and Modulates Genes Expression in Kidney Tissues of db/db Mice." J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Jan 2. PMID: 29249162
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 165.62 |
| Cas No. | 1115-70-4 |
| Formula | C4H12ClN5 |
| Synonyms | Metformin hydrochloride |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥30.7 mg/mL in H2O; ≥8.3 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 3-(diaminomethylidene)-1,1-dimethylguanidine;hydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CN(C)C(N=C(N)N)=N.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
|
AMPK assay |
For the AMPK assay, cells were seeded in six-well plates at 1.5 × 106 cells/well in DMEM containing 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 10% FBS, 100 nM insulin, 100 nM dexamethasone, and 5 μg/ml transferrin for 4 hours. Cells were then cultured in serum-free DMEM for 16 hours followed by treatment for 1 hour or 7 hours with control medium, 5-amino-imidazole carboxamide riboside (AICAR), or metformin at concentrations indicated. For a 39-hour treatment, cells for both control and metformin (10 or 20 μM) groups were cultured in DMEM plus 5% FBS and 100 nM insulin, and the fresh control and metformin-containing medium were replaced every 12 hours (last medium change was 3 hours before harvest). After treatment, the cells were directly lysed in digitonin-containing and phosphatase inhibitor–containing buffer A , followed by precipitation with ammonium sulfate at 35% saturation. AMPK activity was determined by measurement of phosphorylation of a synthetic peptide substrate, SAMS (HMRSAMSGLHLVKRR). |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Rat primary hepatocytes |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is limited. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
10, 20, 500 μM, 2 mM; 39h; |
|
Applications |
Metformin activated AMPK in primary hepatocytes. Moreover, Metformin (2 mM, 3 hours) stimulated AMPK activity in skeletal muscle in association with induction of glucose uptake. Metformin (500 μM) reduced hepatic SREBP-1 expression in rat hepatocytes. |
| Animal experiment: | |
|
Animal models |
Male C57BL/6 mice model; |
|
Dosage form |
200 mg/kg, oral gavage, twice daily for 5 days; or 250 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, for 3 days |
|
Applications |
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity were reduced in metformin-treated rats [1]. Moreover, metformin required LKB1 in the liver to lower blood glucose levels [2]. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: 1. Zhou, G., Myers, R., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Shen, X., Fenyk-Melody, J., Wu, M., Ventre, J., Doebber, T., Fujii, N., Musi, N., Hirshman, M. F., Goodyear, L. J. and Moller, D. E. (2001) Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 108, 1167-1174 2. Shaw, R. J., Lamia, K. A., Vasquez, D., Koo, S. H., Bardeesy, N., Depinho, R. A., Montminy, M. and Cantley, L. C. (2005) The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science. 310, 1642-1646 |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data

Related Biological Data